MCAT Ochem
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Epimers v.s. Anomers
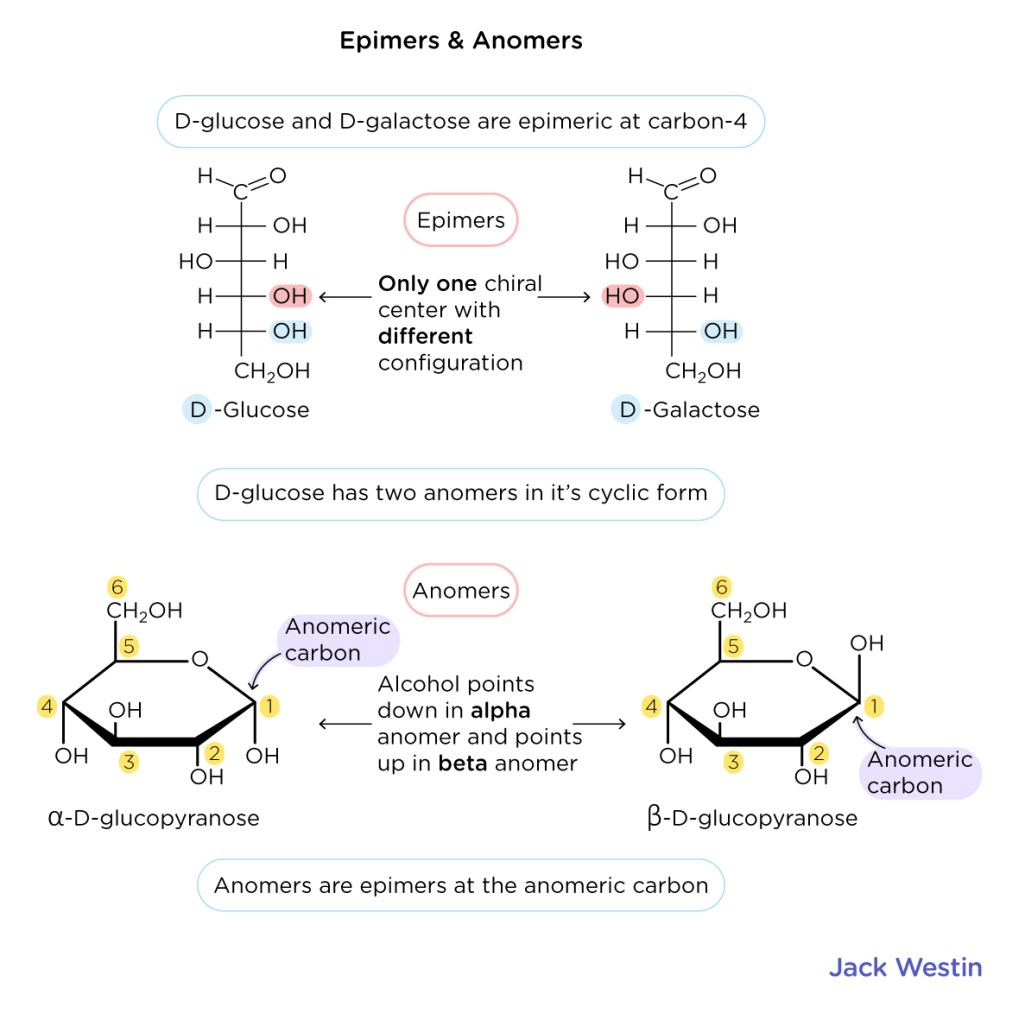
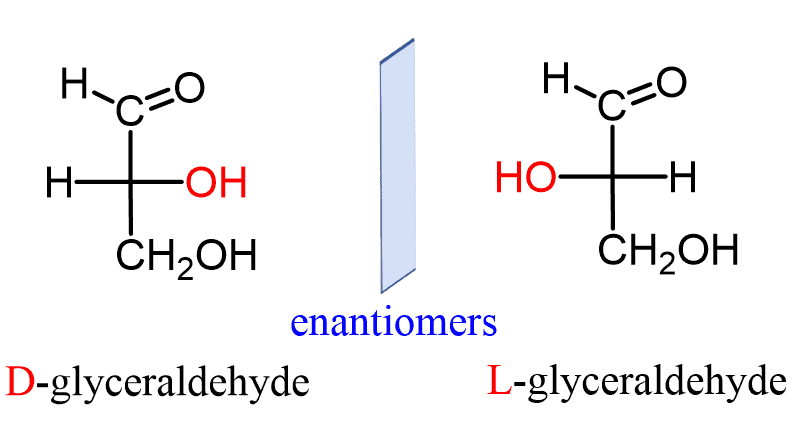
D v.s. L conformation for monosaccharide
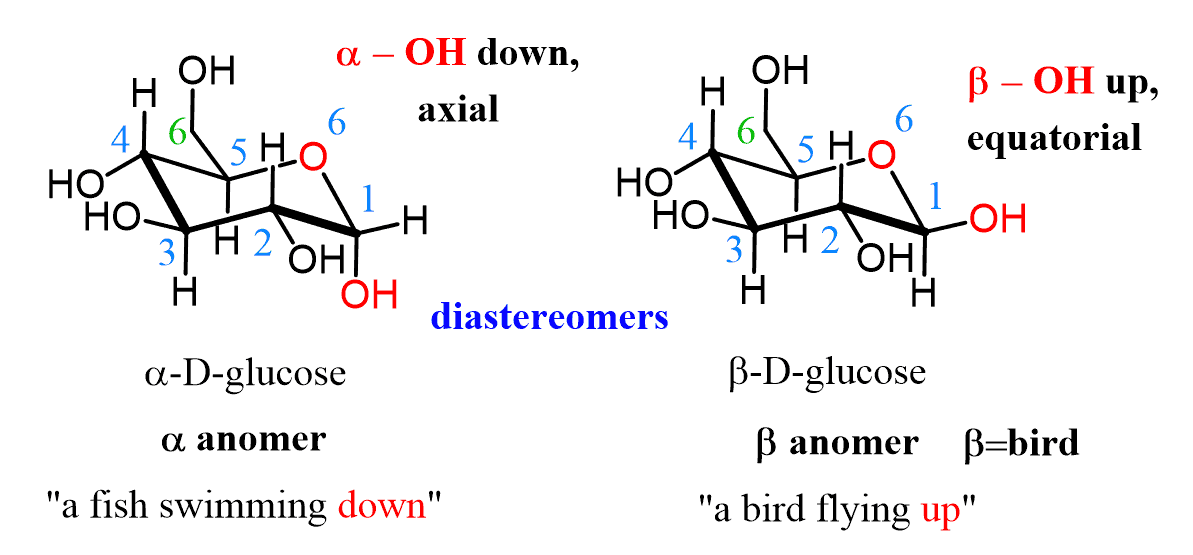
Alpha and Beta monosaccharide conformation
