AP World: Modern - Unit 1: The Global Tapestry
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
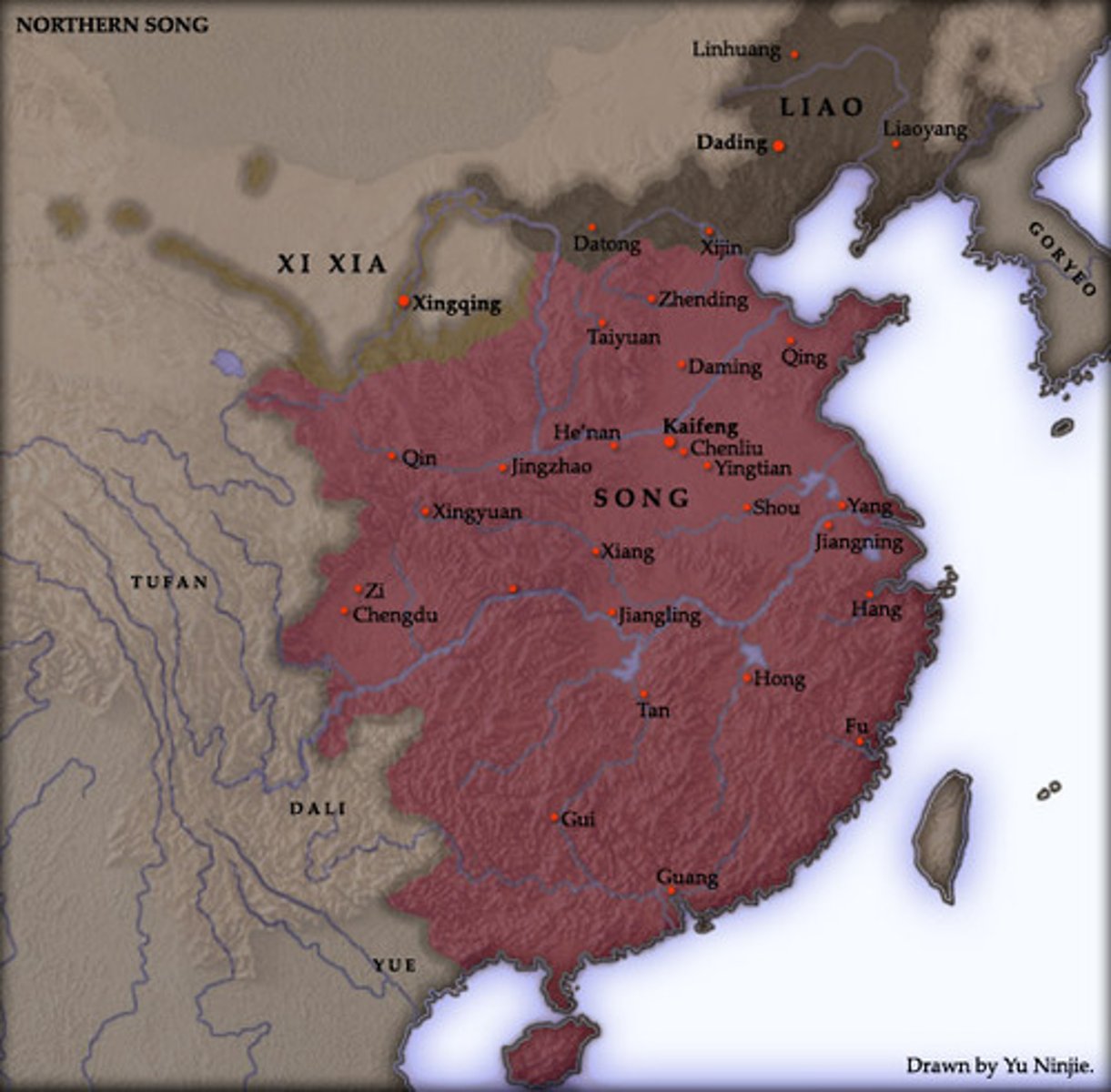
Song Dynasty
Chinese dynasty (960 - 1279 CE) characterized by a merit-based bureaucracy, paper money, a printing press, gunpowder, a navy, the compass, and Neo-Confucianism.
Confucianism
The system of ethics, education, and statesmanship taught by Confucius and his disciples, stressing filial piety, ancestor worship, reverence for parents, and harmony in thought and conduct.

Filial Piety
In Confucian thought, one of the virtues to be cultivated, a love and respect for one's parents and ancestors.

Neo-Confucianism
Term that describes the resurgence of Confucianism and the influence of Confucian scholars during the Tang Dynasty; incorporated some elements of Buddhism
Theravada Buddhism
The oldest of the two major branches of Buddhism. Practiced mainly in Sri Lanka, Thailand, Burma, and Cambodia, its beliefs are relatively conservative, holding close to the original teachings of the Buddha
Mahayana Buddhism
"Great Vehicle" branch of Buddhism followed in China, Japan, and Central Asia. The focus is on reverence for Buddha and for bodhisattvas, enlightened persons who have postponed nirvana to help others attain enlightenment.
Tibetan Buddhism
the religion of Tibet, a form of Mahayana Buddhism. It was formed in the 8th century AD from a combination of Buddhism and the indigenous Tibetan religion. The head of the religion is the Dalai Lama. Teaches that followers can achieve nirvana in one lifetime.

Champa Rice
Quick-maturing rice that can allow two harvests in one growing season; led to increased populations in Song Dynasty China. From Vietnam; sent to China as a tribute gift.

Civil Service Examination System
Exams that Chinese bureaucrats passed to serve in state, based on Confucian concepts.

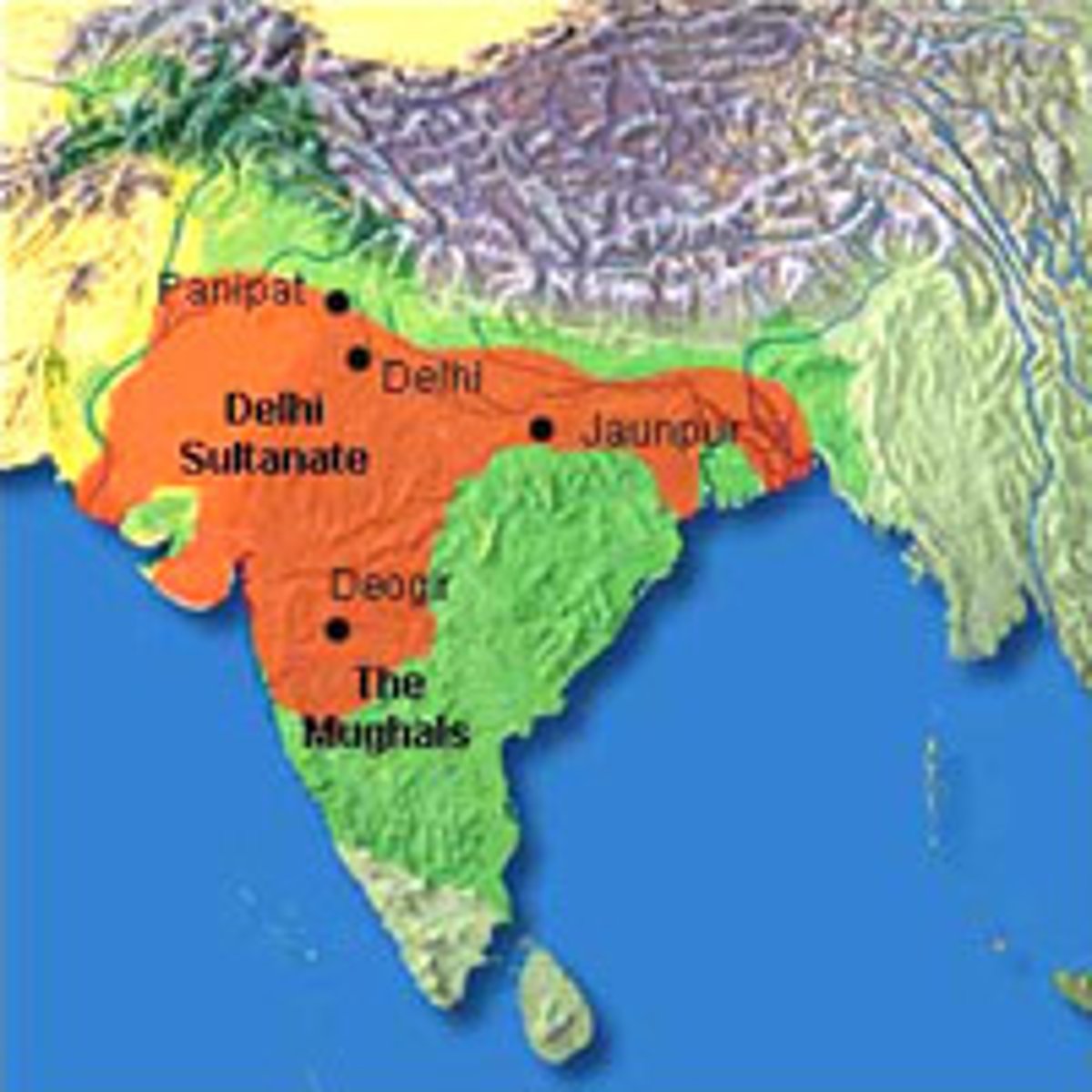
Delhi Sultanate
Centralized Indian empire of varying extent, created by Muslim invaders. Rose after the decline of the Abbasid Empire.
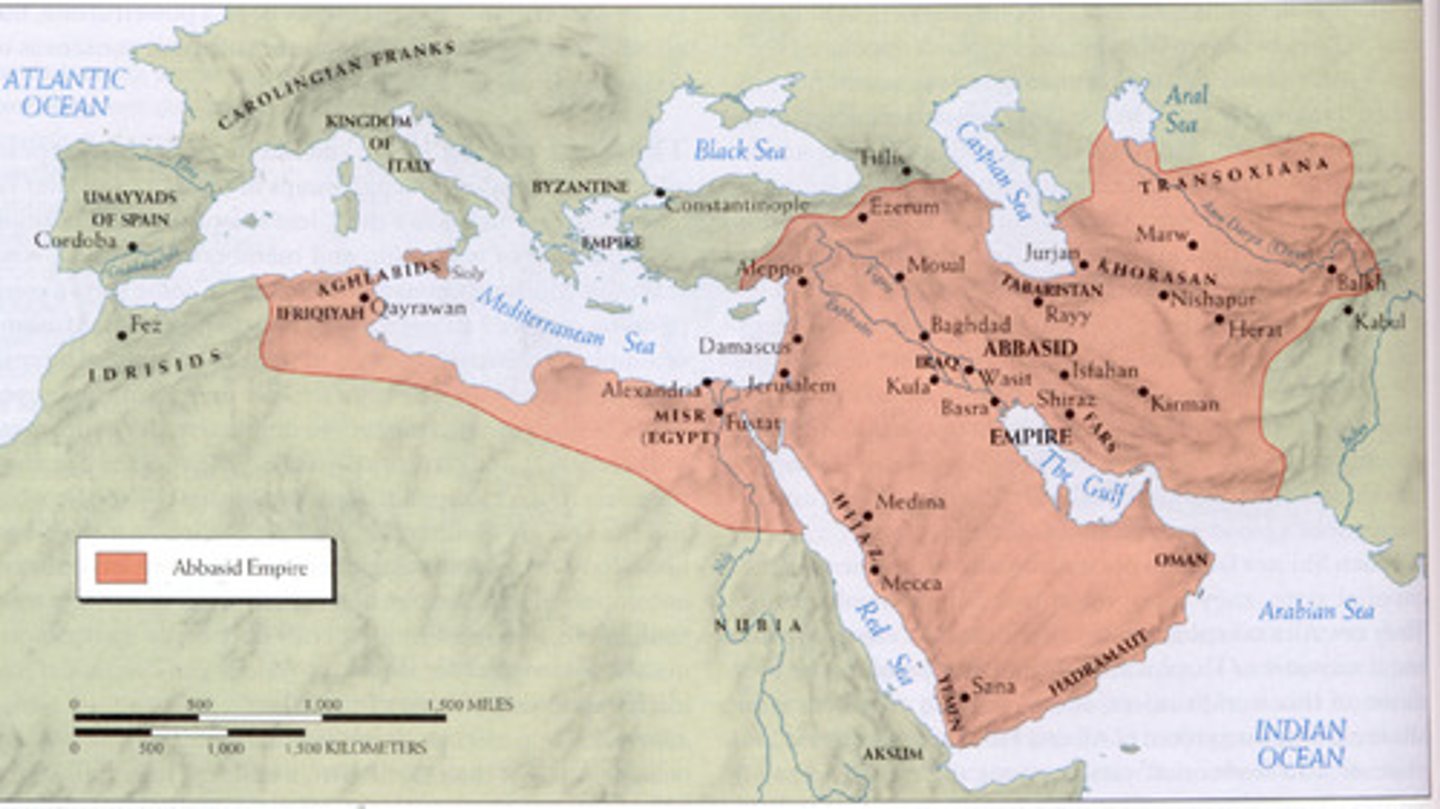
Abbasid Caliphate
(750-1258 CE) The caliphate, after the Umayyads, who focused more on administration than conquering. The "golden age" of Islam with a capital in Baghdad.
House of Wisdom
Large Islamic-based library and learning center in Baghdad. Focus of conversion of Greek and Roman classics and Indian learning into Arabic.

Bhakti Movement
An immensely popular development in Hinduism, advocating intense devotion toward a particular deity. Promoted equality and opposed the caste system.

Sufism
An Islamic mystical tradition that desired a personal union with God- dedicating themselves to fasting, prayer, meditation on the Qur'an, and the avoidance of sin. Missionaries helped spread Islam.

