AP Biology Unit 5 Terms
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Meiosis
A type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms in which DNA is replicated once but two cycles of cell division occur. Meiosis also includes genetic recombination between homologous chromosomes generating genetic diversity. Meiosis produced genetically different haploid gametes.
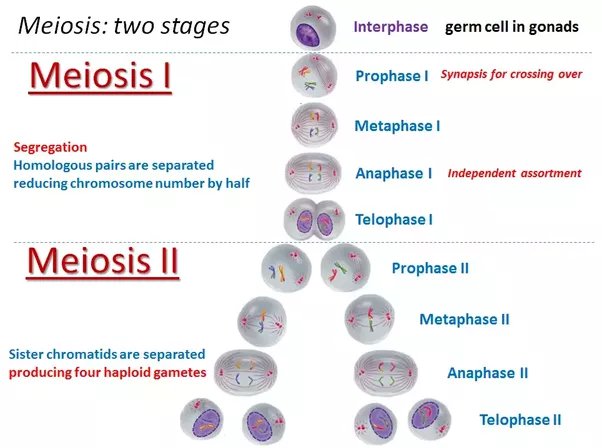
Haploid
A cell containing just one set of chromosomes. Gametic cells are usually haploid. In humans, the typical number of haploid chromosomes is 23.
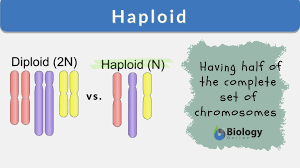
Diploid
A cell containing two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. Somatic cells are usually diploid. In humans, the typical number of diploid chromosomes if 46.
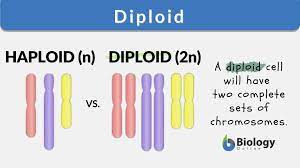
Meiosis I
The first half of meiotic cell division in which genetic recombination occurs and the number of chromosomes is reduced from the diploid to the haploid number.
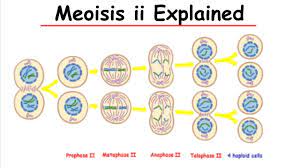
Meiosis II
The second half of meiotic cell division in which haploid cells are formed. Genetic recombination does not occur during meiosis II.
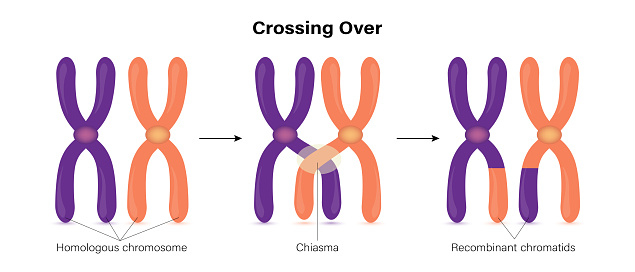
Genetic Recombination
Also known as “crossing over.” Describes the exchange of genetic information between homologous chromosomes. Usually occurs during prophase I of meiosis and increases the genetic diversity of the resulting gametes.
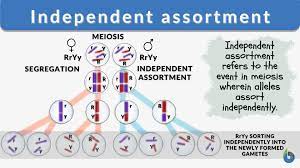
Independent Assortment
Alleles of two genes located on different chromosomes will sort into gametes independently of each other.