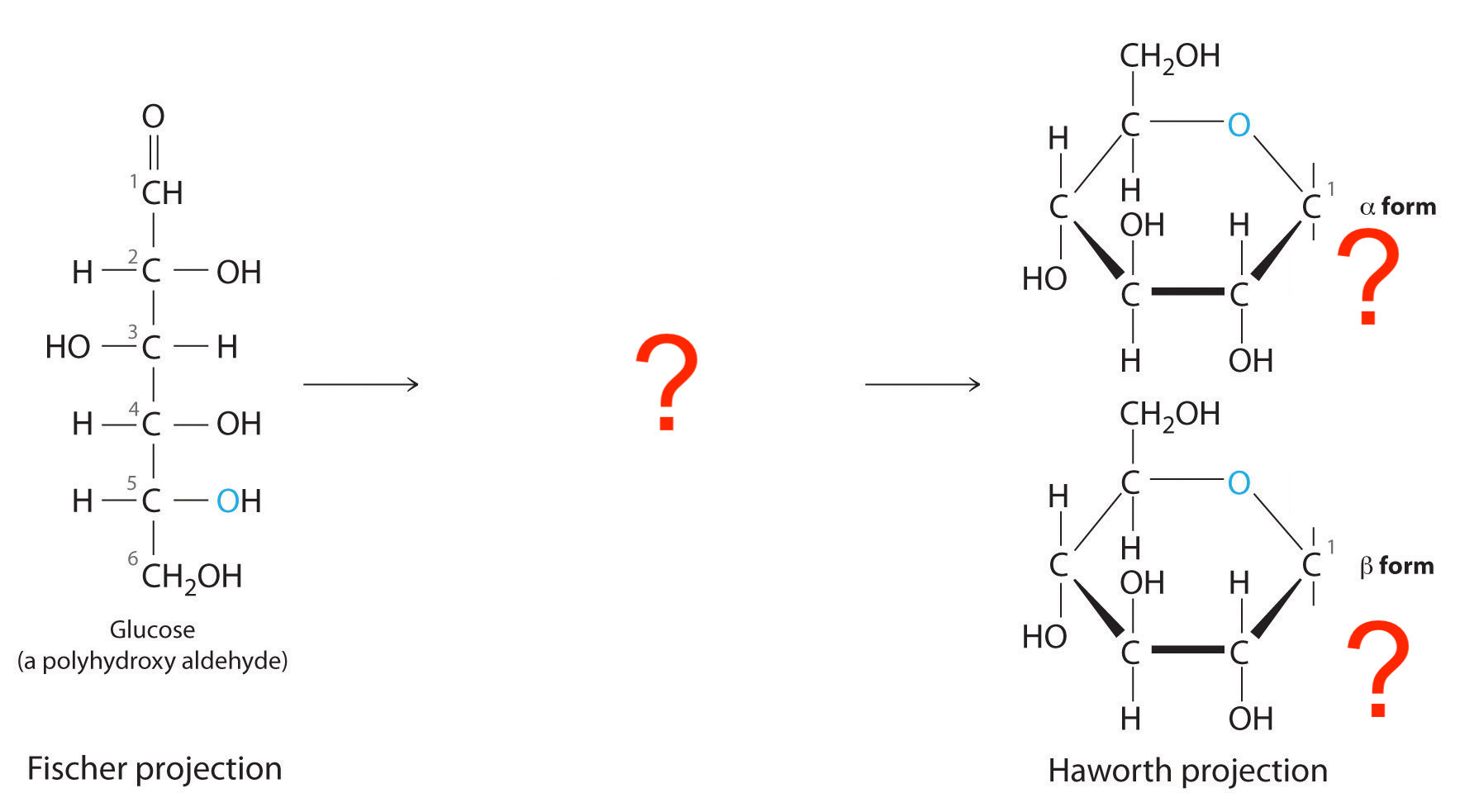
Glucose cyclization, which carbon/hydroxyl attacks which carbon?
In alpha form, does OH point up or down?
In beta form, does OH point up or down?
Hydroxyl on C5 attacks C1
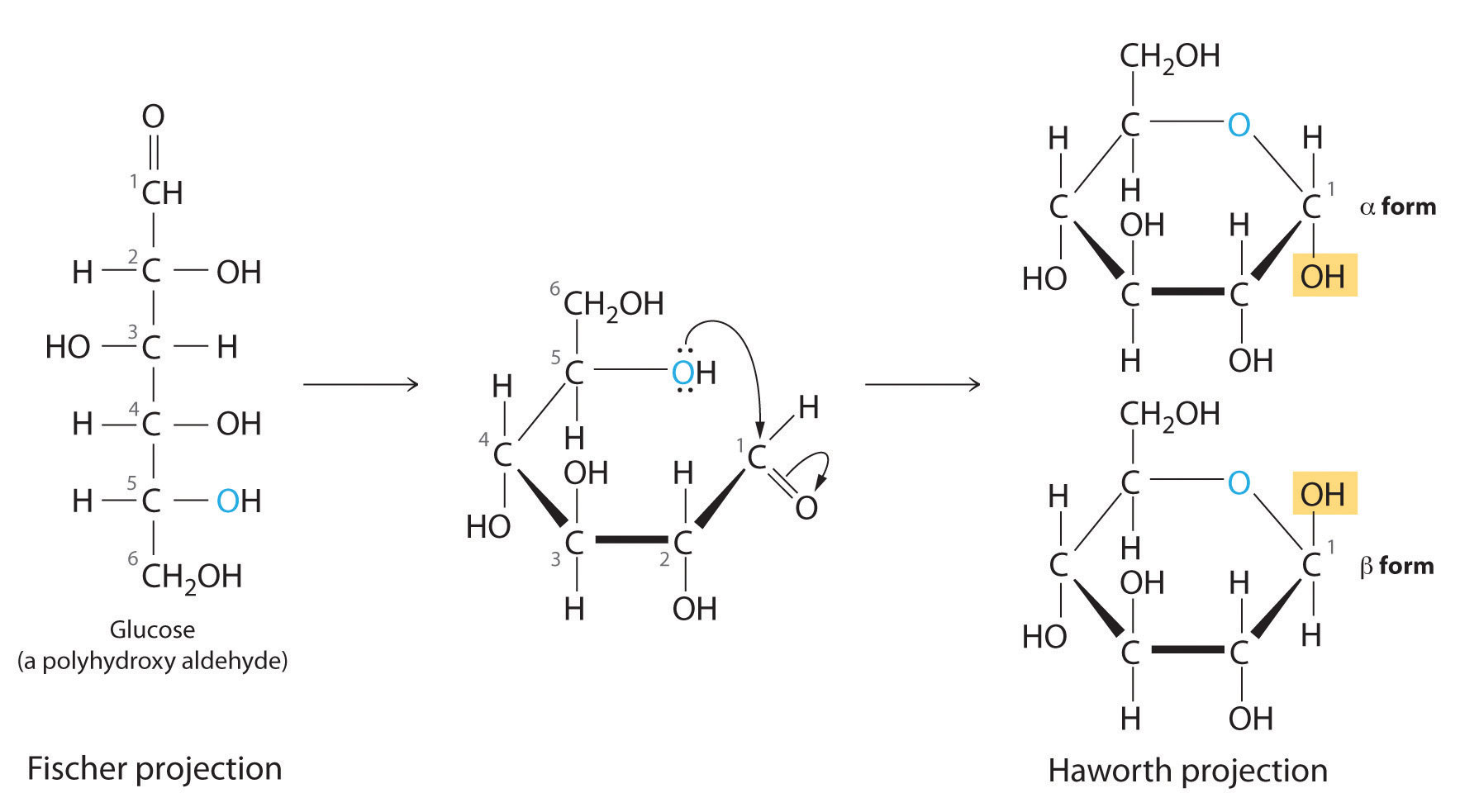
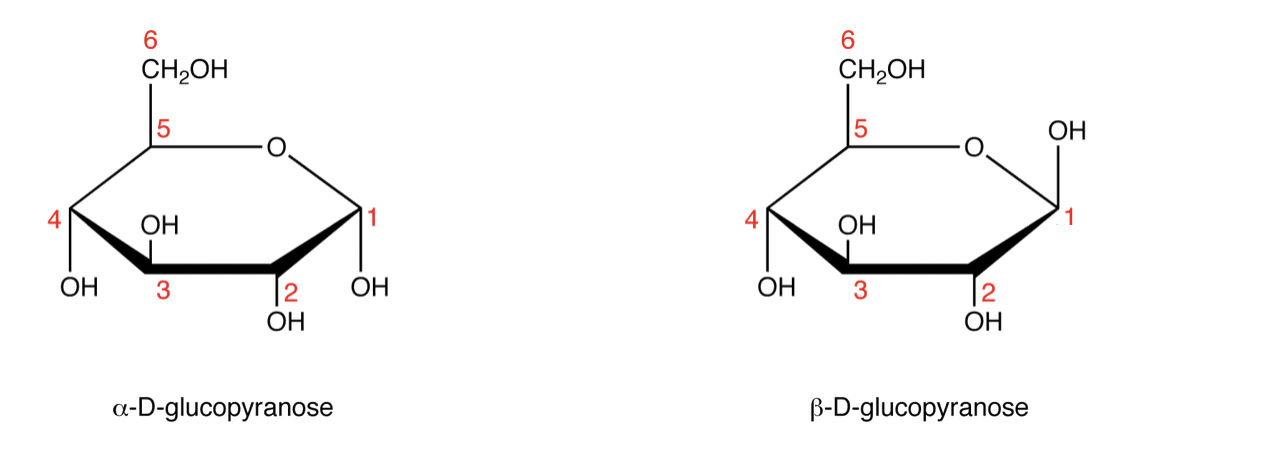
