The Respiratory System
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
To deliver air to the lungs for gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
How do the respiratory and cardiovascular systems work together?
They jointly deliver oxygen to tissues and remove carbon dioxide, considered as the cardiopulmonary system.
What role does the respiratory system play in acid-base balance?
It collaborates with the urinary system to regulate the body's acid-base balance by eliminating CO2.
List the primary functions of the respiratory system.
1. Gas exchange
2. Communication
3. Olfaction
4. Acid-base balance
5. Blood pressure regulation
6. Blood and lymph flow
7. Platelet production (more than half produced in lungs)
8. Blood filtration
9. Expulsion of abdominal contents.
What is the conducting zone of the respiratory system?
passages that serve only for airflow, from the nostrils through the major bronchioles, with no gas exchange.
What is the respiratory zone of the respiratory system?
It consists of alveoli and other regions where gas exchange occurs.
What are the principal organs of the respiratory system?
Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
What are the functions of the nose?
1. Warms, cleanses, and humidifies inhaled air 2. Detects odors 3. Serves as a resonating chamber that amplifies voice.
What is the upper respiratory tract?
The part of the respiratory system located in the head and neck, from the nose through the larynx.
What is the lower respiratory tract?
The part of the respiratory system that includes the organs of the thorax, from the trachea through the lungs.
What are alveoli?
Millions of thin-walled, microscopic air sacs where gas exchange occurs with the bloodstream.
How does breathing affect blood and lymph flow?
Breathing creates pressure gradients between the thorax and abdomen that promote the flow of lymph and blood.
What is the Valsalva maneuver?
A breath-holding technique that assists in urination, defecation, and childbirth.
What is the role of megakaryocytes in the lungs?
More than half of platelets are produced by megakaryocytes located in the lungs.
How does the respiratory system influence blood pressure?
By helping in the synthesis of angiotensin II.
What is the significance of the alveolar wall?
It allows for the exchange of gases between the alveoli and the bloodstream.
What structures shape the facial part of the nose?
The superior half is shaped by nasal bones and maxillae, while the inferior half consists of cartilages and connective tissue.
What is the function of the respiratory system in communication?
It enables speech and other vocalizations.
How does the respiratory system help in blood filtration?
The lungs filter small clots from the blood.
What happens to incoming air in the alveoli?
It stops and exchanges gases with the bloodstream.
What divides the nasal cavity?
The nasal septum.
What are the components of the nasal septum?
It is composed of bone and hyaline cartilage, with the vomer forming the inferior part, the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid forming the superior part, and septal cartilage forming the anterior part.
What bones form the roof of the nasal cavity?
The ethmoid and sphenoid bones.
What forms the floor of the nasal cavity?
The hard palate.
What bones form the nasal septum?
vomer and perpendicular plate of ethmoid
What is the function of the nasal cavity in relation to the oral cavity?
It separates the nasal cavity from the oral cavity, allowing you to breathe while chewing food.
What structures drain into the nasal cavity?
Paranasal sinuses and the nasolacrimal duct.
What is the vestibule of the nasal cavity?
The beginning of the nasal cavity, a small, dilated chamber just inside the nostrils.
What type of epithelium lines the vestibule?
Stratified squamous epithelium.
What are vibrissae?
Stiff guard hairs that block insects and debris from entering the nose.
What are the nasal conchae?
Three folds of tissue (superior, middle, and inferior nasal conchae) that project from the lateral walls toward the septum.
What is the function of the nasal conchae?
They create narrow air passages that ensure most air contacts mucous membranes, cleansing, warming, and moistening the air.
What type of epithelium is the nasal mucosa?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
What role do goblet cells play in the nasal mucosa?
They produce mucus that is propelled posteriorly toward the pharynx.
What is the olfactory epithelium responsible for?
It detects odors and is covered by immobile cilia that bind odorant molecules.
What is erectile tissue in the context of the nasal cavity?
An extensive venous plexus in the epithelium of the inferior concha that swells every 30 to 60 minutes to restrict airflow through that fossa.
What are the three regions of the pharynx?
Nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
What is the function of the nasopharynx?
It passes only air and is lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Contains pharyngeal tonsil
What does the oropharynx contain?
Palatine tonsils and passes air, food, and drink, lined by stratified squamous epithelium.
What is the function of the laryngopharynx?
It passes air, food, and drink and is lined by stratified squamous epithelium.
What is the primary function of the larynx?
To keep food and drink out of the airway, also the voice box
What is the epiglottis?
A flap of tissue that guards the superior opening of the larynx, closing the airway during swallowing.
What are the first three solitary cartilages of the larynx?
