AP Modern World History Unit 3 1450-1750
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Protestant Reformation
A religious movement of the 16th century that began as an attempt to reform the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the creation of Protestant churches.
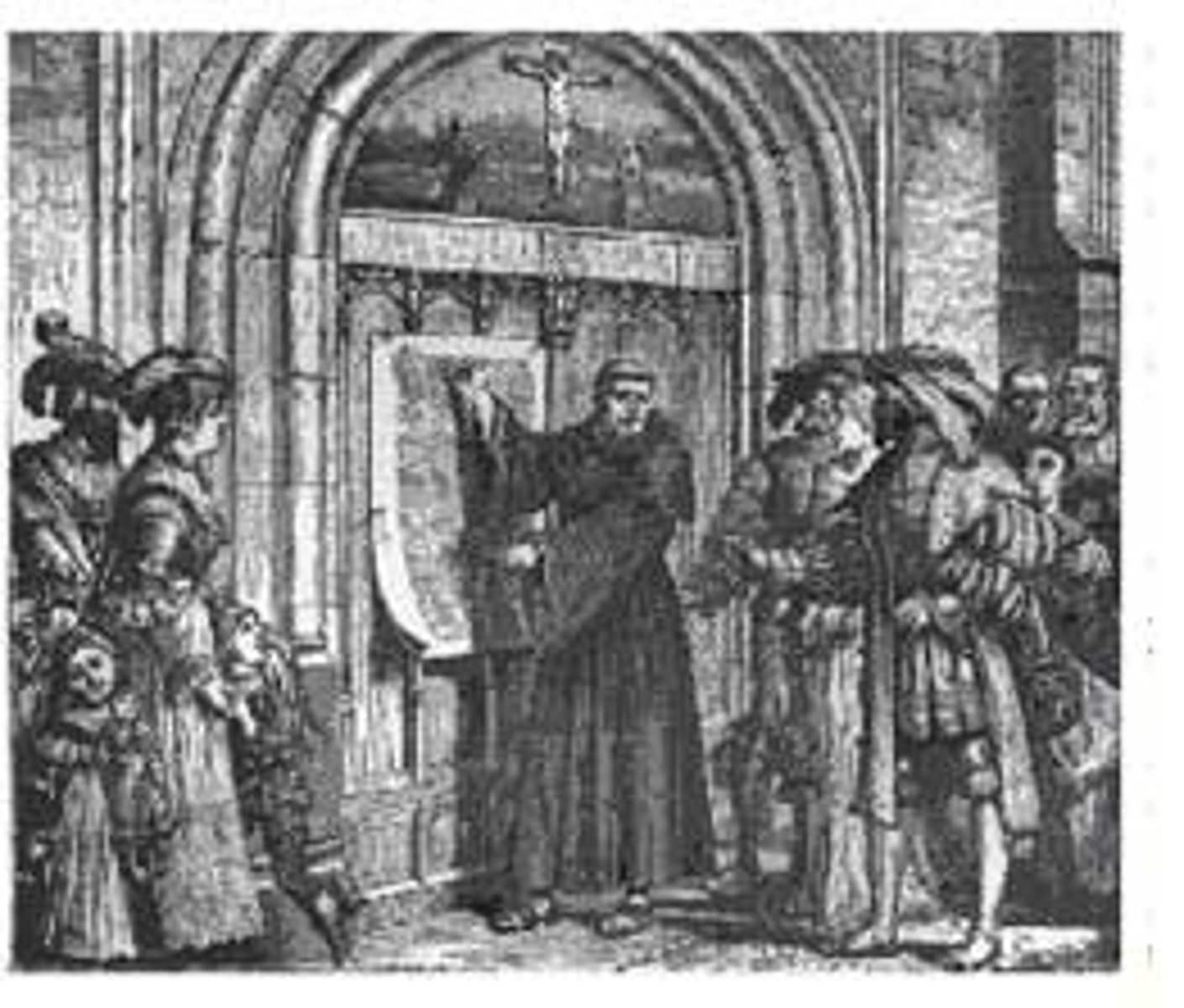

indulgences
Selling of forgiveness by the Catholic Church. It was common practice when the church needed to raise money. The practice led to the Reformation.
Martin Luther
a German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Church. In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices.

Ottoman Empire
Islamic state founded by Osman in northwestern Anatolia. After the fall of the Byzantine Empire, the Ottoman Empire was based at Istanbul (formerly Constantinople) from 1453-1922. It encompassed lands in the Middle East, North Africa, the Caucasus, and eastern Europe. They were known in this period for using the devshirme system to obtain candidates for their advanced bureaucracy and elite jannisary corp that utilized gunpowder. They ruled with religious tolerance toward "people of the book" although they had to pay a special tax.
