Biol 2401 Final Exam Review
1/272
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
273 Terms
Anatomy
Study of the structure of the body parts and how these parts are related to each other
Physiology
Study of the function of body parts, how they work
Principle of Complementarity
Function will always be reflected in structure (what a structure is capable of doing depends on its form)Ex: Muscles can contract because they have contractile units
Homeostasis
Ability to maintain stable, favorable internal conditions even though there are changes in the external environment.
Stimulas
produces change in variable
Receptor
detects change
Input
Information sent along afferent pathway to control center
Output
Information sent along efferent pathway to effector
Response
feeds back to reduce the effect of stimulus and returns variable to homeostatic level
Negative Feedback
brings condition back to normal level
Positive Feedback
takes condition further from normal
Superior (cranial)
Toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above Ex: The head is superior to the abdomin
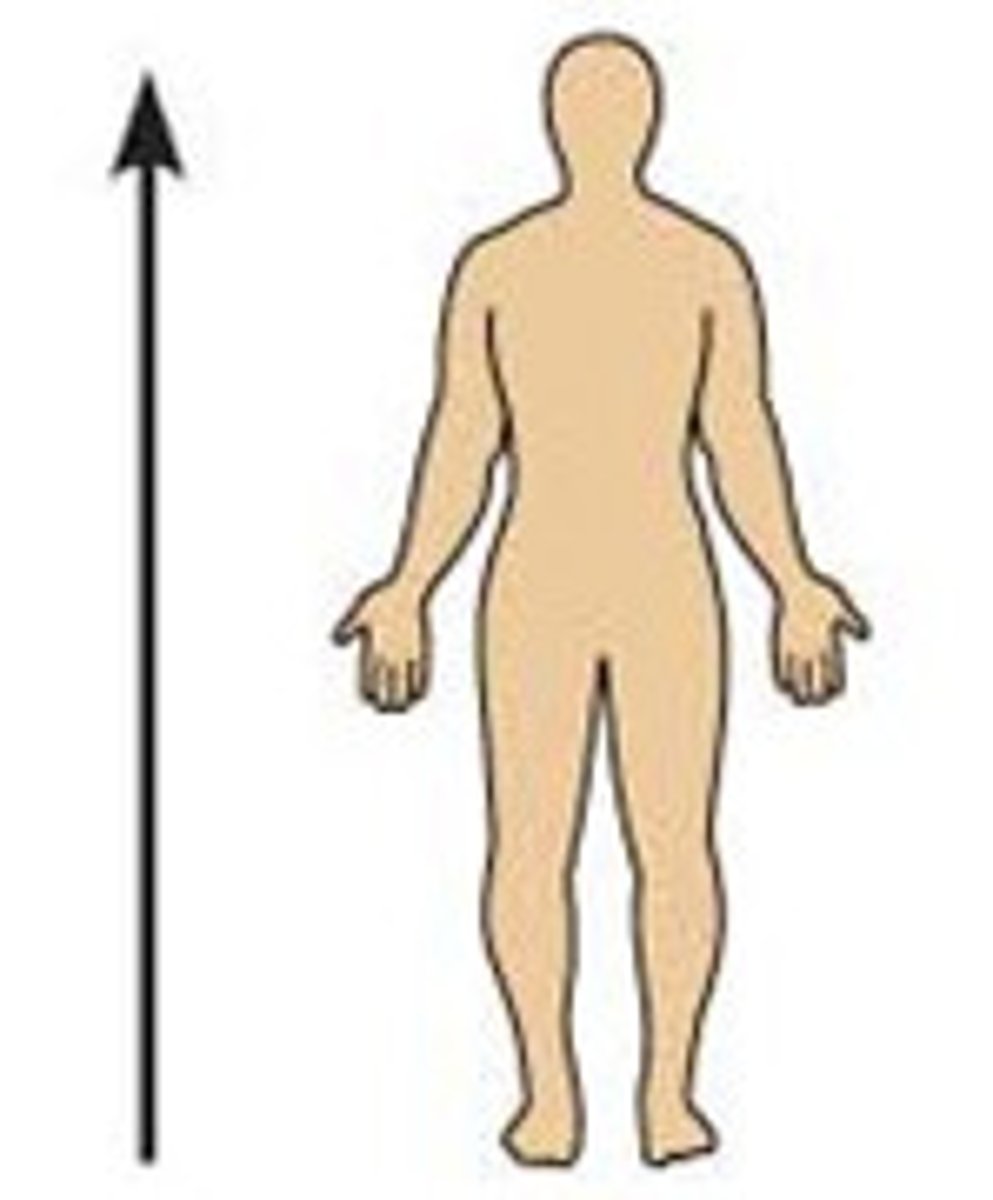
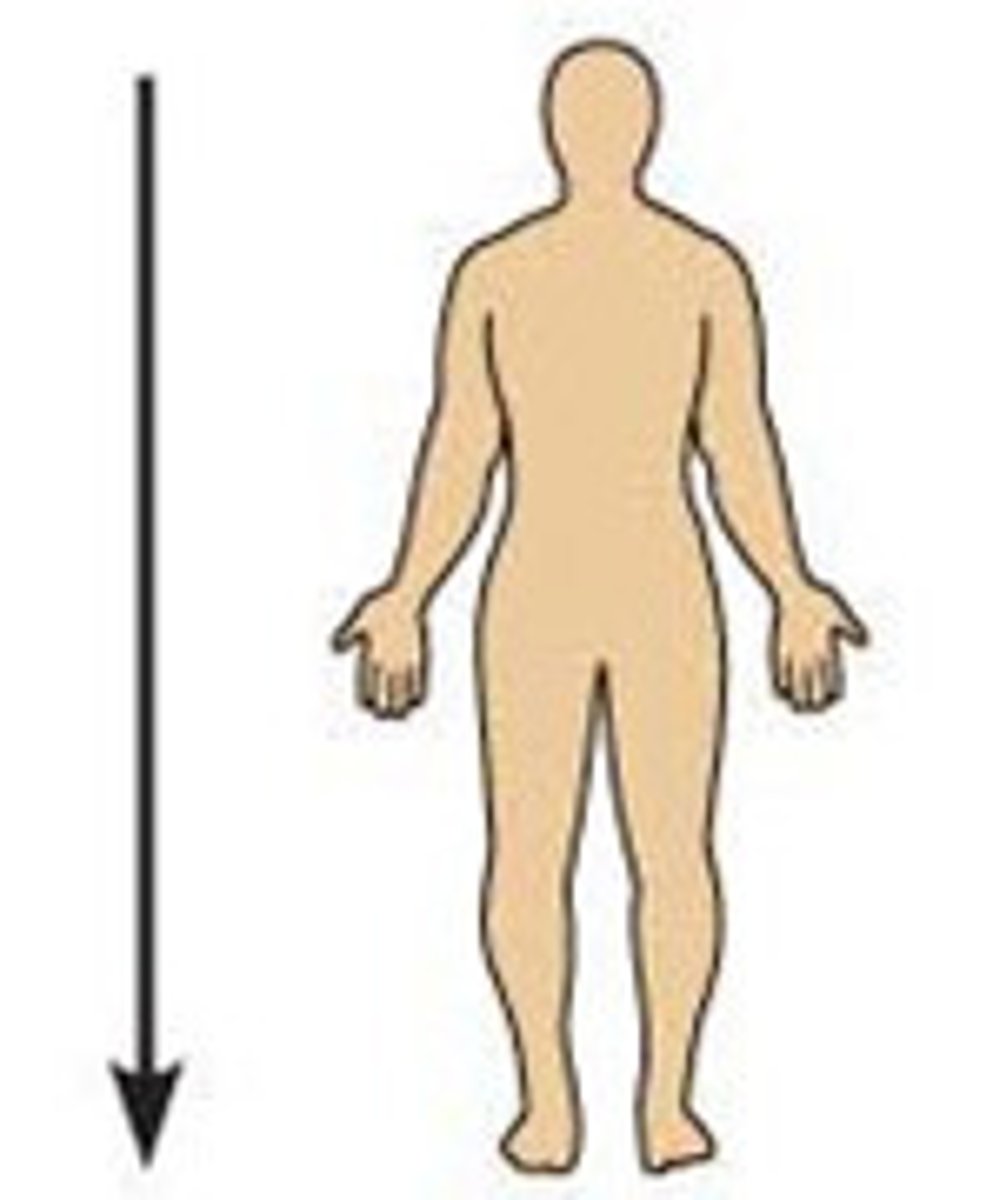
Inferior (caudal)
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below Ex: The navel is inferior to the chin
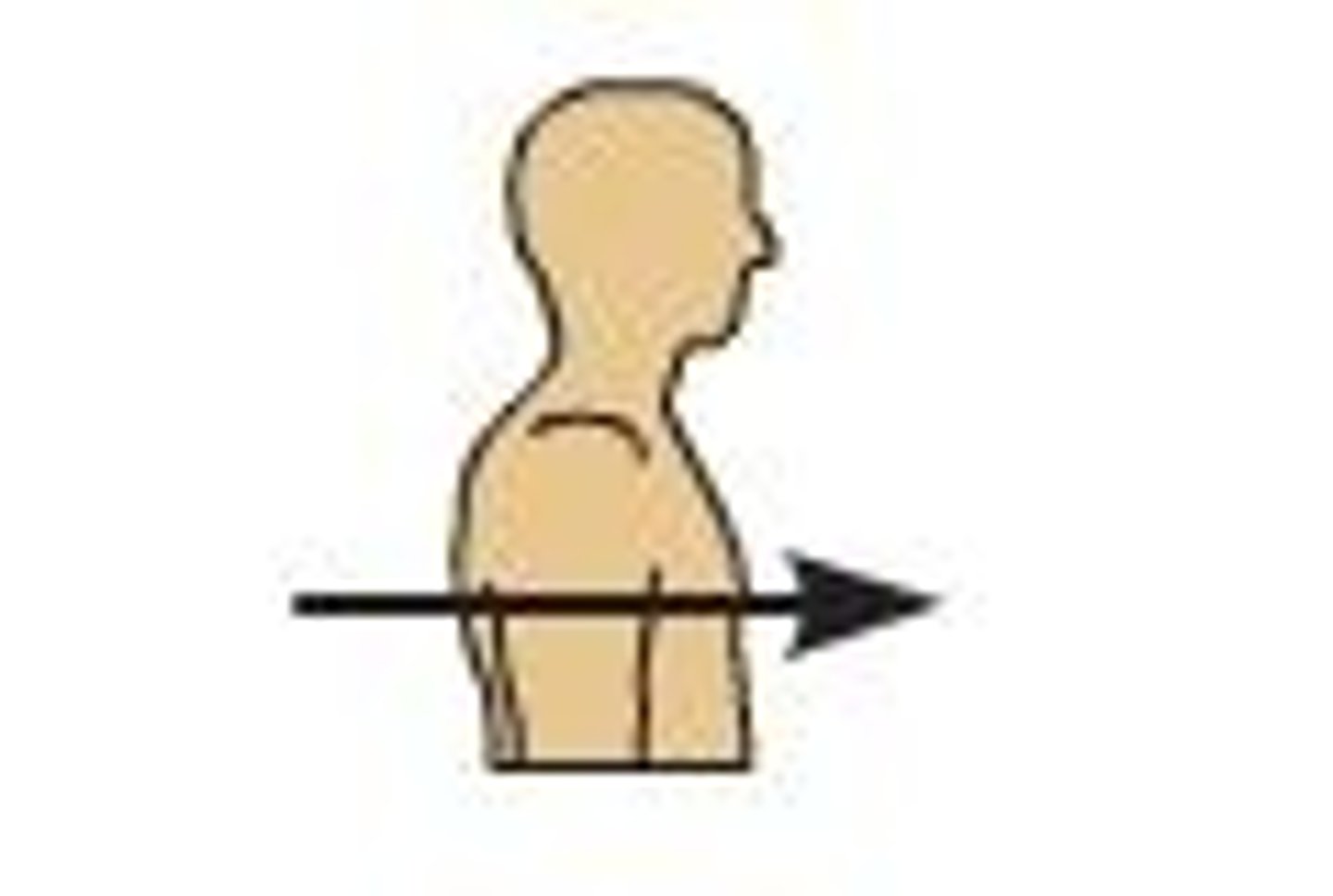
Ventral (anterior)
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of Ex: The breastbone is anterior to the spine
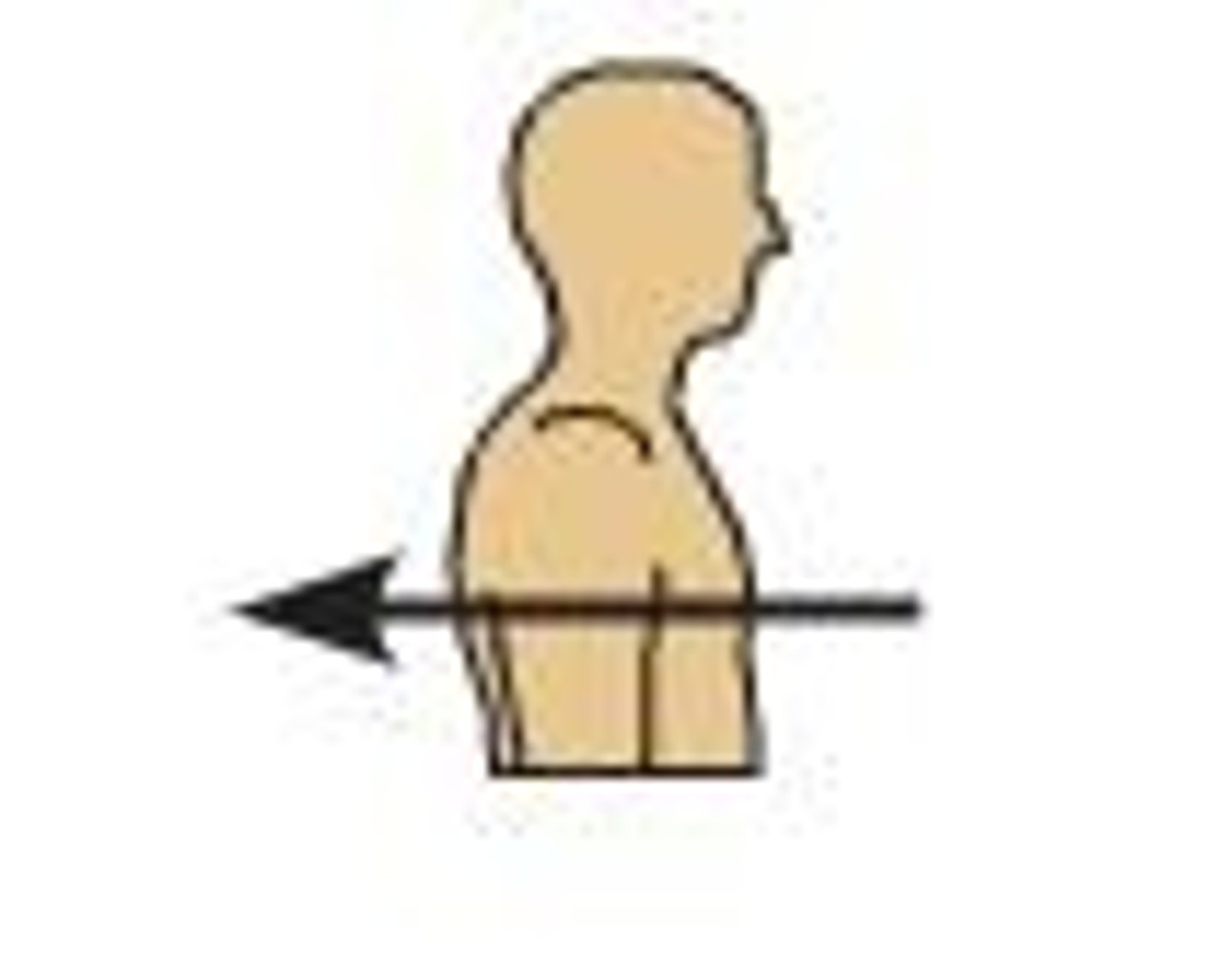
Dorsal (posterior)
Toward or at the back of the body; behind Ex: the heart is posterior to the breastbone.
