AP Bio Unit One: Chemistry of Life
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
4 Major Macromolecules
Proteins - enzymes, workers, structure
Nucleic Acids - genetic material - codes for protein - one gene→ one polypeptide
Lipids
Carbohydrates - sugar - energy, structure,
Carbohydrates
Composition?
Monomer?,
Polymer?
Examples?
Bonds Between Poly>
Composed of C,H,O in 1:2:1 ratio
Monosaccharides Sugars: Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
Disaccharide: Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose
Polysaccharide:
Cellulose (plant cell walls, rigid), Chintin (fungi cell walls and exoskeletons)
Starch: Stored glucose In plants (amylose), Glycogen is stored glucose in animals
Bond: glycosidic linkage
What makes cellulose indigestible to us, or what makes it different than other stuff
cellulose contains both alpha and beta glucose
we cant break the beta linkages
only way we can break it down is with bacteria with enzymes in our gut (muturalistic relationship)
What reaction binds monomers to polymers like proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and DNA
What Takes them Apart?
What specific enzyme breaks down DNA?
Dehydration brings together
Hydrolysis Breaks
nucleases break down DNA
Proteins
composed of?
monomer?
Whats the bond?
CHONS - has sulfur (esential to the experiment for genetic material) - hershey chase
Monomer: Amino acids - composed of ammine group NH2 , Carboxl, R Group (the difference)
peptide bond between the carboxyl and ammine (covalent)
Terminus - N (ammine), C (Carboxl)
Levels of Protein Structure
How does it fold?
Primary Structure: the long string, peptide bonds,
Secondary: Alpba helix or beta pleated, hydrogen bonds - parallel or anti parrlele etc
Tertirary- Covalent bonds, hydrogen, van der walls, hydrophobic interactions, ionic, disulfide bridges or (any bonds), between R groups.
3-d
Finalized if only one peptide
Quartinary - Multiple Peptides to one Protein, Any bonds again, R Group interactions between different peptides
Folding - based on R Group - if Polar, it will be exterior because can form hydrogen bonds, if hydrophobic (interior) and created hydrophobic interactions
Nucleic Acids
Composition
Monomer? What 3 things is it composed of?
Polymer? What 2 types? Difference?
What is special about the phosphate? what can it allow us to do?
What do the ends mean? 3 and 5
CHONP - has phosphate and nitrogen
Nucleotide - made up of phosphate, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base (the letter code)
DNA (T)- or RNA (U) - Deoxyribose (-H) - Ribose (OH)
Phosphate → negative charge → makes it good for electrophoresis
3 means hydroxide end, and 5 is phosphate end
Purines are double A,G
Pyrdimadine is CUT single
Very Basic - high pH
Nucleic Acid Structures and Bonds
DNA?
RNA?
similar?
Purines vs Prymadine
Bonds for them?
How are the bonds broken in crossing over
DNA is a double helix and anti-parallel. Uses hydrogen bonds to pair the base pairs
RNA is single-stranded
Phosphodiester Linkage keeps nucleotides together
Purines are double A,G
Pyrdimadine is CUT single
A-T 2 bonds,, C-G, 3 bonds
Double or Single Rule can be broken sometimes
The Endonucleases break (hydrolysis) the covalent bonds that link the nucleotides, breaking between the sugar and the phosphates
Hershey and Chase Experiment
They used radioactive Sulfur and Phosphorous to mark Proteins and DNA. They found that the genetic material transfered in transduction it Phosphrous (DNA)
Lipids
Composition
What makes them different than the other macromolecules?
Monomer?
Polymer Types?
Saturated vs Unsaturated Fatty Acids
CHO (P - in phospholipids)
They are non-polar
Fatty Acids Monomer, lots of polymers
Glycerol -
Glycerol (3 Fatty Acids)
Saturated means all single bonds → packed tightly - solid
Unsaturated means at least one double bond → kink → wont pack completely - liquid
Phospholipids - e
polar head and non polar tail
Phosphate is polar
2 fatty acids is nonpolar tail
Assembles to bi layer - membrane
Steroids -
4 rings
Ligands - intracellular lipid receptors -
Cholestrol is used for hormone synthesis and is used in plasma membranes to make it more rigid
What makes something polar or not
What is polar?
Lots of C ,H → non polar
Has a good amount of O, P, S - polar
Polar means sharing electrons unequally which causes slight charges - covalent bonds
The more electronegative will pull electrons
hydrogen bonds
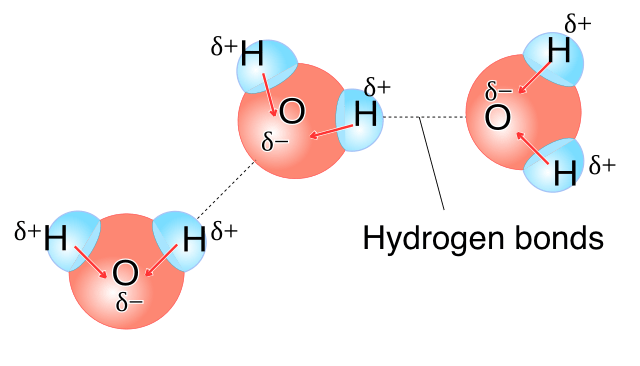
Water Properties
Why is water polar?
How does the fact of it being polar change things
Polar →Oxygen partially negative because more electronegative and hydrogen becomes partially positive
Cohesion - water attracted to other water with hydrogen bonds → surface tension, specific heat and etc
Adhesion - water attraction to other polar substances → Water can climb up plant xylem (capillary action) because of less pressure (transpiration) and going up
Universal Solvent - it can dissolve any that is polar (charged) like salts
Other Water Properties
Less Dense as a Solid - crystalized and uses more space - allows for ice to form on top and float
High specific heat - requires a lot of energy (joules) to increase the water
this allows for body tempeature to be better regulated with evaporative cooling
regulates temp in costal reigons
pH - high pH (low protrons), low pH (high protons)
relevant in Mitocondria (prton pumps protons from the matrix (inside) to matrix to intromembrane space (out), chloroplast pumps protons from thje stroma (out) to the thylakoid (inside)
Questions regarding pH could come up
High Heat of Evaporation
What are isomers, entanomers, cis trans
same chemical formula but have different structure
this is seen in glucose a or b
What do proteins do
do work
enzymes, defensive proteins (antibodies), stroage, transport, homronal, receptor, structural, contractile and motor
what does CO2 do to oceans
it can acidify it because it can turn into carbonic acid andless calcium carbonate
7 characteristics of life
order, interaction, energy, regulation, grwoth and develoipment, reproduction, evolution
Transpiration
respobsible for water moving out of the plant
this is because of cohesion and adheion → caplillary action
this is also because of the low water potential on top bc less pressure