7. Mycotic, parasitic, tumour & other skin diseases in respective pig categories
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(Dermatomycosis, Pediculosis, Sarcoptosis, insect-born diseases, melanoma, carcinoma, Pityriasis...).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is an example of a mycotic skin disease in pigs?
Dermatomycosis (ringworm)
What is the cause of dermatomycosis (ringworm) in swine?
Trichophyton verrucosum, Microsporum nanum/canis/gypseum
What type of organisms cause fungal infections of the skin, hair, and nails in swine?
Dermatophytes (use keratin as a growth factor)
How is dermatomycosis transmitted in swine?
Direct or indirect contact, spores in air, dust, or on surfaces; also rodents
What is the pathogenesis of dermatomycosis in swine?
Penetration of hair follicles, formation of hyphae and spores, causing parakeratosis and skin hyperplasia
What are the clinical signs of dermatomycosis in swine?
Red, scaly, circular rash; mild to no pruritus; round or oval areas of crusting and alopecia (up to 20 cm in diameter) on shoulders, back, and flanks

How is dermatomycosis diagnosed in swine?
By clinical signs, culturing in Sabouraud’s agar, microscopy using KOH, skin biopsy, and Wood’s lamp (Microsporum)
What is the treatment for dermatomycosis in swine?
Usually self-limiting; can use thiabendazole, lime sulphur, iodophors
What are examples of parasitic skin diseases in pigs?
Pediculosis
Sarcoptic mange
Demodicosis
Myiasis
Insect-borne diseases
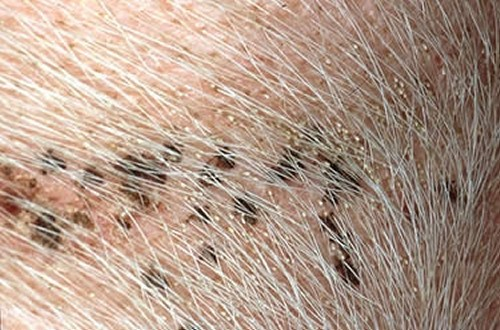
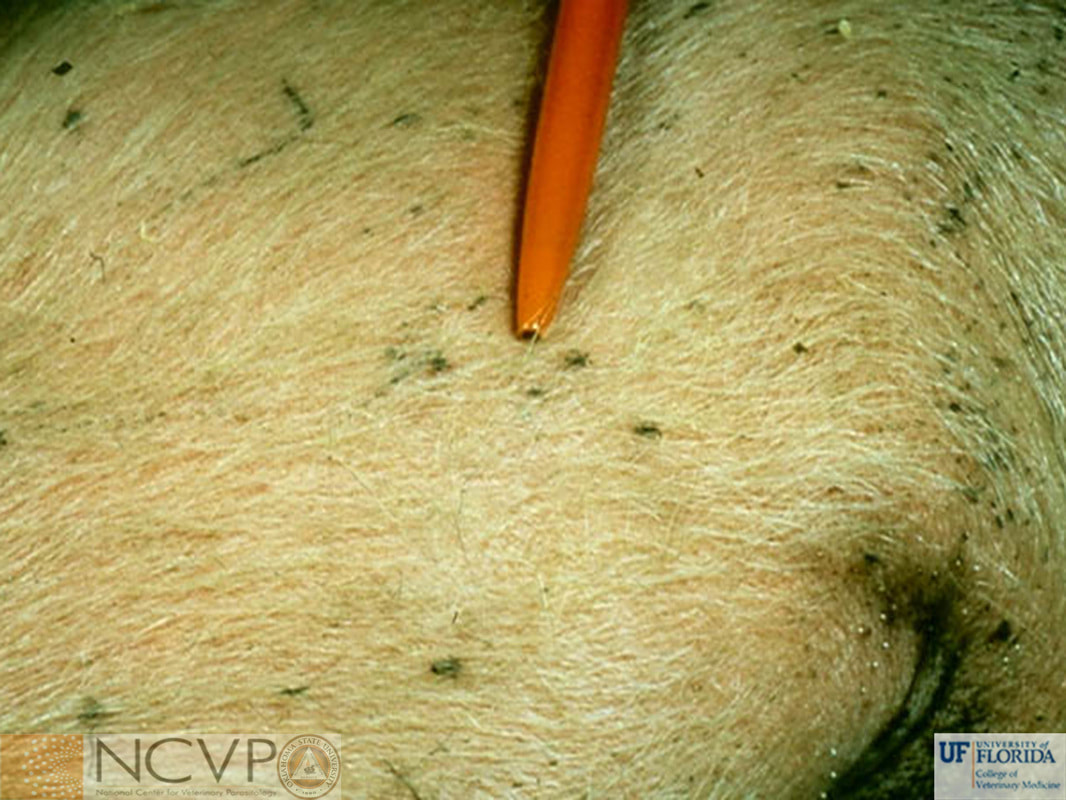
What is the main parasite causing lice infestation (pediculosis) in swine?