Epiglottic cartilage, thyroid cartilage, and cricoid cartilage.
What is the largest laryngeal prominence?
The thyroid cartilage, also known as the Adam's apple.
What are the two types of folds in the interior wall of the larynx?
Superior vestibular folds (which close the larynx during swallowing) and inferior vocal folds (which are involved in sound production).
What do the inferior vocal cords produce when air passes between them?
Sound.
What type of epithelium covers the inferior vocal cords?
Stratified squamous epithelium.
True vs false vocal cords
True vocal cords (vocal folds) help produce sounds
False vocal cords (vestibular vocal folds) are superior to the true. they play no role in the production of sound
What is the function of intrinsic muscles in relation to the vocal cords?
They control the vocal cords by pulling on corniculate and arytenoid cartilages to abduct or adduct the cords.
What sound is produced when air is forced between adducted vocal cords that are taut?
A high-pitched sound.
How do adult male vocal cords compare to female vocal cords?
They are usually longer and thicker, vibrate more slowly, and produce lower-pitched sounds.
What is the length and diameter of the trachea?
The trachea is 12 cm (4.5 in.) long and 2.5 cm (1 in.) in diameter.
What structure reinforces the trachea and prevents collapse during inhalation?
16 to 20 C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage.
What is the function of the trachealis muscle?
It spans the opening in the C-rings and adjusts airflow by contracting or relaxing.
What type of epithelium lines the trachea?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
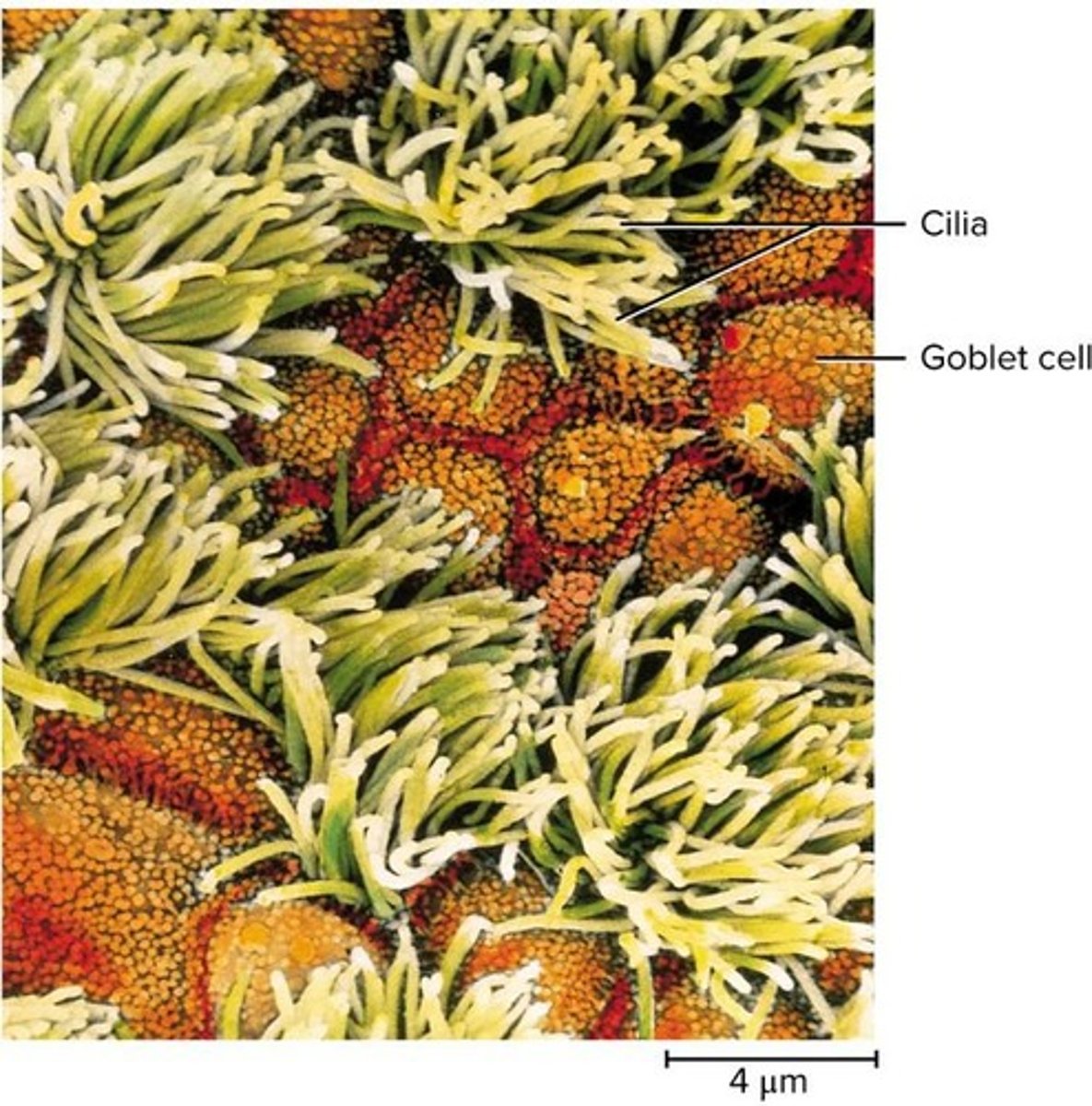
What is the mucociliary escalator?