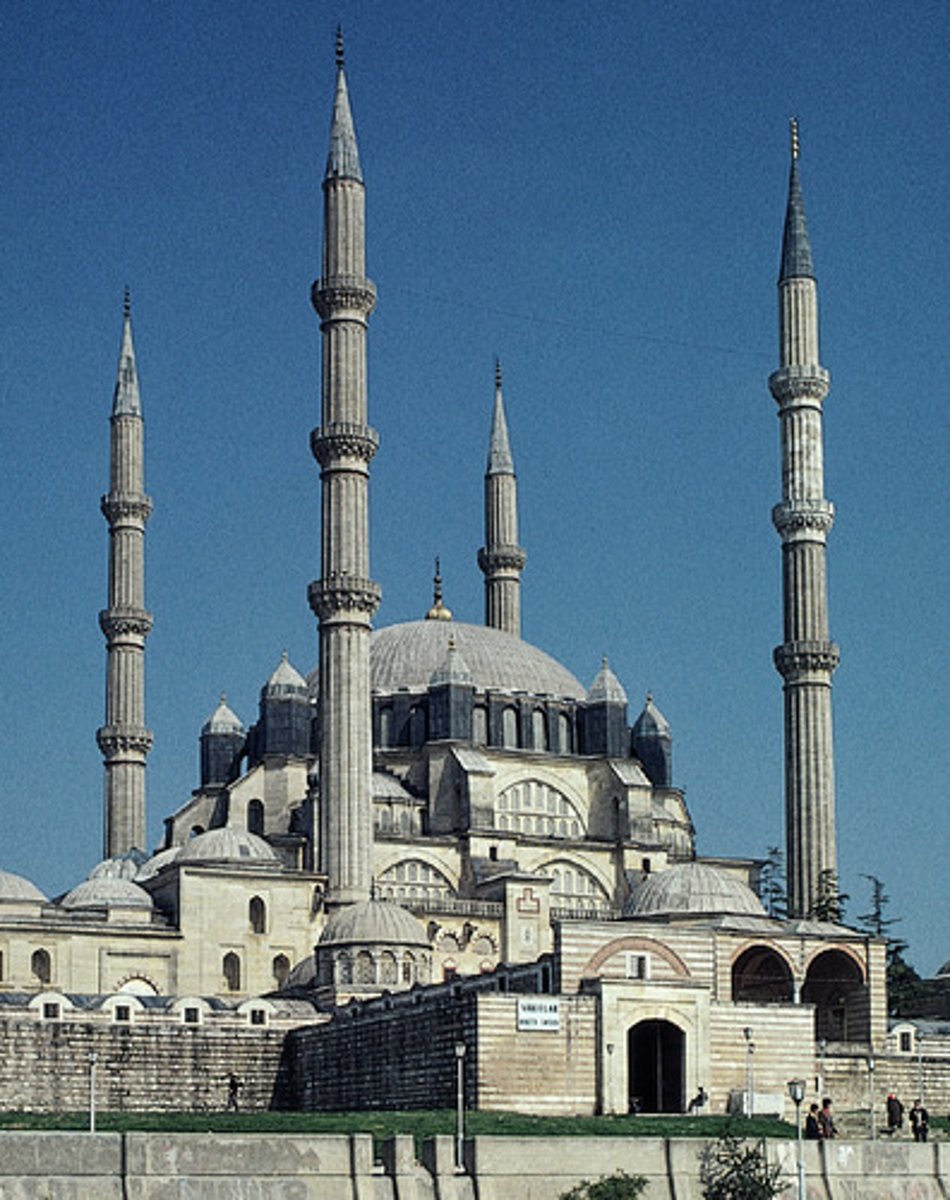

Mughal Empire
Muslim state that expanded over most of India utilizing gunpowder in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, allowed for religious tolerance (especially under Akbar)

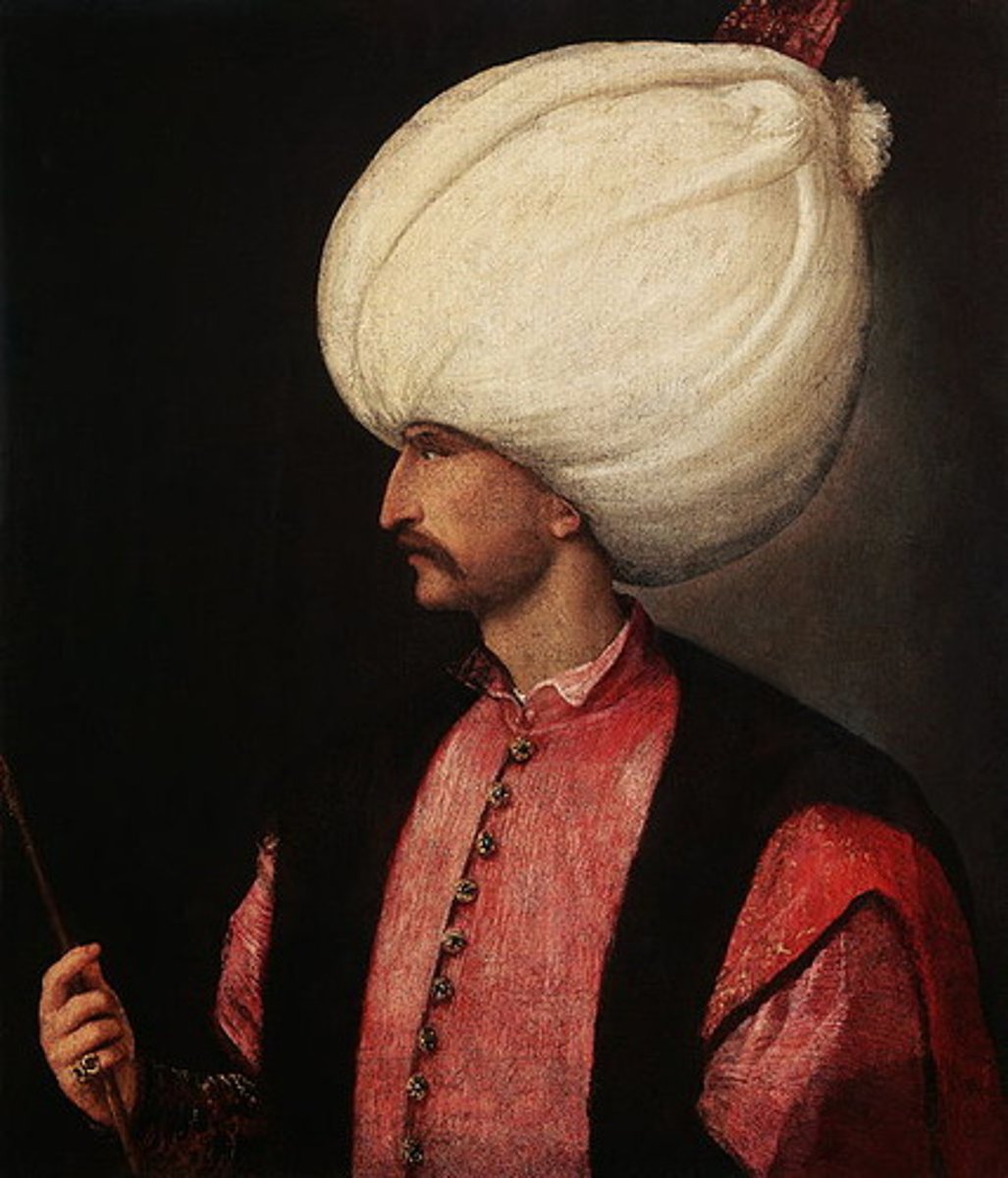
Suleiman the Magnificent
The most illustrious sultan of the Ottoman Empire (r. 1520-1566); also known as 'The Lawgiver.' He significantly expanded the empire in the Balkans and eastern Mediterranean.

