HUG AP Test
1/558
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
559 Terms
Mercator projection
PROS
Navigation - easy to plot
Centers Europe
Widely used for navigation until the 1960s
CONS
Increased distortion the further away from the equator you are
Northern hermisphere looks much bigger
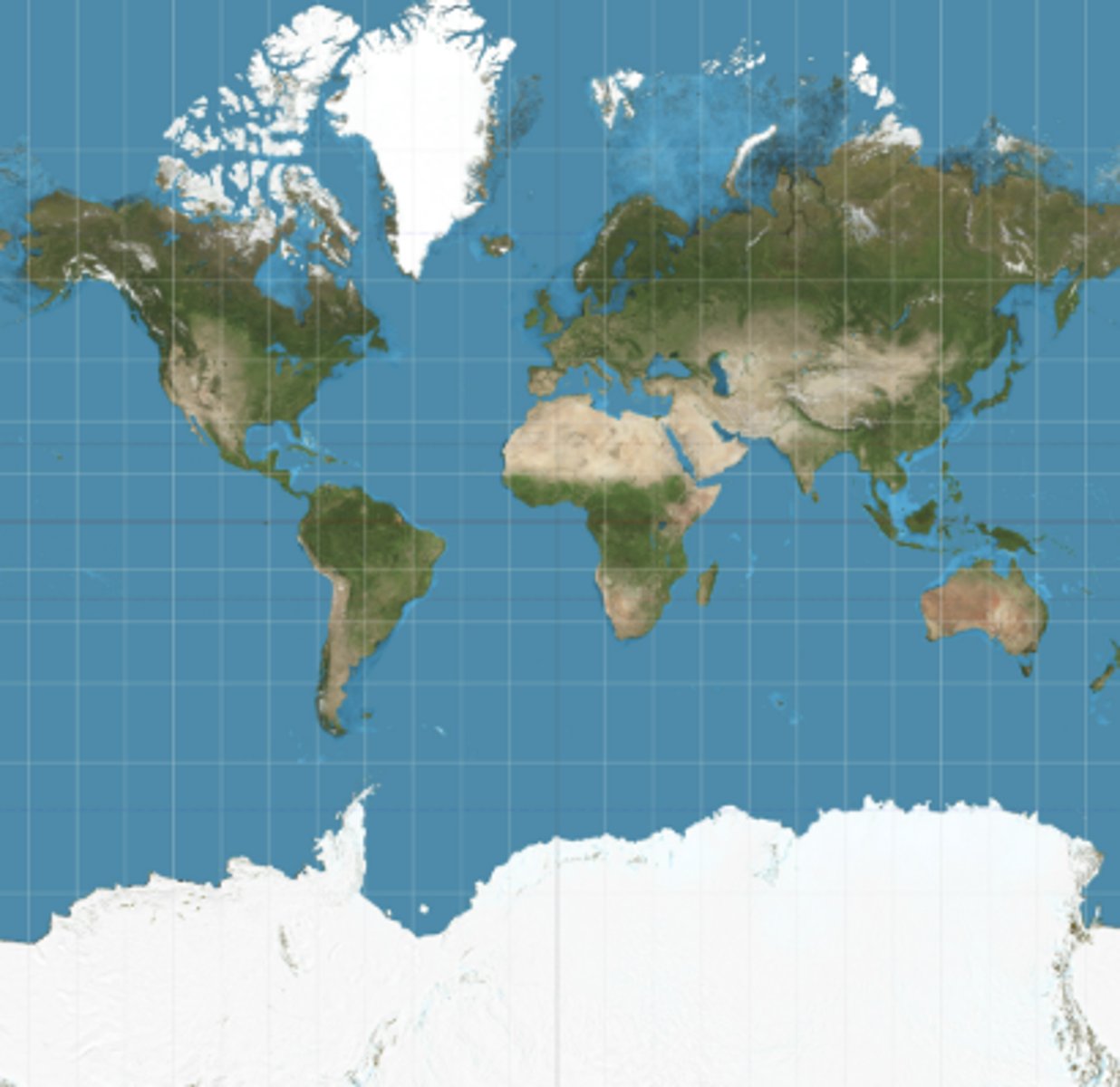
Gall-peters / Peters projection
PROS
more accurately shows southern hemisphere as larger than the northern hemisphere
CONS
continents are elongated and shape is distorted
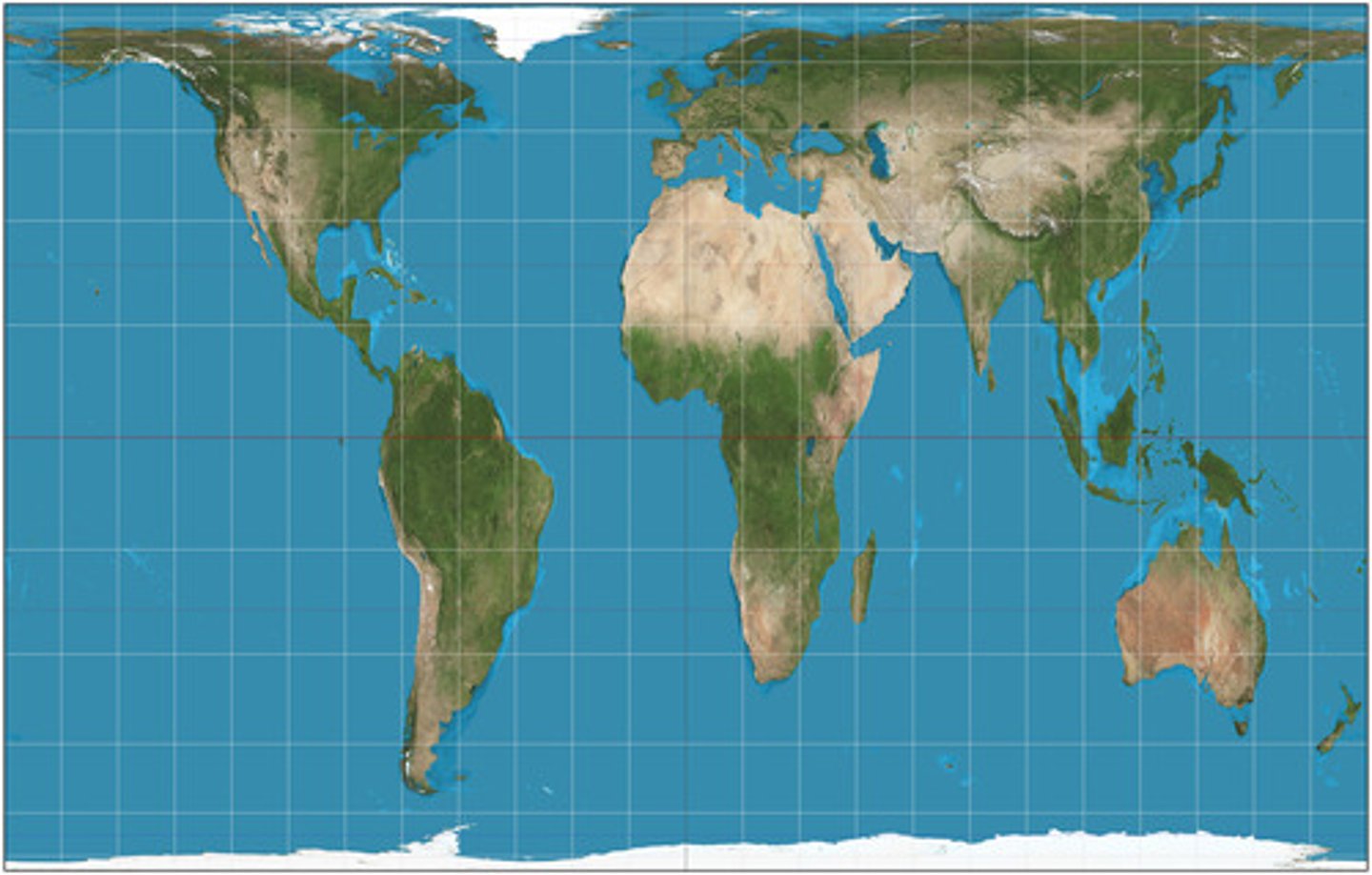
Robinson projection
PROS
More accurately shows the area near the poles
Used to show proportions of land to water
Distorts cardinal directions and distance
CONS
Extreme pole distortion
Not suitable for direction
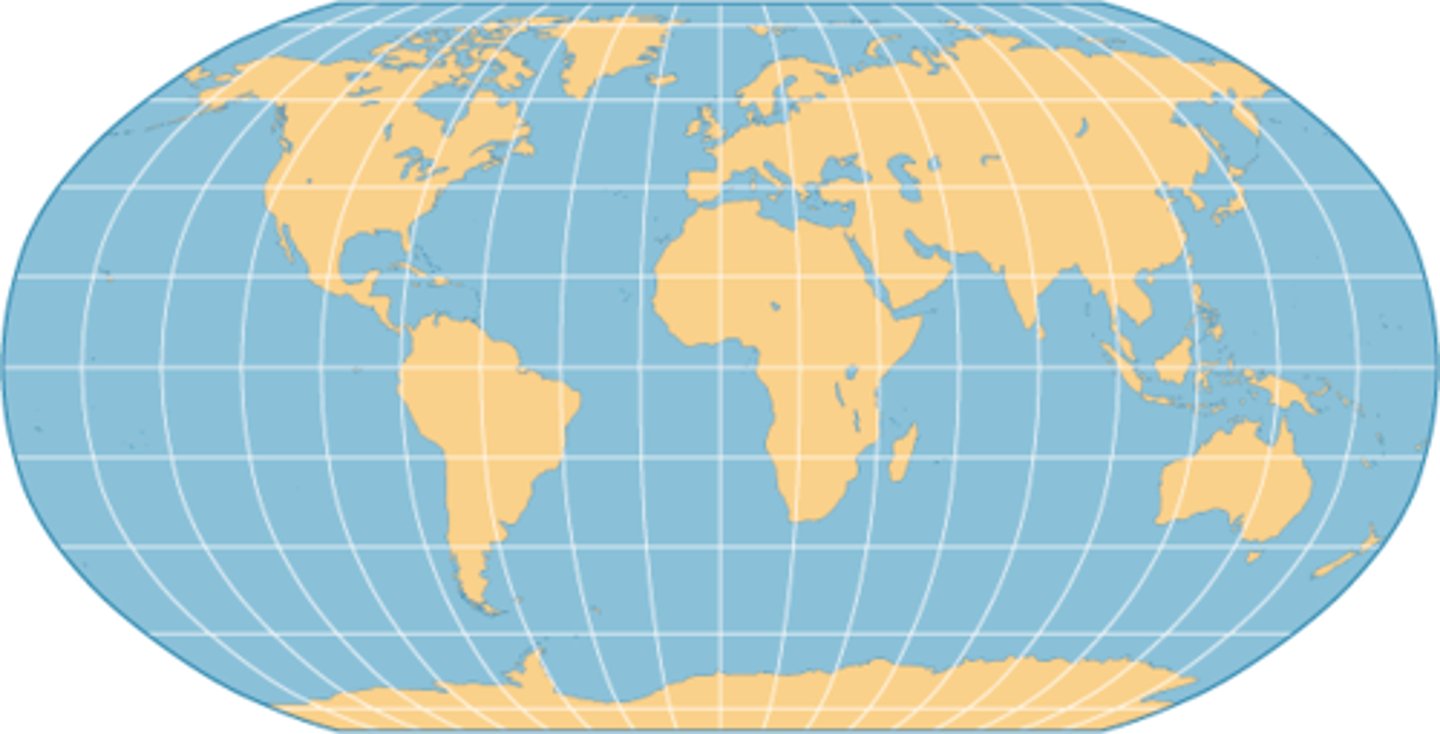
Azimuthal
PROS
doesnt center any one continent
more globe like
distance from center is correct
poles are correct
CONS
hard to see distances between continents
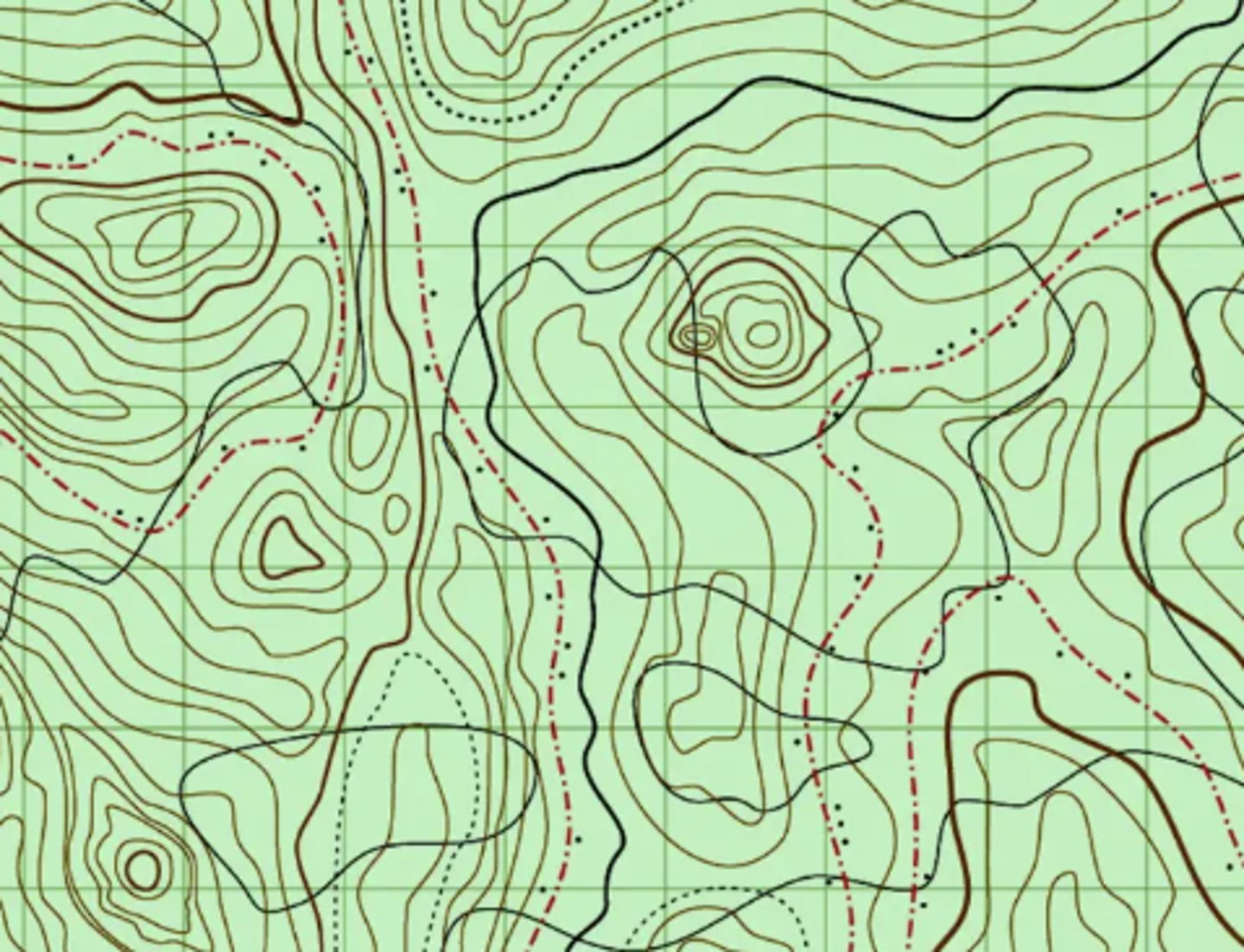
topographic map