Haematopinus suis (sucking lice/Anoplura)
Where are lice most commonly found on swine?
On the back and thin-skinned areas such as ears and inner legs
What are the clinical signs of lice infestation in swine?
Intense scratching, alopecia, skin thickening, pruritic skin damage
How is lice infestation diagnosed in swine?
By observing the lice visually and noting intense scratching
What is the treatment for lice infestation in swine?
Ivermectin and amitraz
How can lice infestation be prevented in swine herds?
Regular ectoparasite treatment and treating new animals with insecticides before adding them to the herd
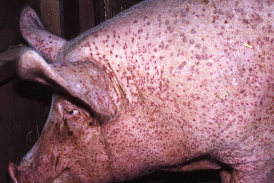
What is sarcoptosis in swine?
Infestation by Sarcoptes scabiei var. suis, a burrowing mite (itch mite)
Where do Sarcoptes scabiei mites infest swine?
Inner ear, behind the ear, nose, neck, and bends of joints
How is sarcoptosis transmitted in swine?
Direct pig-to-pig contact
What is the life cycle of Sarcoptes scabiei in swine?
Copulation on the skin, females dig burrows up to 1 cm in the epidermis, lay 1-3 large eggs per day, larvae hatch, and develop through nymphal stages to adults
What are the clinical signs of sarcoptosis in swine?
Allergic reactions to mite antigens → Itching, erythema, papules, parakeratosis, skin crusts, alopecia, weight loss, poor growth rates, death in piglets, rubbing, chronic head shaking, and crusty exudate in the ear canal
How is sarcoptosis diagnosed in swine?
By finding mites in ear wax and deep skin scrapings
What is the treatment for sarcoptosis in swine?
Ivermectin and amitraz spray
What is the prevention strategy for sarcoptosis in swine?
Whole herd treatment every 6 months; sows treated 7-14 days before farrowing
What is demodicosis in swine?
Infestation by Demodex phylloides (burrowing mite), seen in immuno-suppressed animals
What are the clinical signs of demodicosis in swine?
Red skin, pustules, and alopecia. NO PRURITUS!!!

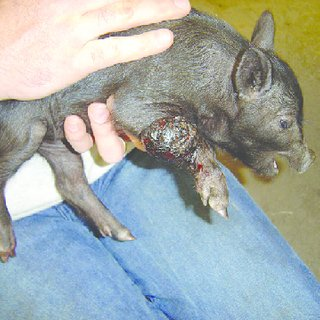
What is myiasis in swine?
Parasitic infestation by larval stages (maggots) of dipterous flies
Which fly families are associated with myiasis in swine?
Muscidae, Calliphoridae, Sarcophagidae, and Oestridae
What are the types of myiasis?
Blowfly
Screw-worm
What are the species of flies causing blowfly myiasis in swine?