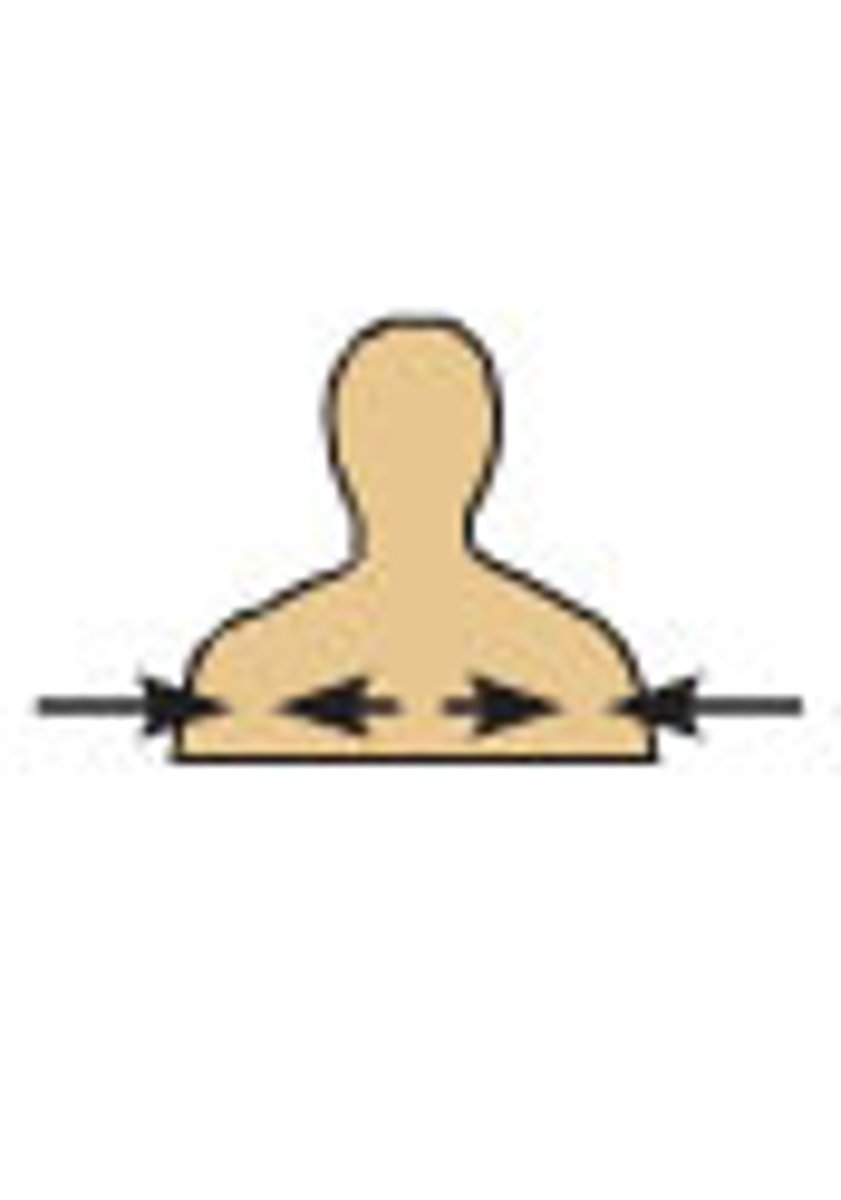
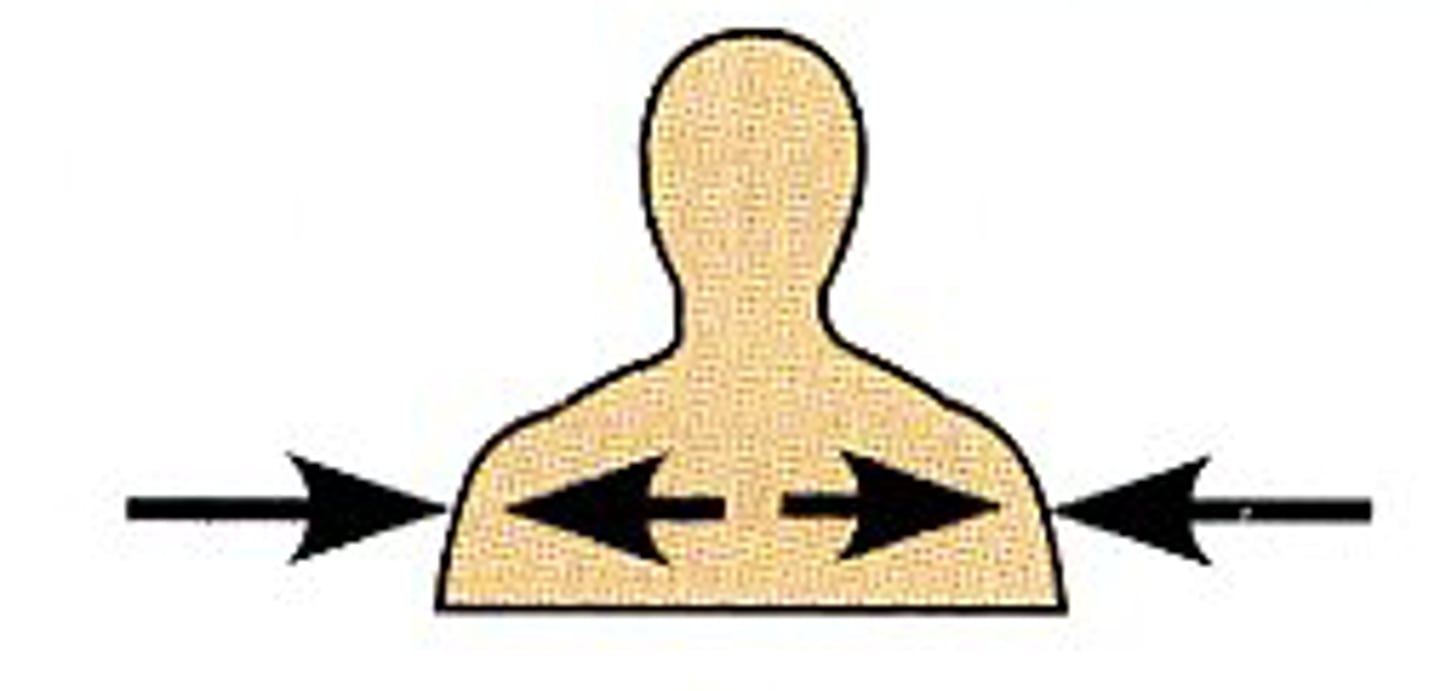
Medial
Toward or at the mid-line of the body; on the inner side of. Ex: the heart is medial to the arm.