A map that shows the surface features of an area - shows elevation with contouring lines
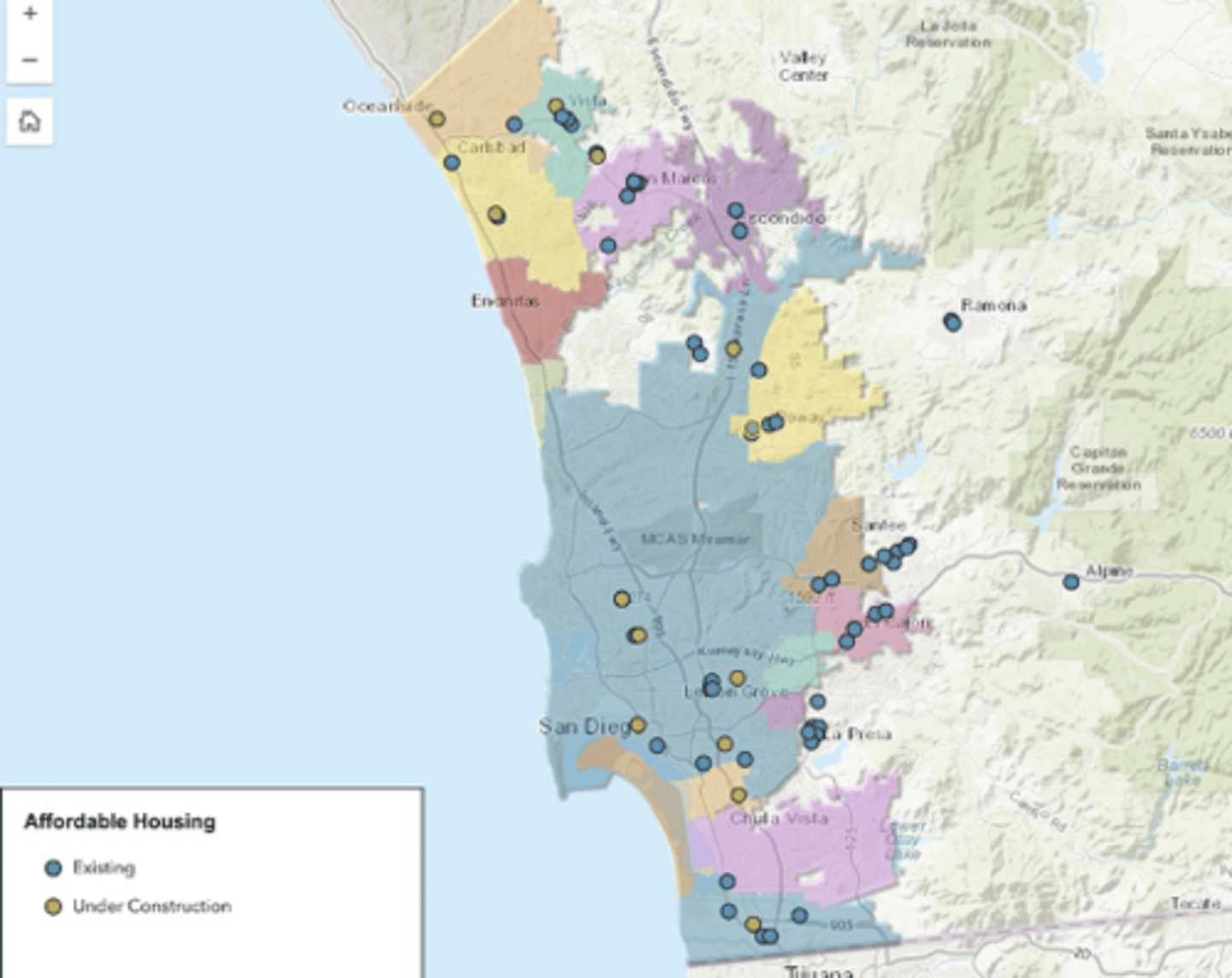
Thematic maps
show a theme or topic
ExL san diego housing cost by zip code
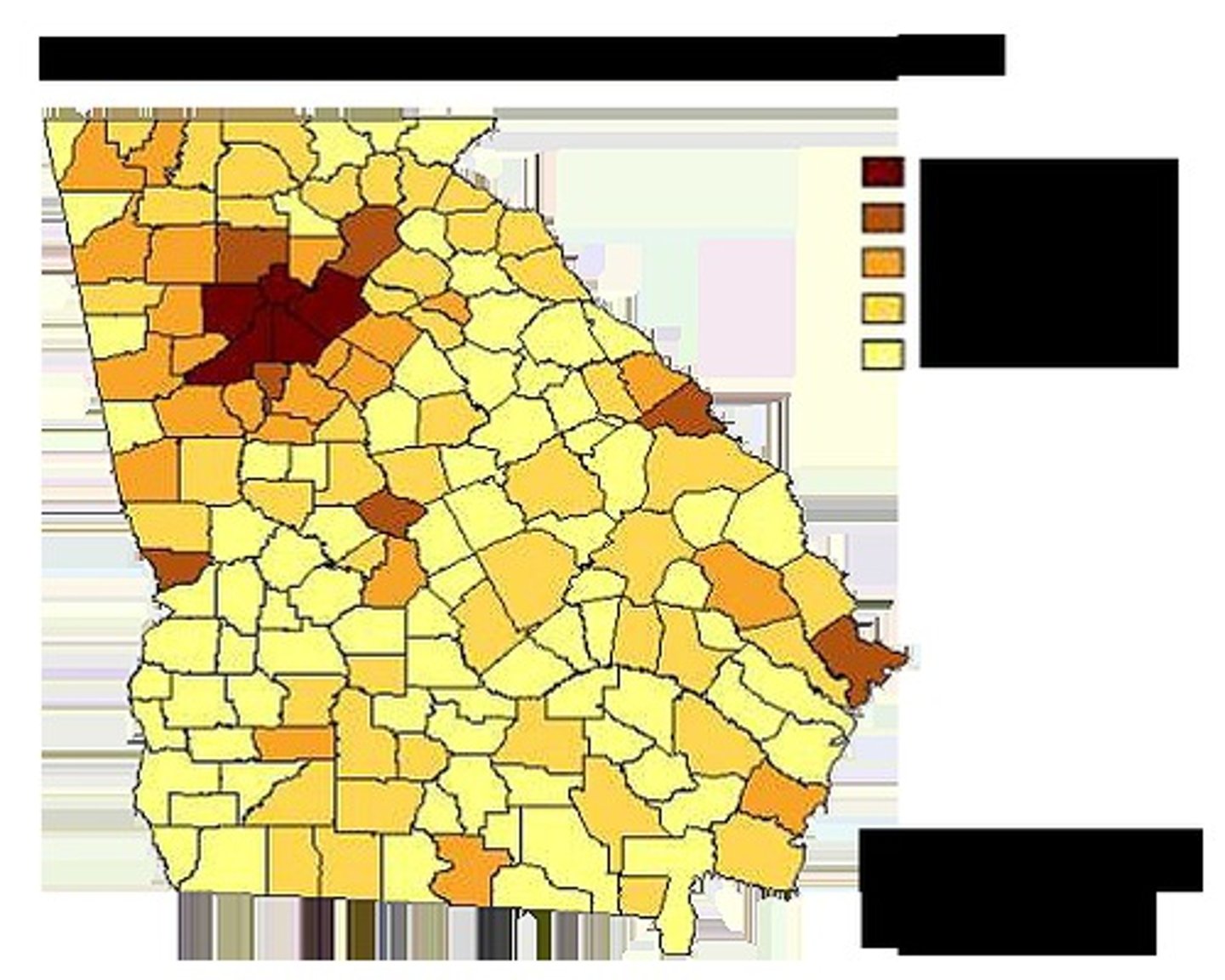
Chloropleth map
Uses a graduation of color to show the trends of something
Ex: literacy rates would be darker in areas where lots of people can read but lighter where they can't
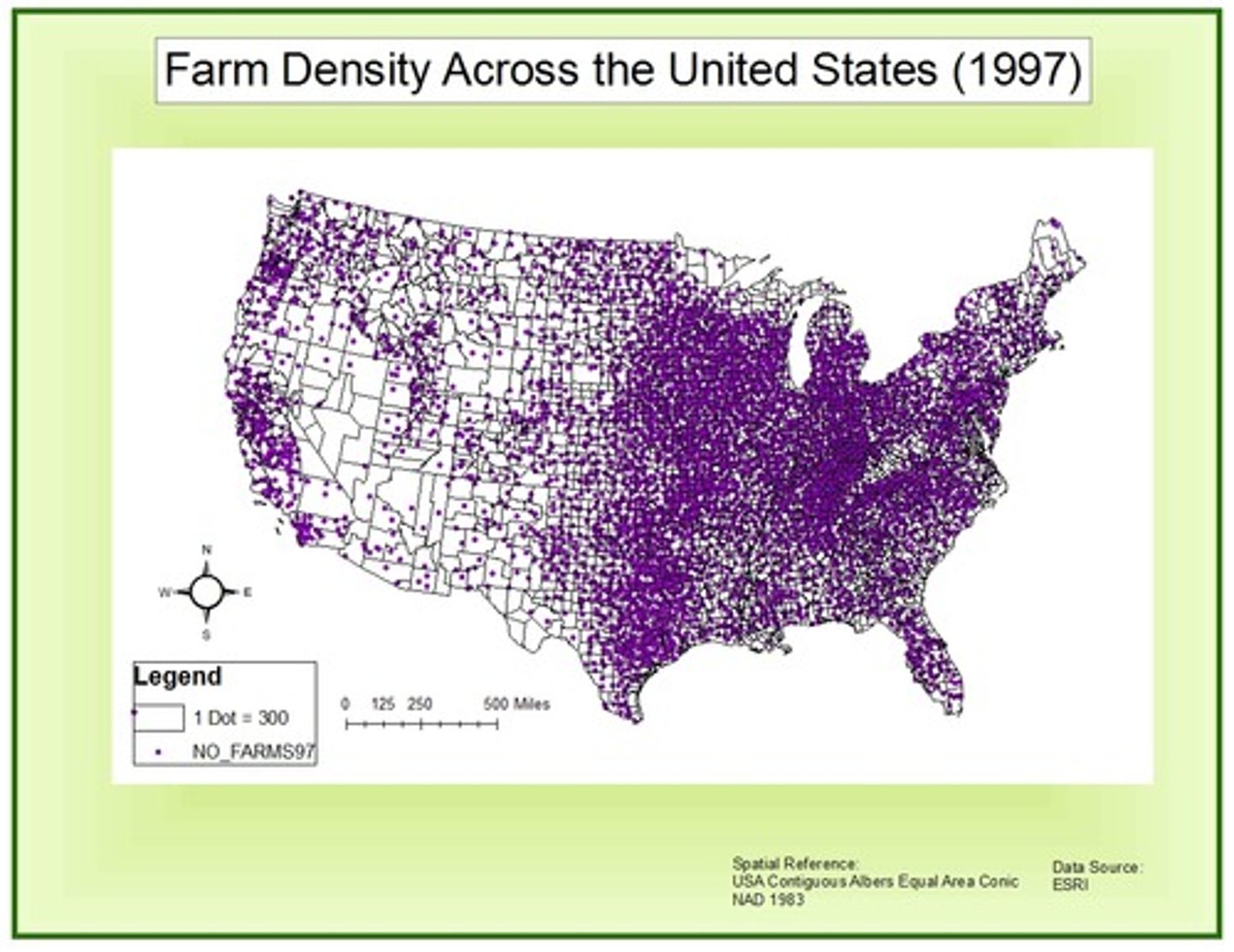
Dot density map
Uses dots to represent the amount of something
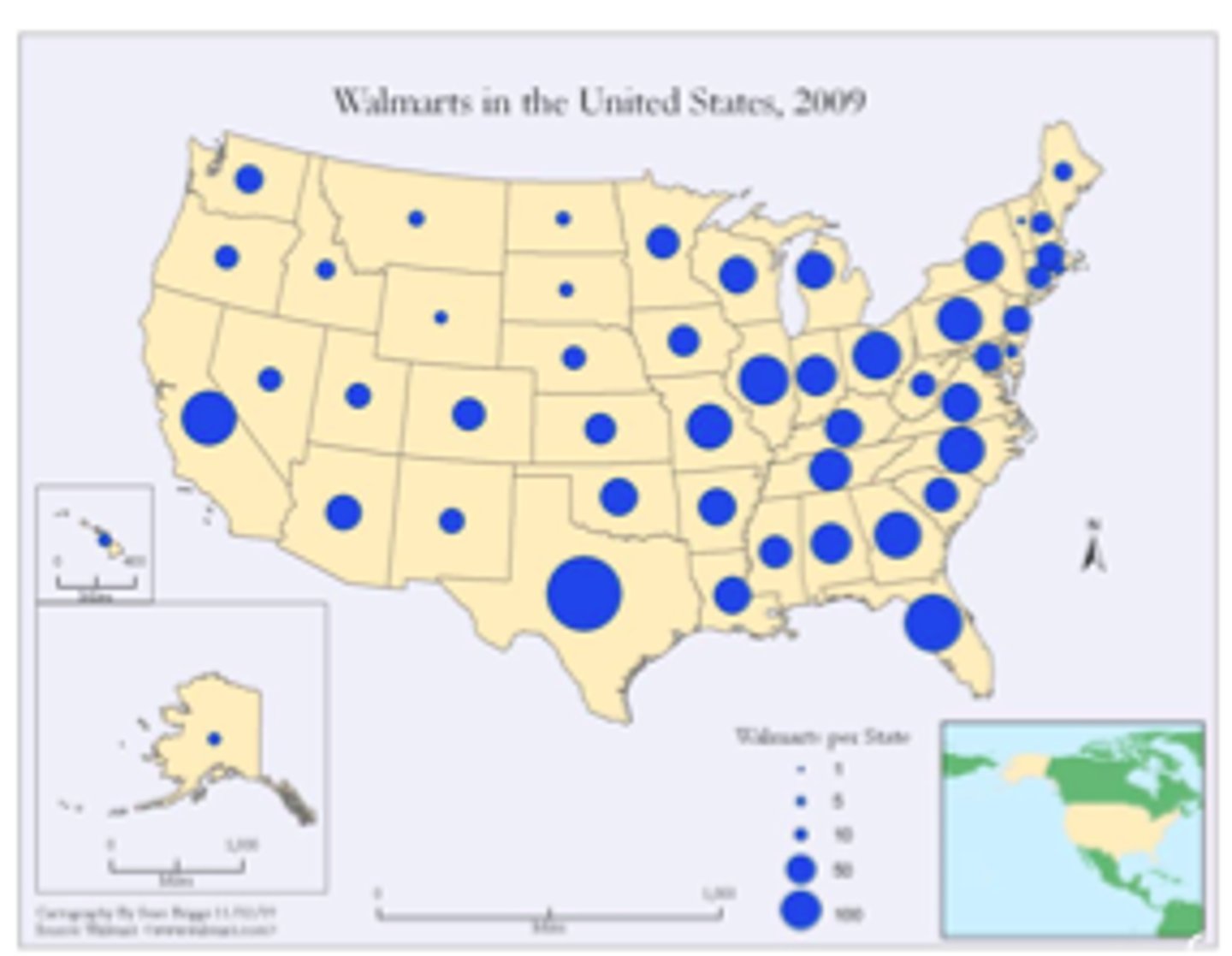
graduated symbol map
Symbols that change in size according to its value
Ex: Covid (the big map that was always on the news)
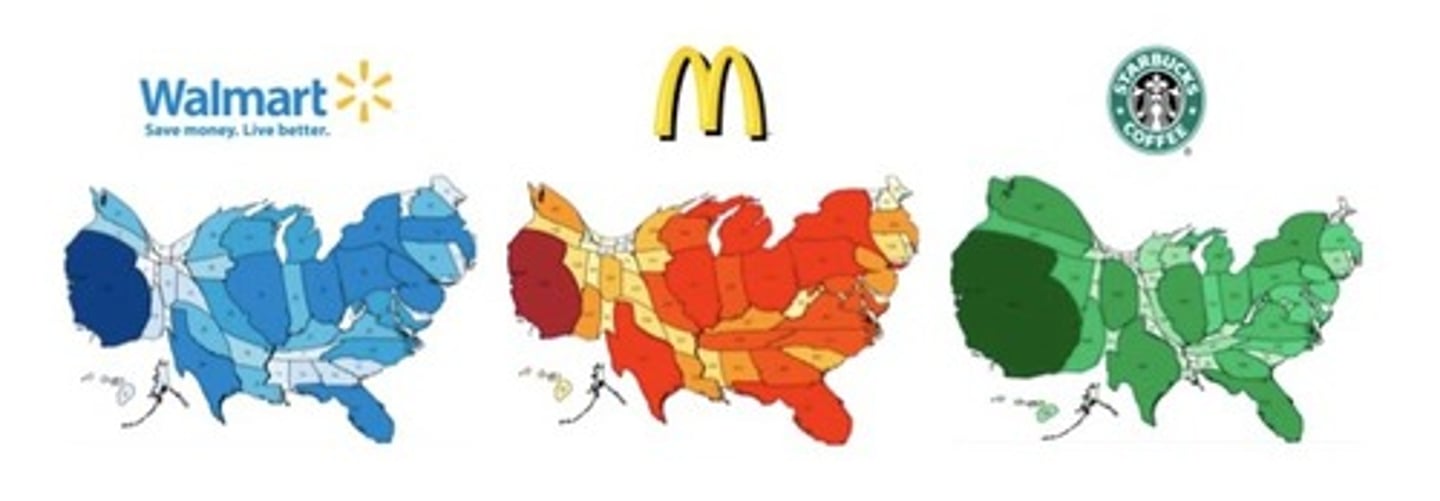
Cartogram
Use distortion to intentionally convey a trend
Ex: population
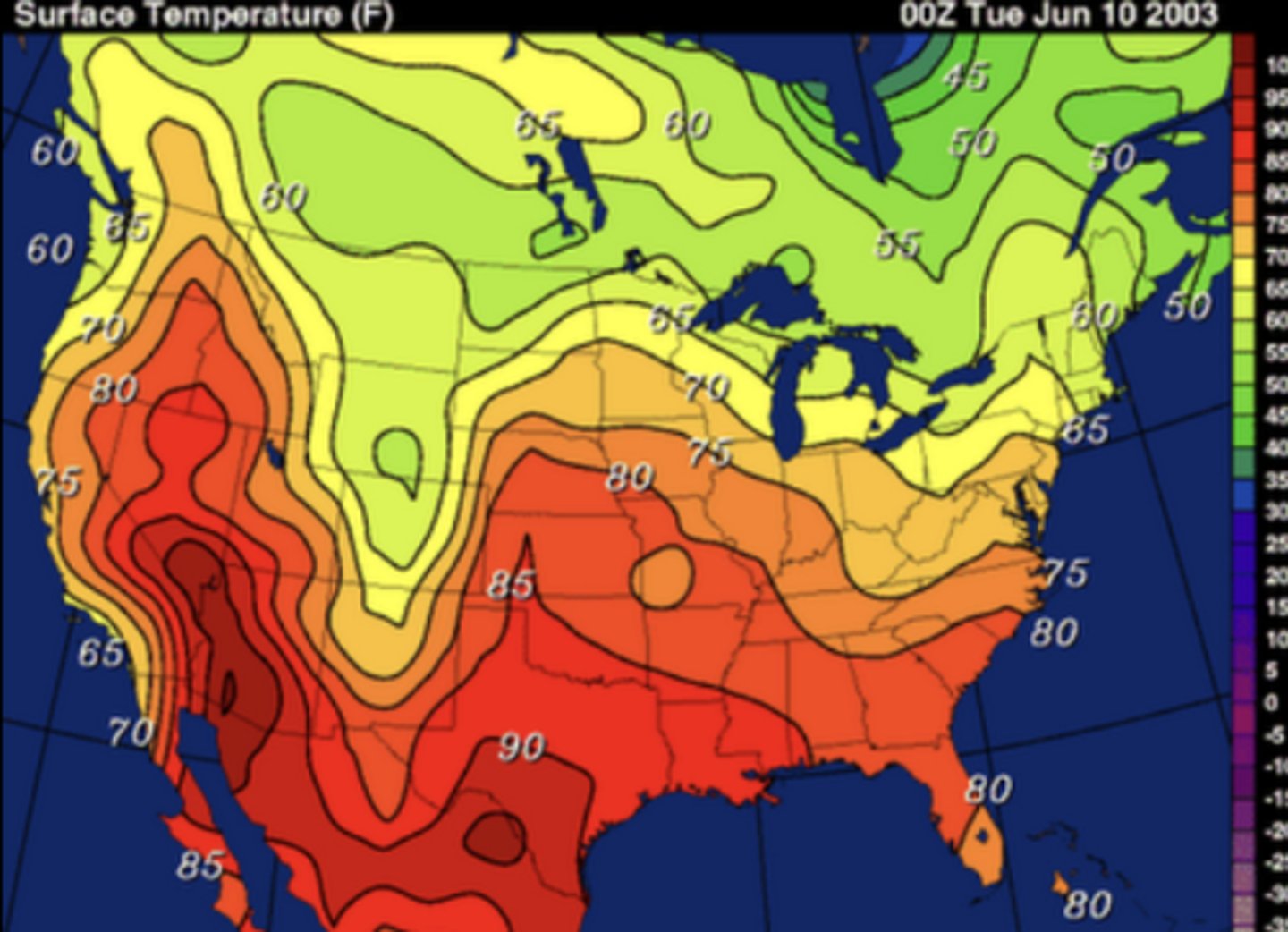
Isoline map
Use lines to connect places that are similar in quality of quantity
Ex: temperatures
Located charts
map of a place with an additional layer / theme on top
Ex: percent population
place
A specific point on Earth distinguished by a particular character. In geography, associated with a name, and unique cultural/historic traits
region
an area defined by one or more natural or cultural characteristics that set it apart from other areas; in human geography 3 different forms are recognizable
Toponym
The name given to a portion of Earth's surface
Ex: boston, Maine, Georgio
space
in human geography, the study of the distribution of human/physical characteristics across the surface of the Earth; one of main concepts
Diffusion
The process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time; 2 main categories are studied in geography
relocation diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend through human movement of people from one place to another
Ex: I move to london and I show people how to play waterpolo

Contagious Diffusion
The distance-controlled spreading of an idea, innovation, or some other item through a local population by contact from person to person.