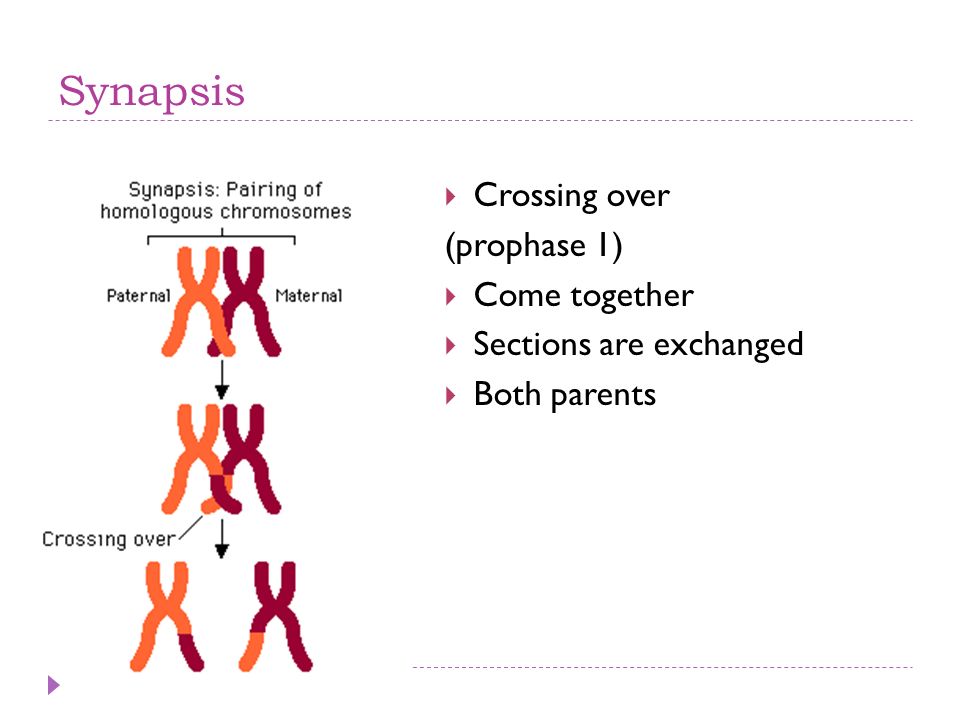
Synapsis
The pairing of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which can result in the exchange of genetic information between the chromosomes.
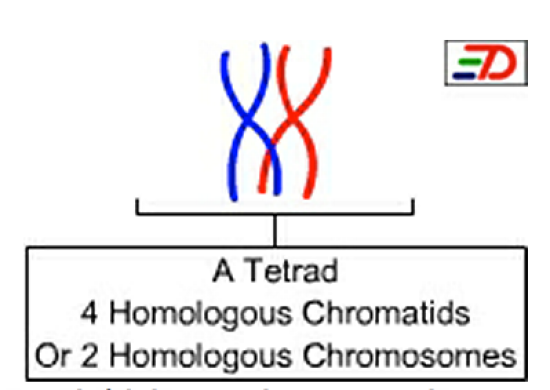
Tetrads
The structures formed by two homologous chromosomes during synapsis; consists of four chromatids.
Chromatin
The complex of DNA and histone proteins that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes. Chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes in preparation for cell division.
Chromatid
One half of a duplicated chromosome.
Chromosome
A structure containing DNA and its associated histone proteins in a cell. Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear. Before DNA replication during the S phase of the cell cycle, eukaryotic chromosomes consist of one chromatid. After DNA replication, eukaryotic chromosomes consist of two chromatids. Prokaryotic chromosomes are circular.
Centromere
The region in a chromosome that attaches the two chromatids.
Translocations
Genetic recombination between nonhomologous chromosomes. Translocations can inactivate genes or create new gene products. Translocations can also result in errors in meiosis.
Nondisjunction
When homologous chromosomes do not separate during anaphase of meiosis. Nondisjunction can result in an atypical number of chromosomes in a cell, known as aneuploidies.
Aneuploidy
An atypical number of chromosomes in a cell. Aneuploidies include both monosomies and trisomies.
Monosomy
The condition in which a cell has only one copy of a chromosome instead of the typical number of two copies.
Trisomy
The condition in which a cell has three copies of a chromosomes instead of the typical number of two copies.
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
Two alleles for a heritable trait will separate during gamete formation, leaving one of each allele in each gamete. While Mendel did not know of the existence of chromosomes, we now know that segregation of alleles occurs because each pair of chromosomes separates into different gametes during meiosis.
Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment
The segregation or separation of alleles for one trait does not affect the segregation of alleles for another trait. While Mendel did not know of the existence of chromosomes, we now know that independent assortment applies to genes that are unlinked (on separate chromosomes) or far apart (on same chromosome).
Pedigree
A visual representation of the inheritance of a trait through generations of a family. In a pedigree, makes are represented as squares, females as circles. Individuals expressing the trait are shaded shapes. Horizontal lines represent pairs producing offspring, which are connected to their offspring through vertical lines.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism (the alleles an organism possesses).
Phenotype
The physical expression of the genetic content of an organism. Phenotypes are influenced by both genotype and environment.
Homozygous
Having two copies of the same allele for a trait (for example, AA or aa).
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a trait (for example, Aa).
Dominant
An allele is dominant if only one copy of the allele is necessary for the trait encoded by that allele to be expressed.
Incomplete Dominance
Occurs when an organism with a heterozygous genotype expresses a phenotype that is between the dominant and recessive phenotypes—for example, if RR individuals were red, rr individuals were while, and Rr individuals were pink.
Codominance
Occurs when both alleles in an individual with the heterozygous genotype are expressed in the phenotype. For example, in blood typing, IAIB individuals express both the IA and IB alleles.
Recessive
An allele is recessive if two copies of the allele are necessary for the trait encoded by that allele to be expressed.
Monohybrid Cross
A cross between two organisms that are both heterozygous for a trait (for example, Aa x Aa).
Dihybrid Cross
A cross between two organisms that are both heterozygous for the same two traits (for example, AaBb x AaBb).
Test Cross
A cross between an individual with the dominant phenotype of unknown genotype and an individual with the recessive phenotype. A test cross is used to determine if an individual with the dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous. If homozygous, all the offspring from a test cross will express the dominant phenotype. If heterozygous, 50% of the offspring from a test cross will express the dominant phenotype and 50% will express the recessive phenotype.
Linked Genes
Genes that are close together on the same chromosome (same piece of DNA) and are more likely to be inherited together. Linked genes do not follow the laws of Mendelian genetics.
Unlinked Genes
Genes that are on different chromosomes (different pieces of DNA), or far apart on the same chromosome, and assort independently. Unlinked genes tend to follow the laws of Mendelian genetics.
Map Units
The relative distance between two genes on the same chromosome. Map units are stated in centimorgans (cM) and are calculated from recombination frequencies. A recombination frequency of 1% is equivalent to 1 cM in map units.
Karyotype
A visual representation of the chromosomes in a cell arranged by size in homologous pairs.
Autosome
A chromosome that is not a sex chromosome.
Sex Chromosome
A chromosome involved in determining the sex of an organism. In humans, the sex chromosomes are X and Y, with biological males typically having one X chromosomes and one Y chromosome and biological females typically having two X chromosomes.
Sex-Linked Genes
Genes that are on sex chromosomes. The inheritance pattern of sex-linked genes is different between biological makes and biological females.
Multiple Gene Inheritance
When multiple genes act together to produce a phenotype. Examples of multiple gene inheritance are eye color and height.
Nonnuclear Inheritance
Describes the inheritance of genes outside of the nucleus, usually genes that are present in mitochondrial or chloroplast DNA.
Mitochondrial DNA
DNA contained within the mitochondria (mtDNA). Because gametes from females are much larger that gametes from males, mitochondrial DNA is passed from the mother to her offspring. Biological males typically do not pass on mitochondrial genes to their offspring.
Chloroplast DNA
DNA contained within the chloroplast (cpDNA). Because gametes from females are much larger than gametes from males, chloroplast DNA is passed from the mother to her offspring. Biological males typically do not pass on chloroplast genes to their offspring.
Phenotypic Plasticity
The ability of the same genotype to produce different phenotypes in response to different environmental factors.