Akbar the Great
known for religious tolerance. grandson of Babur who created a strong central government

Gunpowder Empires
Qing Dynasty, as well as the Muslim empires of the Ottomans, Safavids, and the Mughals that employed cannons and gunpowder to advance their military causes.
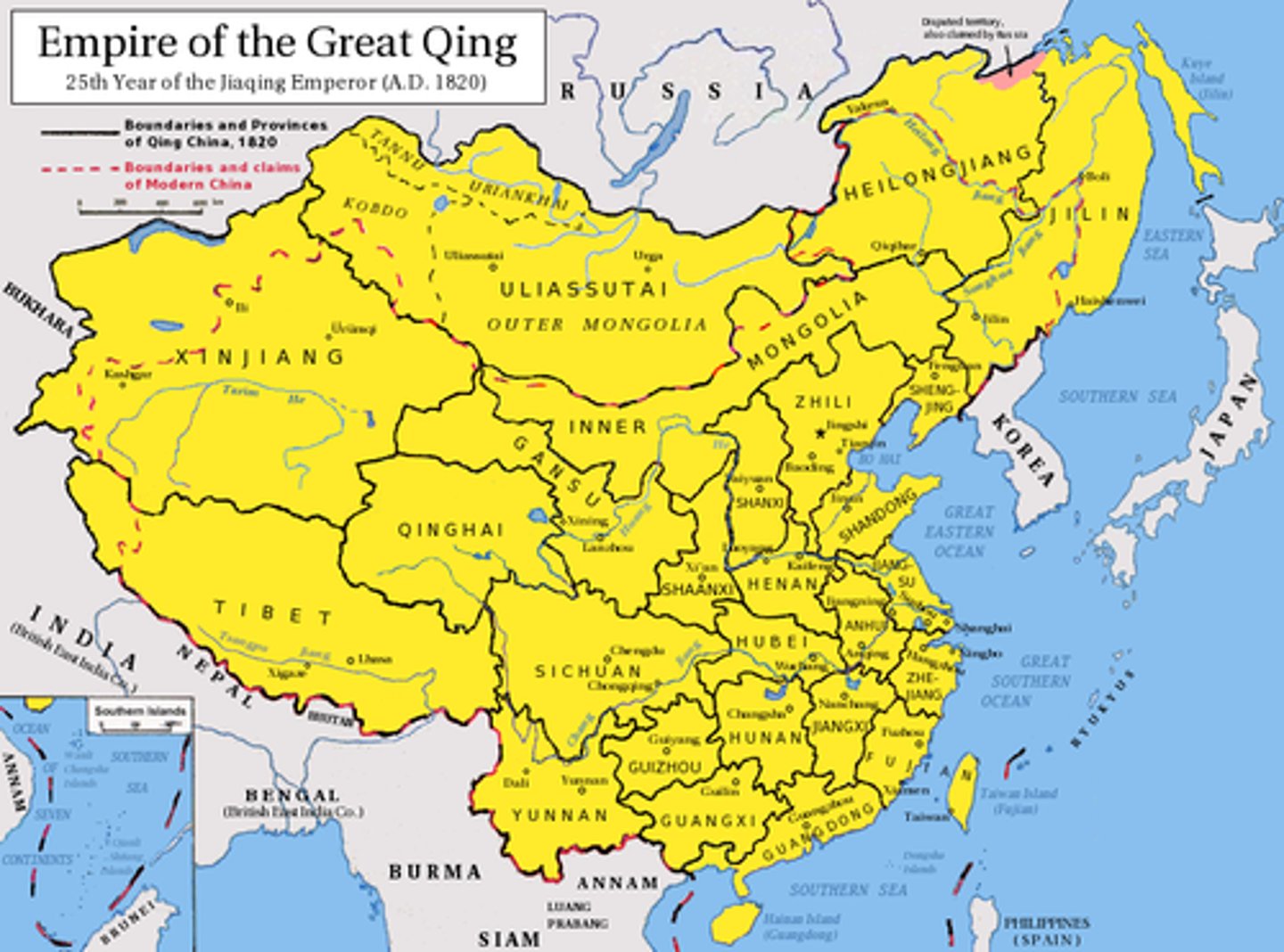
Qing Dynasty (1644-1911)
Minority Manchu rule over China that incorporated new territories, experienced substantial population growth, and sustained significant economic growth.