Lucilia sericata, Phormia terraenovae, Calliphora erythrocephala, and Calliphora vomitoria
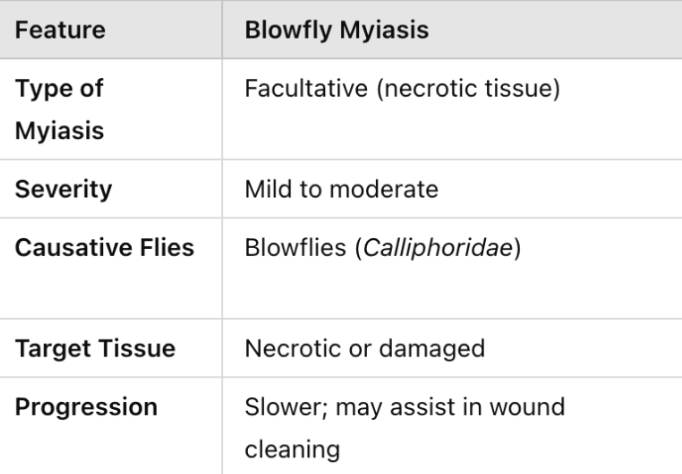
What are the species of flies causing screw-worm myiasis in swine?
Cochliomyia hominivorax (new world) and Cochliomyia bezziana (old world)

What is the pathogenesis of myiasis in swine?
Fly larvae secrete enzymes that degrade epithelial cells, causing exudate formation, inflammation, and immunological reactions
What are the clinical signs of myiasis in swine?
Inflammation, pruritus, exudative dermatitis, necrosis, secondary infections, and ammonia intoxication from larvae
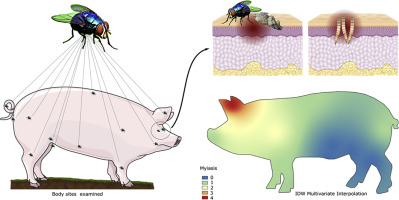
How is myiasis diagnosed in swine?
By inspecting the skin and body openings and identifying larvae based on morphology and molecular methods
What is the treatment for myiasis in swine?
Removal of larvae, cleaning wounds, and applying insect cream/powder (organophosphates, pyrethroids, carbamates) at 2-3 day intervals; systemic antibiotics if needed
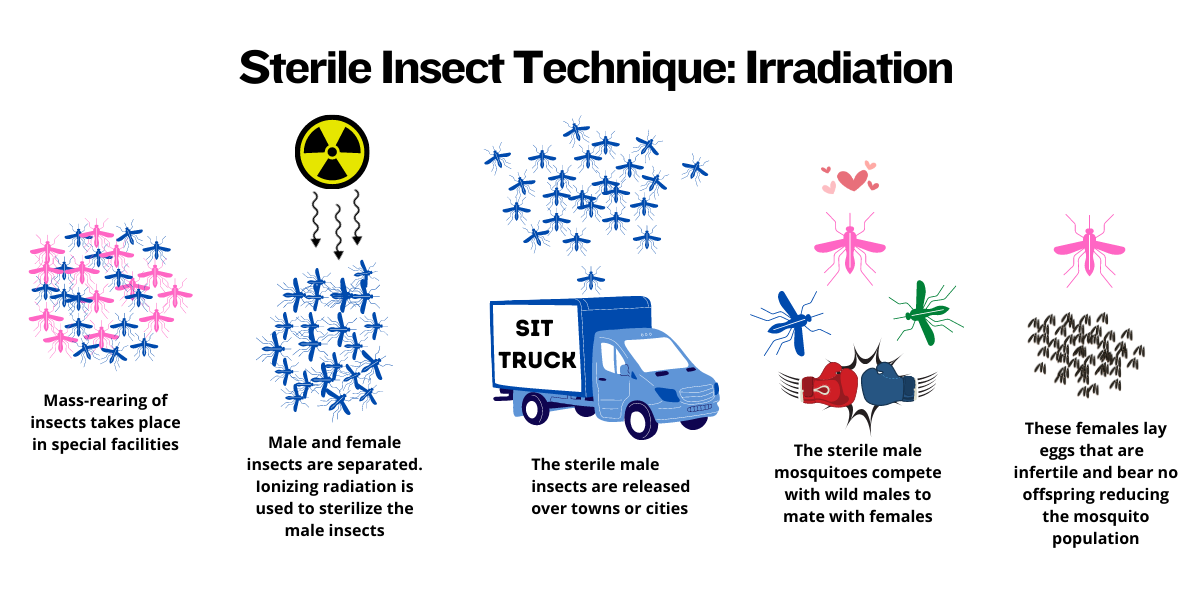
What are the prevention measures for myiasis in swine?