A mechanism for debris removal where mucus traps inhaled particles and cilia move it to the pharynx to be swallowed.
What does the middle tracheal layer contain?
Connective tissue, lymphatic nodules, mucous and serous glands, and tracheal cartilages.
Where is adventitia generally found?
Outside the abdominopelvic cavity
What is the adventitia of the trachea?
The outermost layer made of fibrous connective tissue that blends into the adventitia of other mediastinal organs.
Where does the trachea fork into the right and left main bronchi? How can you tell the difference between the left and right branch?
At the level of the sternal angle.
The right side is more straight and vertical than the left.
How many lobar bronchi do the right and left side of the lungs have?
The right side has 3, left has 2
Do the right and left main bronchi contain trachialis?
No
What is the carina?
The internal medial ridge in the lowermost tracheal cartilage that directs airflow to the right and left bronchi.
What is a tracheotomy?
A procedure to make a temporary opening in the trachea and insert a tube to allow airflow.
What is a tracheostomy?
A permanent opening in the trachea.
What are potential problems associated with a tracheostomy?
Inhaled air bypasses the nasal cavity, leading to dry mucous membranes and potential infection.
What is intubation?
A procedure where air is introduced directly into the trachea, often for patients on a ventilator.
What are the base and apex of the lungs?
The base is the broad concave portion resting on the diaphragm, and the apex is the tip projecting just above the clavicle.
How many lobes does the right lung have, and what are they?
The right lung has three lobes: superior, middle, and inferior.
What distinguishes the left lung from the right lung?
The left lung is taller and narrower due to the heart's position and has two lobes separated by a single oblique fissure.
What is the bronchial tree?
A branching system of air tubes in each lung that extends from the main bronchus to 65,000 terminal bronchioles.
What is unique about the right main bronchus compared to the left?
The right main bronchus is wider and more vertical, making it more likely for aspirated foreign objects to lodge there.
What supports the lobar and segmental bronchi?
Crescent-shaped cartilage plates.
How many right lobar bronchi are there and what are they?
Three: superior, middle, and inferior.
How many left lobar bronchi are there and what are they?
Two: superior and inferior.
How many segmental (tertiary) bronchi are present in the right and left lungs?
10 on the right and 8 on the left.
What type of epithelium lines all bronchi?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
What happens to the cells and epithelium as we progress distally in the bronchial tree?
Cells grow shorter and the epithelium becomes thinner.
What is found in the lamina propria of the bronchi?
An abundance of mucous glands and lymphocyte nodules (MALT).
What type of connective tissue is abundant in all divisions of the bronchial tree?
Elastic connective tissue.
What is the function of the smooth muscle layer in the mucosa of the bronchi?
It contracts or relaxes to constrict or dilate the airway, regulating airflow.
What closely follows the bronchial tree on their way to the alveoli?
Pulmonary artery branches.
What is the diameter of bronchioles?
1 mm or less.
What is a pulmonary lobule?
The portion of the lung ventilated by one bronchiole.
What type of epithelium do bronchioles have?
Ciliated cuboidal epithelium.
What do terminal bronchioles measure in diameter?
0.5 mm or less.
What do terminal bronchioles lack?
Mucous glands or goblet cells.
What do terminal bronchioles give off?
Two or more smaller respiratory bronchioles.
What characterizes respiratory bronchioles?
They have alveoli budding from their walls and are the beginning of the respiratory zone.
What do respiratory bronchioles divide into?
2 to 10 alveolar ducts.
What surrounds each alveolus?
A basket of capillaries supplied by the pulmonary artery.