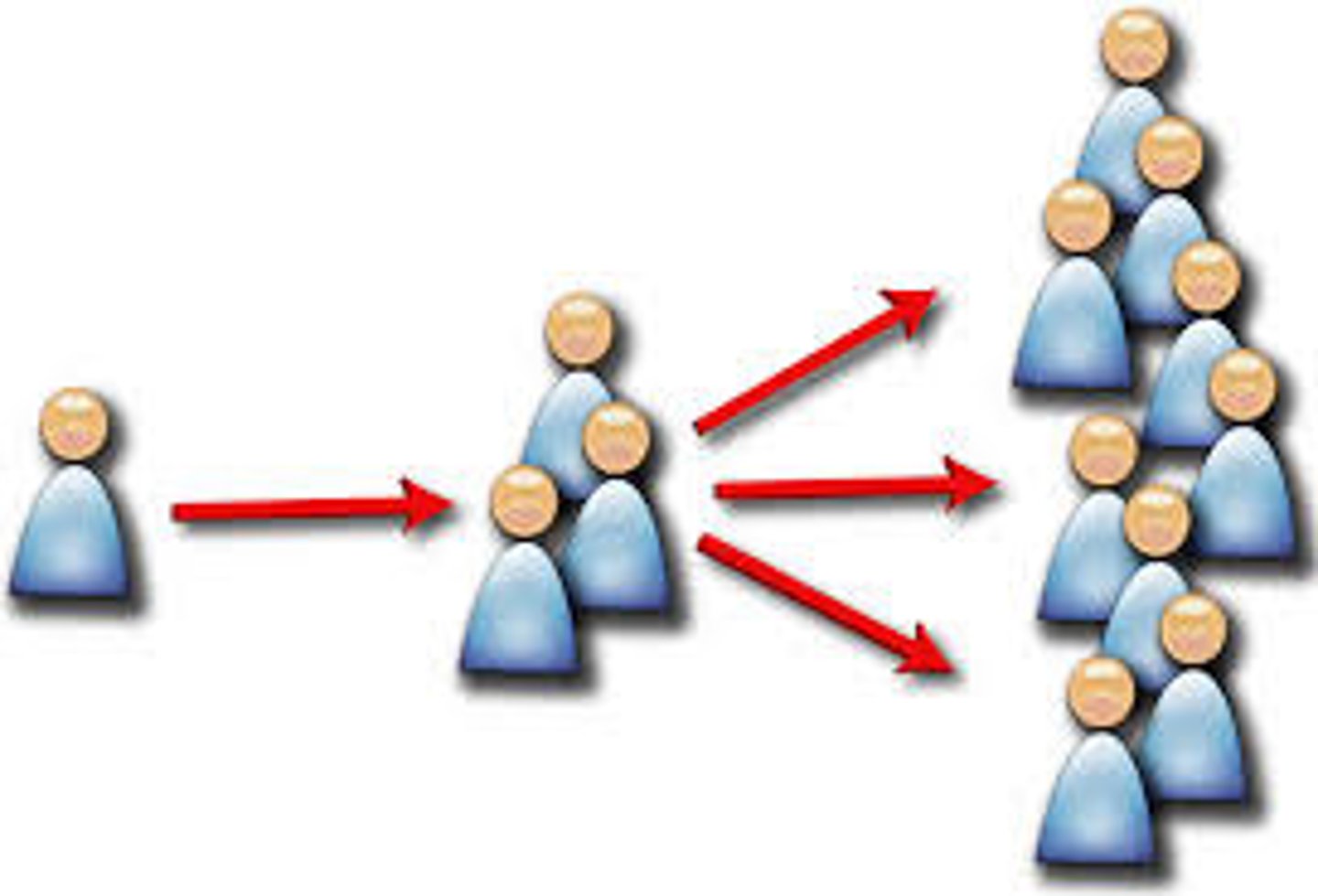
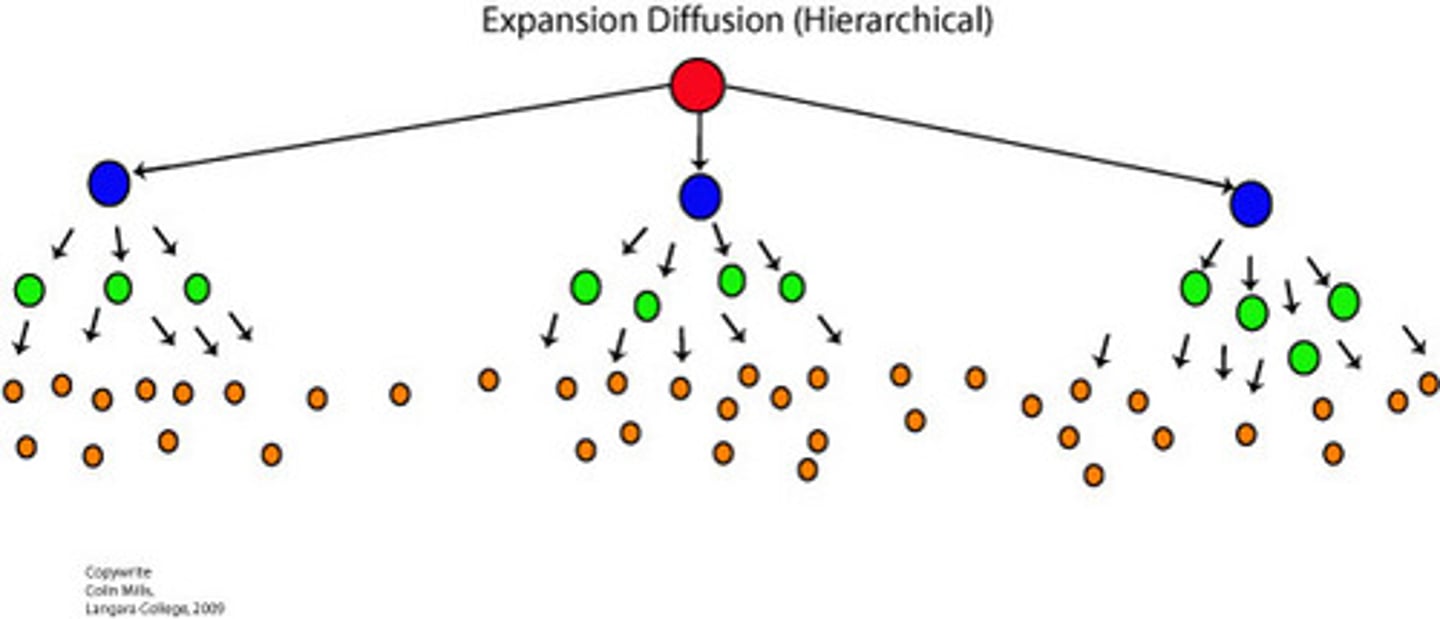
Hierarchical Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places
Ex: taylor swift culture
Stimulus Diffusion
The spread of an underlying principle, even though a specific characteristic is rejected
ex: mcdonalds is global but the menu is different in the US compared to Thailand

scale of analysis
a scale that determines what is being studied based on the size of the area being examined
Ex: poverty can be studied at the local level, national level, and even global level
connection
Relationships among people and objects across the barrier of space
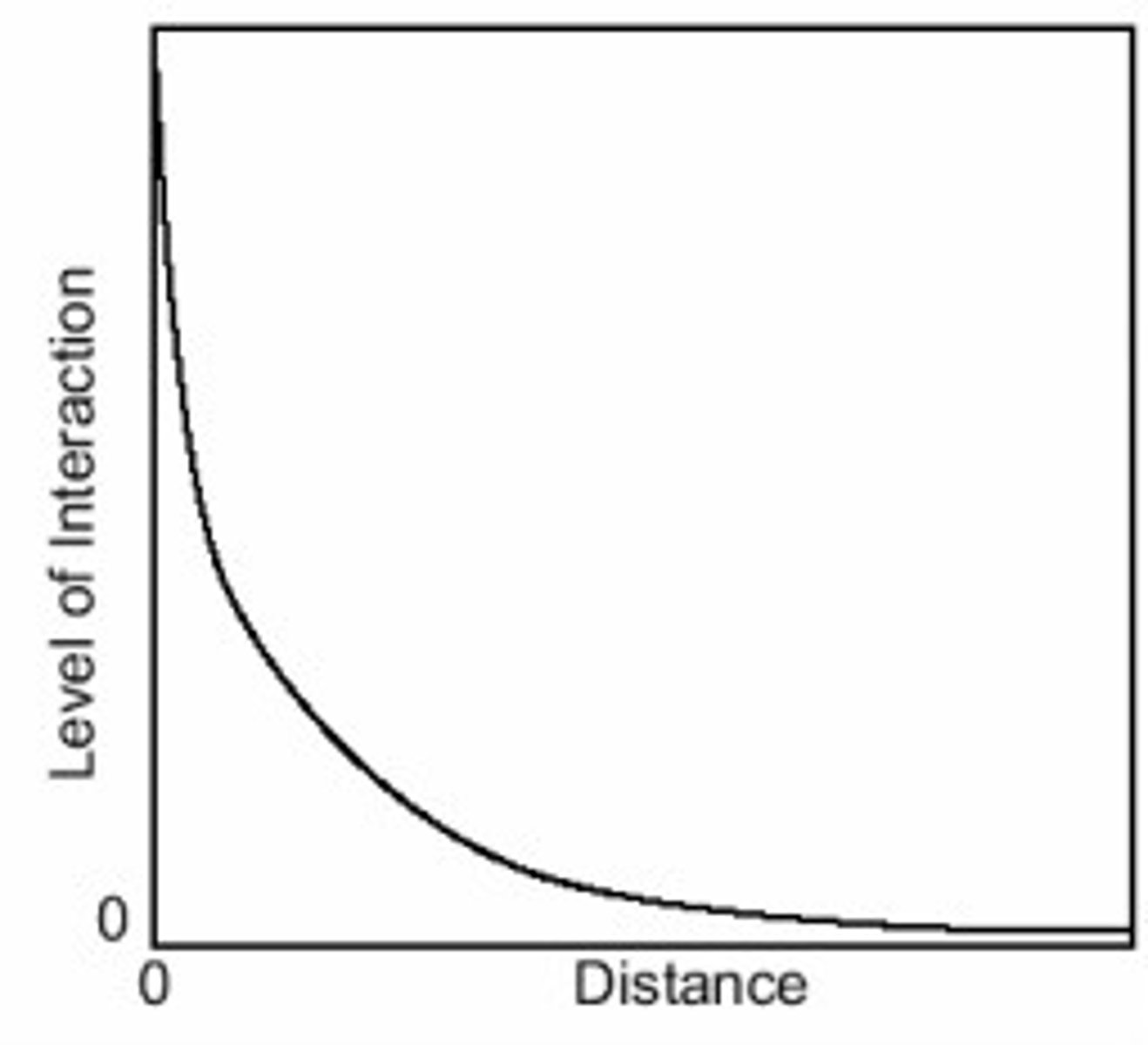
Distance Decay
The diminishing in importance and eventual disappearance of a phenomenon with increasing distance from its origin.