Feudalism
A political system in which nobles are granted the use of lands that legally belong to their king, in exchange for their loyalty, military service, and protection of the people who live on the land
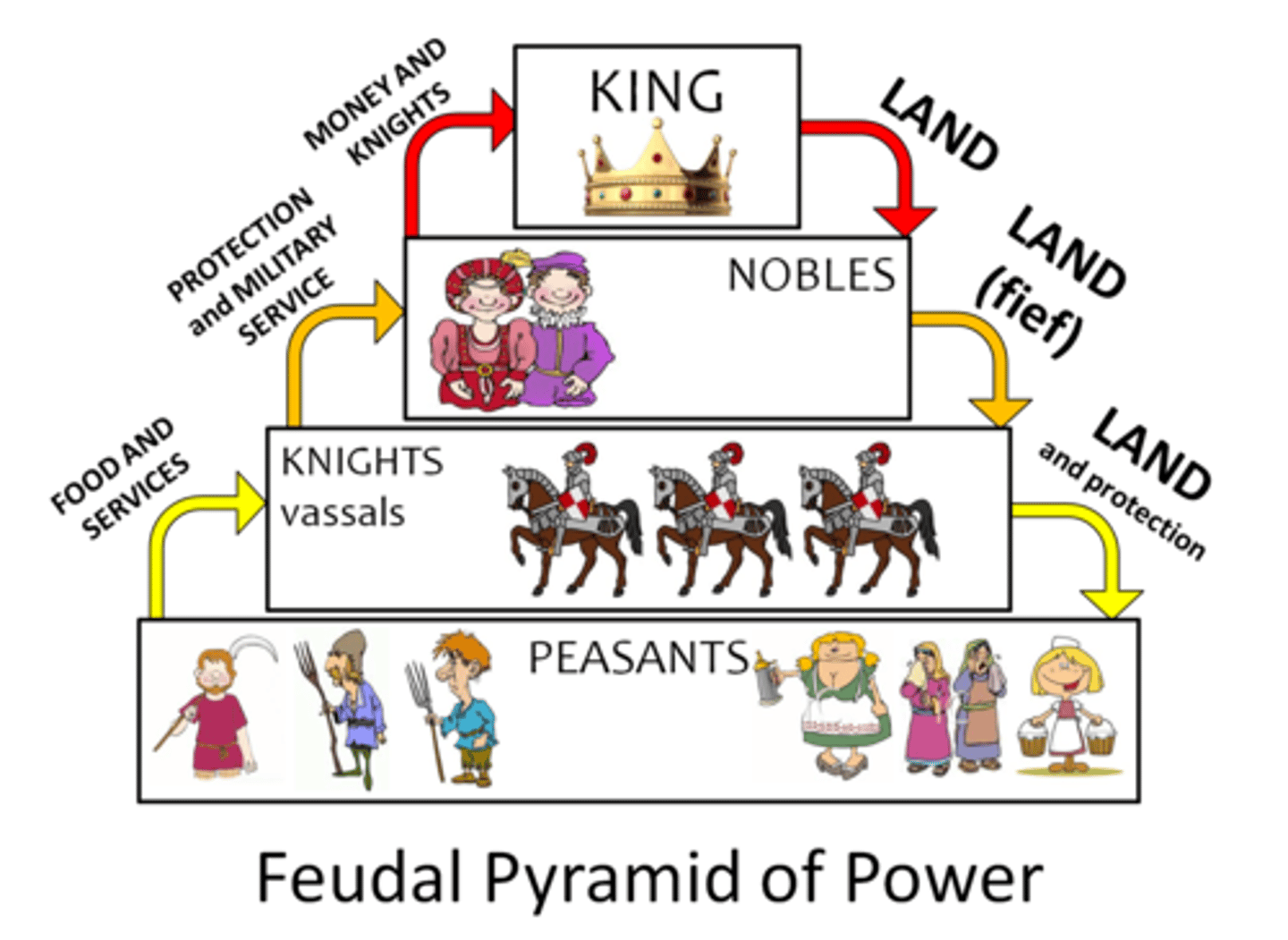
Serfdom
A type of labor commonly used in feudal systems in which the laborers work the land in return for protection but they are bound to the land and are not allowed to leave or to peruse their a new occupation.

Manorialism
Economic system during the Middle Ages that revolved around self-sufficient farming estates where lords and peasants shared the land.; the economic aspect of feudalism.

Great Zimbabwe
A powerful state in the African interior that apparently emerged from the growing trade in gold to the East African coast; flourished between 1250 and 1350 C.E.

Maya
Mesoamerican city-states concentrated in Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula and Central America. Major contributions were in mathematics, astronomy, and development of the calendar.

Syncretism
The unification or blending of opposing people, ideas, or practices, frequently in the realm of religion. For example, when Christianity or Buddhism was adopted by people in a new land, they often incorporate it into their existing culture and traditions.

Nasir al-Din Tusi
Persian mathematician and cosmologist who inspired Copernican model of the solar system. Represents the mathematical innovations from Arabs in this period.

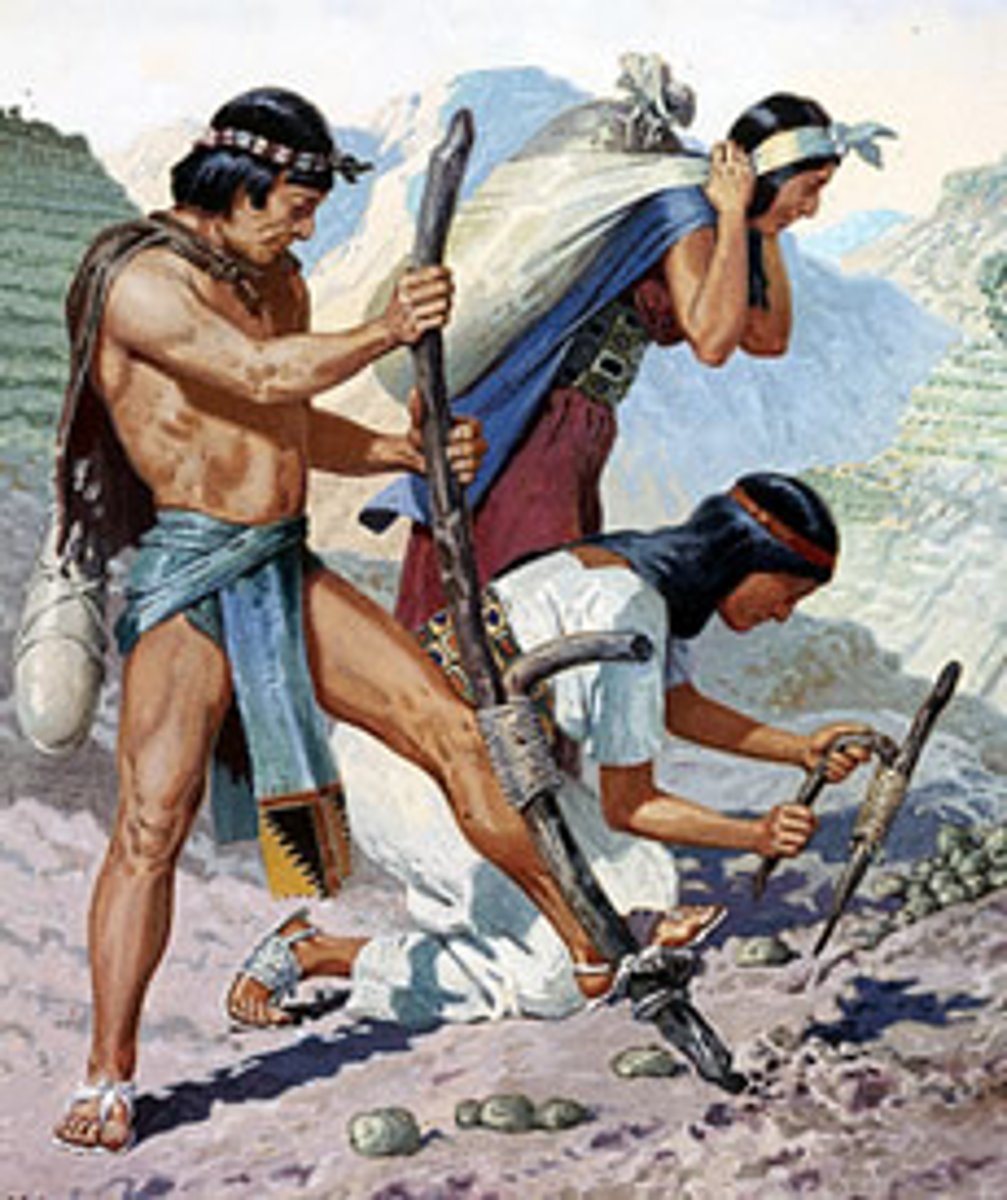
Mita System
Economic system in Inca society where people paid taxes with their labor and what they produced; men and women were expected to contribute this labor to the state yearly

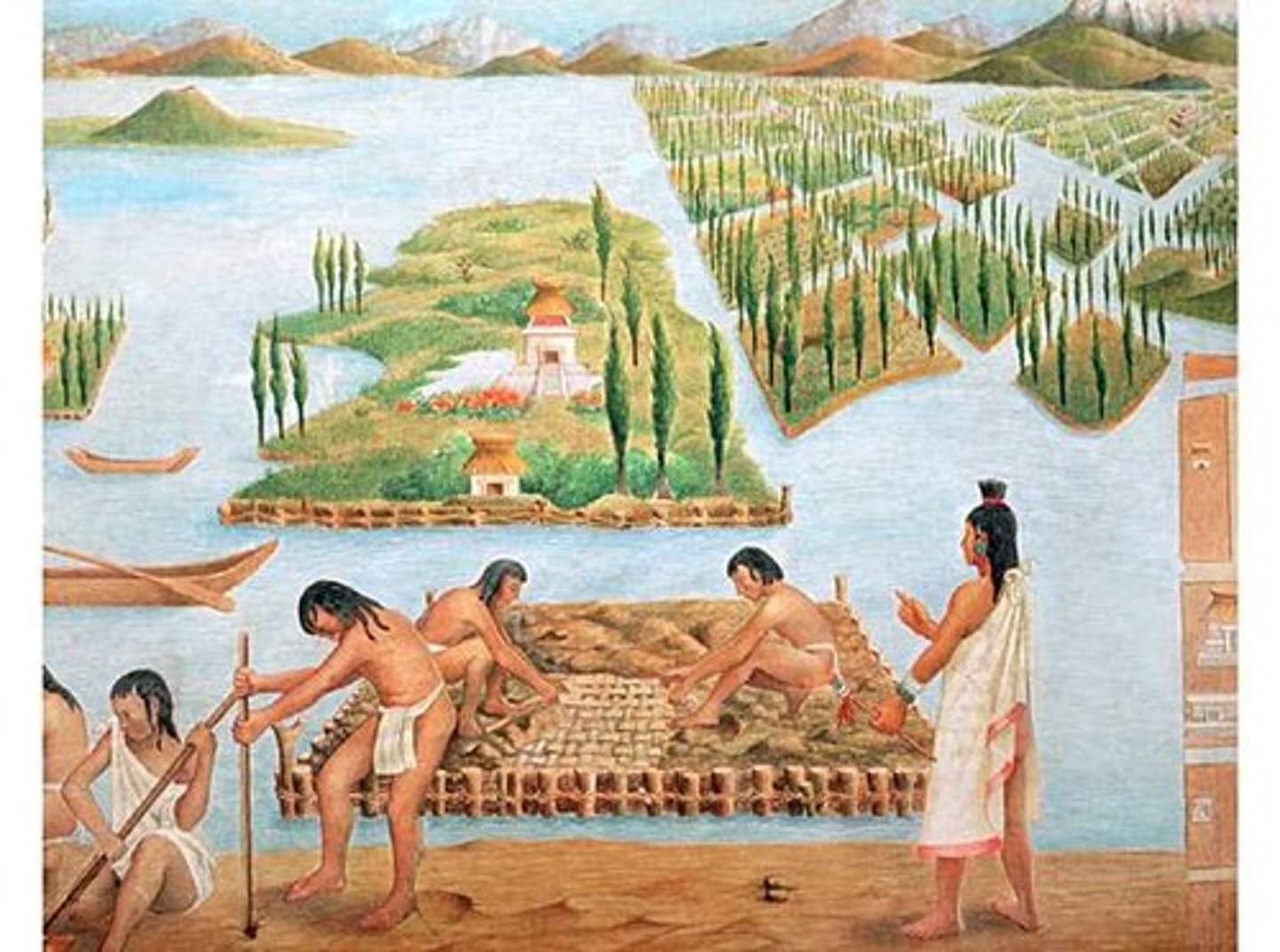
Chinampas
Floating gardens constructed along lake shores by the Mexica/Aztecs to increase agricultural yields.

Bodhisattva
a person in Mahayana Buddhism who has attained enlightenment but who has postponed nirvana in order to help others achieve enlightenment
Bureaucracy
A system of managing government through departments run by appointed officials; the Song Dynasty had a merit-based bureaucracy.

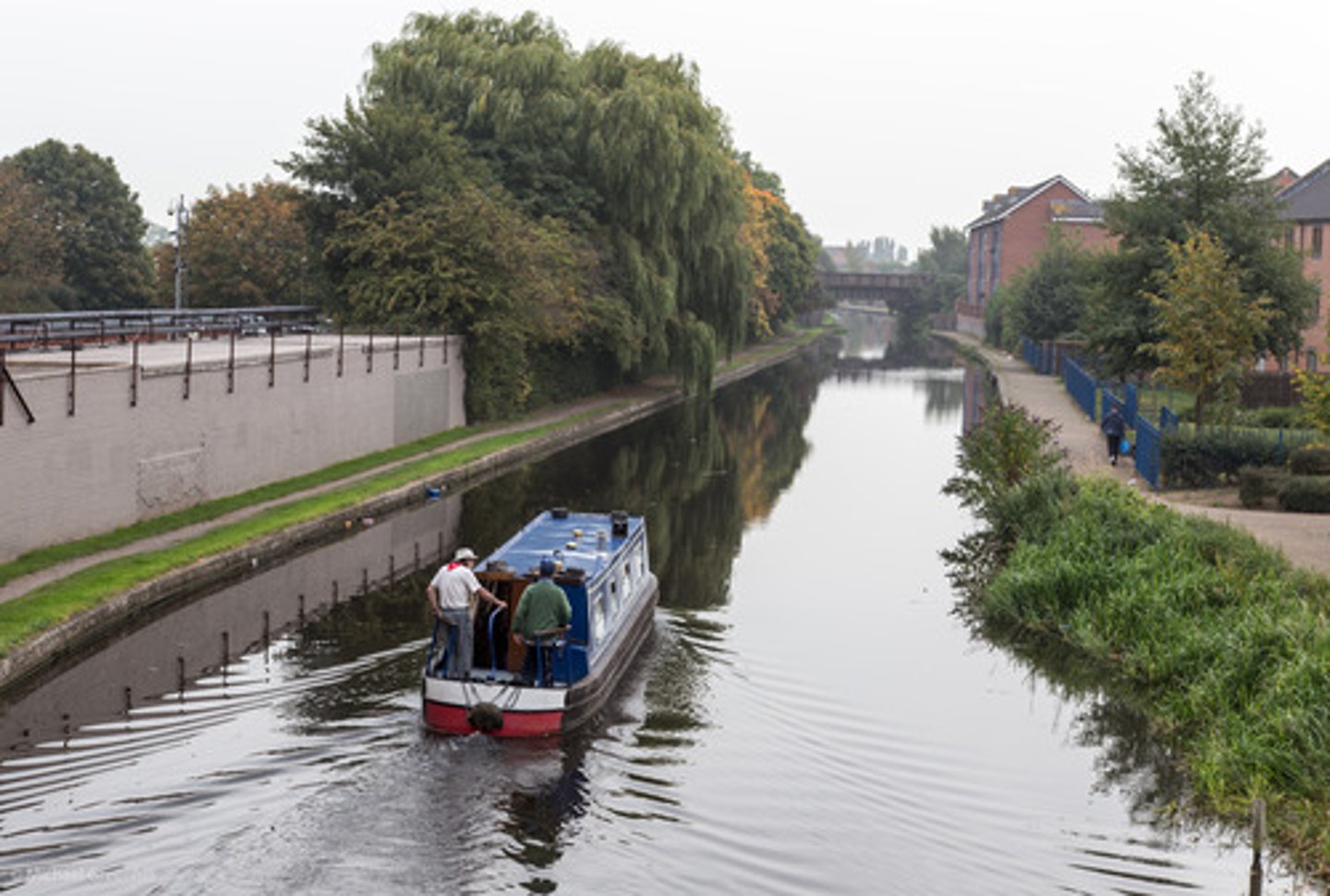
Grand Canal
A canal linking northern and southern China; helped trade flourish during the Song Dynasty

Dar al-Islam
an Arabic term that means the "house of Islam" and that refers to lands under Islamic rule
Islam
A religion based on the teachings of the prophet Mohammed which stresses belief in one god (Allah), and a body of law written in the Quran.