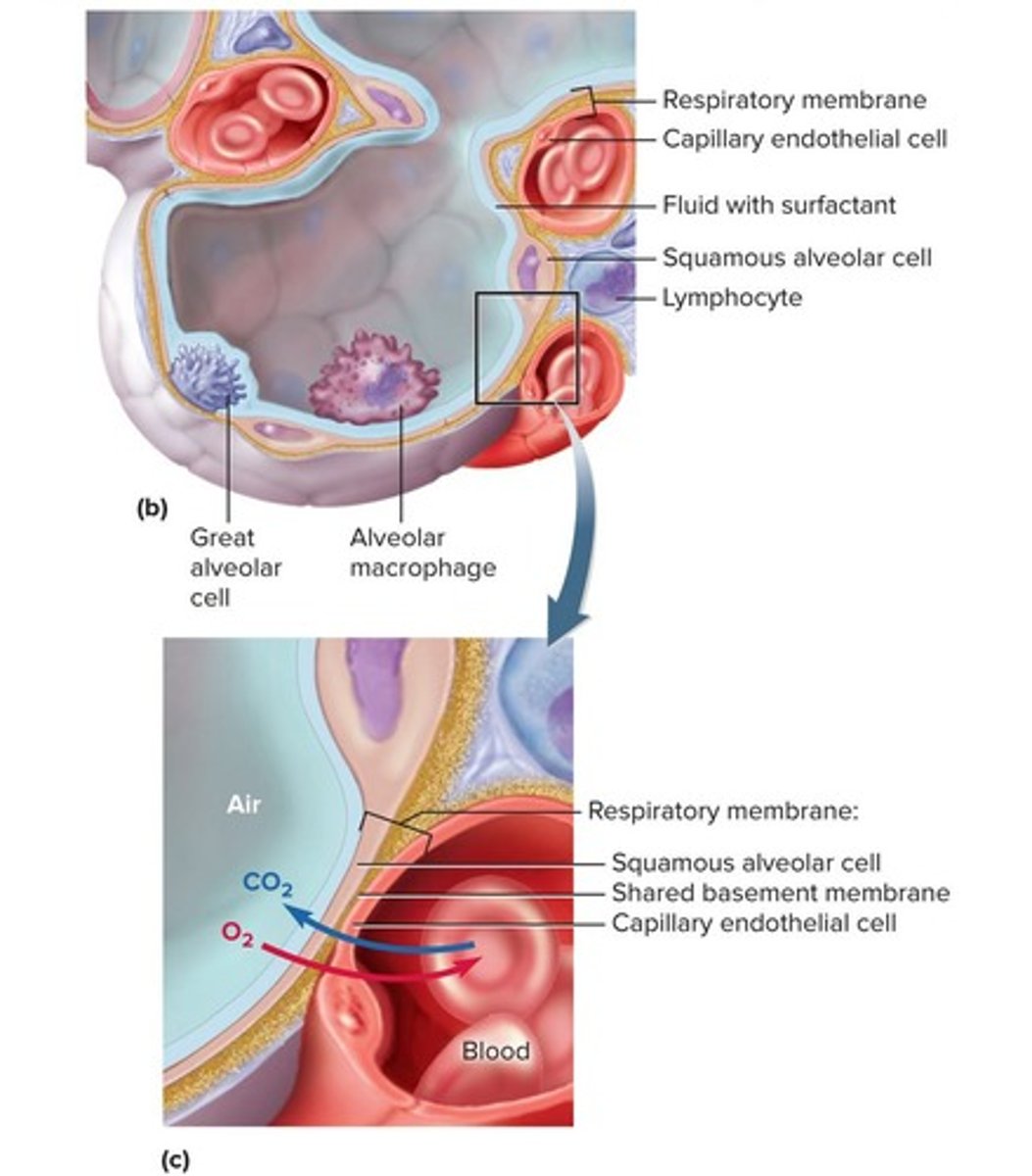
What are the three types of cells in the alveolus?
1. Squamous (type I) alveolar cells, 2. Great (type II) alveolar cells, 3. Alveolar macrophages (dust cells).
What is the function of squamous (type I) alveolar cells?
They allow rapid gas diffusion between air and blood and cover 95% of the alveolus surface area.
What is the role of great (type II) alveolar cells?
They repair the alveolar epithelium and secrete pulmonary surfactant.
What is the function of pulmonary surfactant?
It prevents alveoli from collapsing during exhalation.
What is the function of alveolar macrophages (dust cells)?
They keep alveoli free from debris by phagocytizing dust particles.
What is the respiratory membrane?
The thin barrier between the alveolar air and blood, consisting of squamous alveolar cells, endothelial cells of blood capillaries, and their shared basement membrane.
What are the two types of pleurae?
Visceral pleura and parietal pleura.
What is the pleural cavity?
The potential space between pleurae that normally contains a film of slippery pleural fluid.
What are the functions of pleurae and pleural fluid?
1. Reduction of friction, 2. Creation of a pressure gradient to assist lung inflation.