space-time compression
The farther away something is, the less likely you are to interact with it
Ex: You're more likely to go to a store 5 minutes from your house than one 2 hours away.
space-time compression

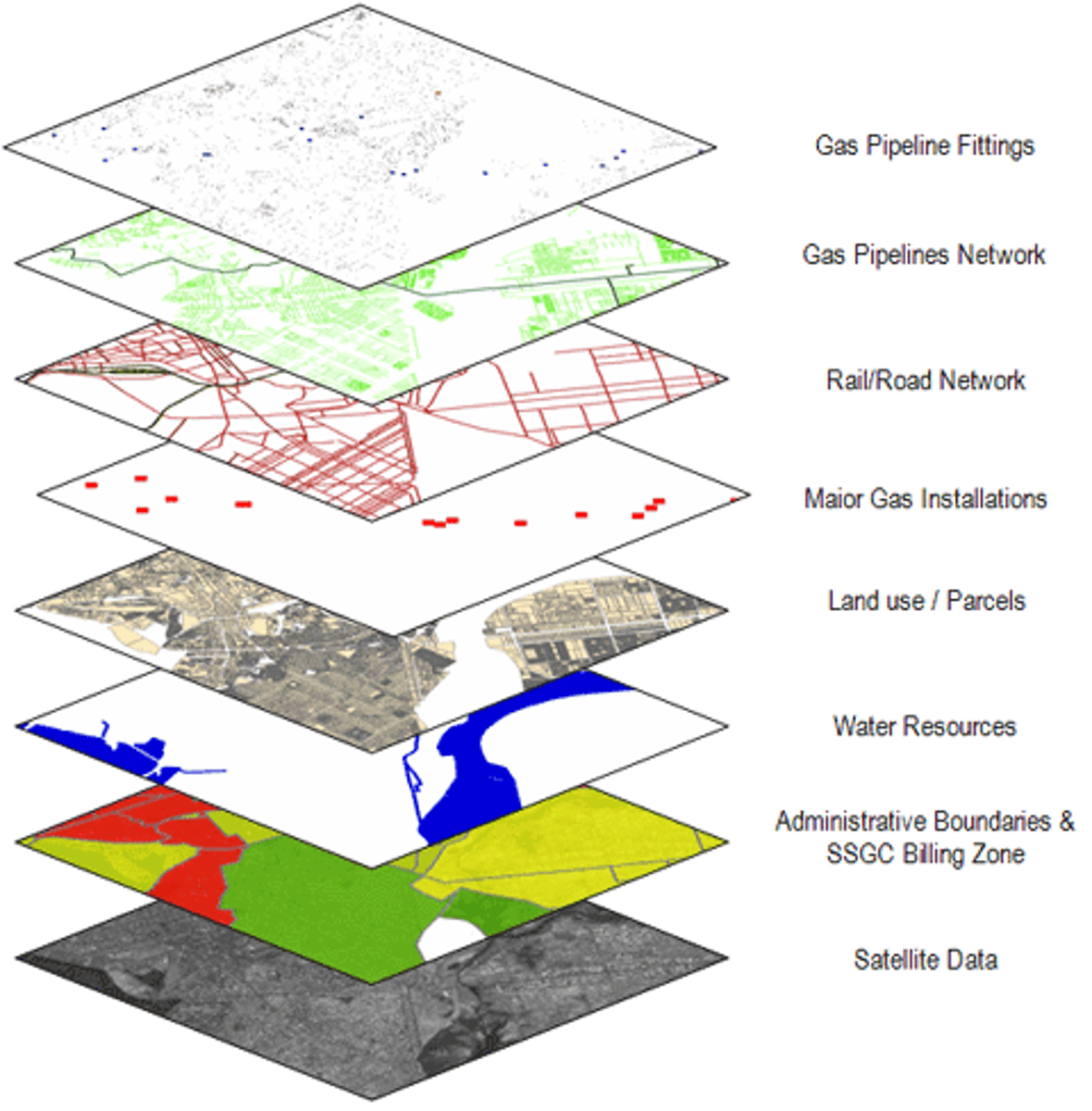
GIS
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
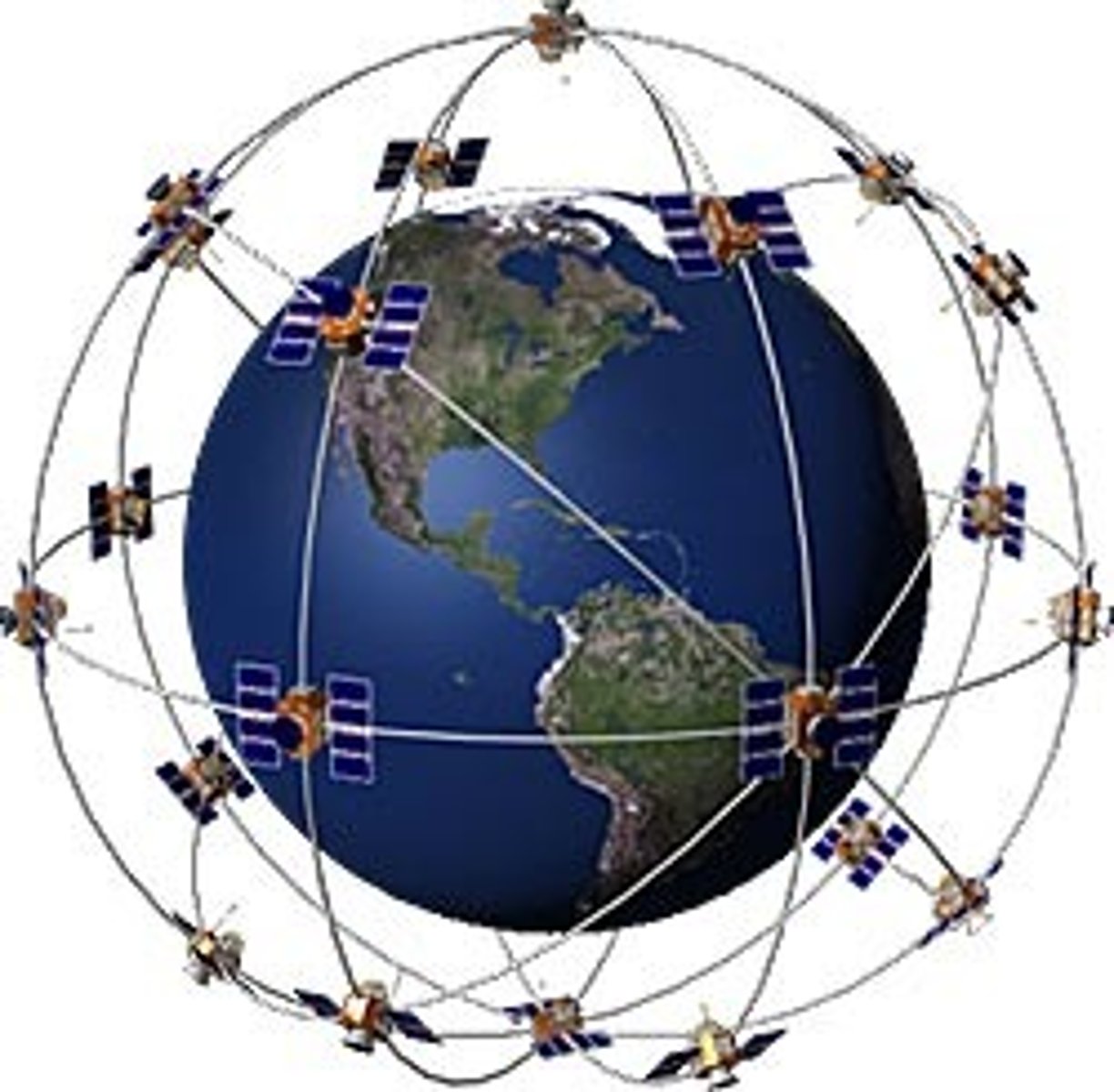
GPS
A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
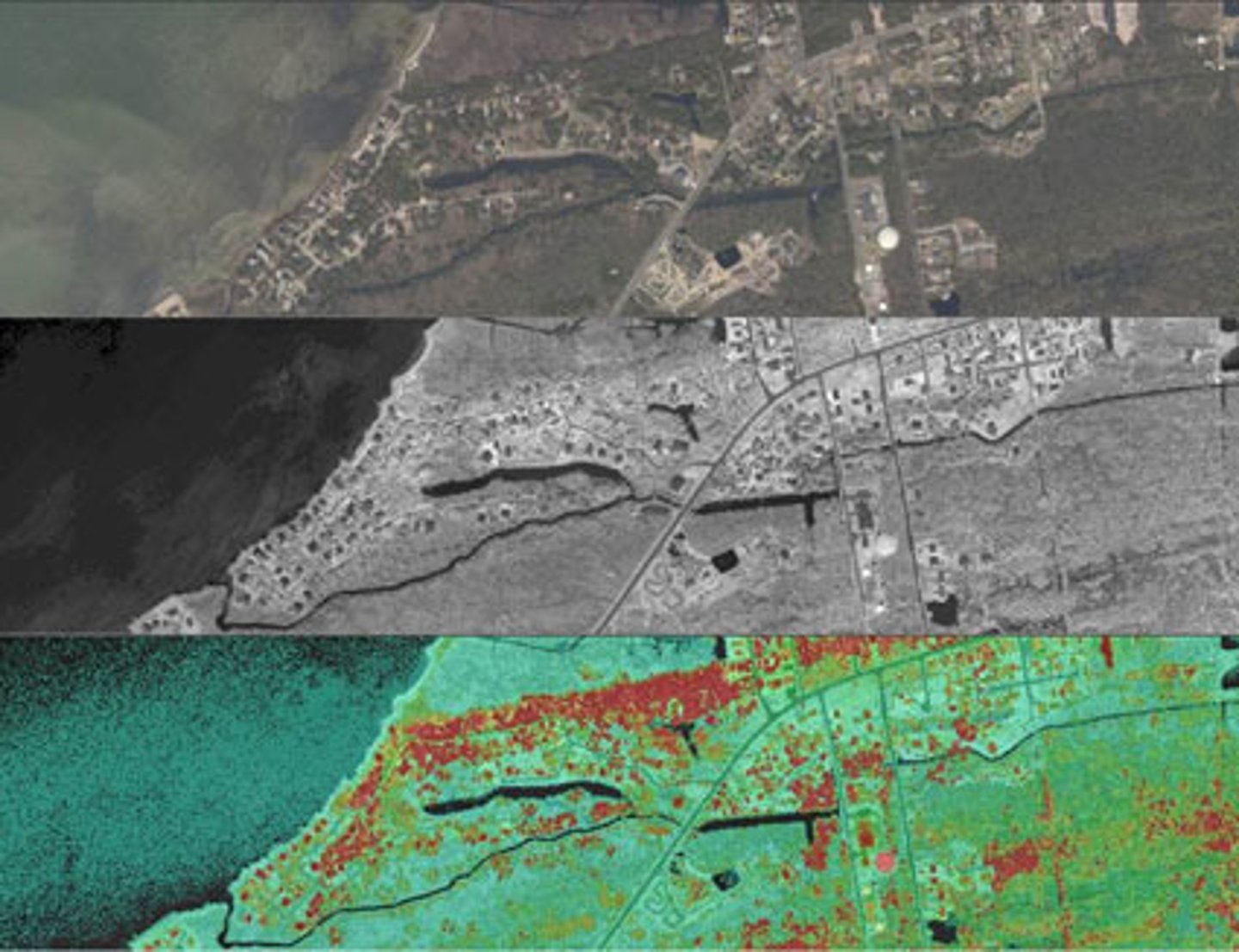
remote sensing
The acquisition of data and images about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods.