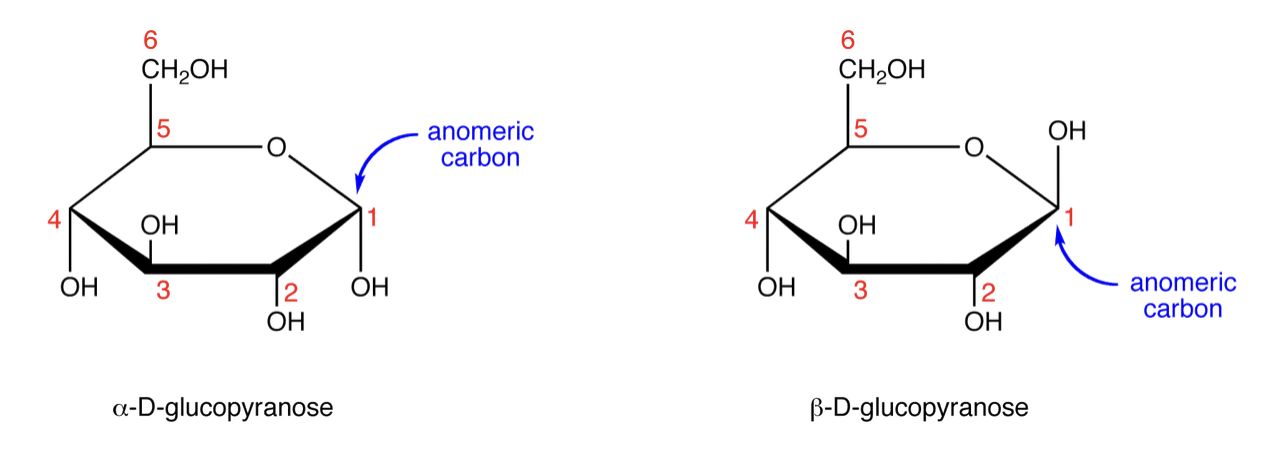
Where is the anomeric carbon? Define it.
Carbon atom in a cyclic carbohydrate that was the carbonyl carbon in its open-chain form
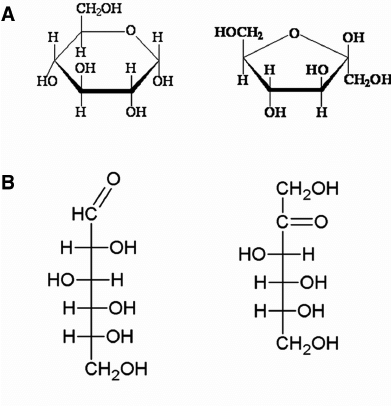
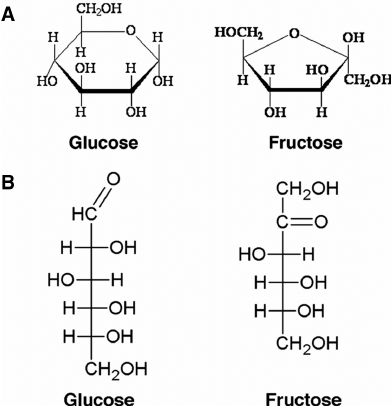
Which are glucose, fructose, and galactose?