Christianity
the religion based on the person and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth, or its beliefs and practices.

Judaism
A religion with a belief in one god. It originated with Abraham and the Hebrew people. Yahweh was responsible for the world and everything within it. They preserved their early history in the Torah.

Sunni
A branch of Islam whose members acknowledge the first four caliphs as the rightful successors of Muhammad
Shi'a
the branch of Islam whose members acknowledge Ali and his descendants as the rightful successors of Muhammad
Crusades
A series of holy wars from 1096-1270 AD undertaken by European Christians to free the Holy Land from Muslim rule. An opportunity for the pope to bring unity to Western Europe.

Great Schism
the official split between the Roman Catholic and Byzantine churches that occurred in 1054

Buddhism
Belief system that started in India in the 500s BC. Happiness can be achieved through removal of one's desires. Believers seek enlightenment and the overcoming of suffering.
Artisanal Labor
Skilled craftsmen that created various products that required skill to make. This type of labor is different from labor forms such as mit'a, serfdom, etc as it requires skill.
Korea
The Han Dynasty in Chinese temporarily conquered this region and introduced it to both confucianism and buddhism. They compensated china with a tribute system. They wanted to adopt china's administration system but it never caught on fully.
Song China's Tech Innovations
Woodblock and Moveable type
Gunpowder
Compass
Paper
Iron Industry
Tang Dynasty
China's 6th dynasty from 618-907. Considered Chain's golden age as the built on Sui's foundations of unity. This dynasty saw the rise of Ne-Confucianism.
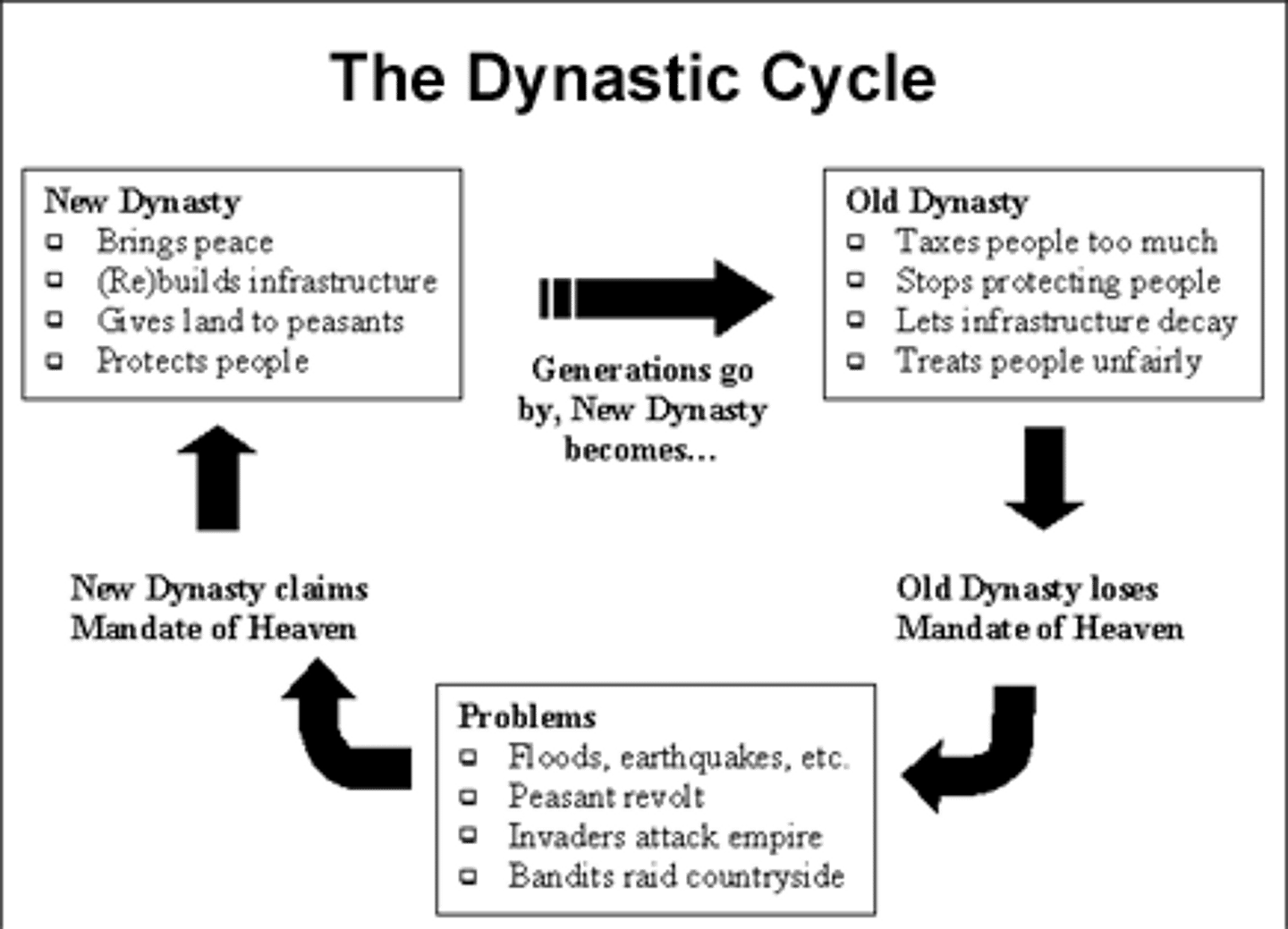
Dynastic Cycle
the historical pattern of the rise, decline, and replacement of dynasties
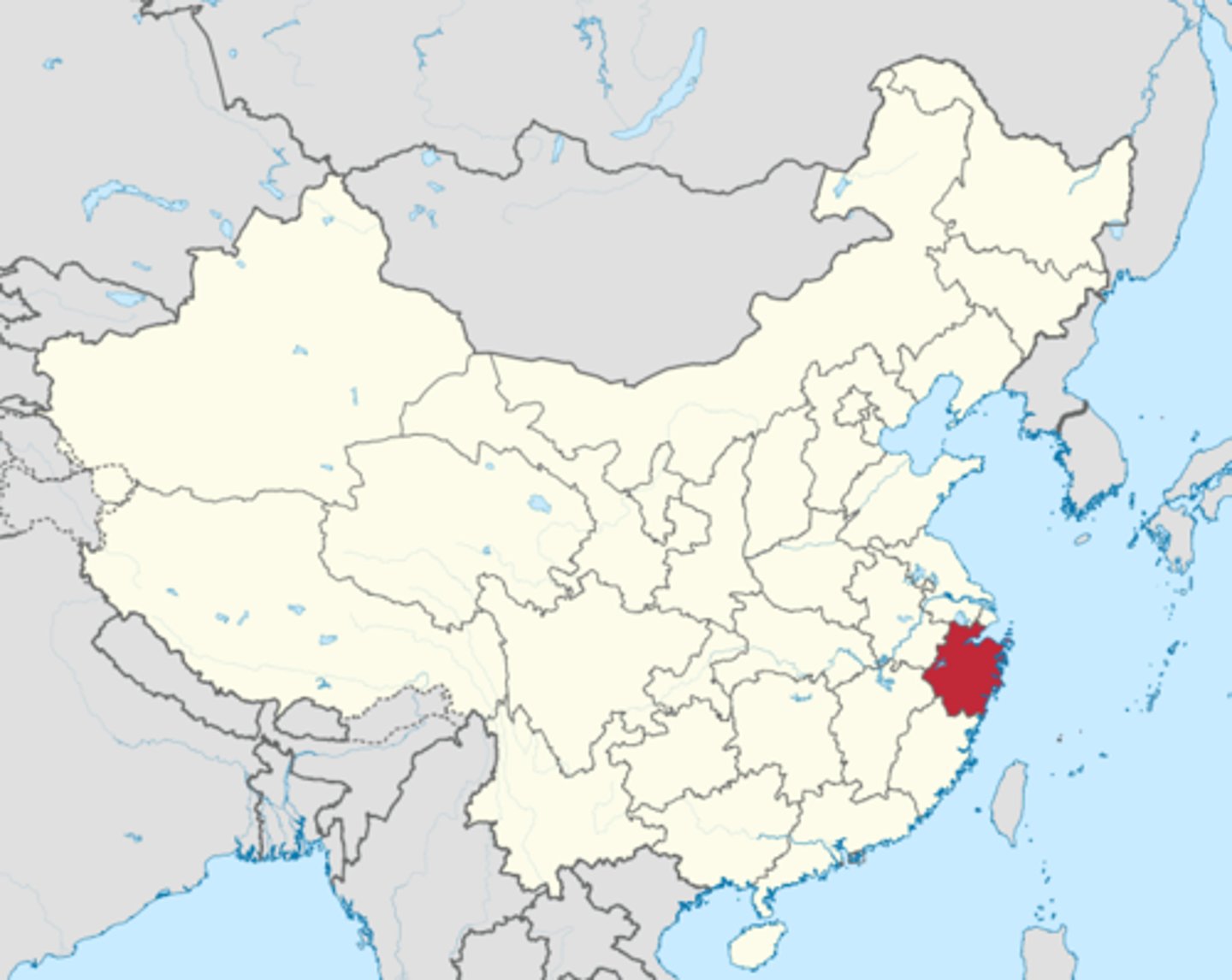
Hangzhou
Capital of later Song dynasty; located near East China Sea; permitted overseas trading; population exceeded 1 million. Represents the power and growth of China to Marco Polo.
Footbinding
Practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet in order to make them smaller; produced pain and restricted women's movement; made it easier to confine women to the household.

tribute system
A system in which defeated peoples were forced to pay a tax in the form of goods and labor.

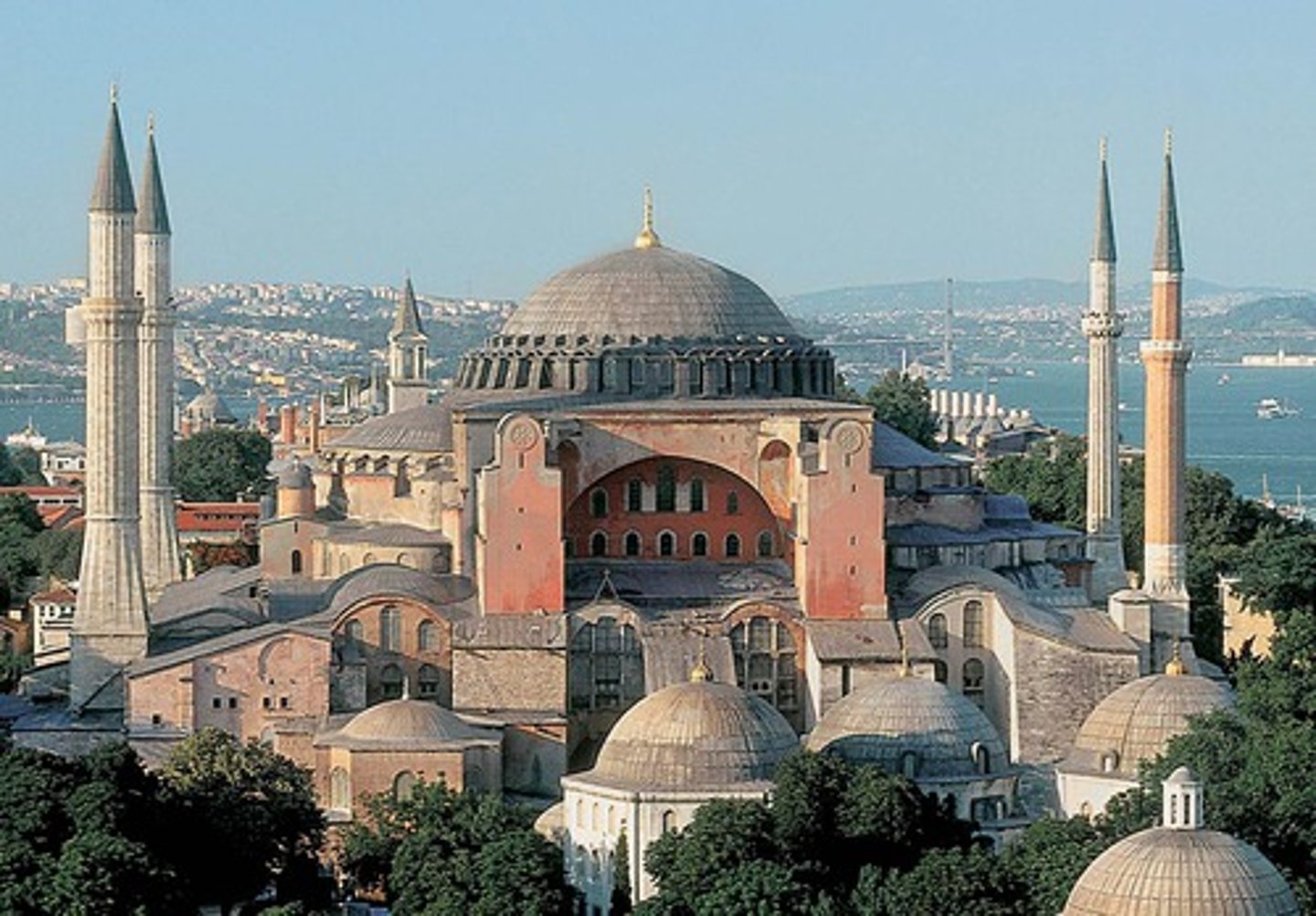
Hagia Sophia
Christian church constructed in Constantinople during reign of Justinian. Most famous example of Byzantine architecture.