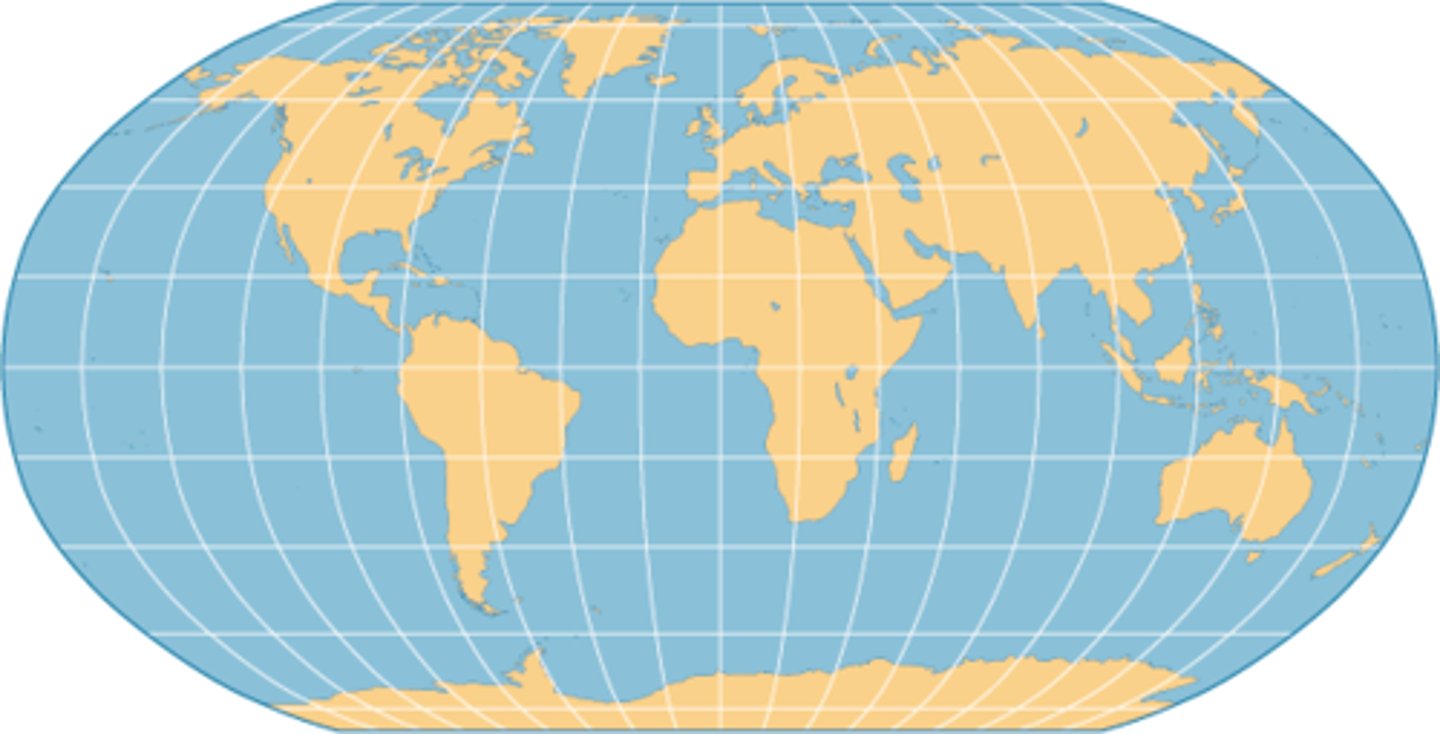
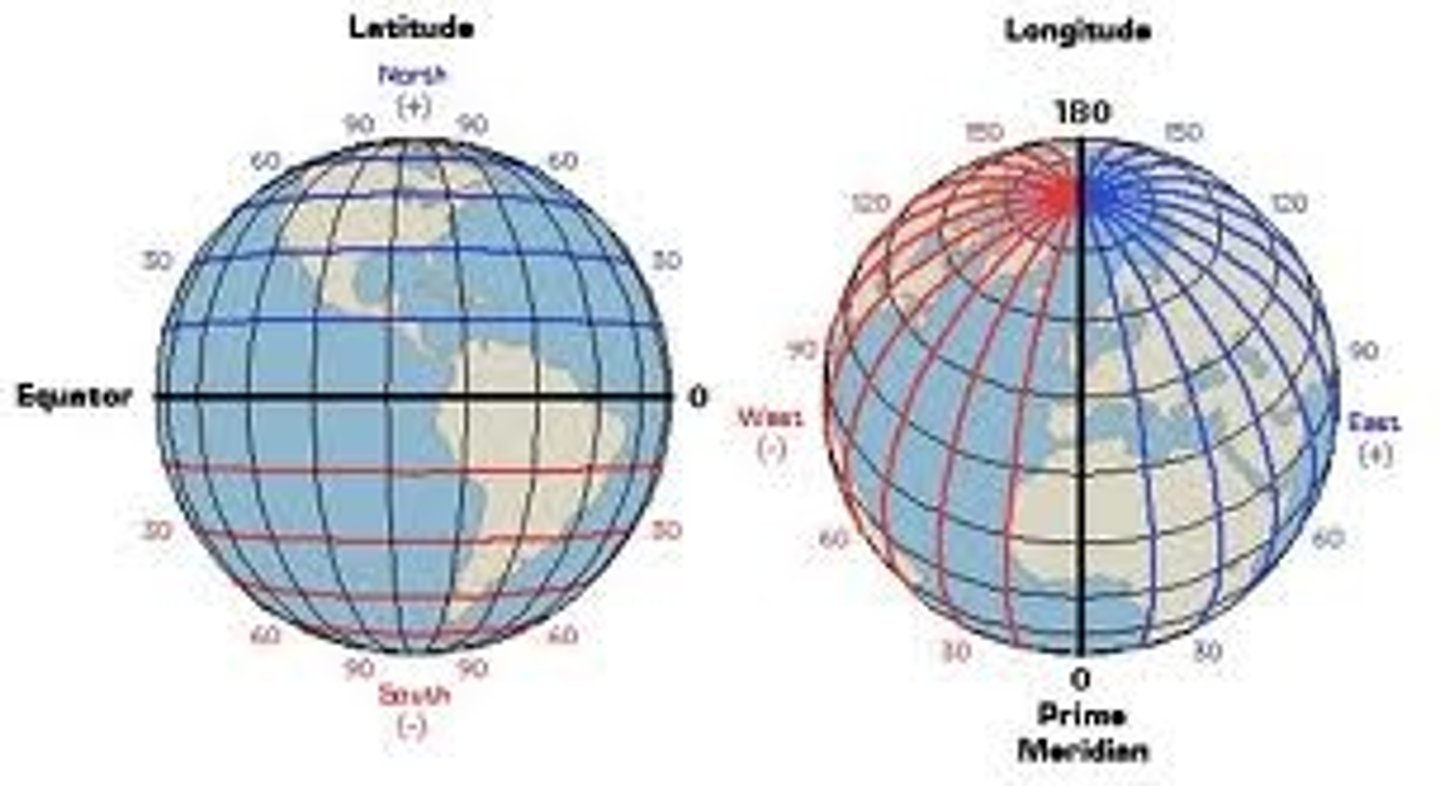
map projection
a way of representing the spherical Earth on a flat surface
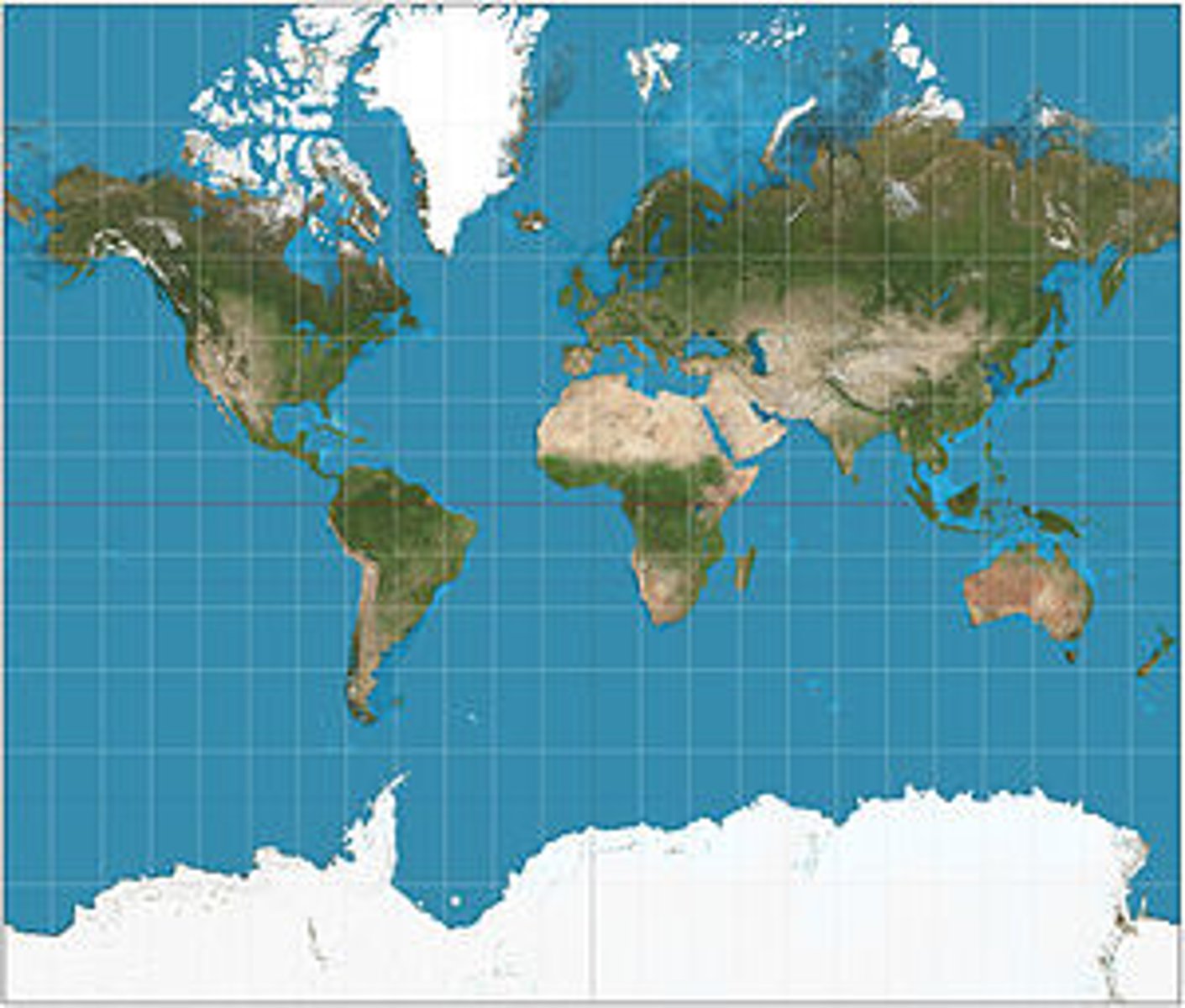
Gerardus Mercator
A Flemish cartographer (1512-1594) was one of the first to produce a world map that accurately helped with navigation, but greatly distorted Northern areas
distortion
a change in the shape, size, or position of a place when it is shown on a map
Geographic grid system
System which pinpoints location by using two coordinates (latitude and longitude) in order to accurately measure the position of any place on the surface of the Earth
cultural landscape
the visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape

Formal Region (Uniform Region)
An area in which everyone shares in common one or more distinctive characteristics
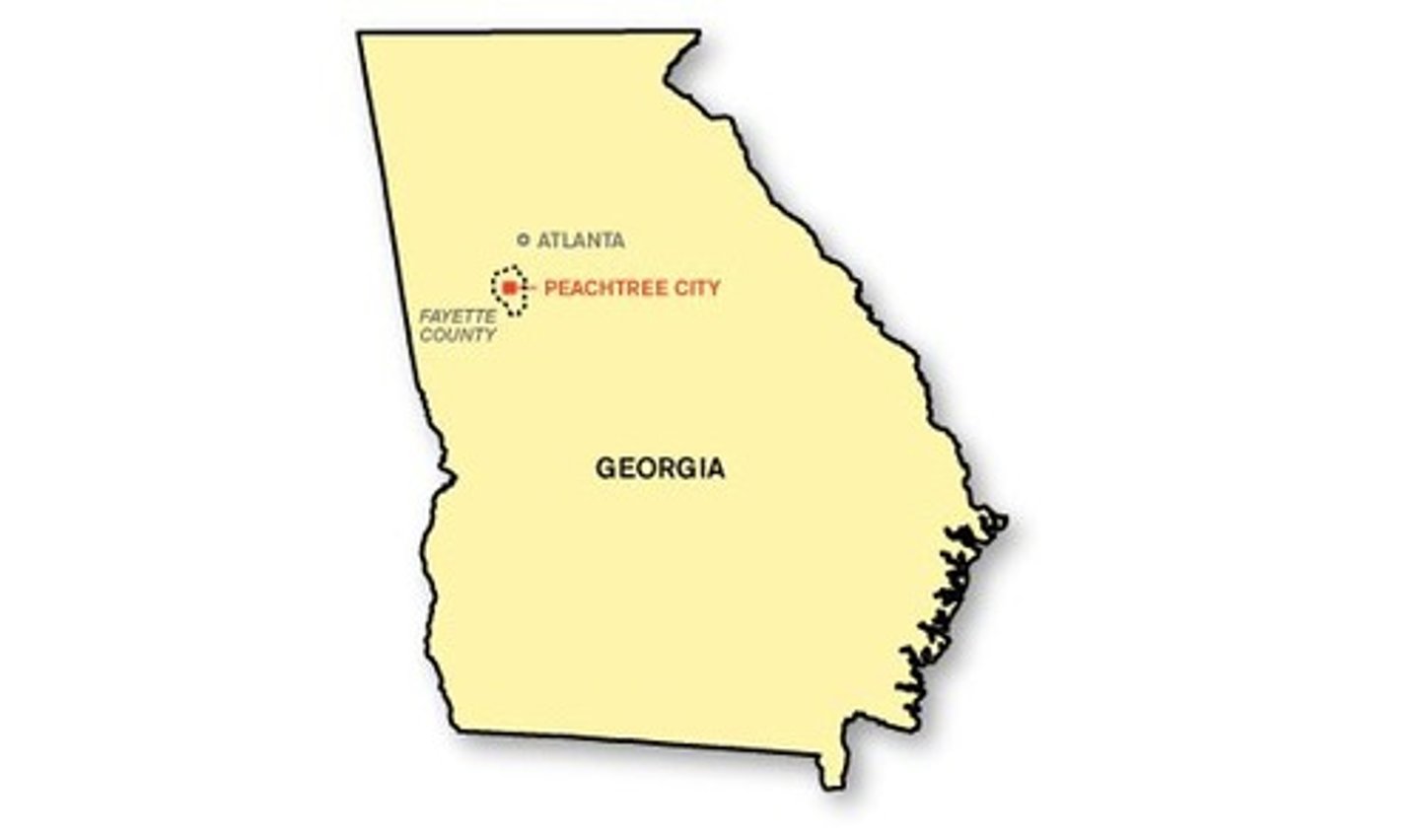
Functional Region (Nodal Region)
An area organized around a node or focal point which serves up to a certain distance before no longer influencing
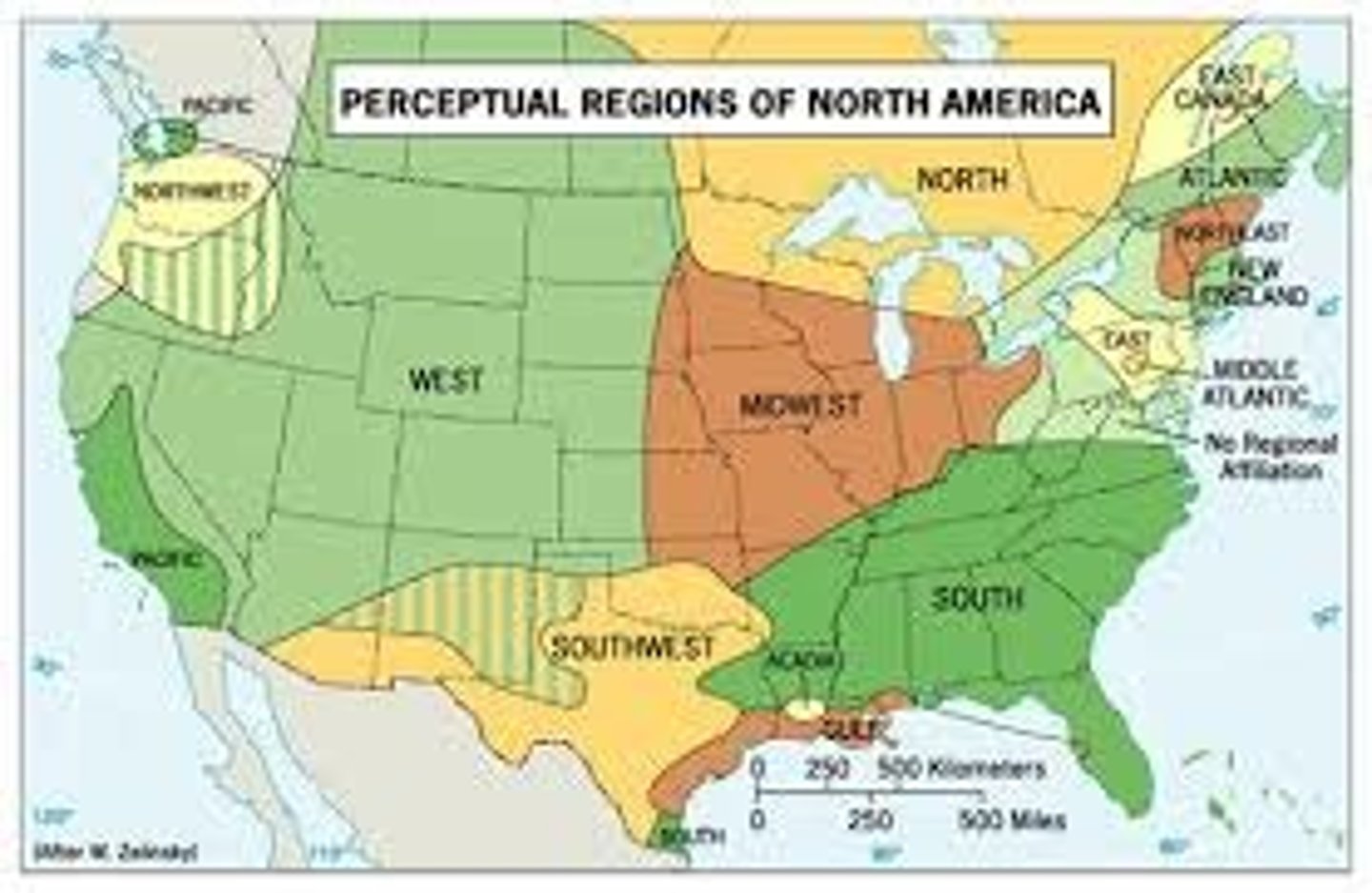
Vernacular region (or perceptual region)