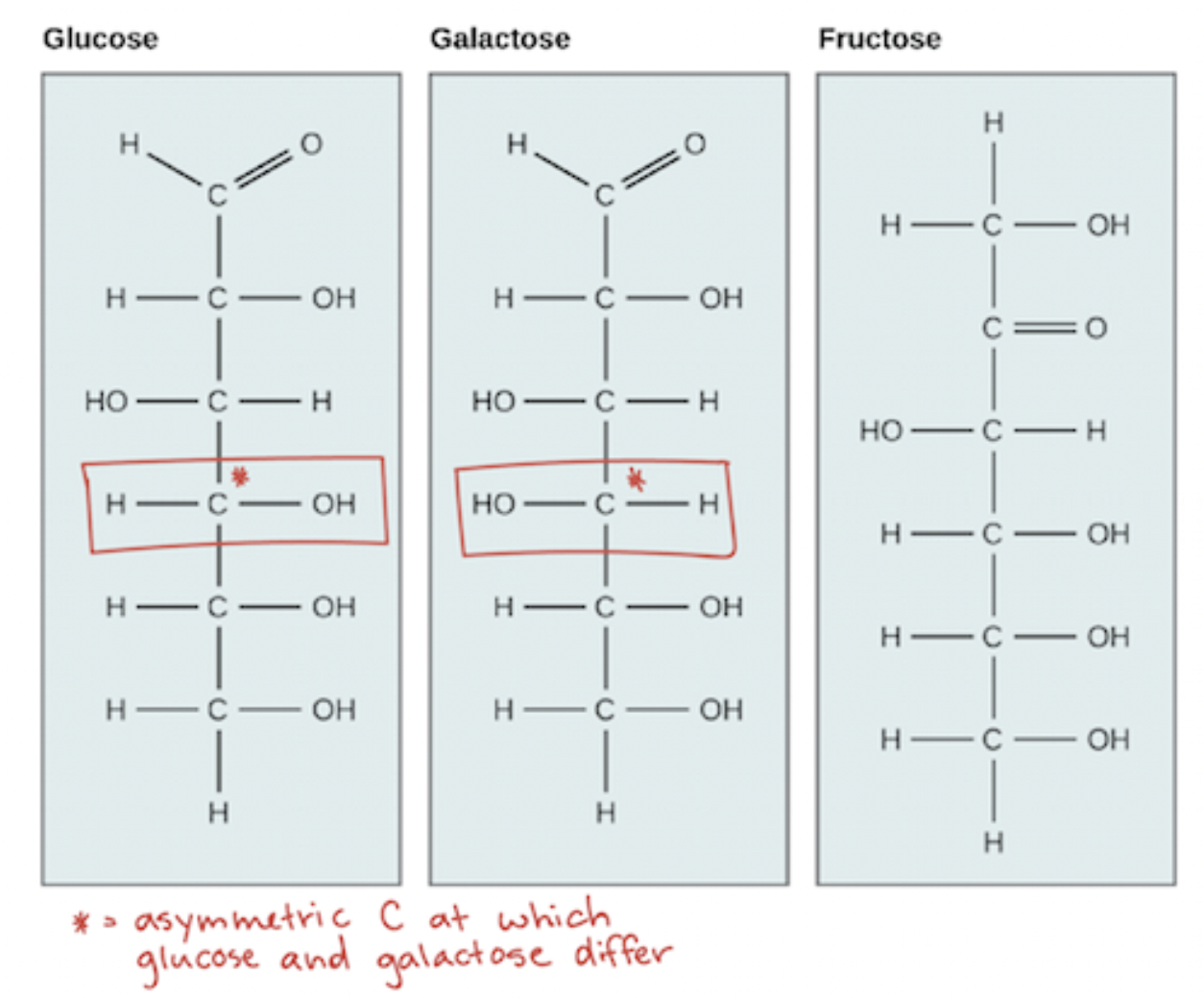

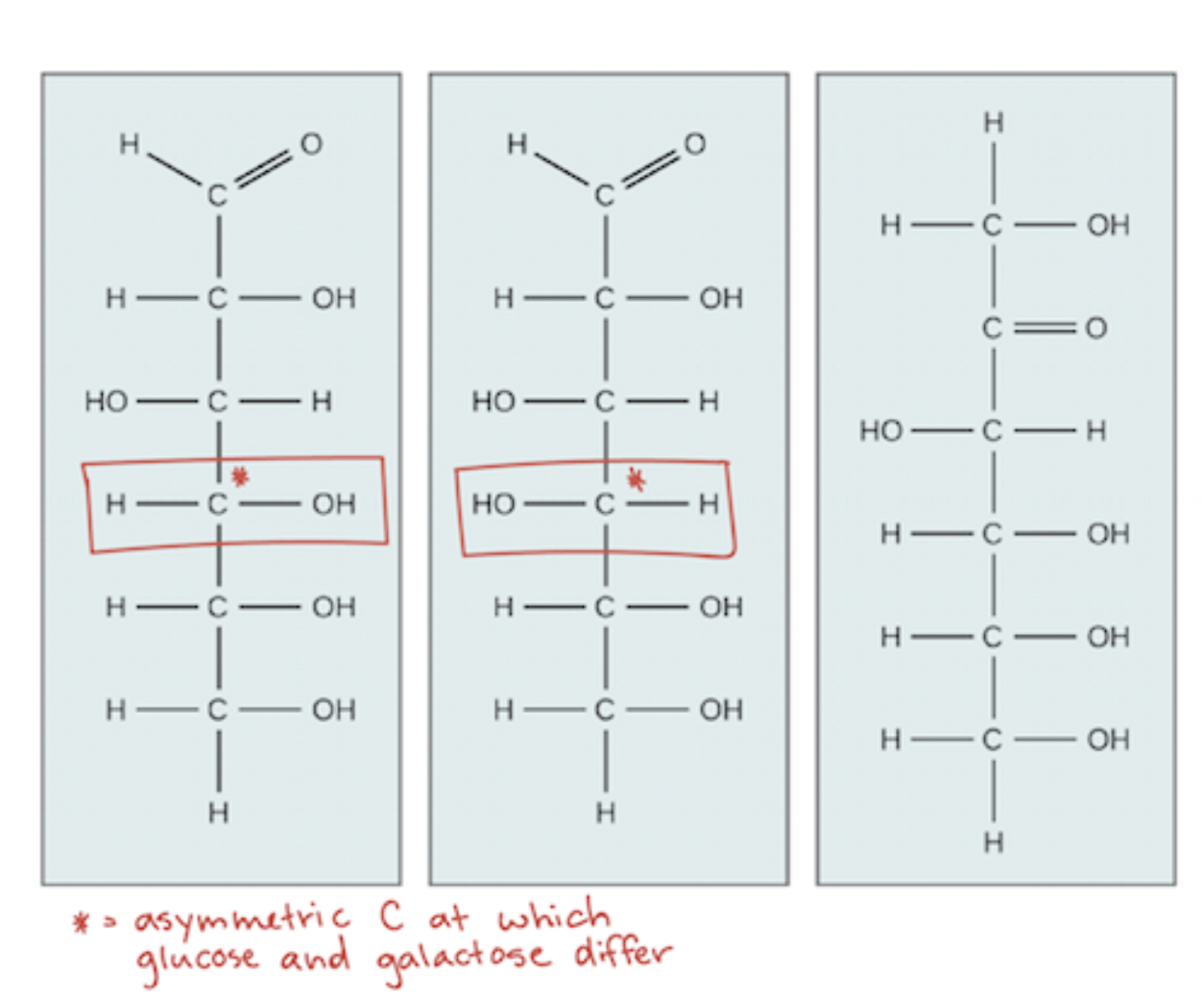
Which is galactose and glucose?