Safavid Empire
Turkish-ruled Iranian kingdom (1502-1722) established by Ismail Safavi, who declared Iran a Shi'ite state.
Safavid-Mughal Conflict
The two empires clashed, primarily over Kandahar, a strategic city that was seen as the gateway into South Asia.
Bureaucracy
A large, complex governmental organization composed of appointed officials
Tax farming
A government's use of private collectors to collect taxes. Individuals or corporations contract with the government to collect a fixed amount for the government and are permitted to keep as profit everything they collect over that amount. (used in Ottoman Empire)
Devshirme System
The practice by which the Ottoman Empire conscripted boys from Christian families (of a conquered people), who were converted to Islam and trained to become Janissary soldiers or members of the bureaucracy loyal to the sultan
Divine Right of Kings
European Doctrine that states that the right of ruling comes from God and not people's consent
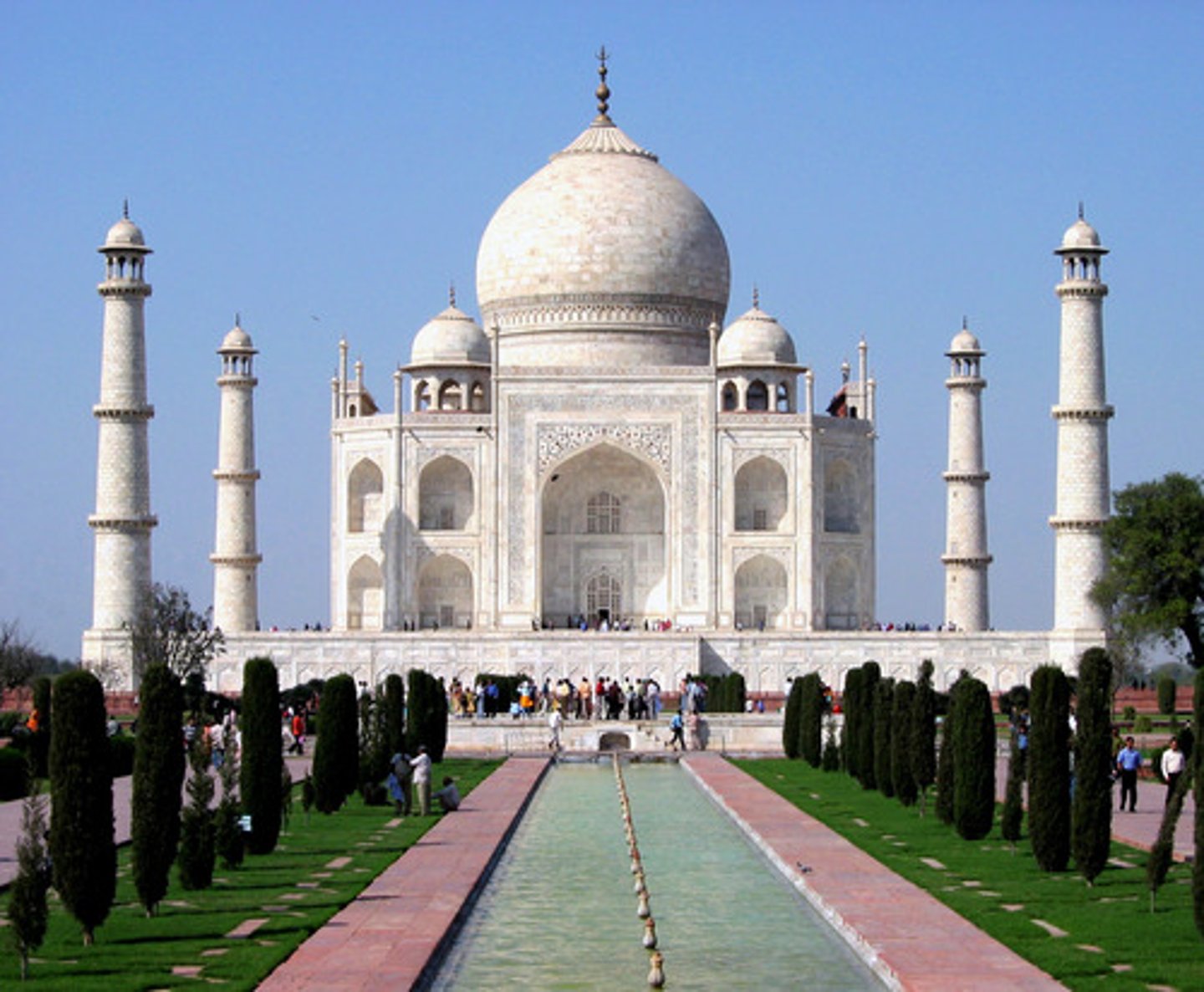
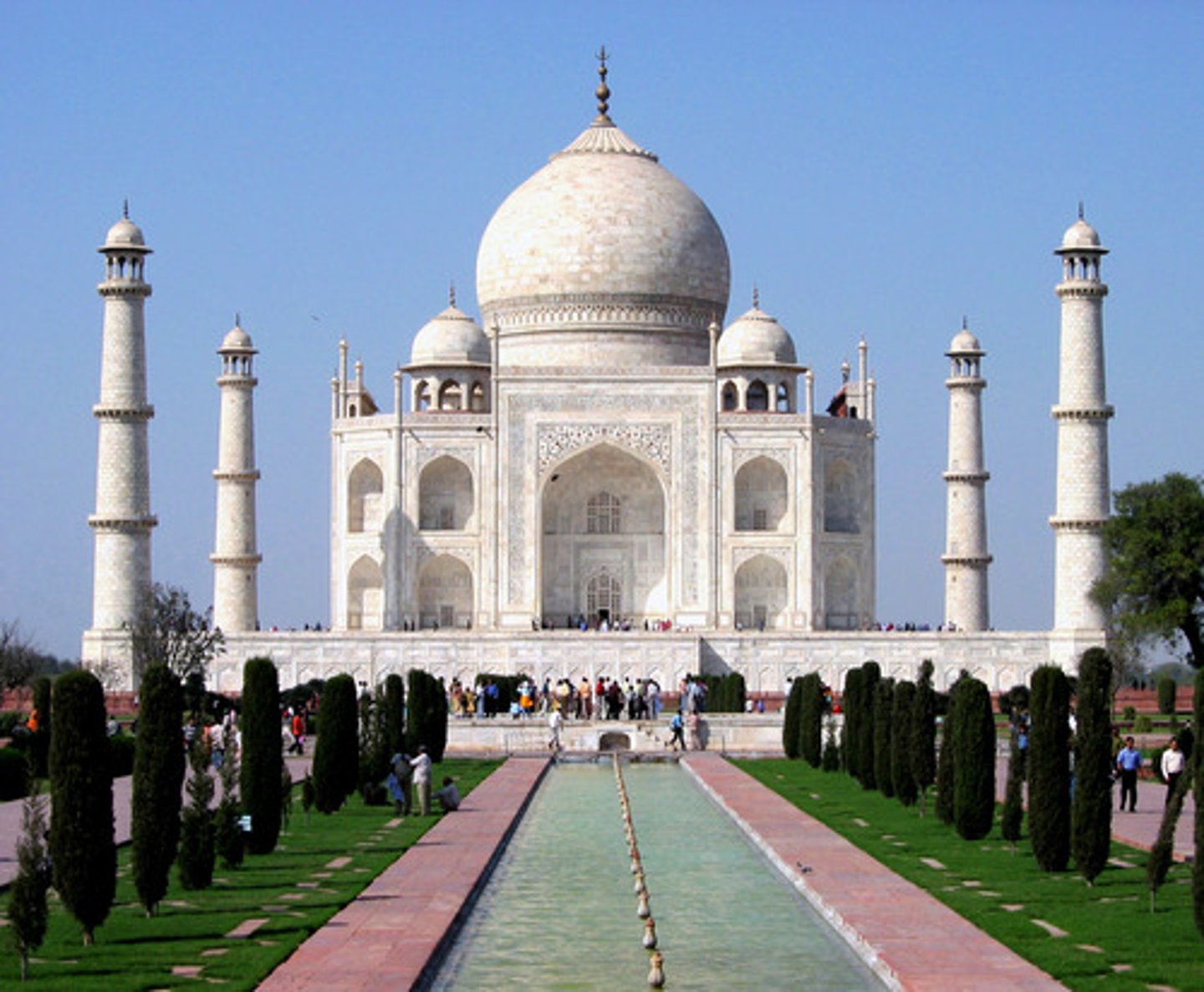
Taj Mahal
beautiful mausoleum at Agra built by the Mogul emperor Shah Jahan (completed in 1649) in memory of his favorite wife - an example of monumental architecture