Sterile insect technique, habitat management, quarantine suspect animals, prompt treatment of wounds, and veterinary check before herd addition
What are examples of insect-borne skin diseases in pigs?
Pig pox
African Swine Fever
Vesicular Stomatitis
What is the virus causing pig pox in swine?
Suipoxvirus (Poxviridae, Suipoxvirus) transmitted by Haematopinus suis
What are the vectors for African swine fever?
Ornithodoros spp., biting flies, and mosquitoes
What is the virus causing vesicular stomatitis in swine?
Vesiculovirus (Rhabdoviridae), transmitted by blood-feeding insects like sand flies and black flies
What are examples of tumours in pigs?
Melanoma
Carcinoma
What is melanoma in swine?
A malignant neoplasm of melanoblasts and melanocytes found on the skin
What breeds of swine are predisposed to melanoma?
Small breeds, such as Sinclair miniature pigs, and Duroc

What are the clinical signs of melanoma in swine?
Pigmented macules or patches with smooth borders, raised or ulcerated pigmented lesions, or slightly raised blue masses
How is melanoma diagnosed in swine?
By clinical signs and biopsy
What is the treatment for melanoma in swine?
None
What is the prevention strategy for melanoma in swine?
Do not breed affected animals
What is carcinoma in swine?
A malignant epithelial neoplasm, including squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma, rare in pigs
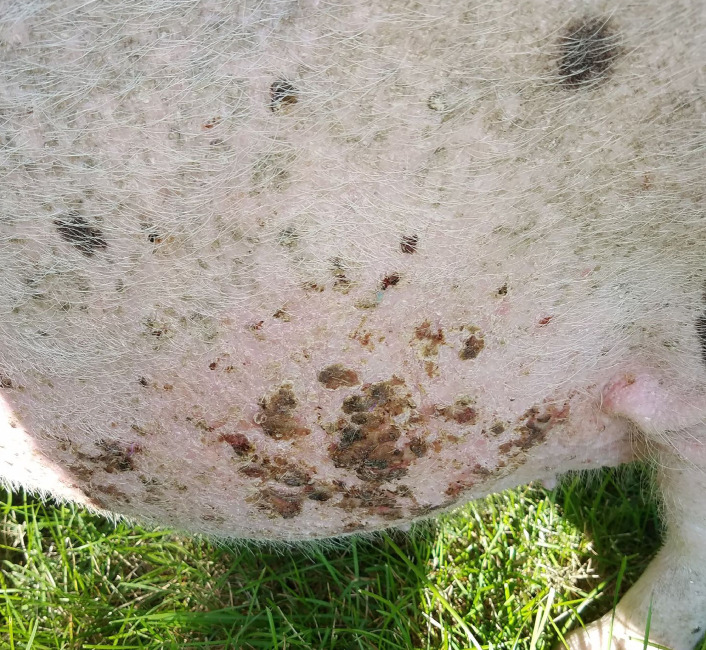
What is pityriasis in swine?
A non-contagious dermatitis that sporadically occurs in 3-16 week old pigs
What breed of swine is predisposed to pityriasis?
Landrace
What are the clinical signs of pityriasis in swine?