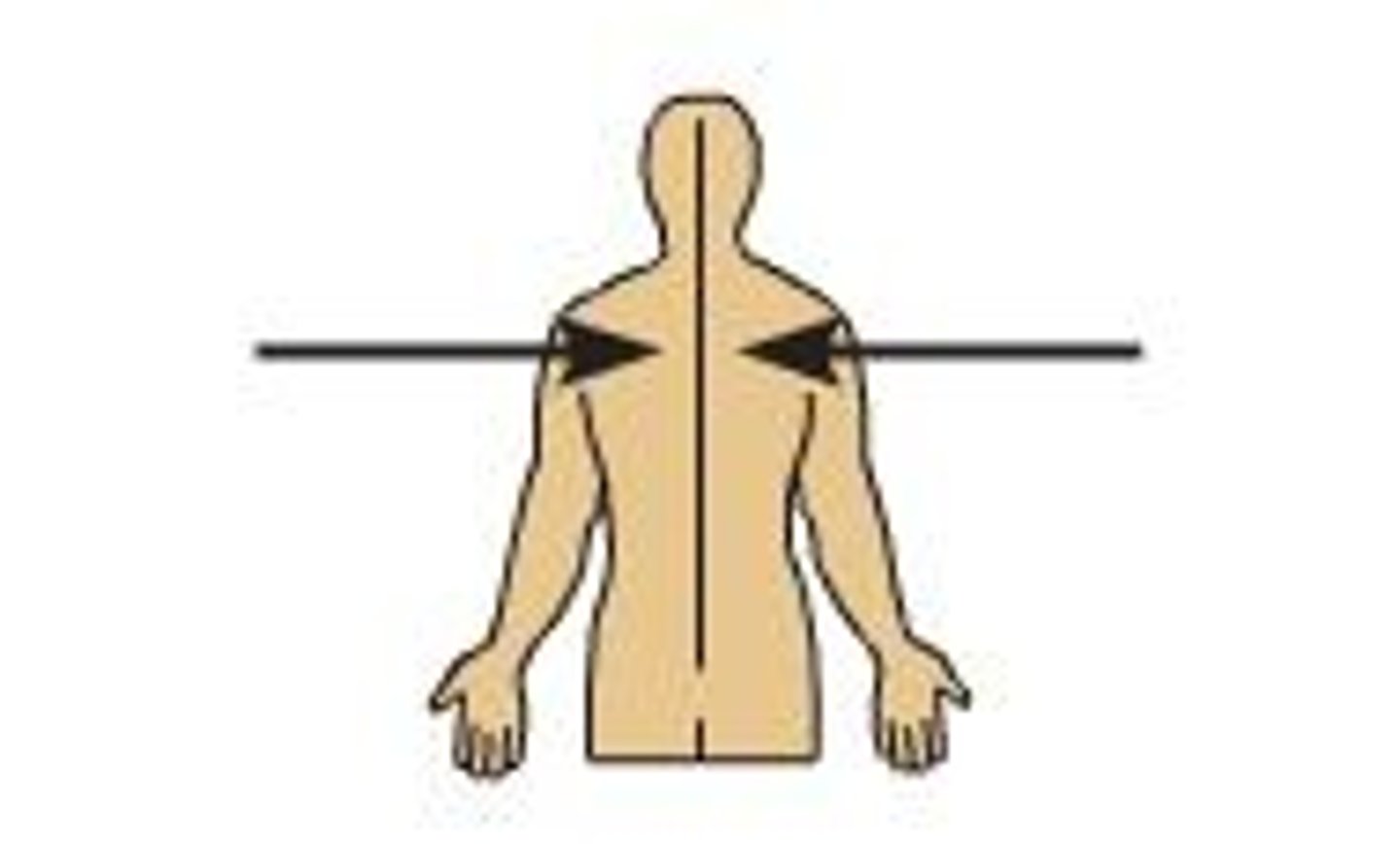
Lateral
Away from the mid-line of the body; on the outer side of. Ex: the arms are lateral to the chest.
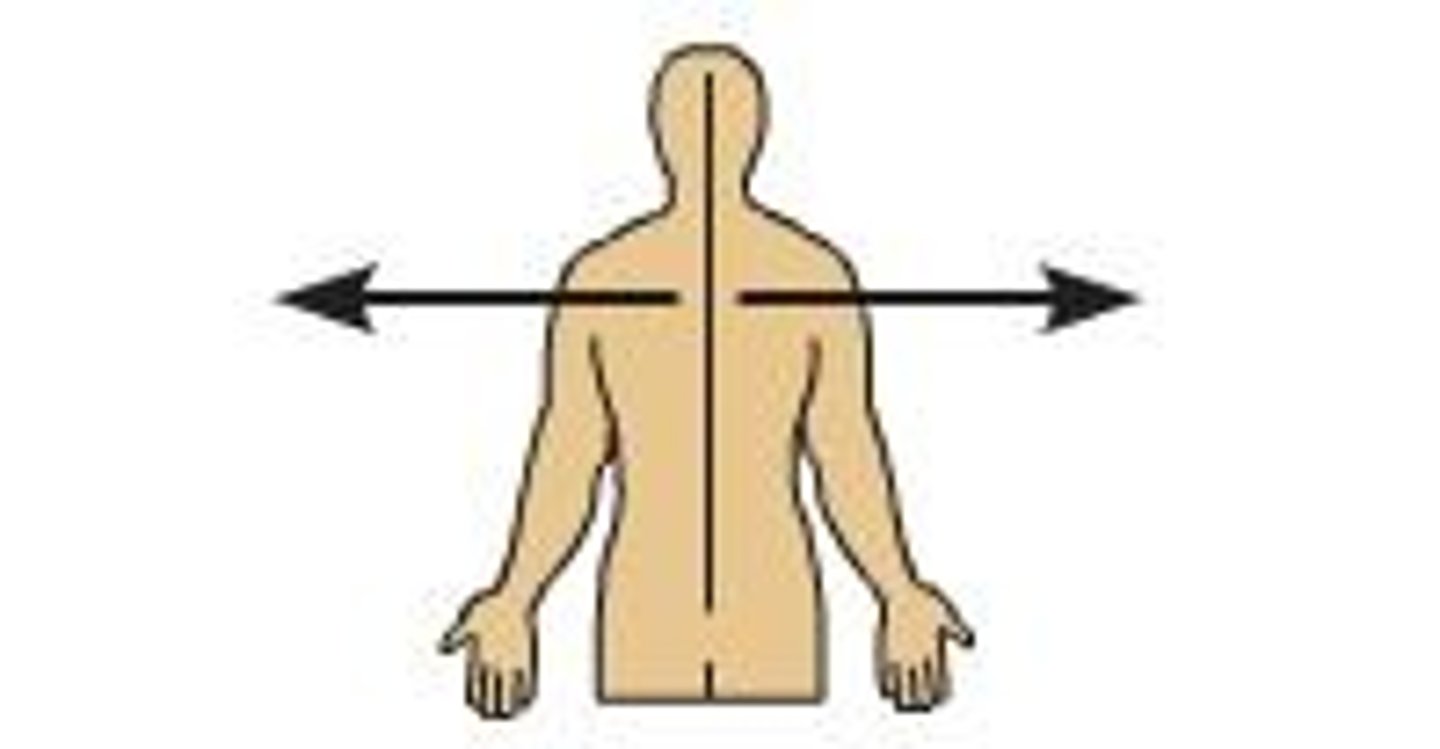
Intermediate
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure. Ex: the collarbone is intermediate between the breastbone and shoulder
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk. Ex: the elbow is proximal to the wrist.
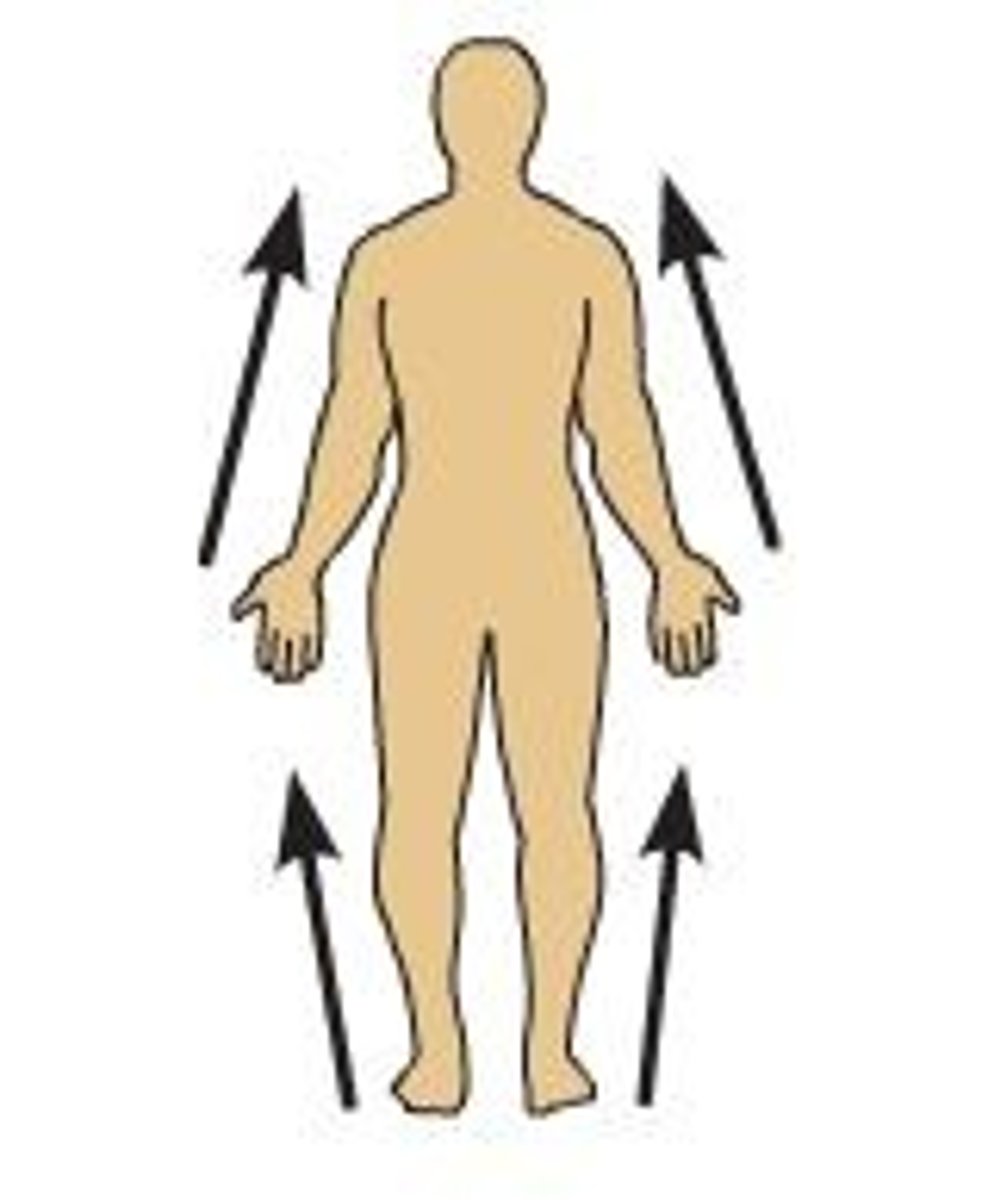
Distal
Farther from the origin of a body point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk. Ex: the knee is distal to the thigh.