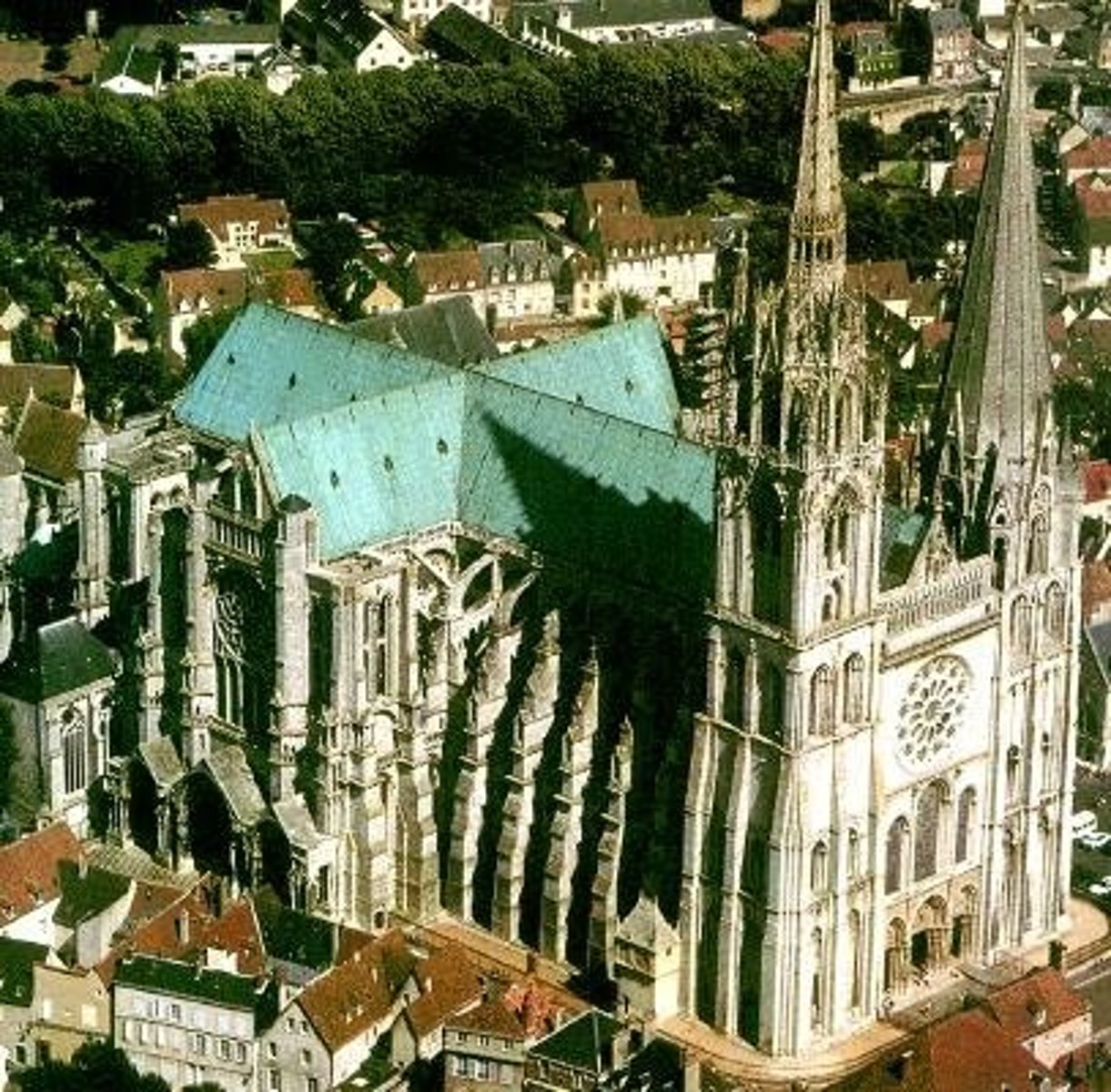
Chartres Cathedral
Gothic cathedral in Chartres, France with sculptures, stained glass windows, and carvings of Bible stories.

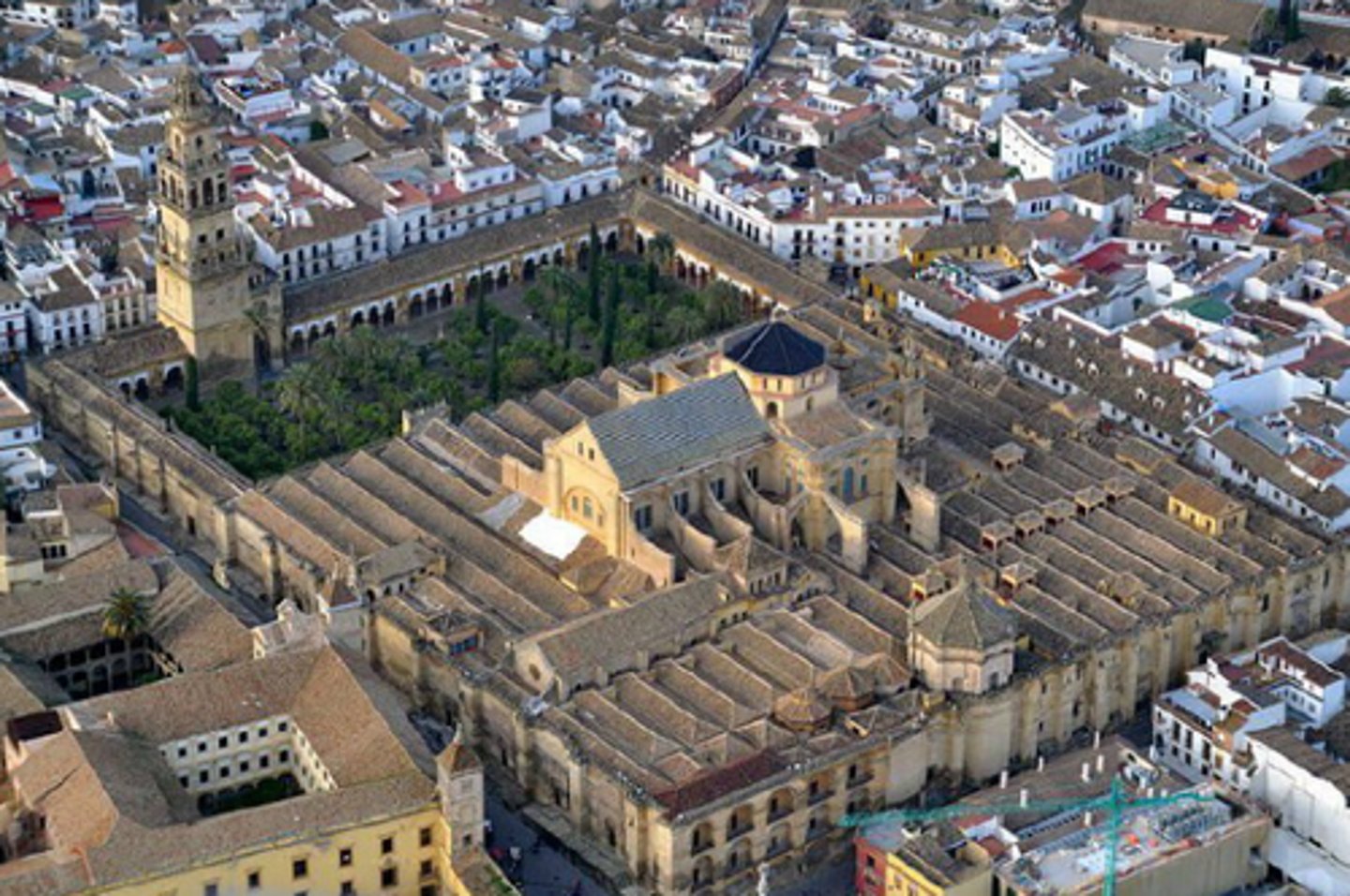
Great Mosque of Cordoba
A graceful Mosque that was built on the ruins of a ruined Christian Church, Famous for its horseshoe arches, it provides a striking example of the sophistication provided by the fusion of Jewish, Muslim and Christian art.

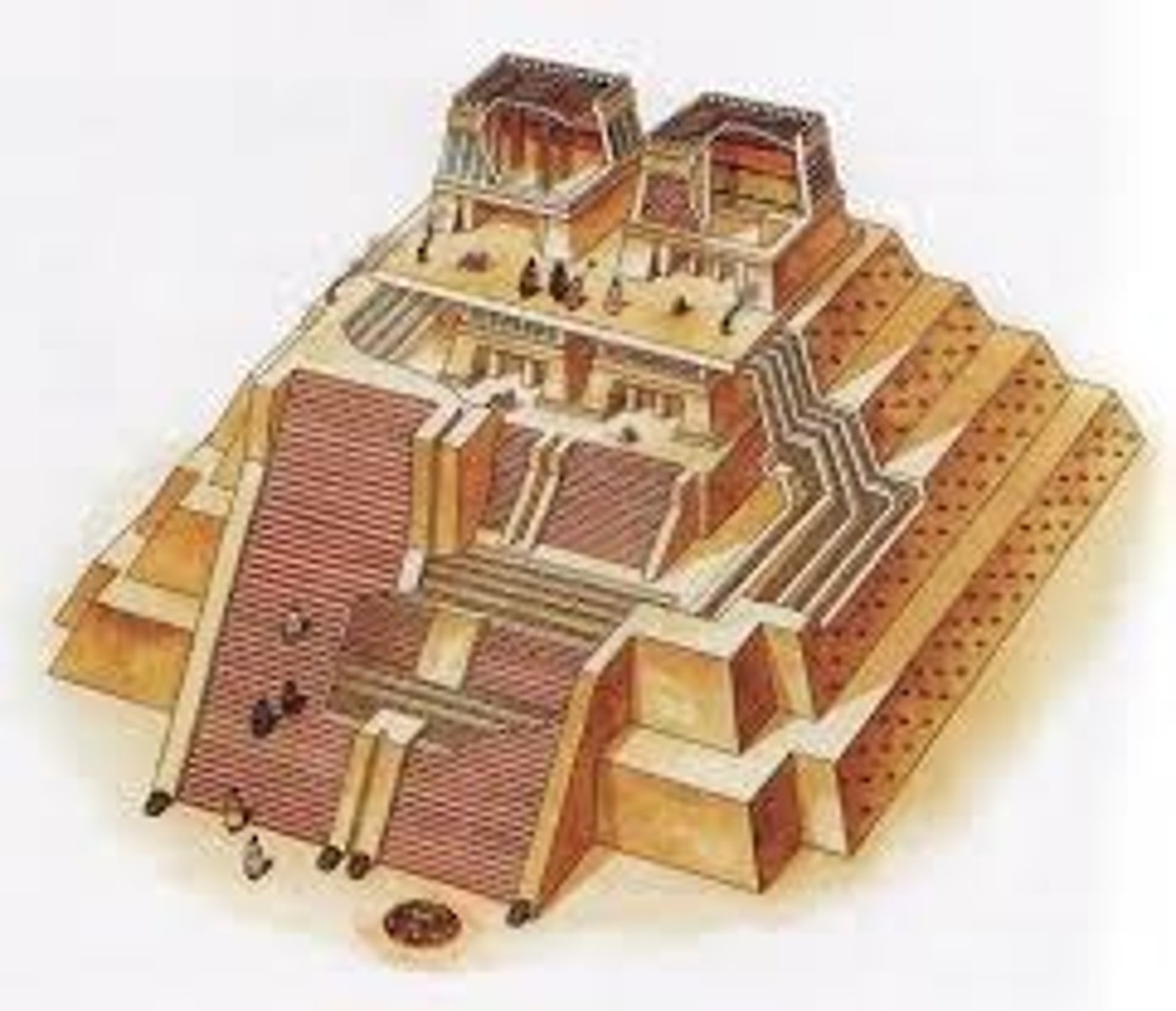
Templo Mayor
the major temple in the centre of Aztec's capital of Tenochtitlan, dedicated to the god Huitzilopochtli

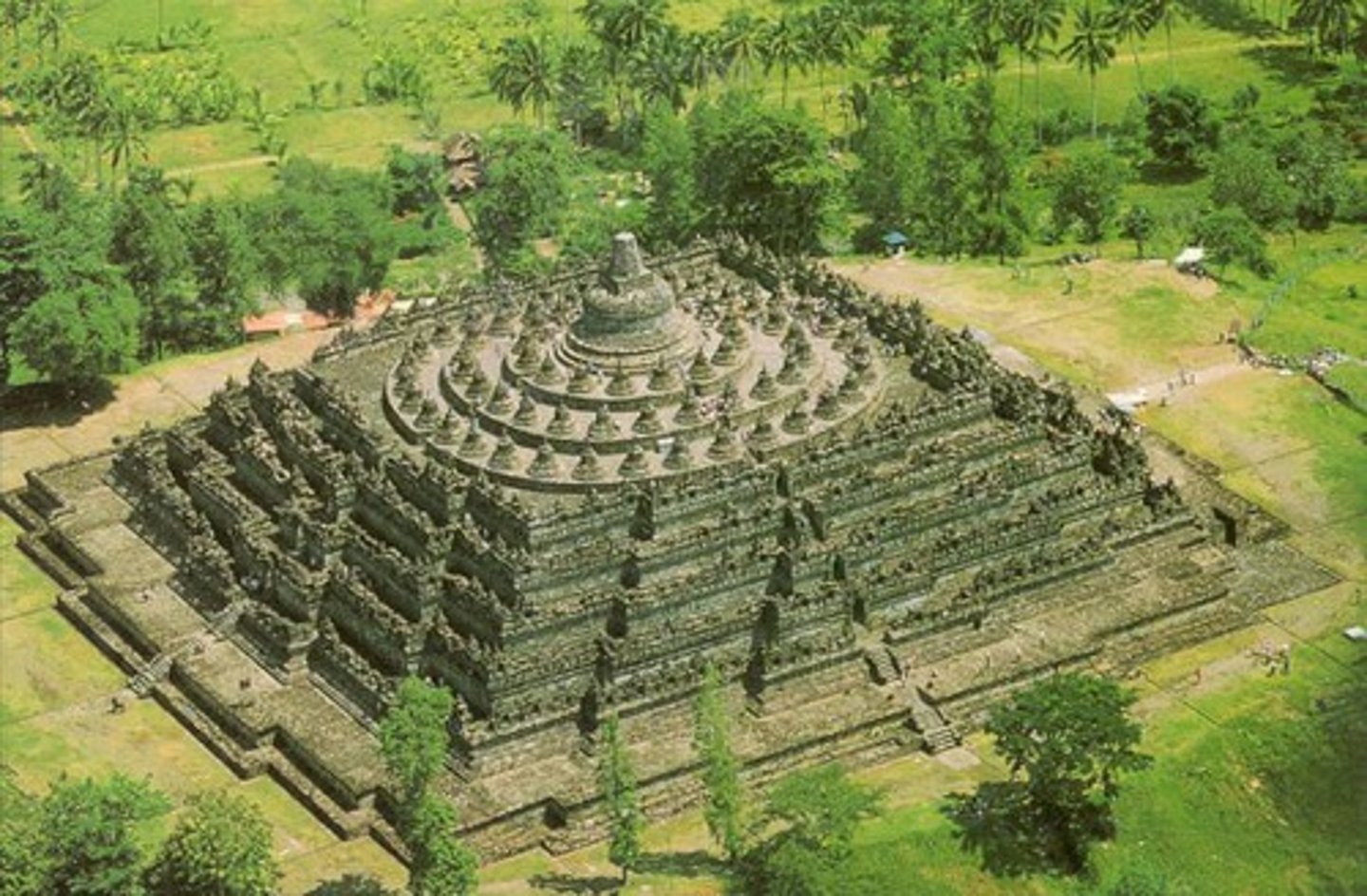
Borobudur Temple
- Central Java, Indonesia
- volcanic-stone masonry