Large, circular lesions on the abdomen and hind legs, appearing during stress like weaning
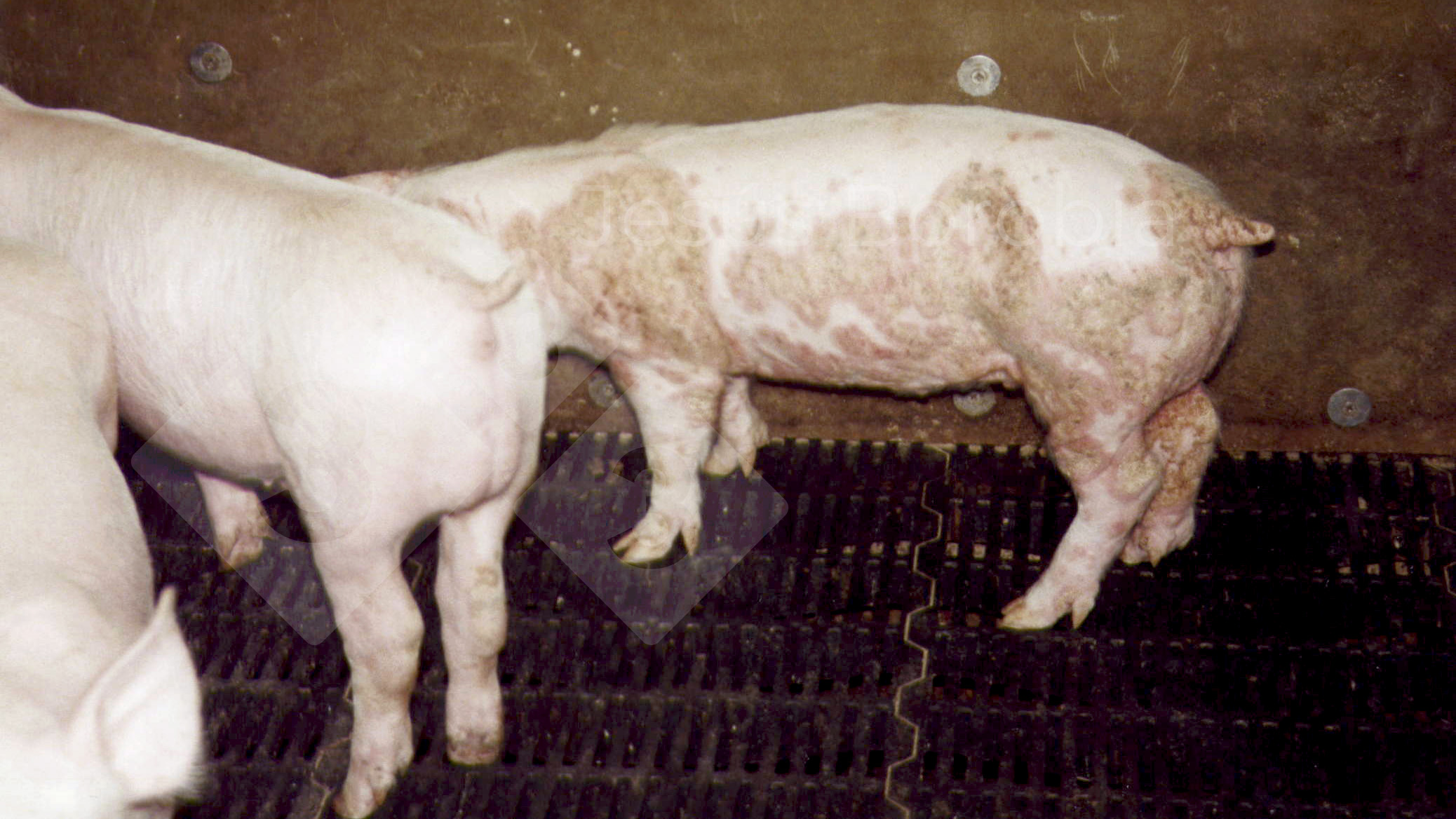
How is pityriasis treated in swine?
It resolves by itself in 6-8 weeks and is not pruritic; only differentiation from other skin lesions (ringworm) is needed
Where does demodicosis present?
On the face
What are ectoparasites treated with in pigs?
Ivermectin (1ml/33kg SC inj)
Amitraz (4ml/L water spray)
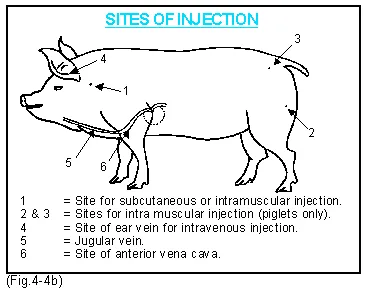
Where are subcutaneous injections given in pigs?
Behind the base of the ear