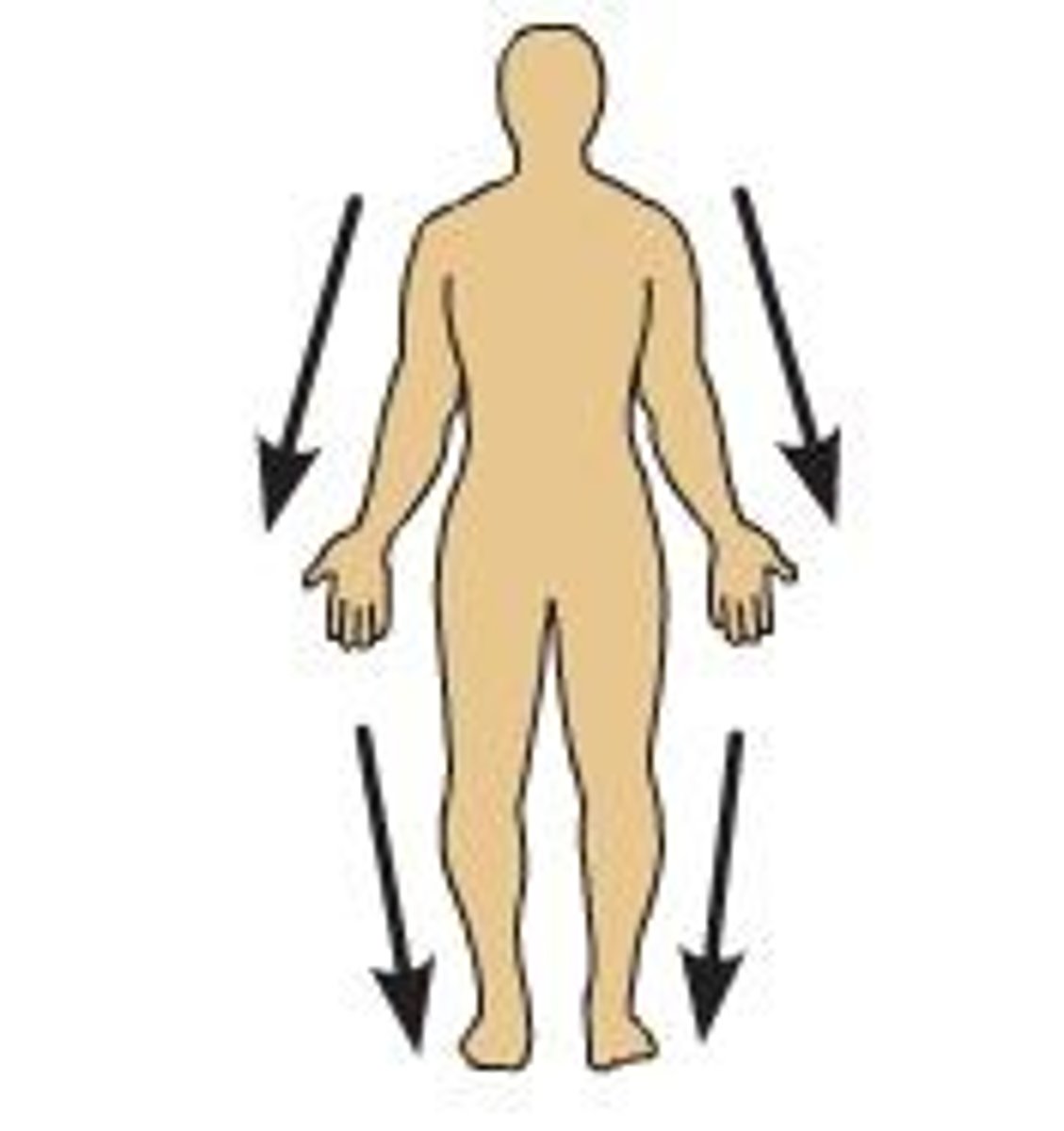
Superficial (external)
toward or at the body surface. Ex: the skin is superficial to the skeletal muscles.
Deep (internal)
away from the body surface; more internal.Ex: the lungs are deep to the skin.