an area that shares a common qualitative characteristic, it's only a region because people believe it's a region, and people may differ in their opinions about it
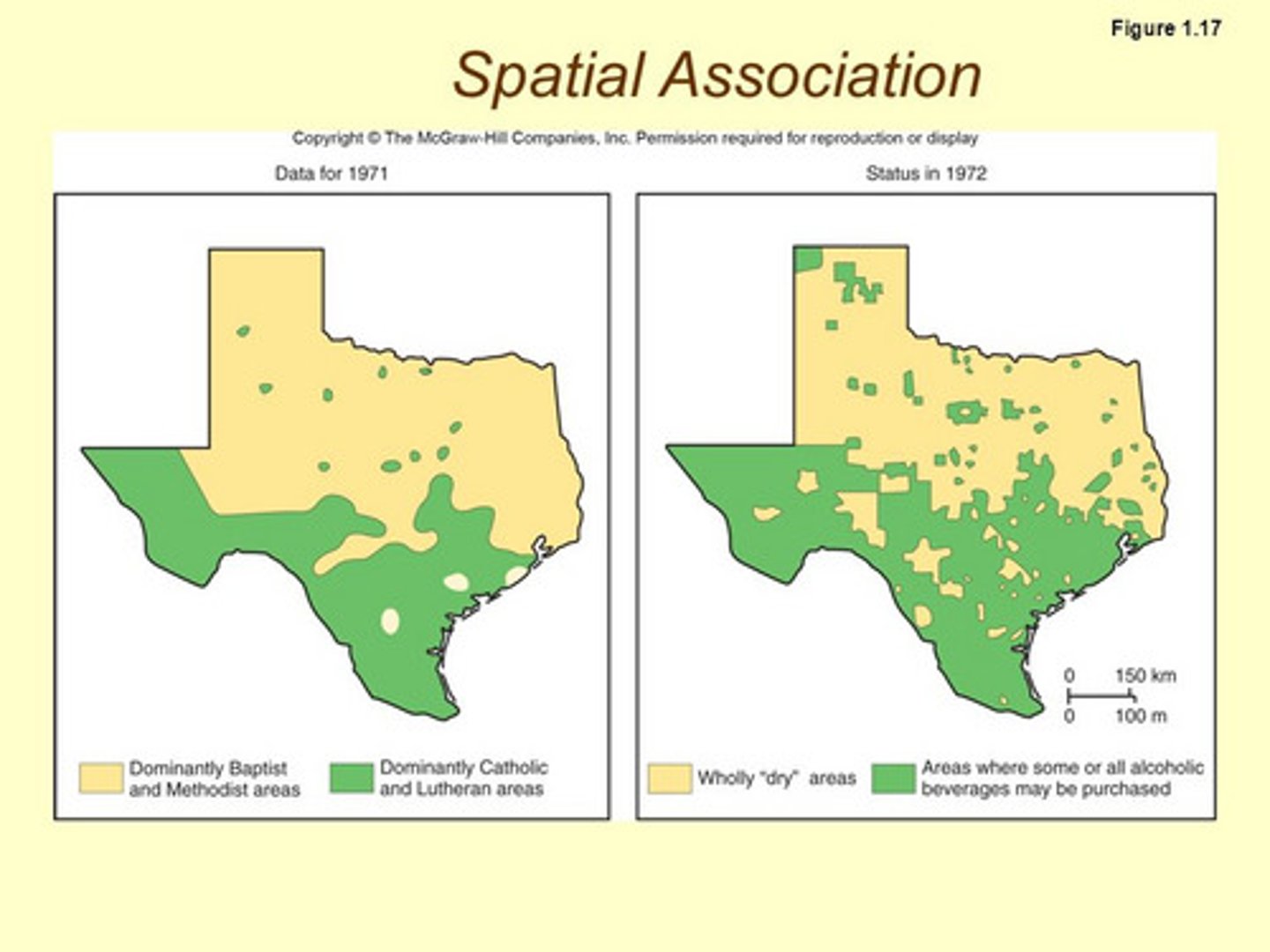
Spatial Association
The relationship between the distribution of one feature and the distribution of another feature; for example the presence of poverty in an large city and the data showing unemployment rates in that city
Transnational Corporation
A company that conducts research, operates factories, and sells products in many countries, not just where its headquarters or shareholders are located; often the driving forces of globalization and uniform landscapes

Uniform Landscape
the spatial expression of a popular custom in one location that will be similar to another

Hearth
The region from which innovative ideas originate
Sustainability
meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs

environmental determinism
the cultural ecology viewpoint that the natural environment has a controlling influence over various aspects of human life including cultural development; commonly believed historically before Industrialization

Possibilism
The cultural ecology viewpoint that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives.