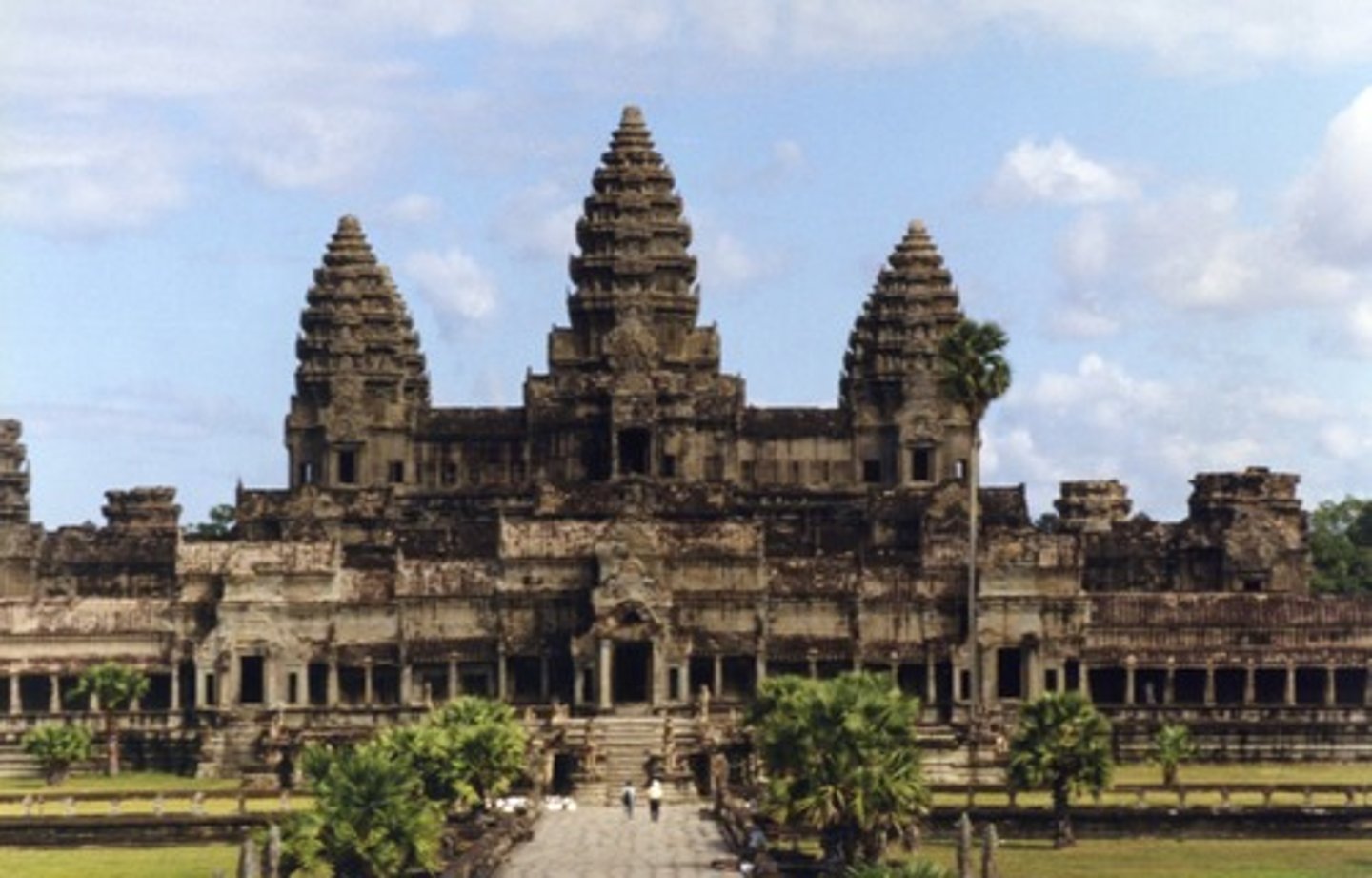
Angkor Wat
A temple complex built in the Khmer Empire and dedicated to the Hindu God, Vishnu.

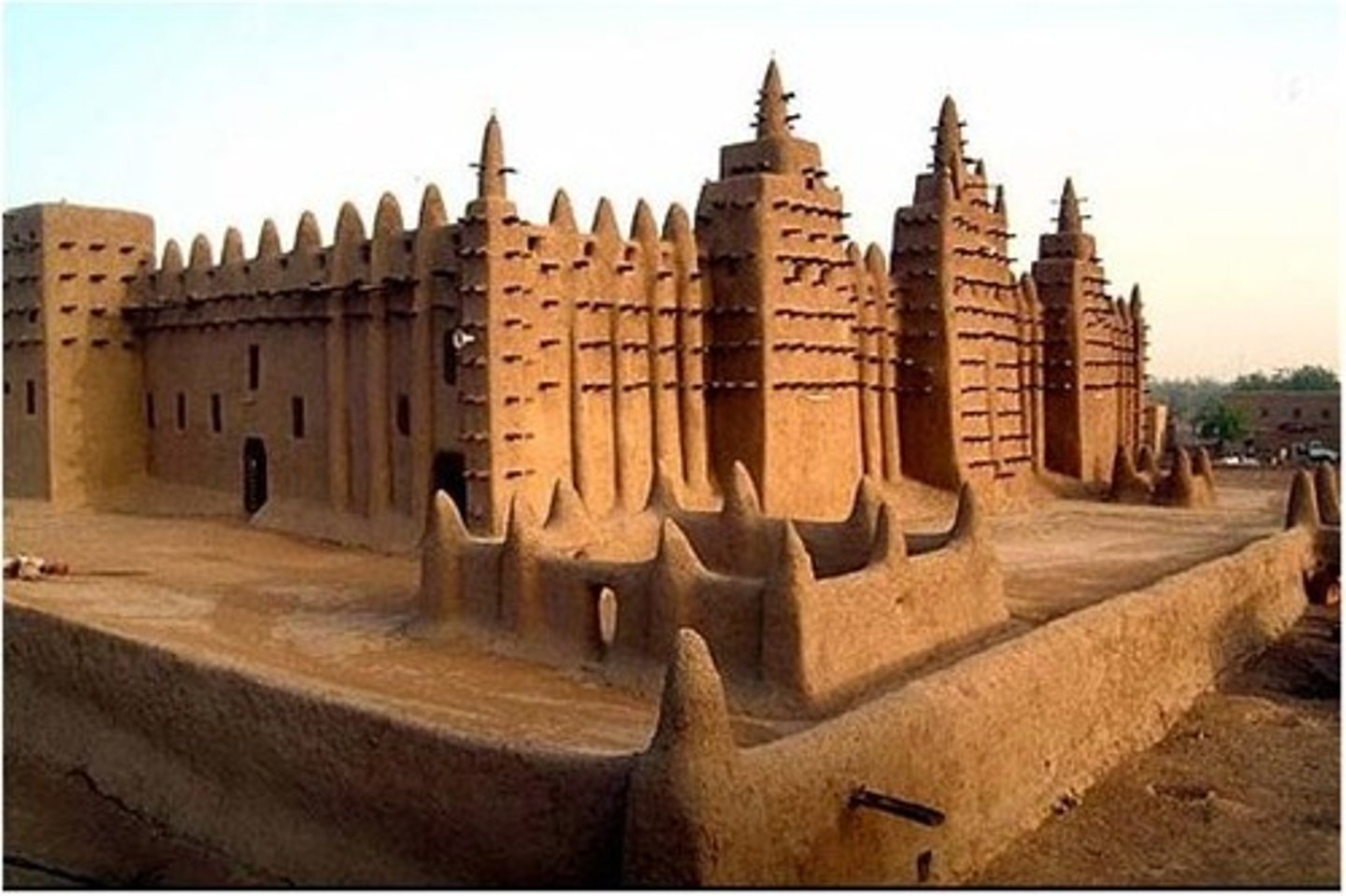
Great Mosque of Djenne
A center of religious and cultural life in Mali found in 1200. A mosque as well as a learning and cultural center. of the south Sahara.

Seljuk Empire
Middle East, 11th-12th centuries
Turkic empire ruled by sultans in Persia and modern day. Established Turks as major ethnic group carrying Islam across Eurasia, along with Arabs and Persians
Demonstrated weakness of Abbasid caliphate in its later years; sultans held real power in the empire. Helped to spread the influence of Islam throughout the region
Hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms