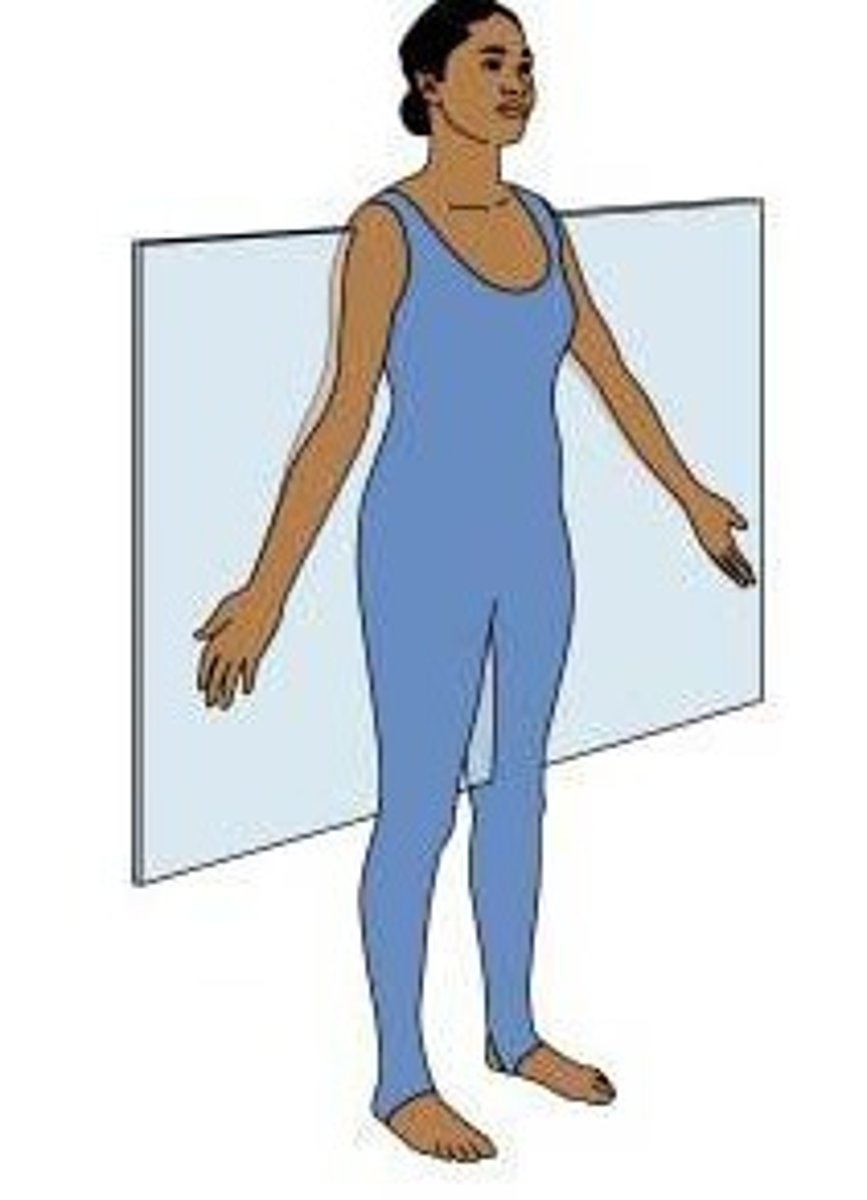
Sagittal Plane
divides body into Left/Right
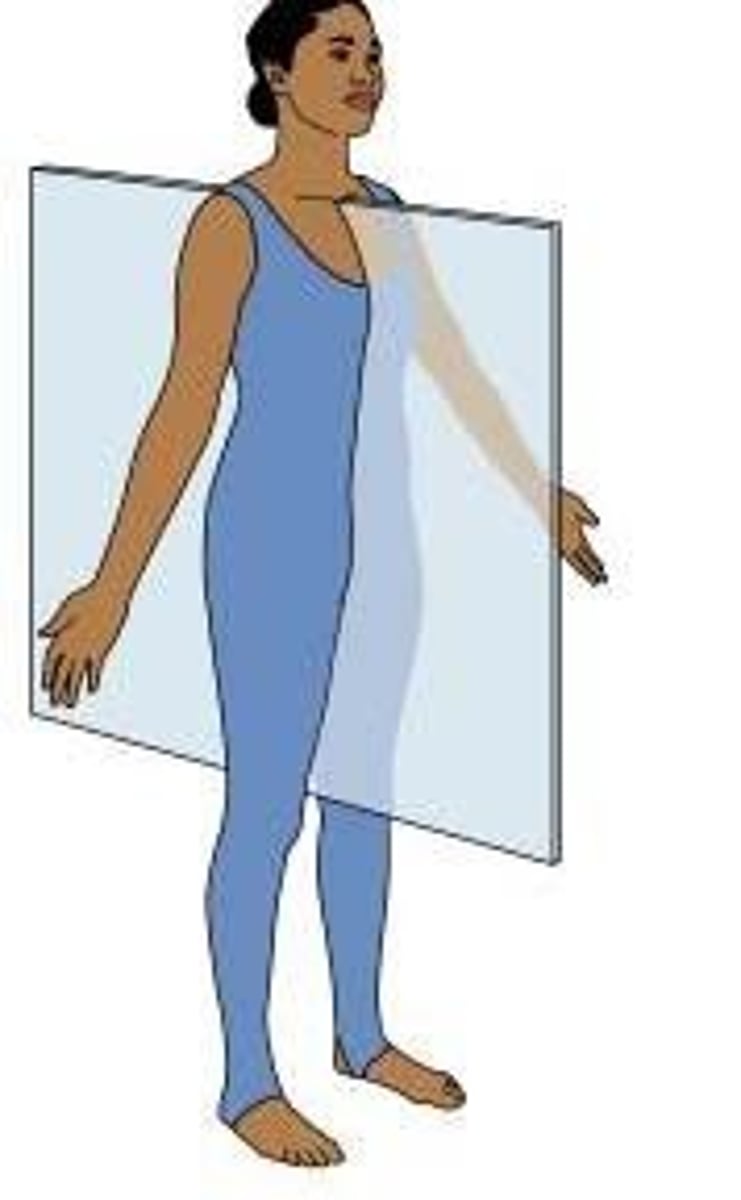
Frontal (coronal) Plane
Divides body into Anterior/Posterior
Transverse Plane
Divides body into Superior/Inferior
Acid
Substance that releases or "donates" H+
Bases
Substances that take up or "accept" H+
pH scale
pH scale measures the hydrogen ion concentration [H+]Range: 0 (acidic) to 14 (basic)
![<p>pH scale measures the hydrogen ion concentration [H+]Range: 0 (acidic) to 14 (basic)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/35f9f5d3-8231-4673-9705-9fbc6dec5115.image/jpeg)