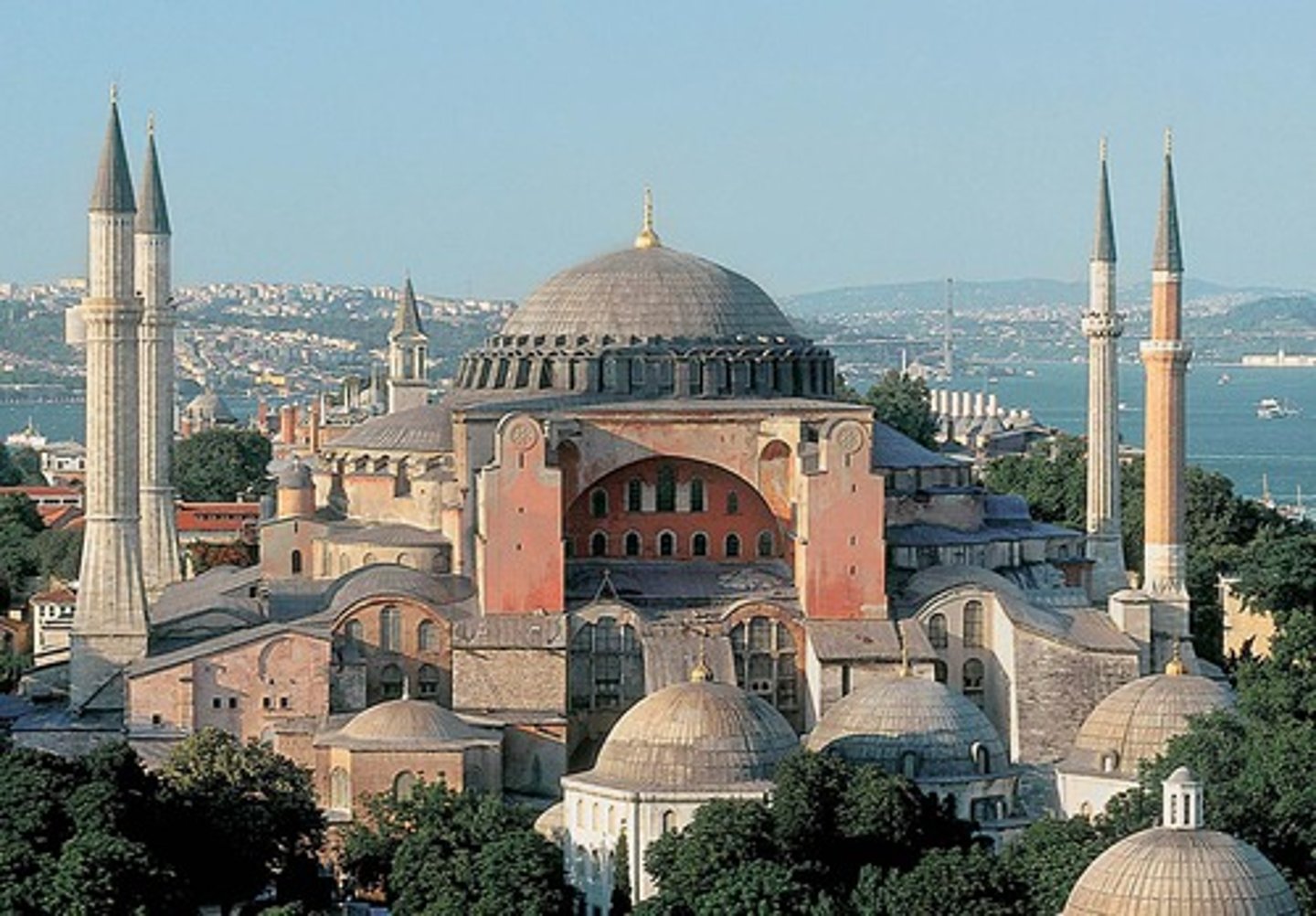
Hagia Sophia
largest cathedral in Constantinople, built by the Byzantine Empire, when Ottoman ruler Mehmed II conquered Constantinople it became a mosque - an example of monumental architecture

Zamindars
tax system of the Mughal empire where local lords collected tax/ tribute for the emperor.
Ottoman-Safavid Conflict
A century-long conflict from 1534-1639 in which the Sunni Ottomans fought the Shiite Safavids.
Sikhism
the doctrines of a monotheistic religion founded in northern India in the 16th century by Guru Nanak, persecuted under the Mughals, and has some similarities to both Hinduism and Islam

Mandate of Heaven
a political theory of ancient China in which those in power were given the right to rule from a divine source
Janissaries
Infantry, originally of slave origin, armed with firearms and constituting the elite of the Ottoman army from the fifteenth century until the corps was abolished in 1826.
Counter Reformation
the reaction of the Roman Catholic Church to the Reformation reaffirming important Church doctrine and renewing efforts to convert people to Catholicism (especially by Jesuit missionaries)
Jesuits
Also known as the Society of Jesus; founded by Ignatius Loyola (1491-1556) as a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism.
Sunni Islam
Muslims belonging to branch of Islam believing that the community should select its own leadership. The majority religion in most Islamic countries.
Shi'ite Islam
One of the two main branches of Islam. Shiites recognize Ali, the fourth caliph, and his descendants as rightful rulers of the Islamic world; practiced in the Safavid empire
Canton System
used to control western trade under the Qing Dynasty: trading confined to port of Canton in South China.
Confucian Exam System
written exam used to select high ranking government officials in China (includes memorization of teachings of Confucius), highly competitive and results in an educated bureaucracy
Gutenberg Printing Press
used movable type to print, increased literacy in Europe and helped spread the Protestant Reformation
Aurengzeb
Mughal ruler who expanded the empire, and was a strict Muslim that was more intolerant of other faiths. Reinstates Jizya tax for non Muslims. Destroyed and defaced many Hindu temples, had the ninth guru of Sikhism killed.
Manchus
Northeast Asian peoples who defeated the Ming Dynasty and founded the Qing Dynasty in 1644, which was the last of China's imperial dynasties.