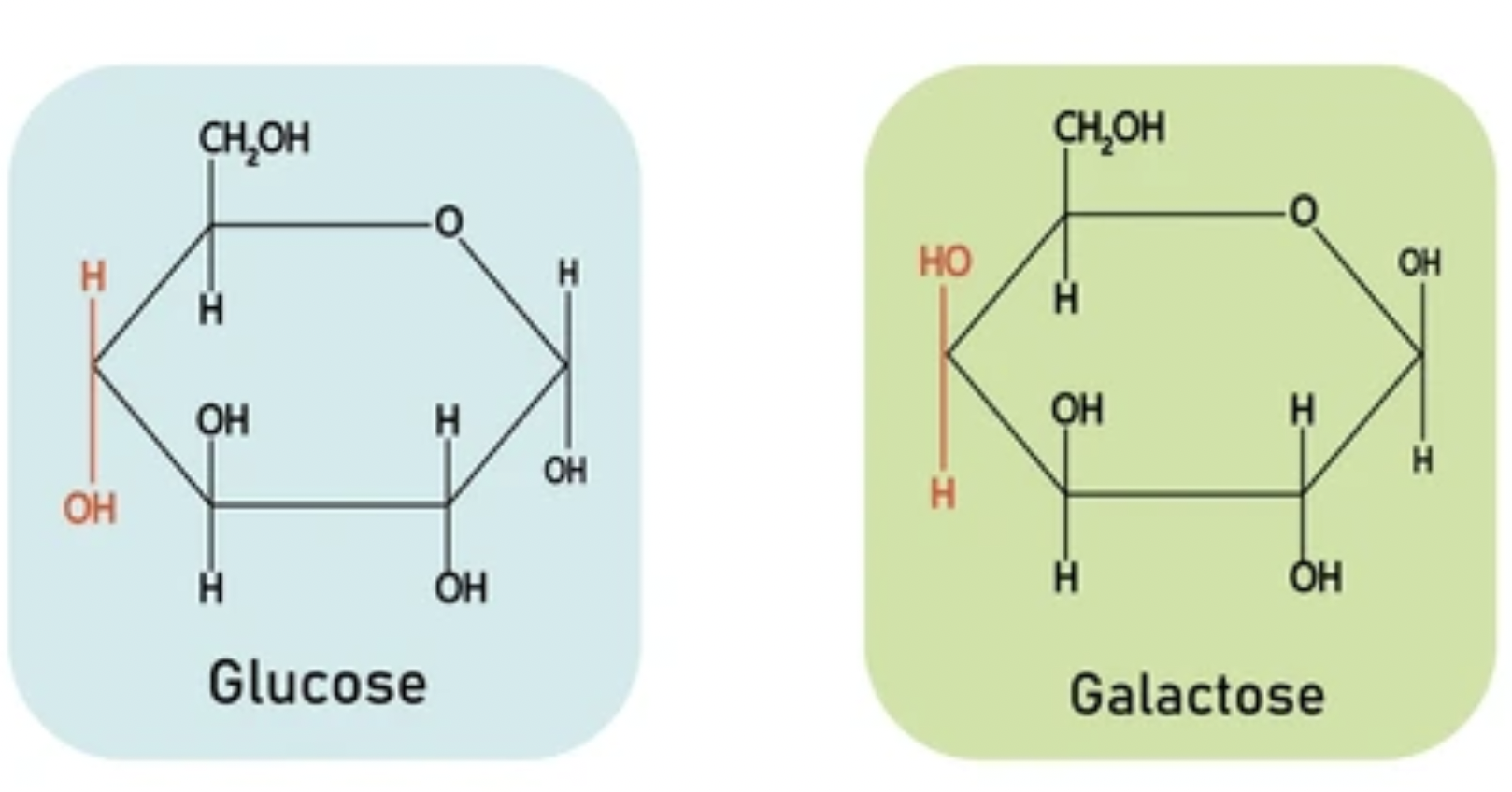
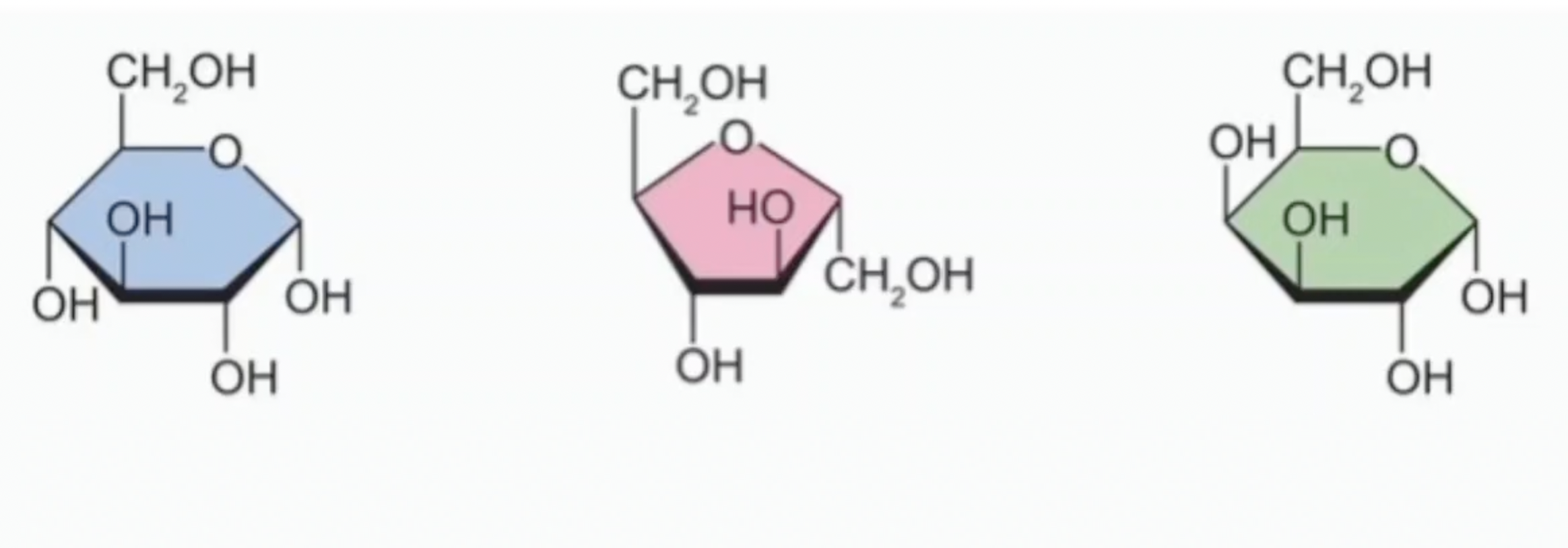
Name the monosaccharides
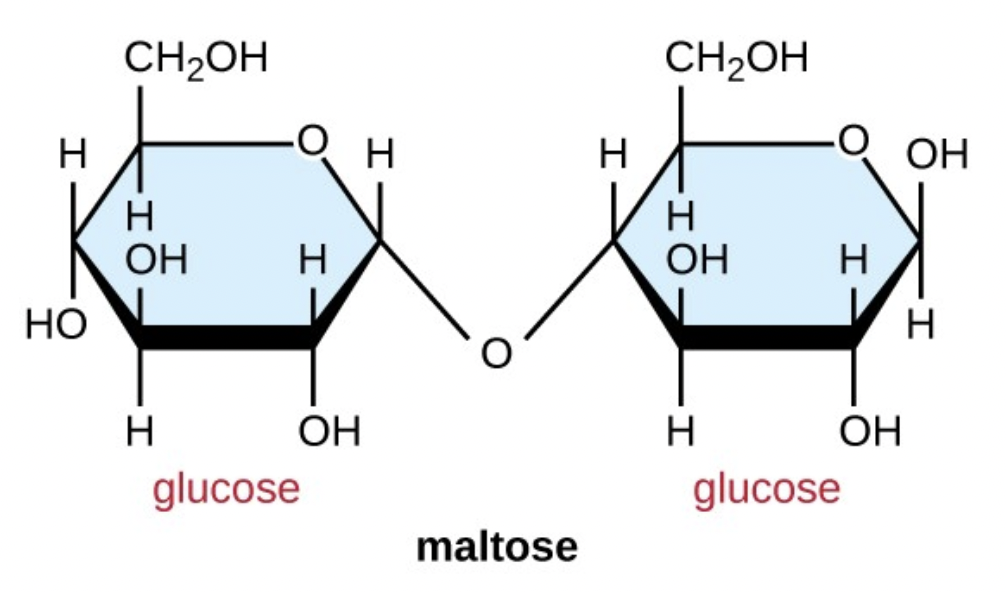
Name this disaccharide: Maltose, lactose or sucrose?
What are the two sugars that compose the disaccharide?