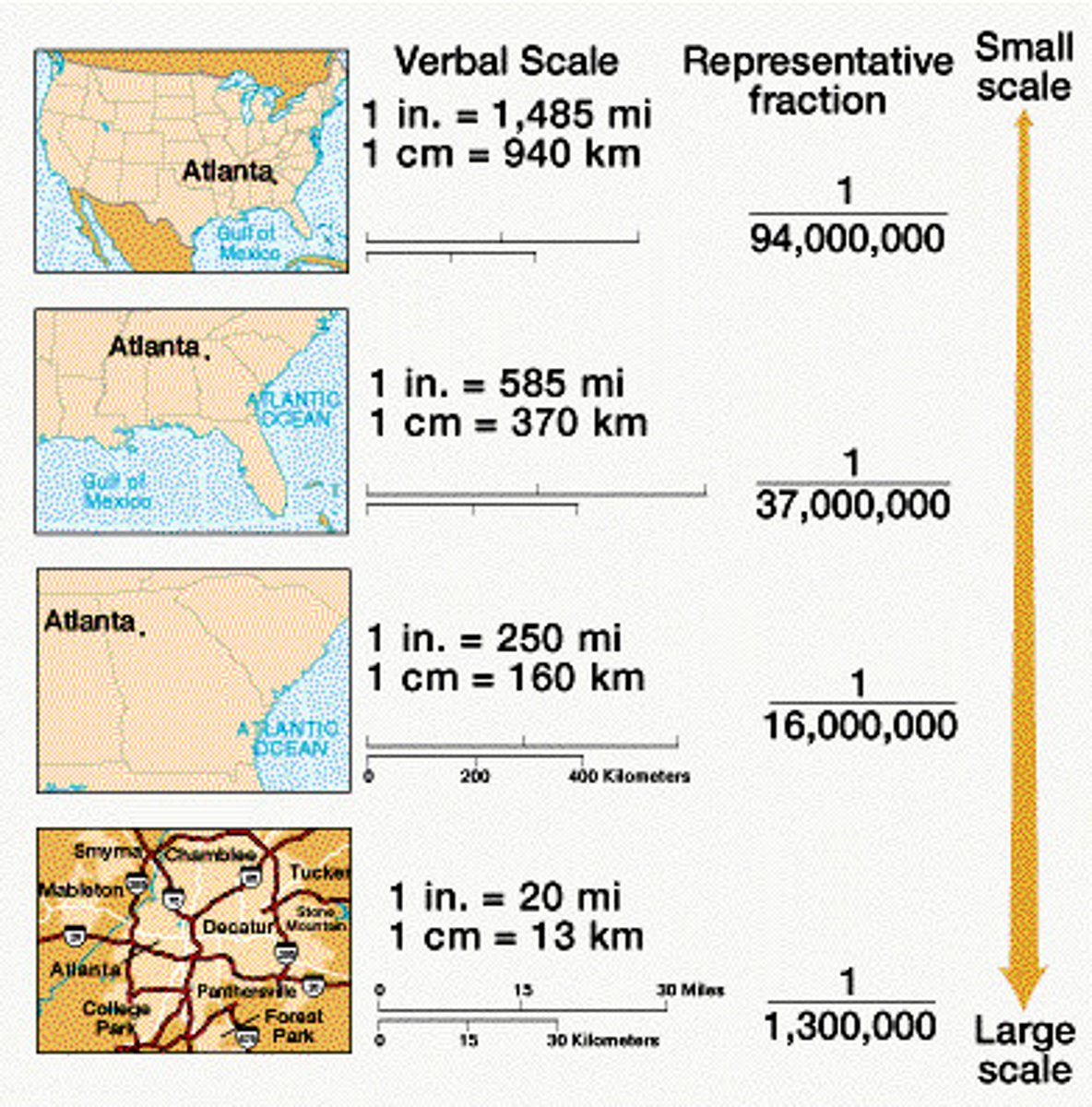
map scale
small scale is less detail and birds eye view
large scale is more detail
space-time compression
describes the reduction in the time it takes for something to reach another place due to increase in technology and connections among people -- closely connected to globalization

distance-decay
the effects of distance on interaction, generally the greater the distance the less interaction between things -- the more they differ over time
reference map
Maps that show the absolute location of places and geographic features determined by a frame of reference, typically latitude and longitude
thematic map
A type of map that displays one or more variables-such as population, or income level-within a specific area.
human migration
the permanent movement of people from one place to another
Arithmetic Density (aka crude density)
the total number of people per unit of land
Pysiological Density
The number of people per unit area of arable land
agricultural density
total number of farmers per unit of arable land
subsistence agriculture
Agriculture designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family
carrying capacity
Maximum population size an environment can sustain
demography
study of statistics such as births, deaths, income, or the incidence of disease, which shows the changing structure of human populations
most populated regions
east asia, south asia, southeast asia, europe
dependency ratio
the ratio of the number of people in a dependent age group (kids and elderly) to the number of people in an economically productive age group (15-65) x 100
demographics
the characteristics of a population with respect to age, race, and gender.
crude birth rate
number of births in a given year, per 1000 people in a given population
crude death rate
number of deaths in a given year, per 1000 people in a given population
3 factors that determine populations growth and decline
1. fertility
2. mortality
3. migration
total fertility rate
average number of children one woman in a given region will have in her childbearing years
rate of natural increase
difference between the cbr and the cdr of a defined group of people
formula: crude birth rate - crude death rate / 100 = % by which a population grows in a year
infant mortality rate
the annual number of deaths of infants under 1 year of age, compared to total live births
doubling time
number of years in which a population growing at a certain rate will double
urbanization
the growth and development of cities
immigrants v emmigrants
into vs exiting a place
neo-malthusian
theory related to the idea that population growth is unsustainable and that the future population can not be supported by earths resources
thomas malthus: theory that population will outpace food production
demographic transition model
a model that represents shifts in the growth of the worlds populations, based on population trends related to birth rate and death rate
Epidemiological Transition Model
A model that describes changes in fertility, mortality, life expectancy, and population age distribution, largely as the result of changes in causes of death
describes why these things are happening (diseases, age)
migration
the permanent or semi-permanent relocation of people from one place to another
intervening obstacles
barriers that hold migrants back from continuing to travel
intervening opportunity
one that causes migrants to voluntarily stop traveling
net migration
difference between the number of emigrants and immigrants in a location
dif between leaving and coming in
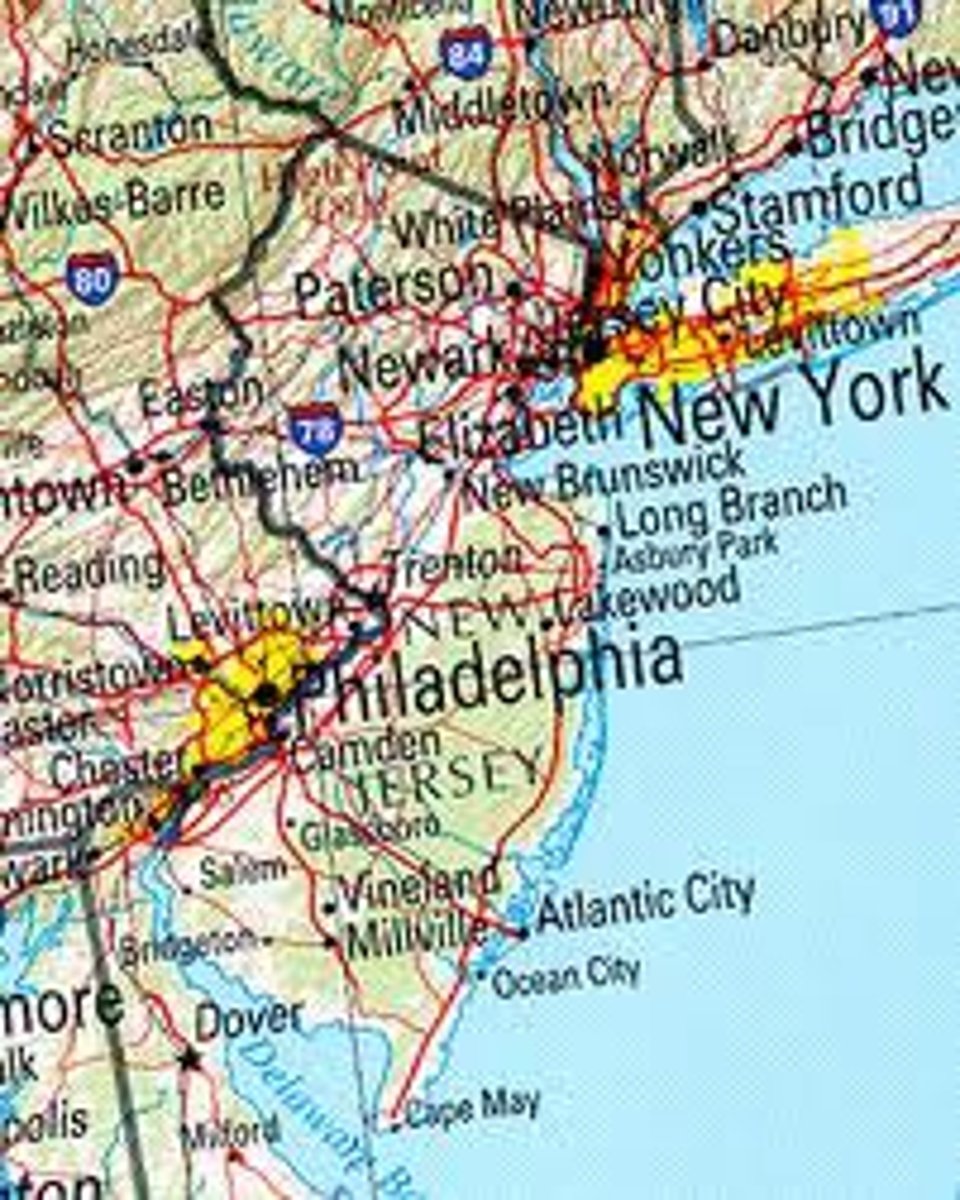
gravity model
a model that predicts the interaction between two or more places (derived from Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation) - Ex: New Mexico and NY v LA and NY --> new mexico larger population = bigger interaction between with NY than LA
intervening obstacle
An environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that hinders migration.
intervening opportunity
An environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that helps migration.
refugee
A person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster
asylum seeker
An asylum seeker is a person who has left their country and is seeking protection from persecution and serious human rights violations in another country, but who hasn't yet been legally recognized as a refugee and is waiting to receive a decision on their asylum claim
internally displaced person
Someone who has been forced to migrate for similar political reasons as a refugee but is staying within borders
internal migration
Permanent movement within a particular country.
interregional migration
Permanent movement from one region of a country to another.
intraregional migration
Permanent movement within one region of a country.
international migration
Permanent movement from one country to another.
transnational migration
Transnational migration refers to people living in another country but maintaining ties back to the country they came from
transhumance
the seasonal movement of livestock (herding) between mountains and lowland pastures
chain migration
migration of people to a specific location because relatives or members of the same nationality previously migrated there
step migration
migrating in steps, aka moving from CA to WA to CO
guest worker (time contract worker)
a person with temporary permission to work in another country (maybe have special skill that was needed)
circular migration
when a migrant worker moves between their home and a host area on a temporary basis, often for employment
human trafficking
The illegal trade of human beings, a modern-day form of slavery, for the purpose of commercial sexual exploitation, forced labor, or involuntary military combat.
skills gap
the difference between the skills required for a job and the skills that an employee or potential employee possesses
brain gain
when a country benefits from skills
brain drain
the loss of highly educated and skilled workers to other countries
relocation diffusion
the spread of cultural traits, ideas, or innovations through the physical movement of individuals or groups from one location to another ( like how overtime the language of spanish traveled elsewhere than its origin country)
remittances
money that migrants send back to family usually in cash
Political geography
The study of the ways in which the world is organized as a reflection of the power that different groups hold over territory
State
A politically organized independent territory with a government, defined borders, and a permanent population—in short a country
US is a state
Sovereignty
The right of a government to control and defend its territory and determine what happens within its borders
Nations
Cultural entities, meaning that they are made up of individuals who have forged a common identity through a shared language, religion, ethnicity, or heritage—often all four of these.