Mansabdars
elite bureaucrats who served the Mughal emperor by furnishing soldiers and collecting taxes; could be Hindu or Muslim
Spanish Inquisition
A program ordered by the Spanish monarchy to investigate and eliminate heresy, or in other words, people going against Catholicism
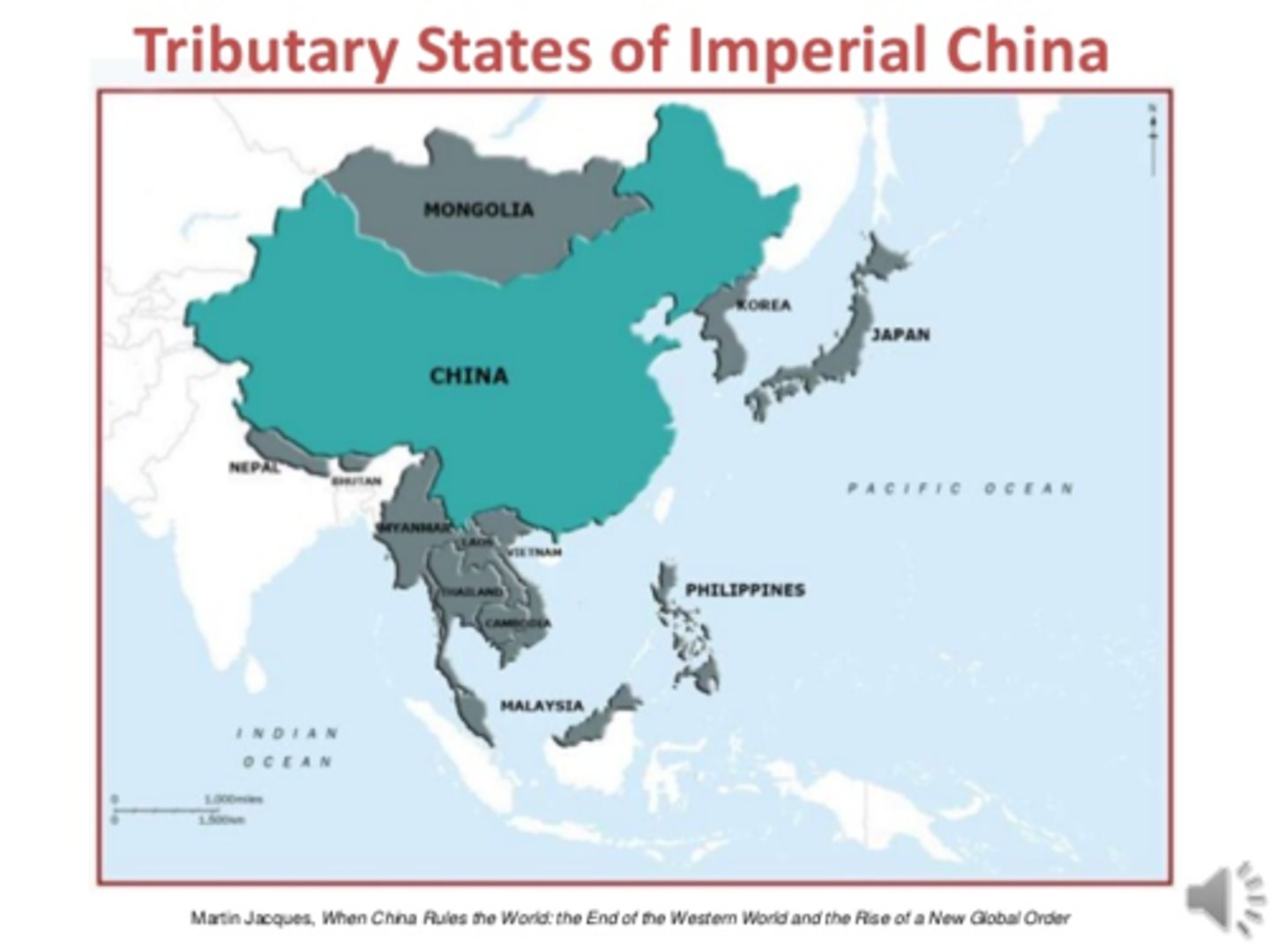
tributary system
A system in which China's neighboring states might acknowledge the superiority of the emperors in China and required a payment of valuable produce
Qianlong Emperor
emperor of the Manchu-led Qing Dynasty (r. 1736-1795), in what was considered China's "Golden Age". In the mid-18th century received pressure to allow for more trade with Europe, but refused.
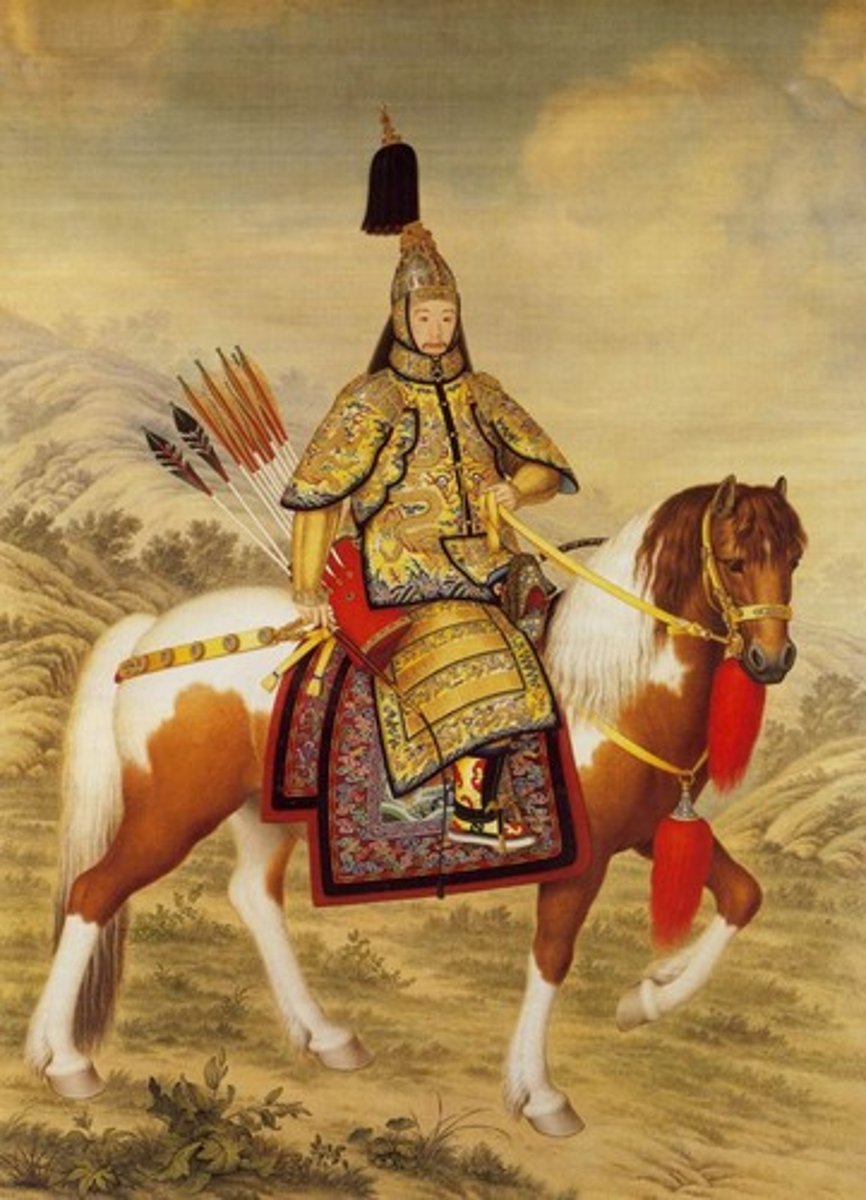

McCartney Mission
The unsuccessful attempt by the British Empire to establish diplomatic relations and further trade with the Qing Empire.