Buddhist monasticism
the fundamental institutions of monks that preserve the teachings of the buddha (Theravada, Mahayana, Tibetan)
Srivijaya Empire
flourished from the 600s to 1200s; controlled the Strait of Malacca, lots of spices, and a critical portion of Indian Ocean trade
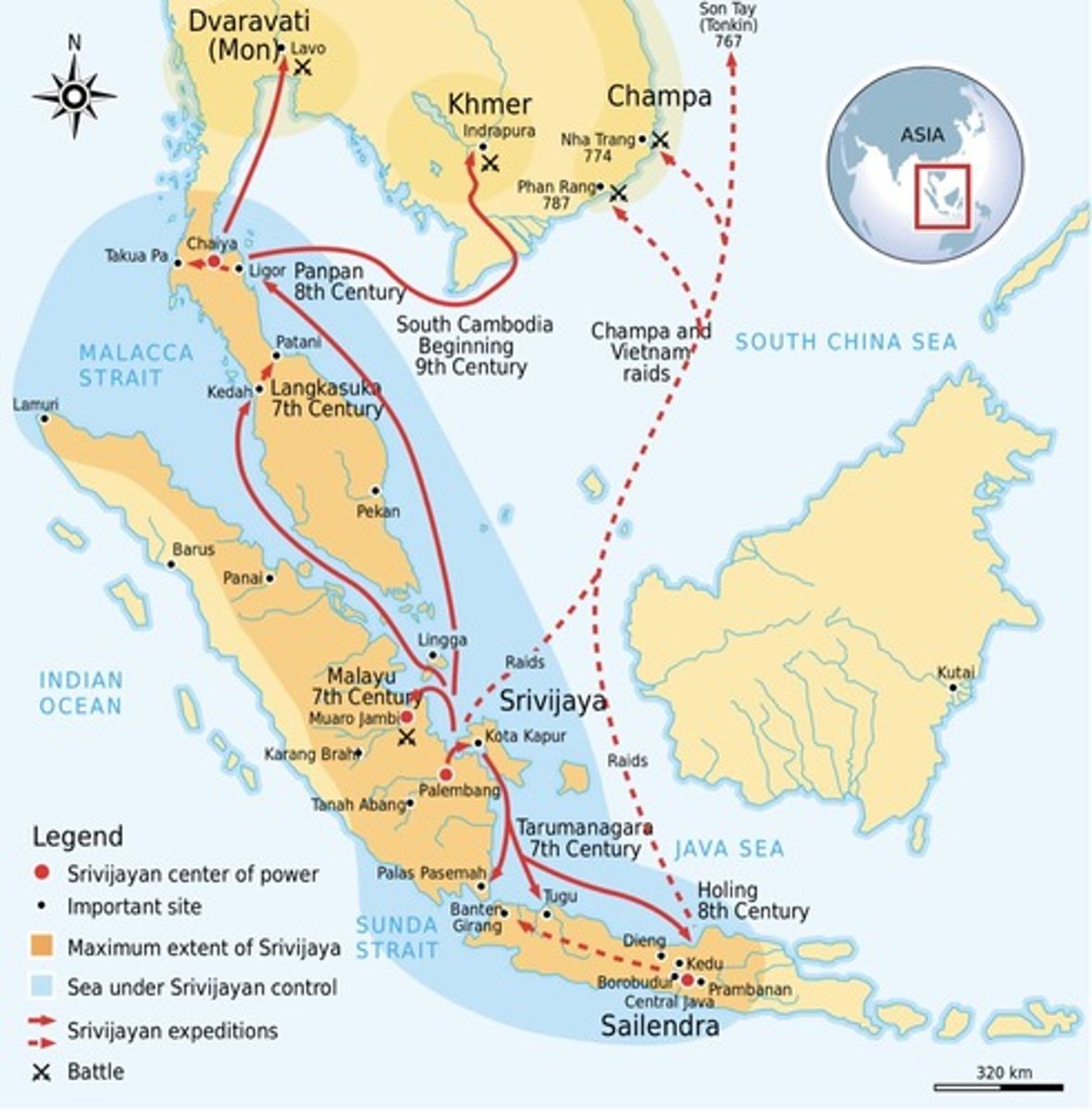
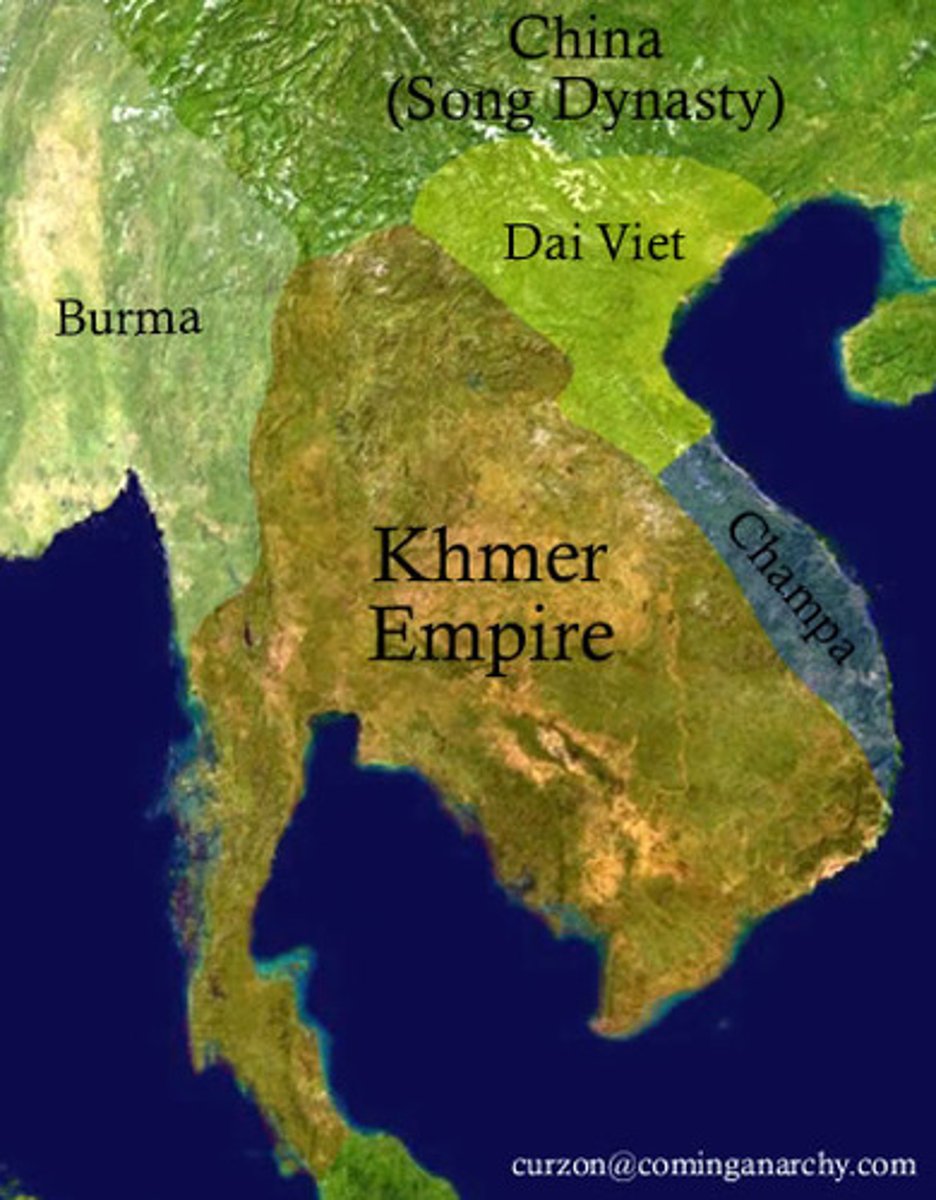
Khmer Empire
a kingdom in modern day Cambodia that was largely influenced by Hinduism and India. They reached their peak in 1219
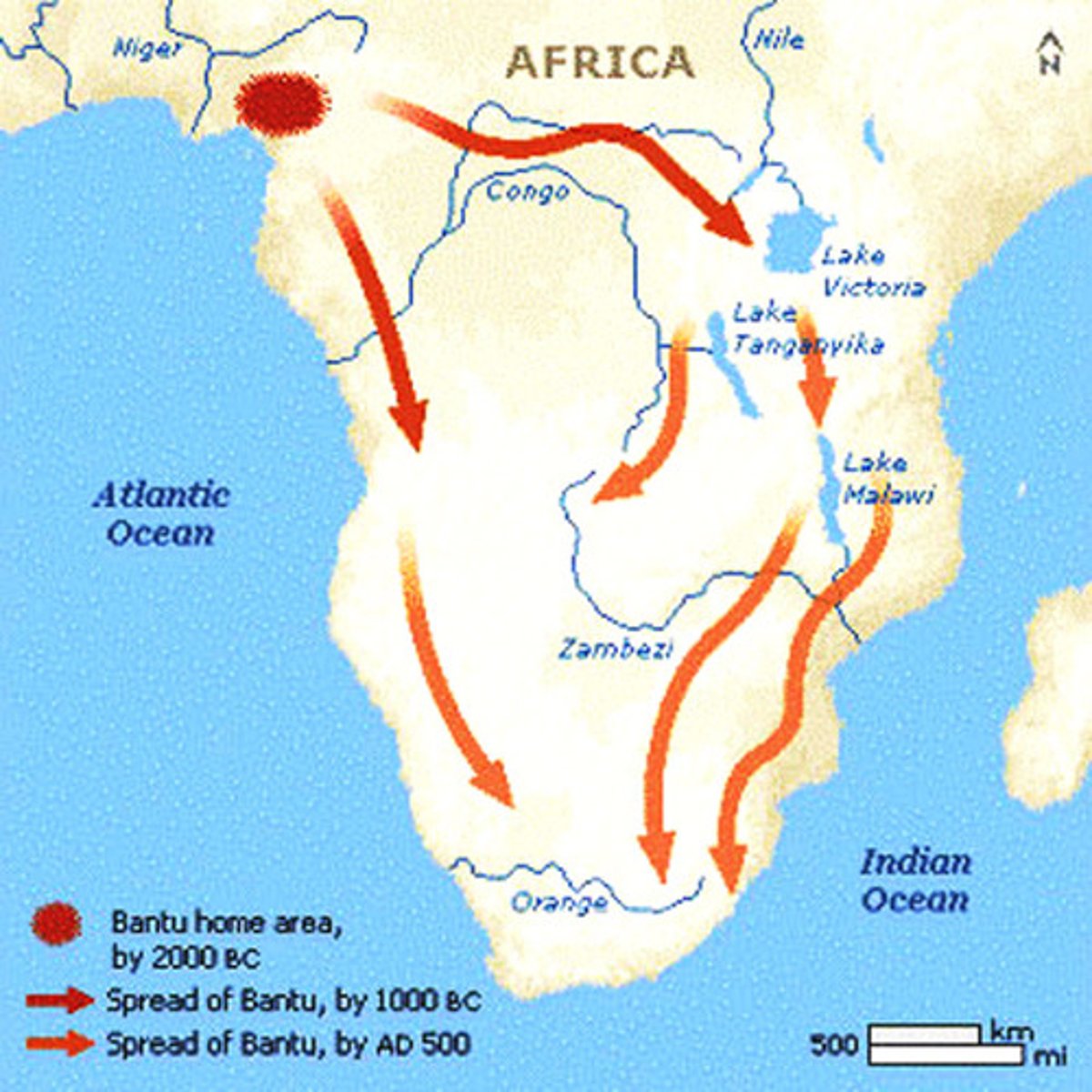
Bantu Migration
The movement of the Bantu peoples southward throughout Africa, spreading their language and culture, from around 500 b.c. to around A.D 1000
Afro-Eurasia
the vast region made up of Africa, Europe, and Asia
Dhimmis
described by Muslims as "the people of the book"-- Jews, Christians
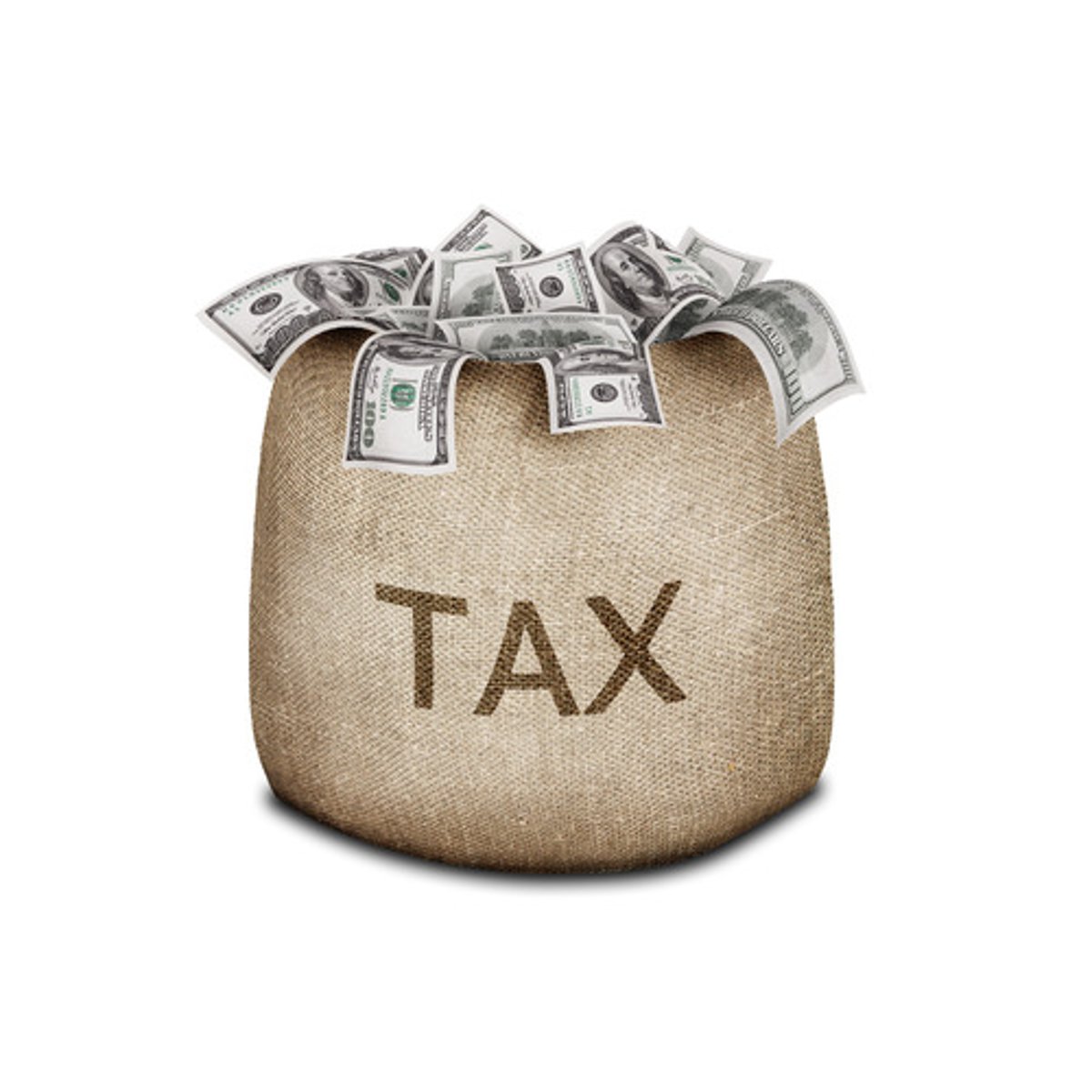
Jizya
Poll tax that non-Muslims had to pay when living within a Muslim empire