Name this disaccharide: Maltose, lactose or sucrose?
What are the two sugars that compose the disaccharide?
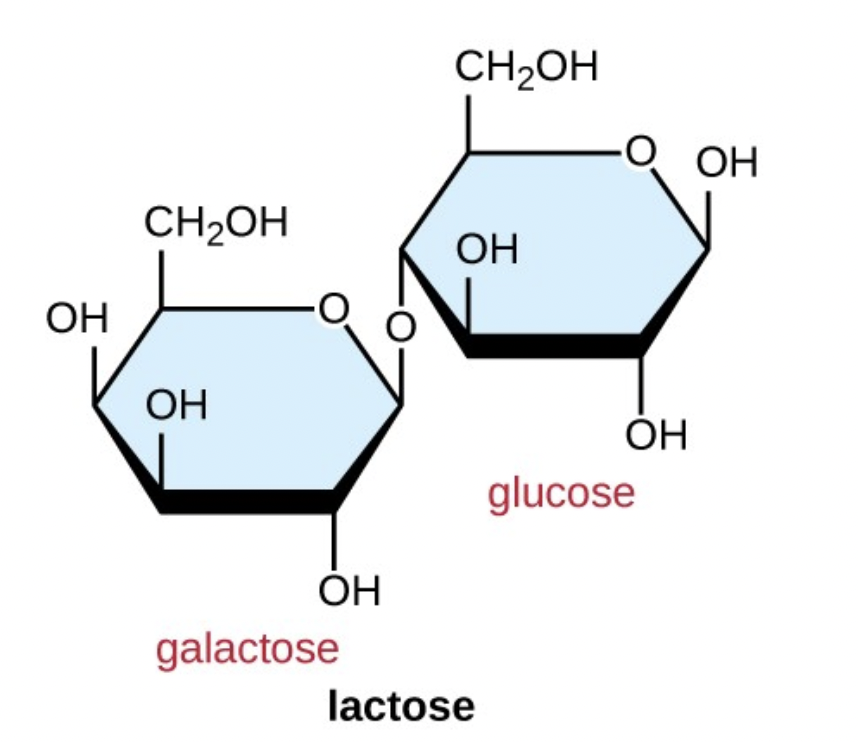
Name this disaccharide: Maltose, lactose or sucrose?
What are the two sugars that compose the disaccharide?