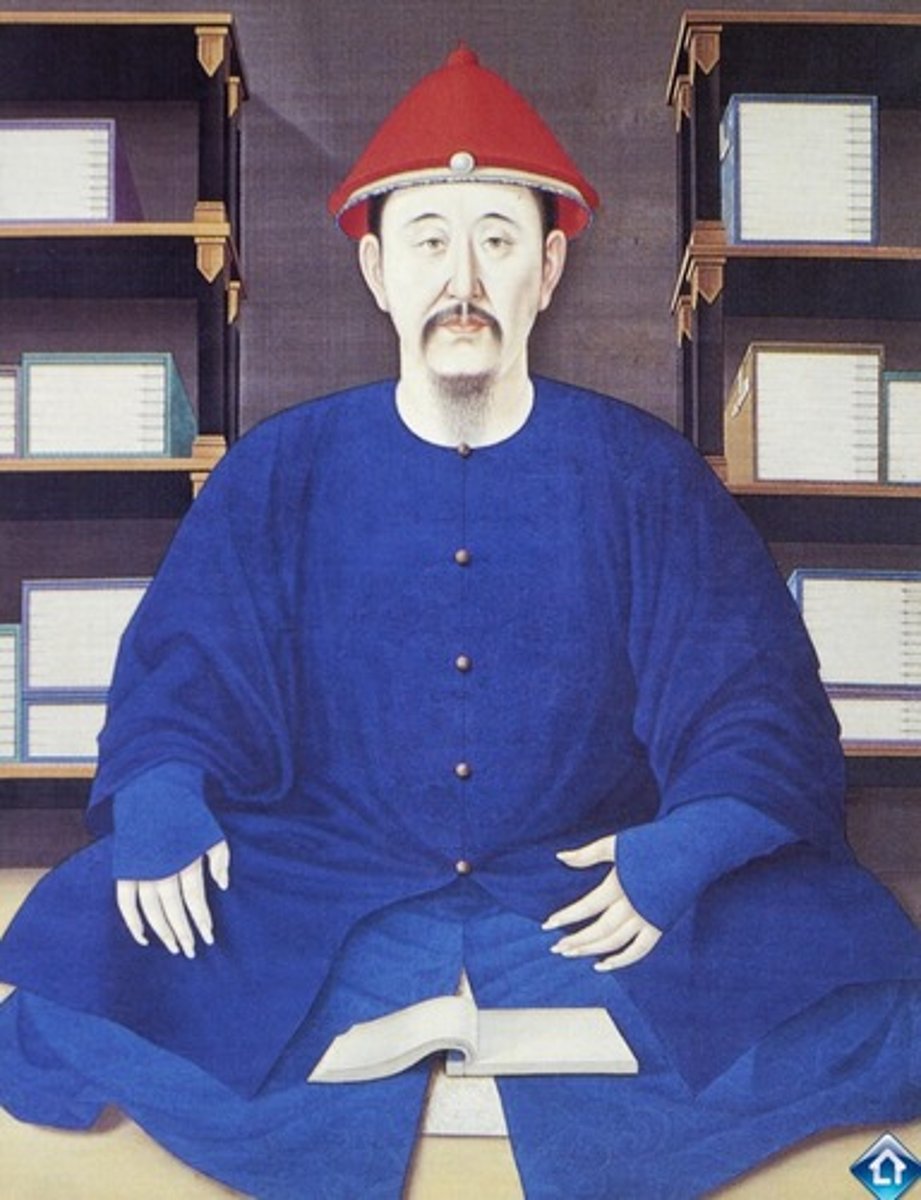
Kangxi Emperor
Ruled in the Qing Dynasty for 61 years, a period of stability and prosperity. Transformed the Manchu way of rulership into a truly Confucian establishment.

Chinese Rites Controversy
Controversy over Jesuit missionaries permitting Chinese converts to practice traditional customs like ancestor worship, ultimately resulted in the prohibition of Catholic preaching in China.
Babar
established the Mogul (Mughal) Empire in India
British East India Company
set up trading posts in India in the 1600s, beginning the British economic interest there

Sharia
Islamic law
Millets
communities of religious minorities in Ottoman Empire (ie Christian or Jewish) - were semi-autonomous and able to govern their own affairs
Jizya
tax that non-Muslims had to pay when living within a Muslim empire

Red Fort
In the city of Delhi, it served as the main residence of the Mughal emperors. Commissioned by Emperor Shah Jahan in 1639 and is an example of monumental architecture.