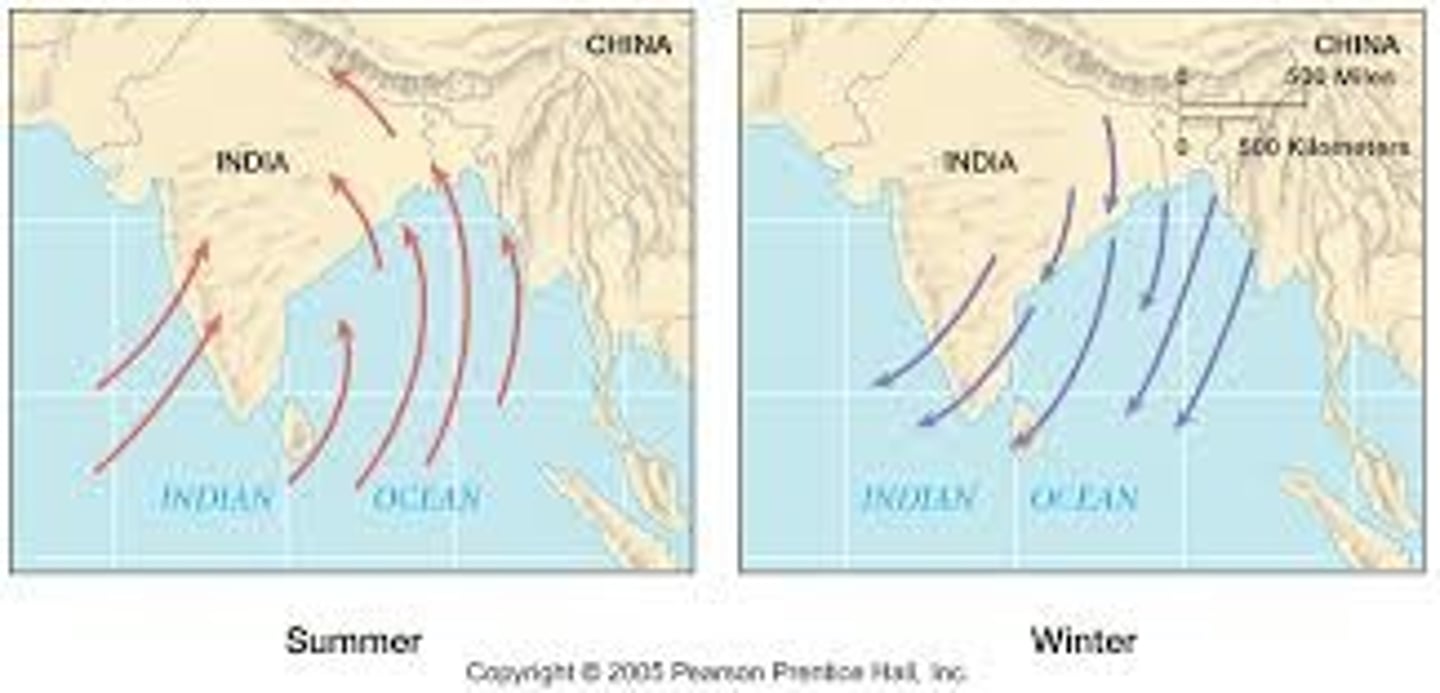
monsoon winds
The seasonal wind of the Indian Ocean and southern Asia, blowing from the southwest in summer and from the northeast in winter. (in India and nearby lands) the season during which the southwest monsoon blows, commonly marked by heavy rains; rainy season. any wind that changes directions with the seasons
Sharia
Body of Islamic law that includes interpretation of the Quran and applies Islamic principles to everyday life
Western Roman Empire
finally fell for many reasons in 476 AD, nearly 150 years after the establishment of Constantinople
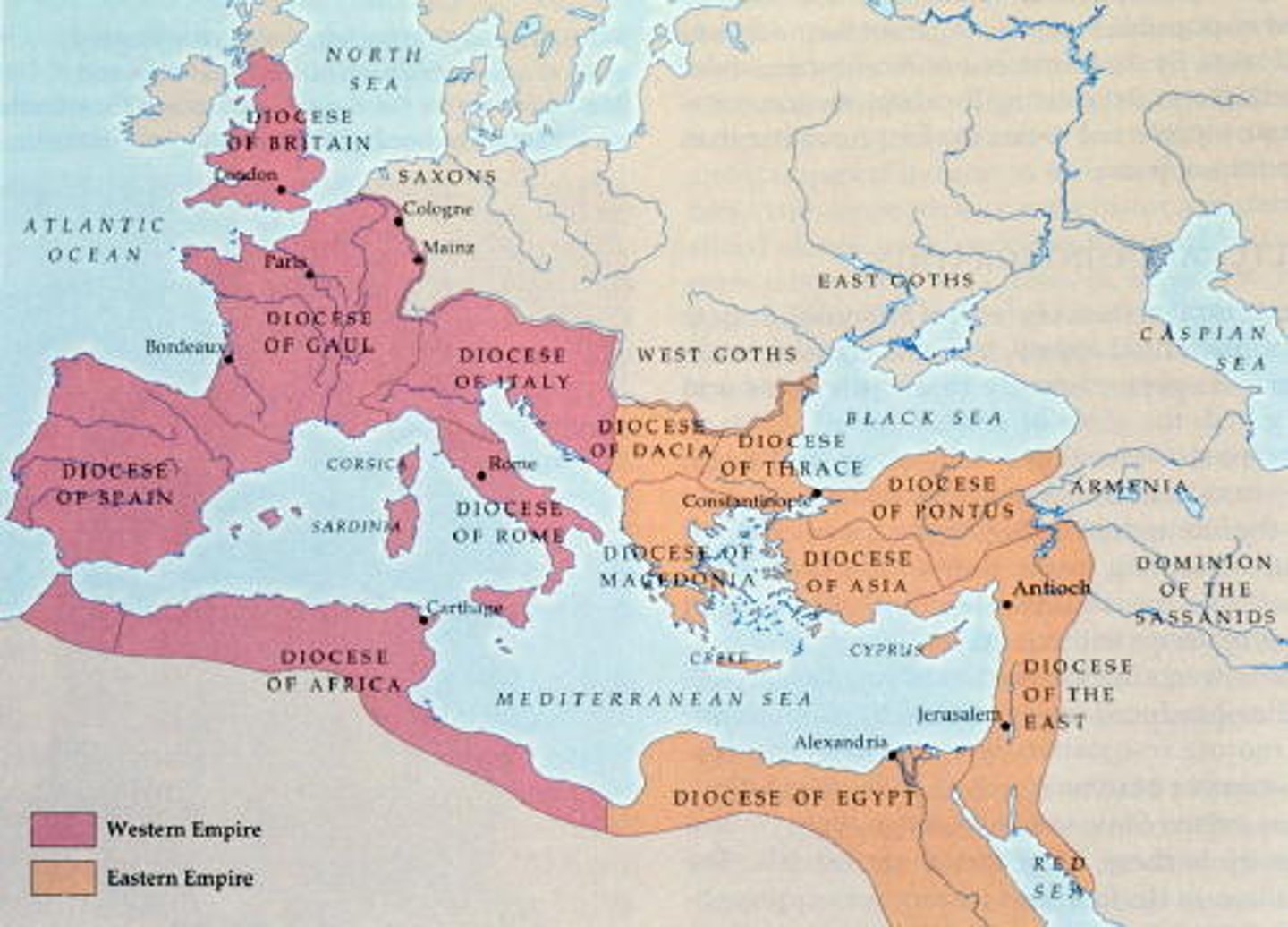
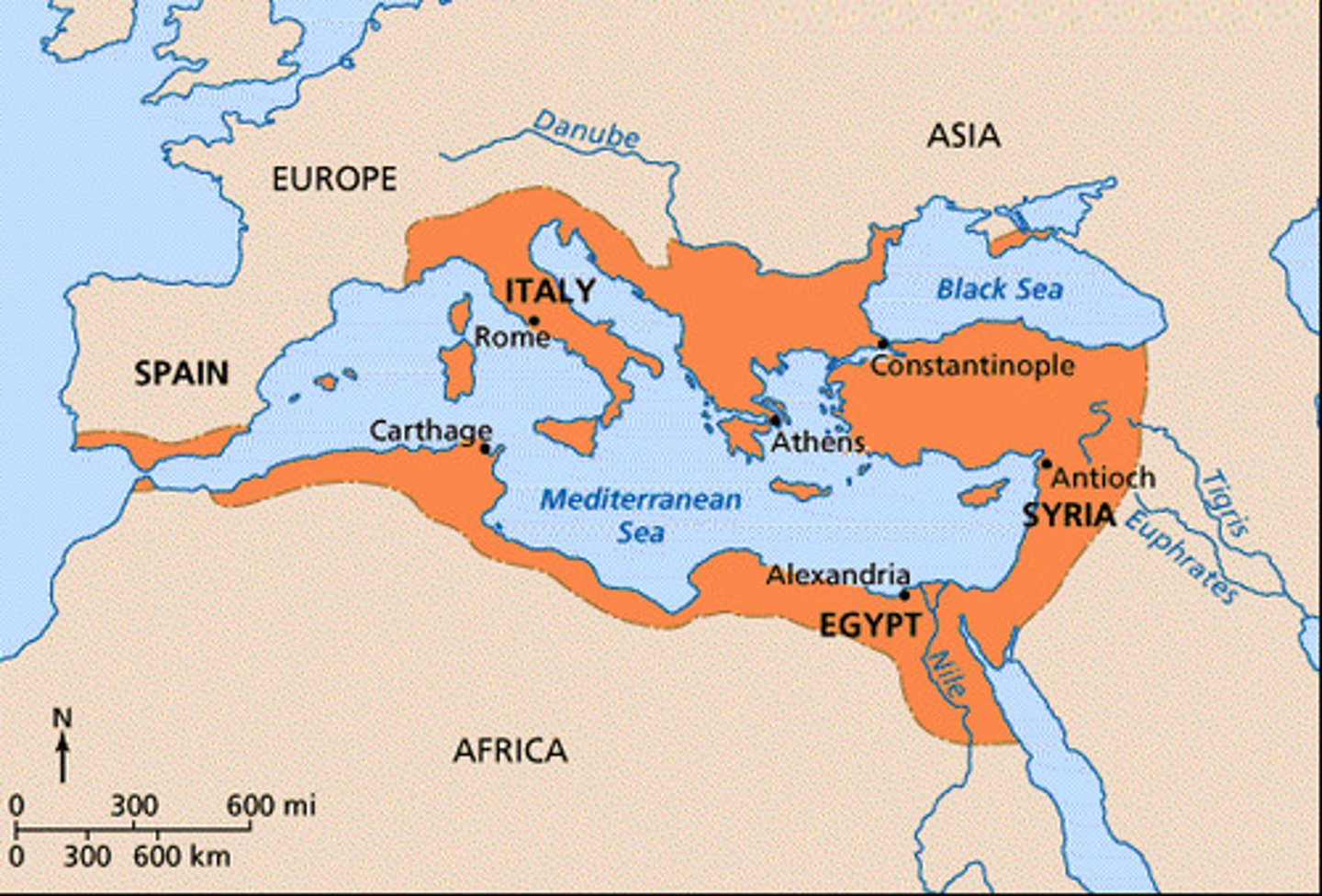
Byzantine Empire
Eastern half of the Roman Empire that survived the fall of the Western half.
Eastern Orthodox Church
Christian followers in the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire); split from Roman Catholic Church and shaped life in eastern Europe and western Asia

Inca Empire
The vast and sophisticated Peruvian empire centered at the capital city of Cuzco that was at its peak from 1438 until 1532. Eventually conquered by Pizarro.
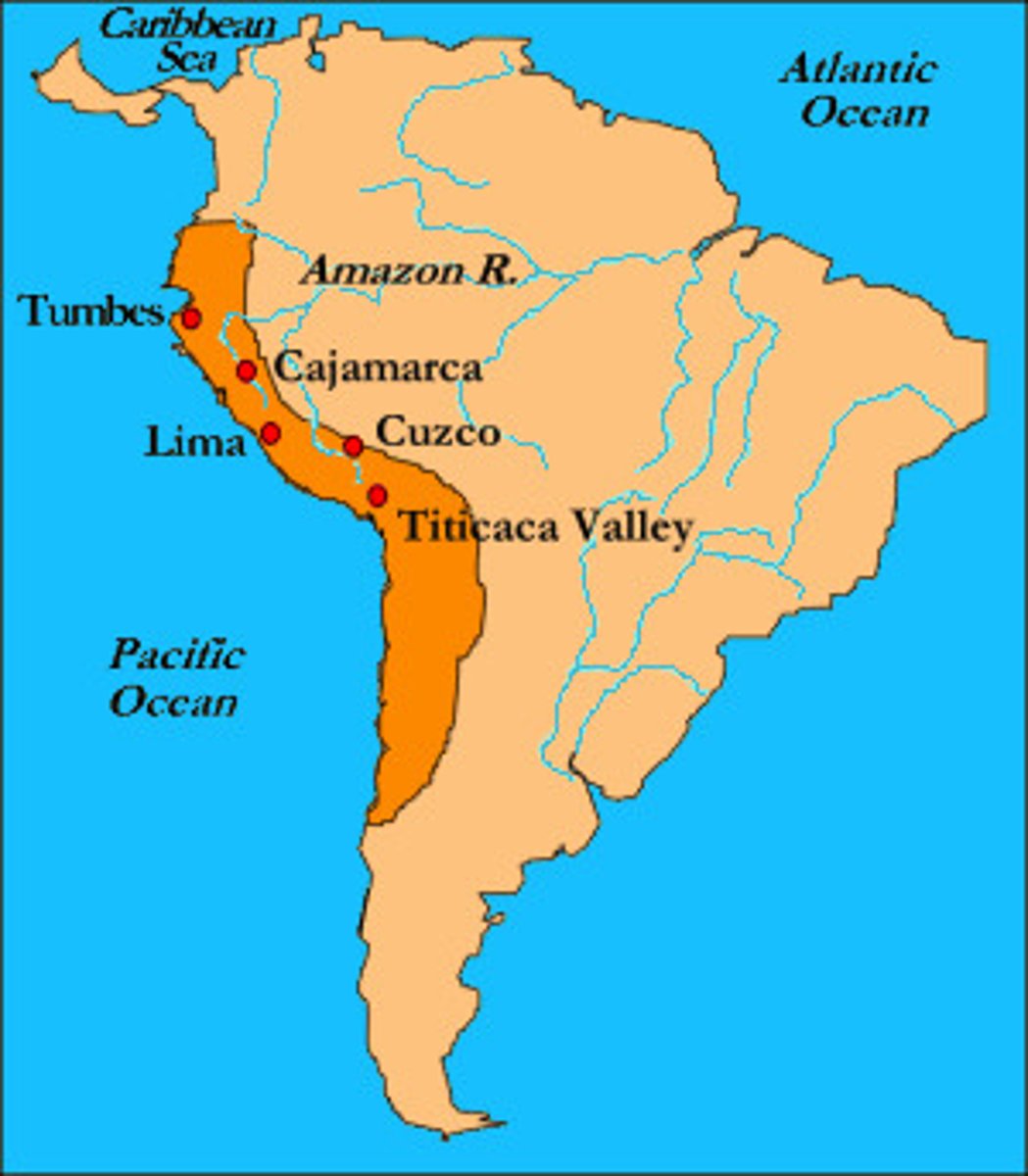
Incan road system
all roads lead to cuzco; allowed armies and news to spread quickly, ordinary people couldn't use this; runners stationed throughout empire to carry messages
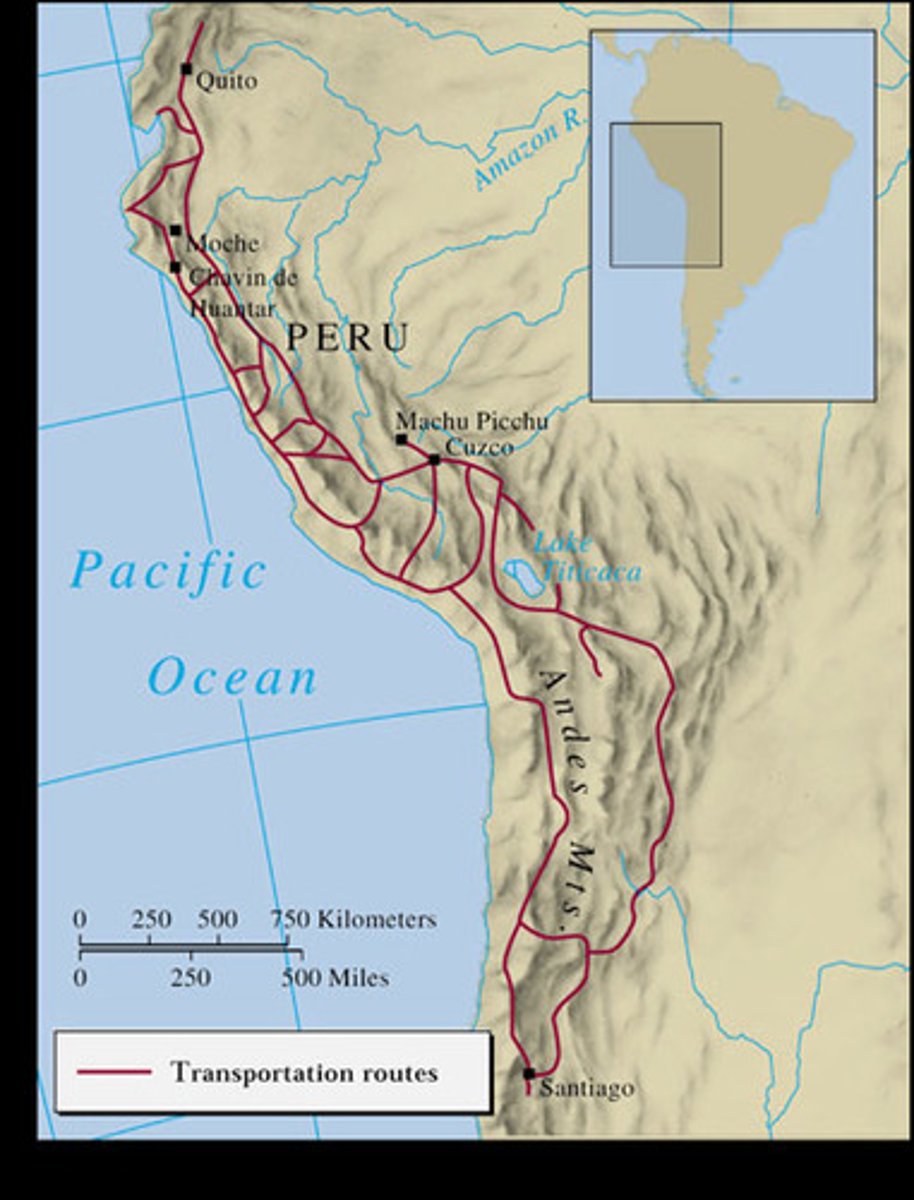
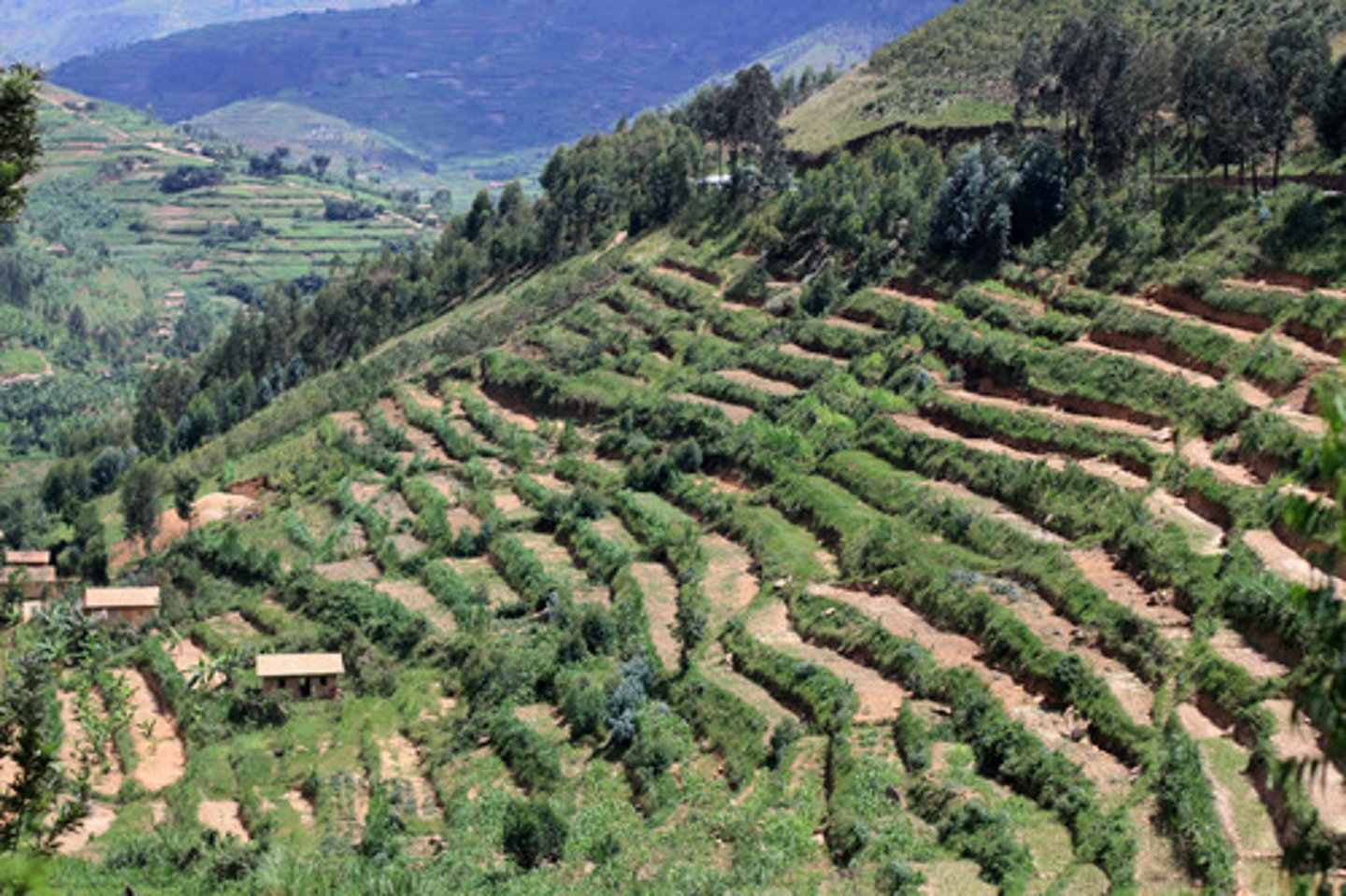
Terrace Farming
a farming system that is in the form of steps going up a mountain

