EXP 6: Dentification of Amino Acid by Paper Chromatography
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Amino Acid
building blocks of proteins.
molecular formula has two functional groups
carboxylic group that imparts acidic properties to the substance
amino group that imparts its basic property
Carboxylic Group (-COOH)
imparts acidic properties
Amino Group (NH3+)
imparts basic property
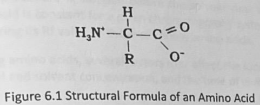
Zwitterion Compounds
contain both a positive and a negative charge as illustrated below
250
no. of identified amino acids
20; 10
__ aa commonly found in plants and animals, __in humans because they cannot be synthesized by the body
Chromatography
a technique that depends on the rate of ligation of the different amino acids
also used in the separation and quantitative analysis of peptides, nucleotides, lipids, and carbohydrates
Stationary Phase
the filter paper’s role in chromatography
Mobile Phase
the organic solvents’ role in chromatography
Paper Chromatography
In this method, a sample of an amino acid is applied as a small spot near one edge of a piece of chromatography paper.
The edge of the paper is then placed in a shallow layer of solvent mixture in a chromatographic tank.
Filter Paper
a good material for the stationary phase because many substances that are soluble in water or other mixed solvents are more or less tightly adsorbed onto the fibers of the paper
Substances not adsorbed on the paper → move at the same rate as the solvent
Substances bound very tightly to the paper → not move very far
Substances that interact weakly with paper → move, but slower than the solvent
As the solvent is drawn up into the paper by capillary action, three possible actions will take place:
water + non-polar solvent
solvent mixture’s usual components (several)
Capillary Action
the process where the mobile phase (solvent) moves up the stationary phase (like paper or a porous material) against gravity due to the combined cohesive forces within the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and the stationary phase
the water in the mixture binds to the hydrophilic paper (cellulose) and creates a liquid stationary phase of many small water droplets
The non-polar solvent continues to move up the paper forming a liquid mobile phase.
As the solvent mixture moves up the paper by capillary action,
An amino acid with a polar R-group
will be more soluble in water than in the non-polar solvent
so it will dissolve more in the stationary water phase
and will move up the paper only slightly
An amino acid with a hydrophobic (non-polar) R-group
will be more soluble in the mobile non-polar solvent than in water
so it will move up the paper with the non-polar solvent.
Ninhydrin Solution
used and sprayed on the paper to make the position of the amino acids clearly visible
Rf (Retention Factor) Value
quantity that defines the movement of amino acids (constant)
measures the movement of an amino acid compared to the movement of the solvent
Origin
At the start of chromatography, the amino acid is spotted and this is called ______
Factors that Affect the Location of the Amino Acid
Temperature
pH and solvent concentration
Time of chromatography
0.5% Aspartic acid
0.5% Lysine
0.5% Phenylalanine
0.5% proline
0.5% unknown solution
distilled water
n-butanol
lacial acetic acid
0.2% Ninhydrin solution
Chemicals
0.5% Aspartic Acid
1st spot
0.5% Phenylalanine
2nd spot
0.5% Proline
3rd spot
0.5% Lysine
4th spot
0.5% Unknown Substance
5th spot