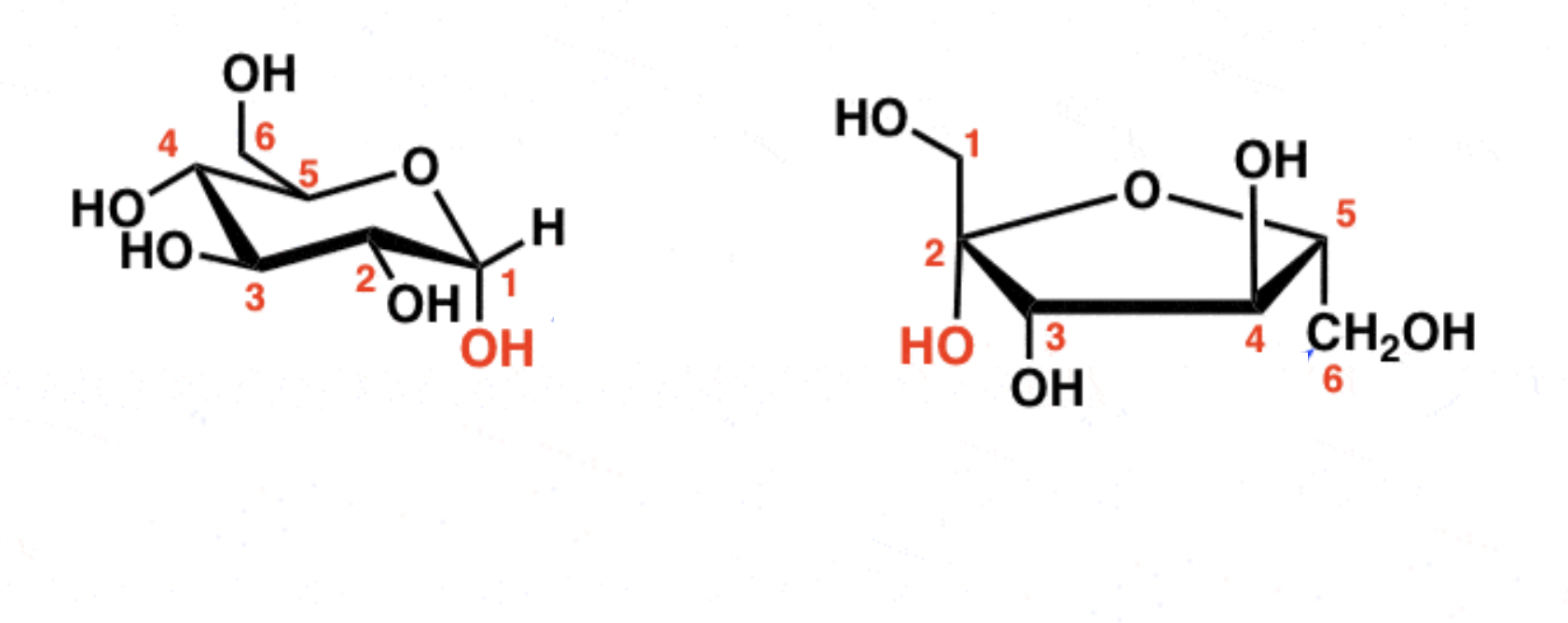
Alpha and beta configurations for monosaccharides:
Trans/opposite = alpha
Cis/same = beta


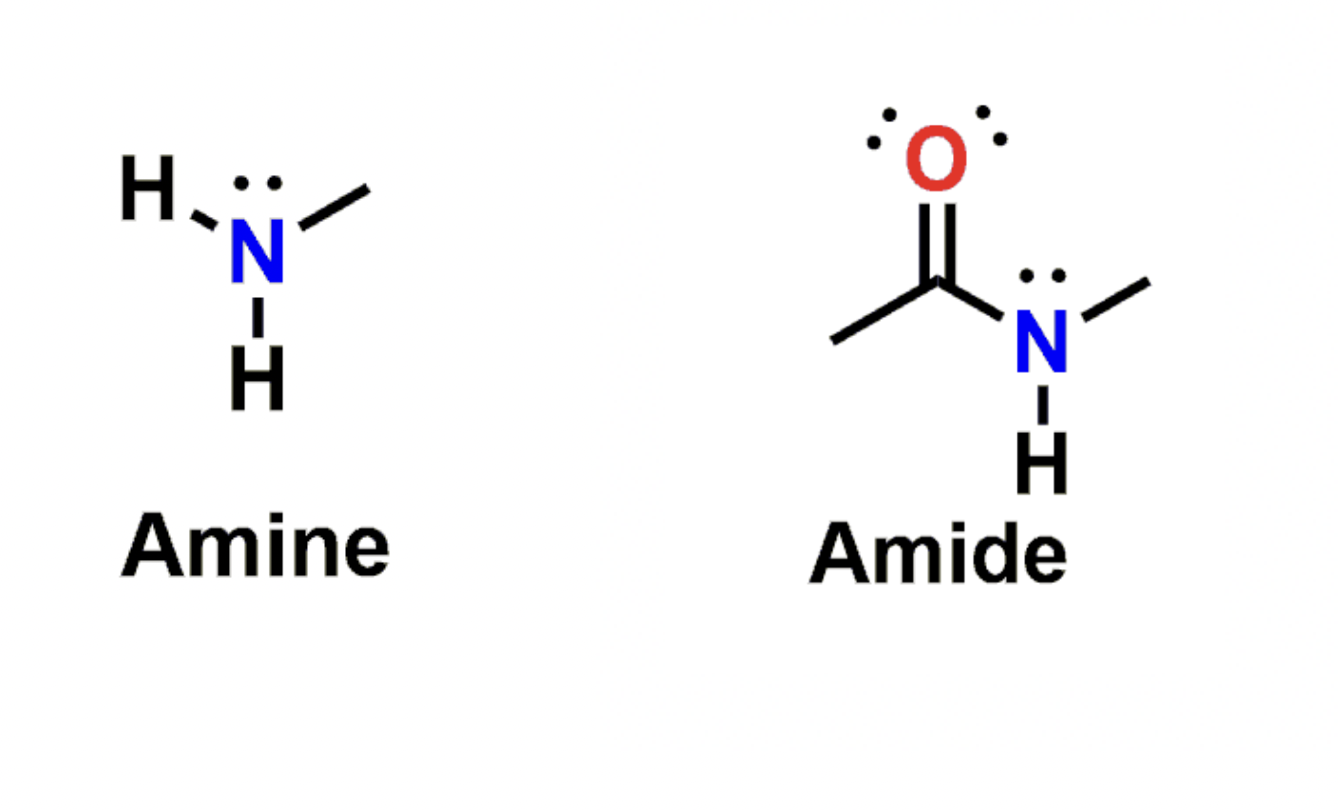
Amide v.s. Amine

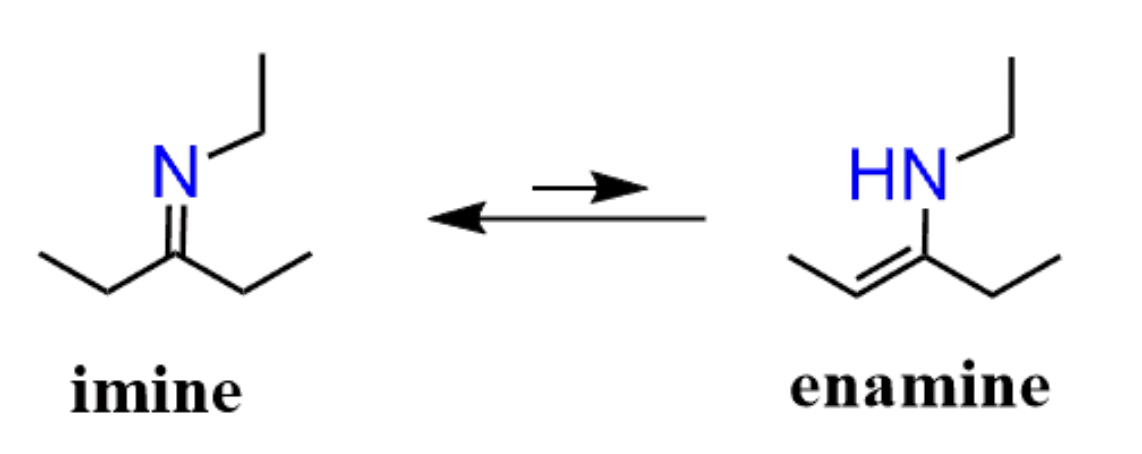
Enamine v.s. Imine
KMnO4
CrO3
Oxidizing agents
Turn alcohols / aldehydes into carboxylic acids
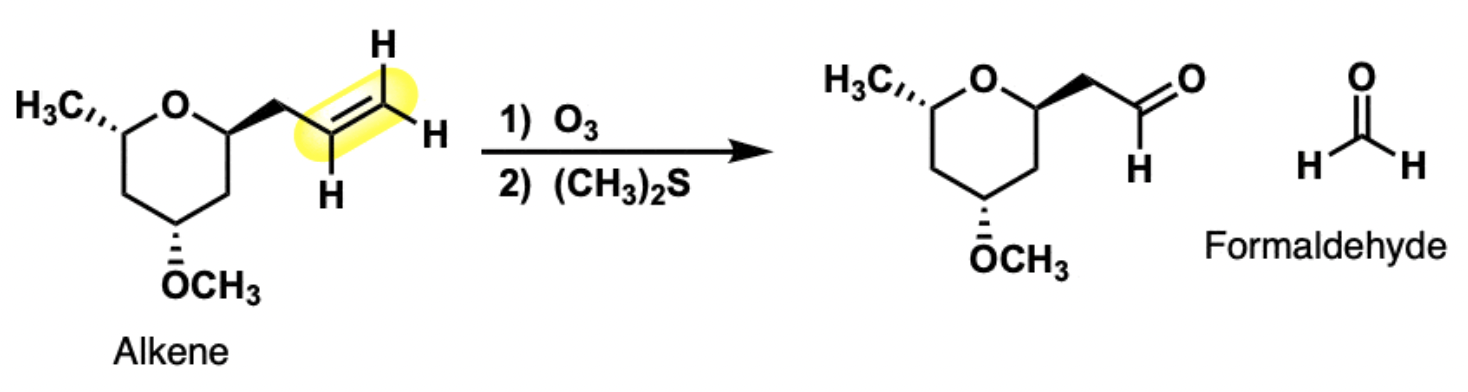
O3
Cleaves alkenes
LiAlH4
NaBH4
H2 (gas) + Pd (catalyst)
Reduces aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids to 1º alcohols
Converts amides and nitriles (CN) to amines