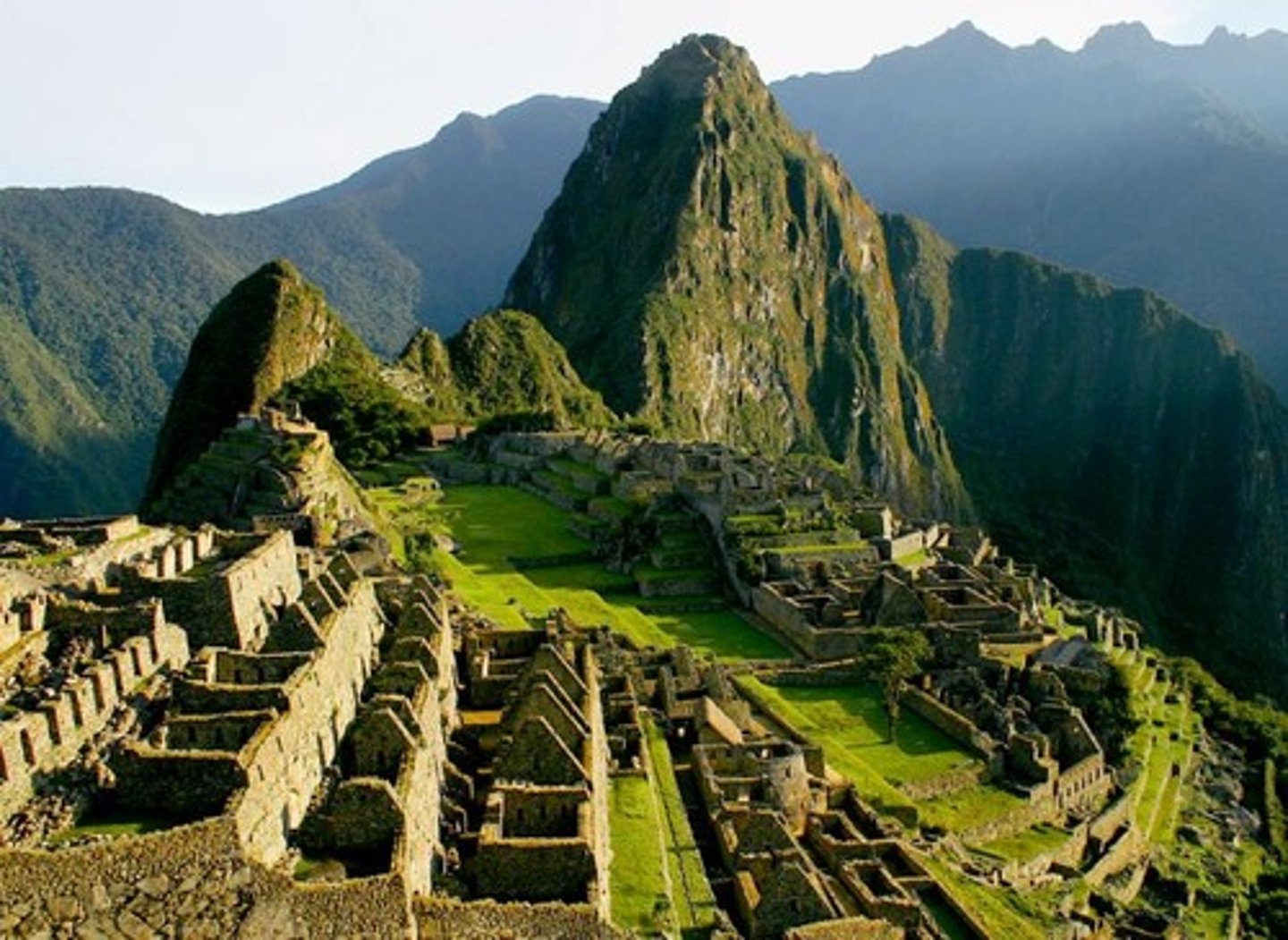
Machu Picchu
Abandoned city high in the Andes mountains that showcases the architectural genius of the Inca

Gender parallelism
Women and men operate in two separate but equivalent spheres
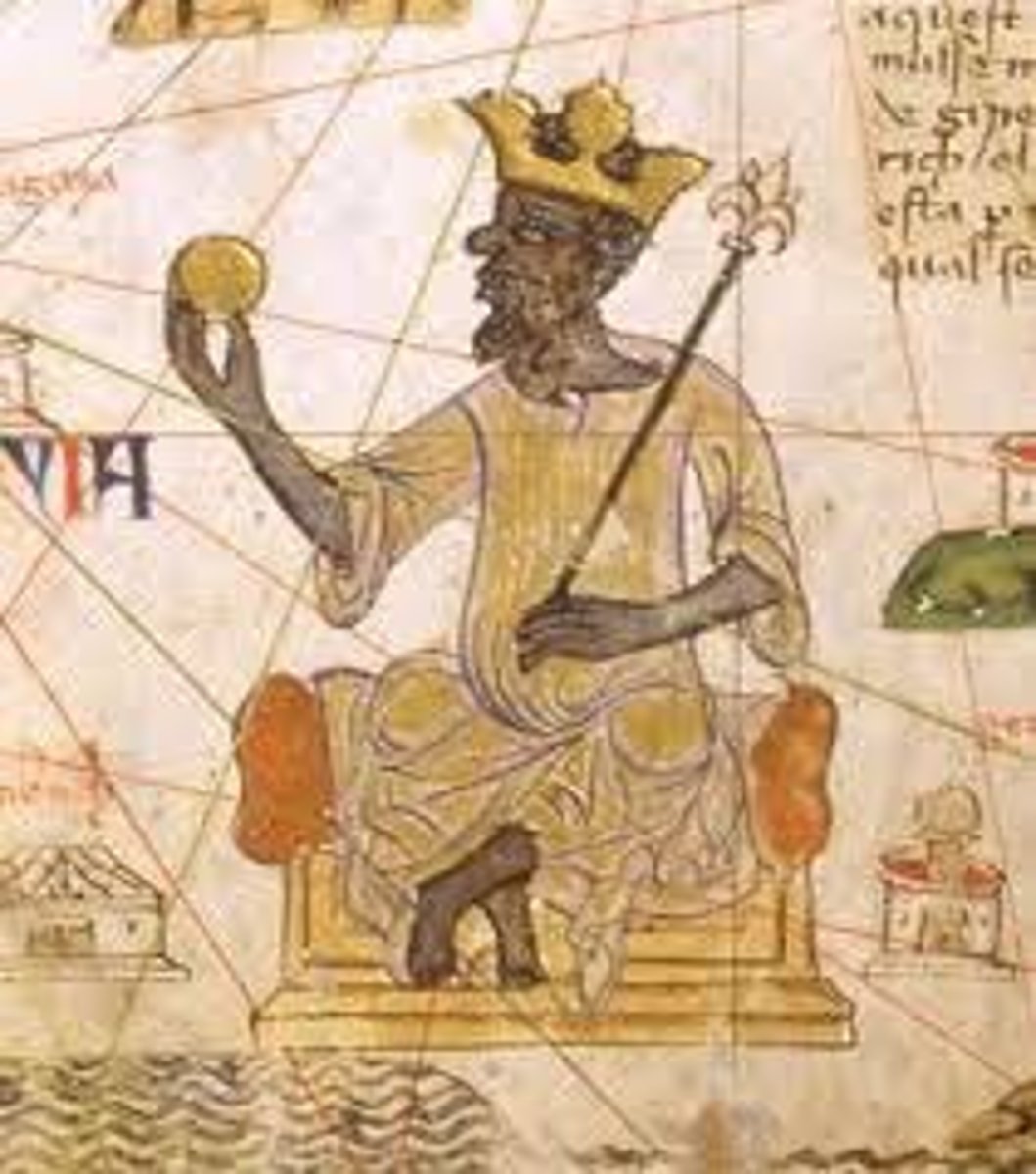
Mansa Musa
Emperor of the kingdom of Mali in Africa. He made a famous pilgrimage to Mecca and established trade routes to the Middle East. He was known for his incredible wealth and gold.

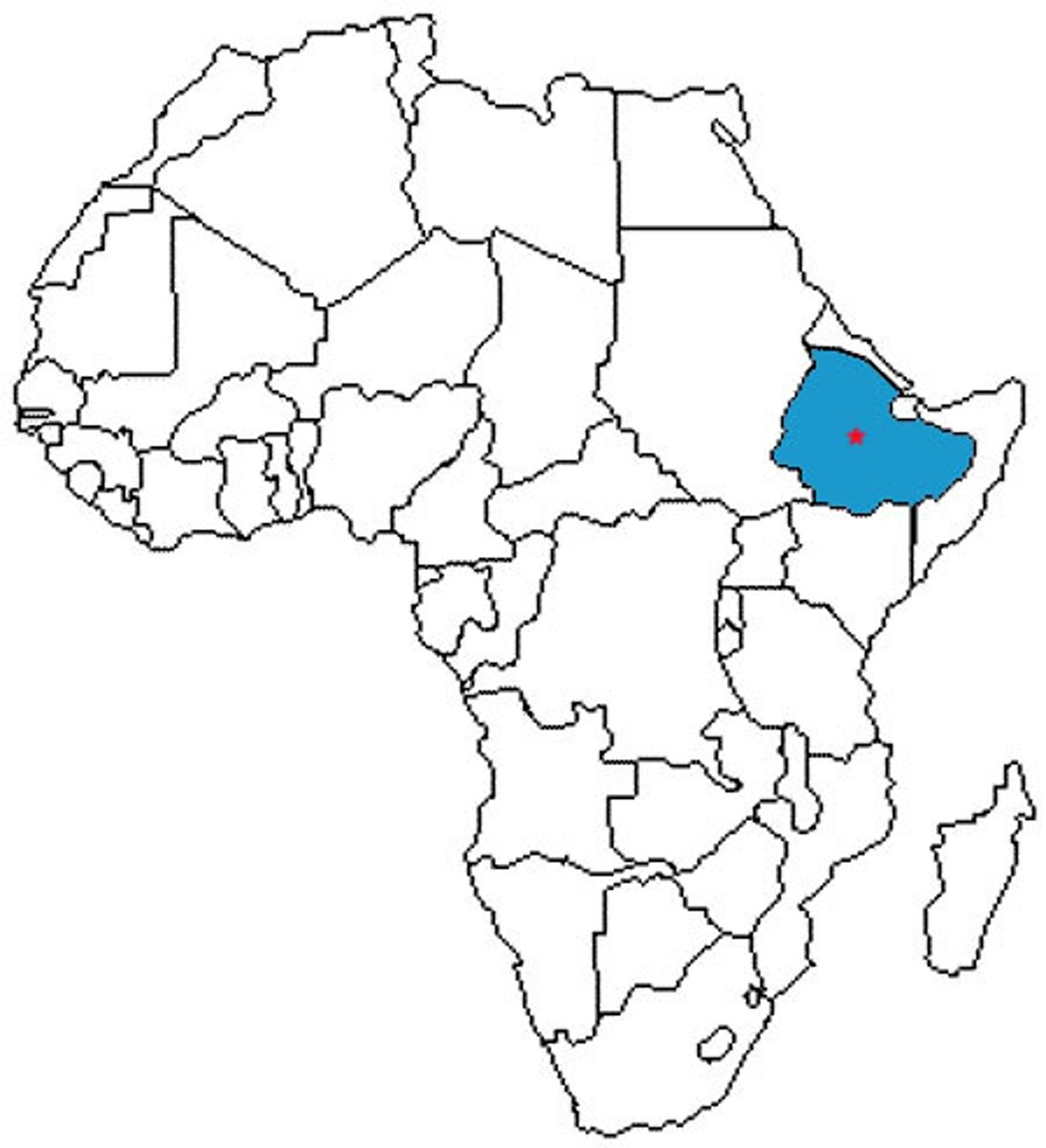
Ethiopia
A Christian kingdom that developed in the highlands of eastern Africa that retained Christianity in the face of Muslim expansion elsewhere in Africa
The Dark Ages
The first part of the Middle Ages from around 500-1000 A.D.
Middle Ages
Also known as the medieval period, the time between the collapse of the Roman Empire in the fifth century AD and the beginning of the Renaissance in the fourteenth century in Europe. Placed an emphasis on feudalism and manorialism.

Pope
Head of the Roman Catholic Church

3 field system
The field rotation system of the Middle Ages that kept one field barren per season
Effects of the Crusades
• cultural diffusion between Europeans & Muslims
• trade between Europe and Middle East