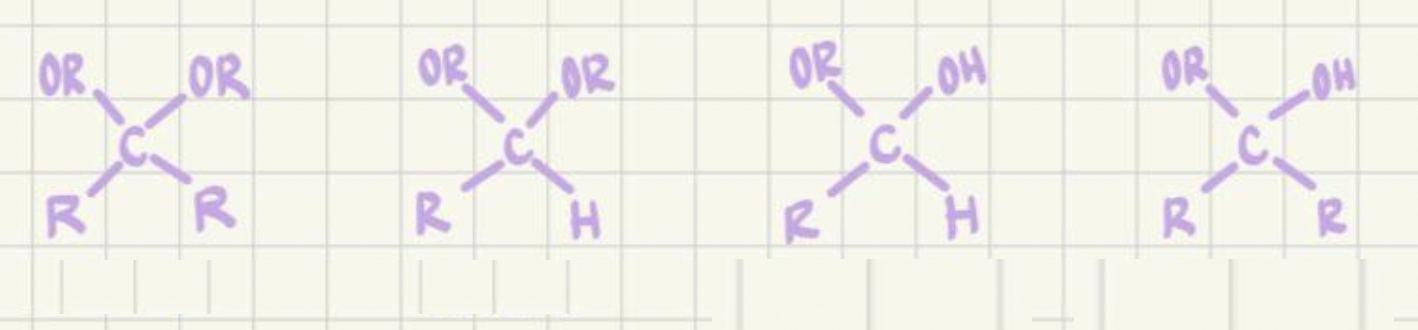
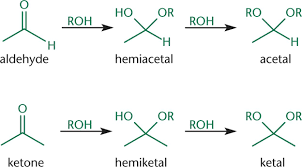
Label: acetal, ketal, hemiacetal, hemiketal
Which come from ketones, which come from aldehydes?
Tollen’s reagent:
Purpose
(Strong/weak?) (Oxidizing/reducing?) agent
Identifies aldehydes (by converting them into carboxylic acids)
Weak oxidizing agent?
All reducing sugars will give a (+)
Benedict’s reagent:
Purpose
(Strong/weak?) (Oxidizing/reducing?) agent
Identifies aldehydes (+ = red solution)
Weak oxidizing agent
All reducing sugars will give a (+)