Maintaining blood pH
Involves the respiratory and urinary systems
blood buffers
-binds to H+ ions if solution is too acidic
-releases H+ ions if solution is too basic
Organic Compounds
Contain carbon-hydrogen bonds Ie:
-Proteins
-Carbohydrates
-Lipids
-Nucleic Acids
Passive transport
no energy required; substances moved with concentration gradient (from more concentrated to less concentrated areas)
Simple diffusion
no transporter
Facilitated diffusion
uses membrane transporter
Osmosis
diffusion of water
Active transport
ATP required; substances moved against concentration gradient (from less concentrated to more concentrated)
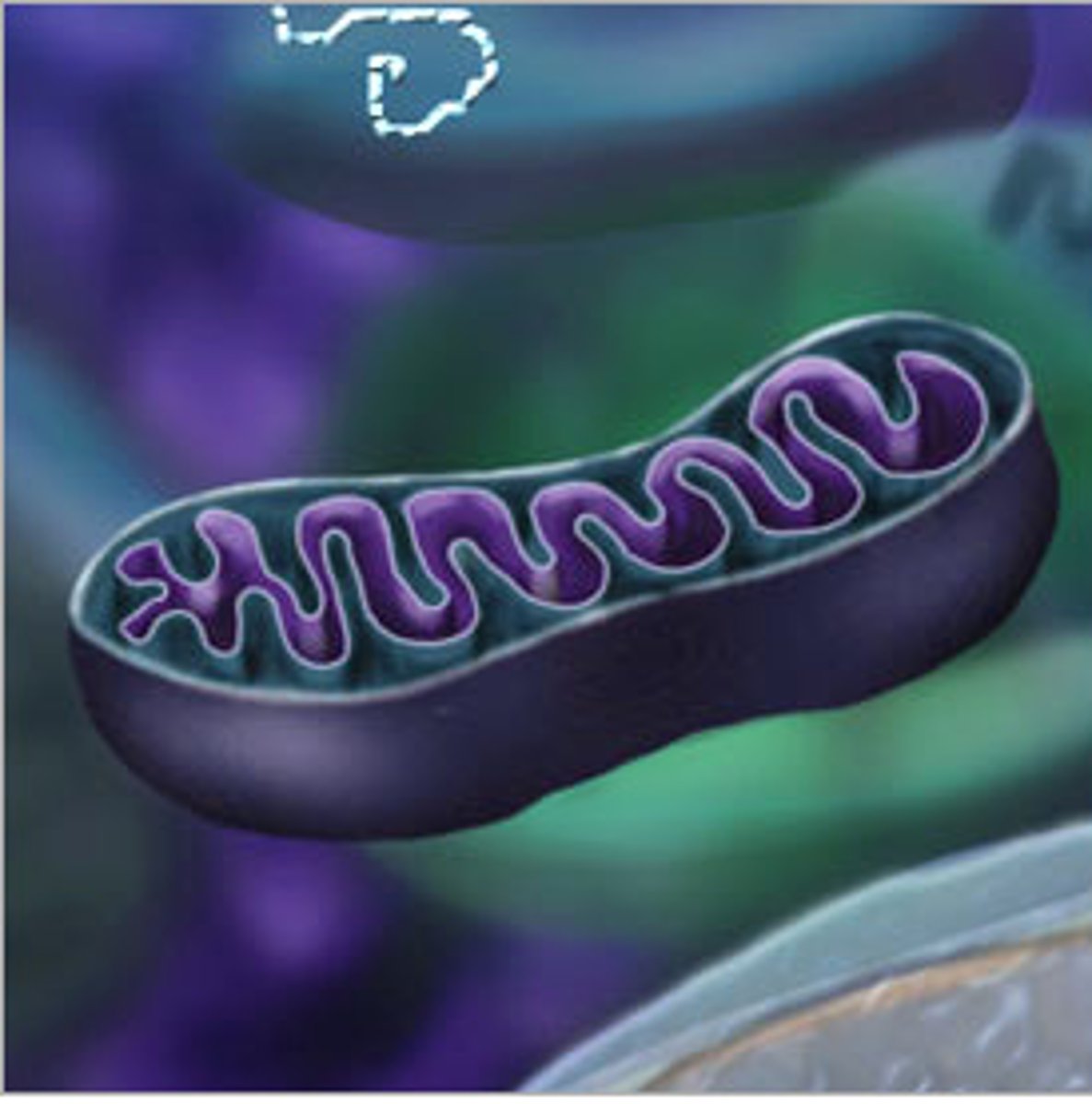
Mitochondria
site of ATP synthesis
Rough ER
site of protein synthesis
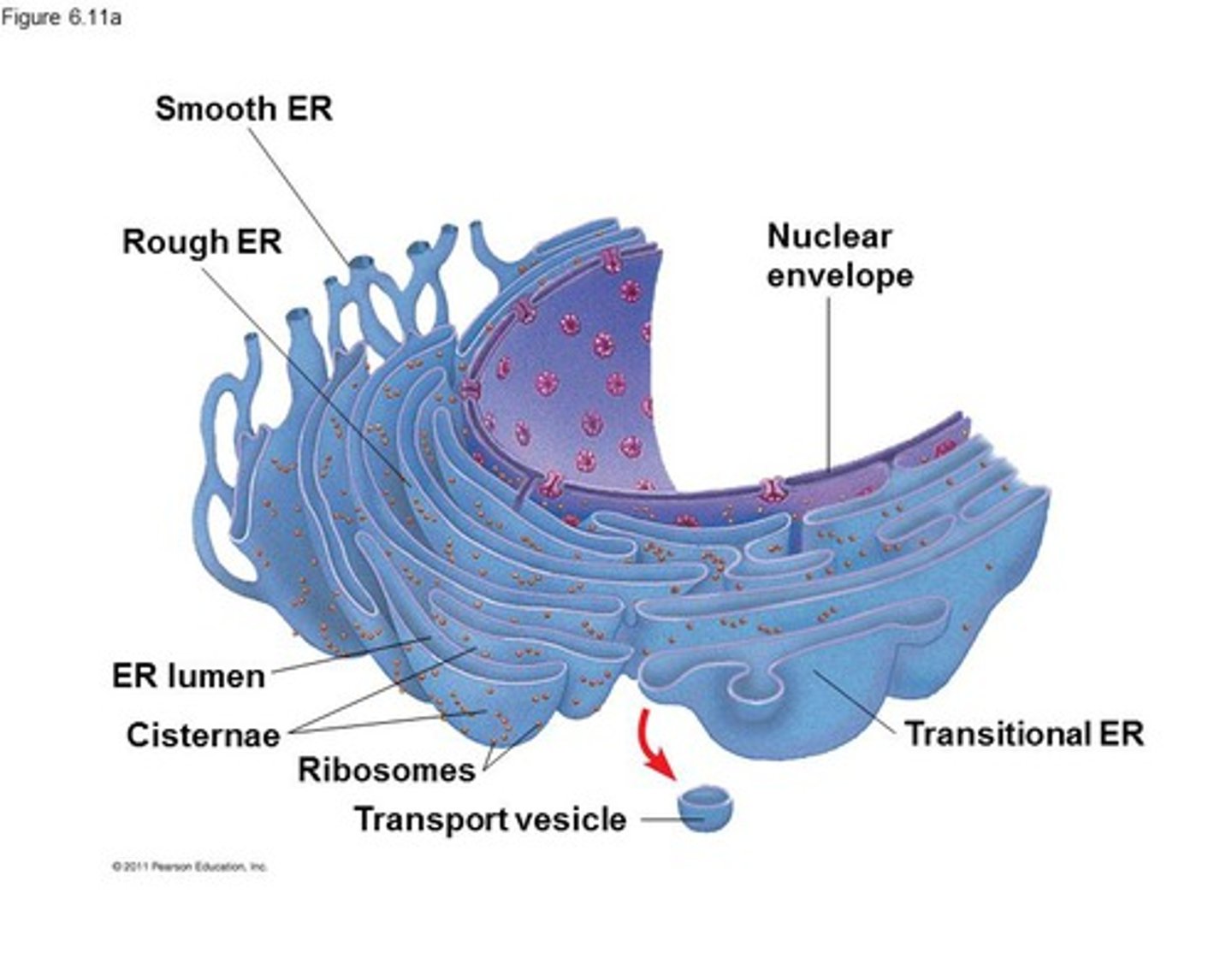
Smooth ER
site of lipid synthesis
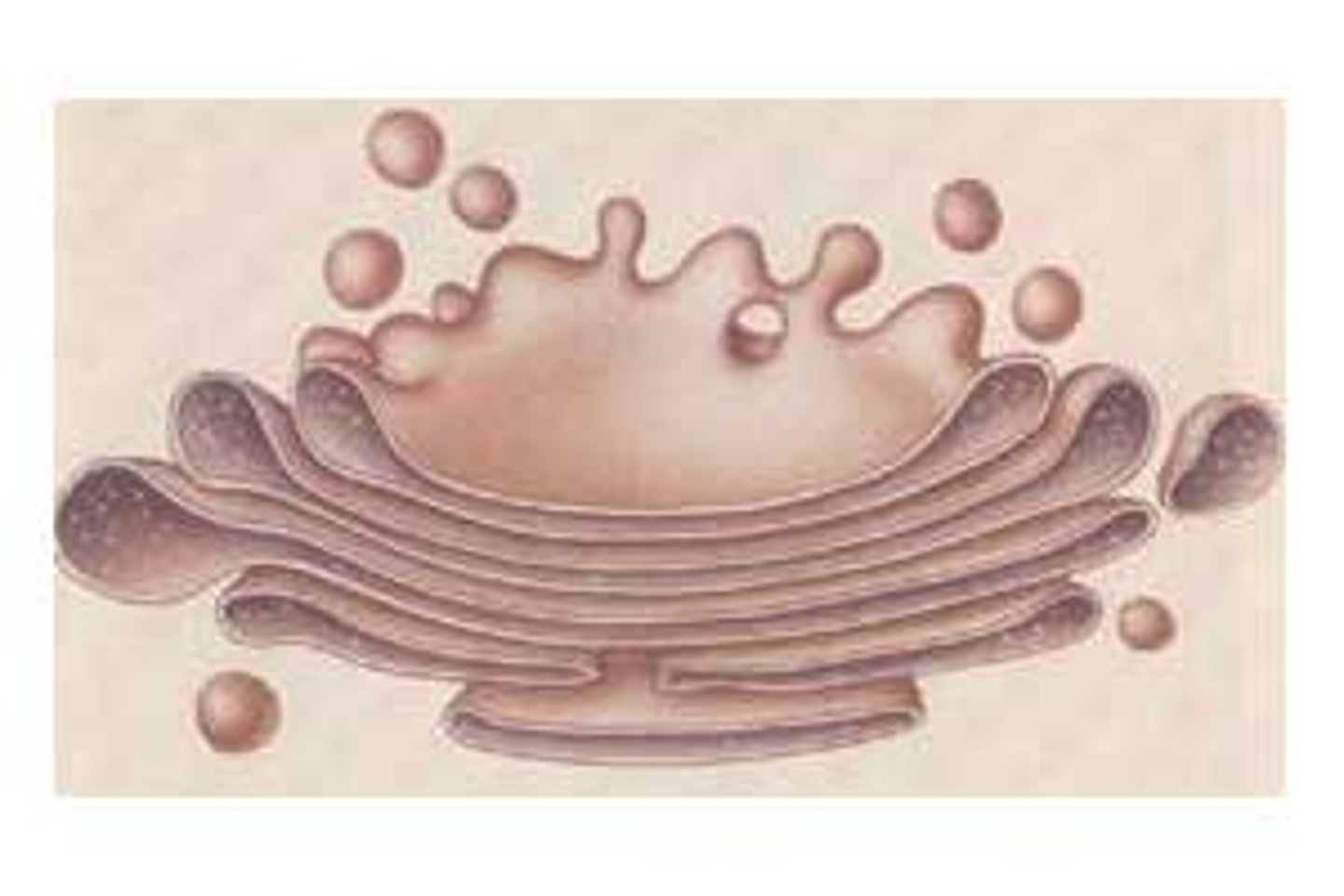
Golgi apparatus
site of protein packaging for secretion
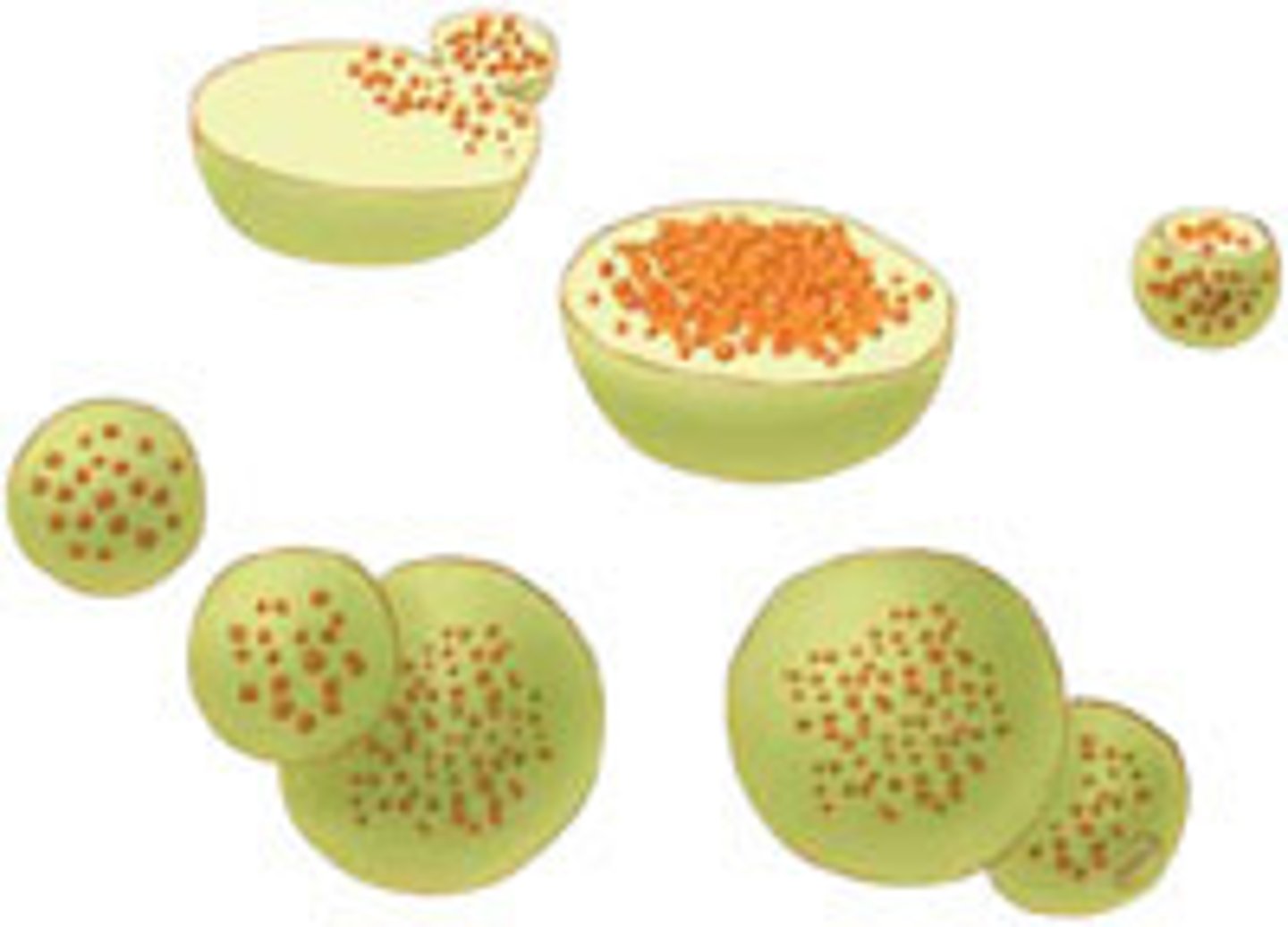
Lysosome
contains digestive enzymes
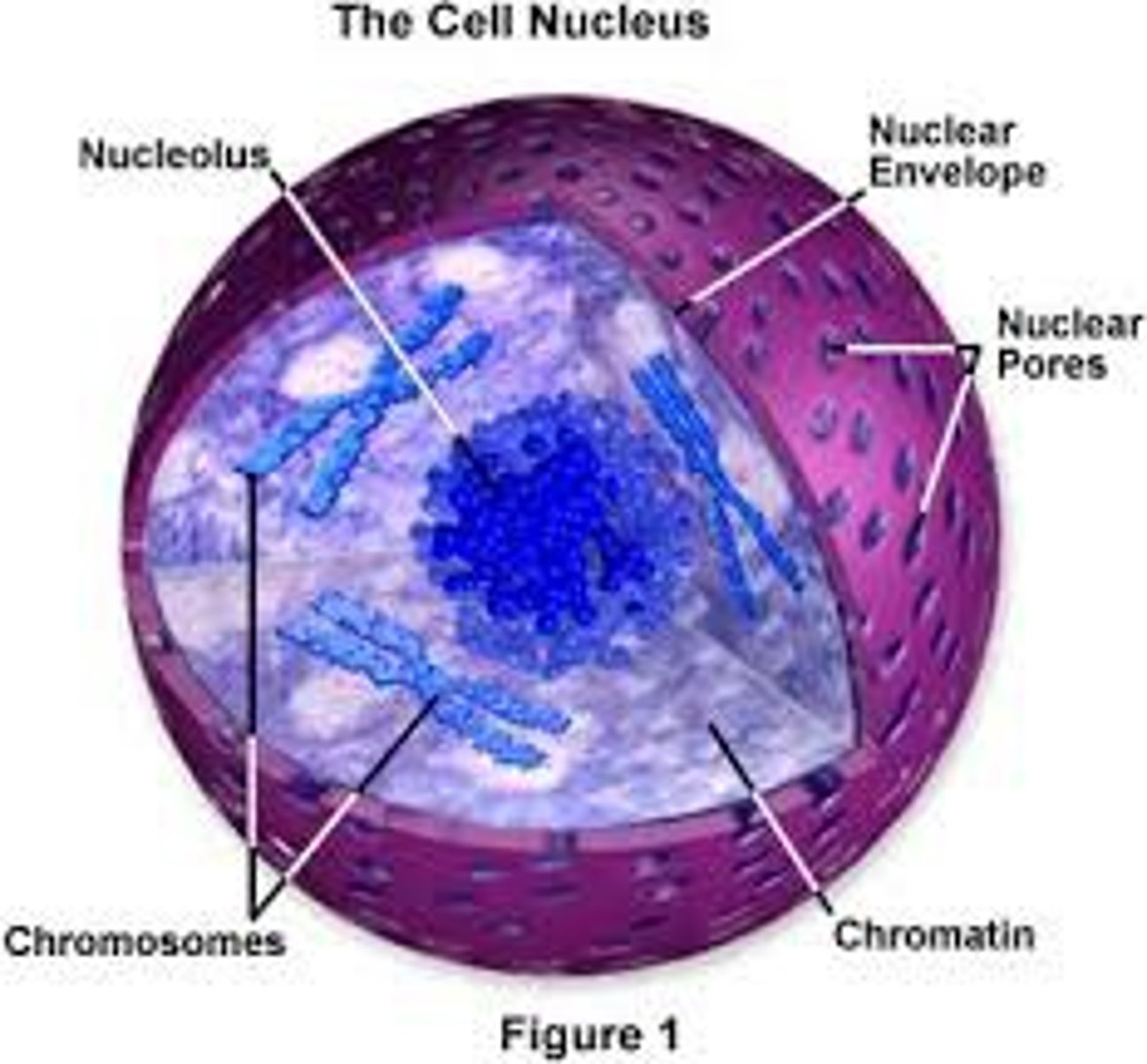
Nucleus
contains DNA
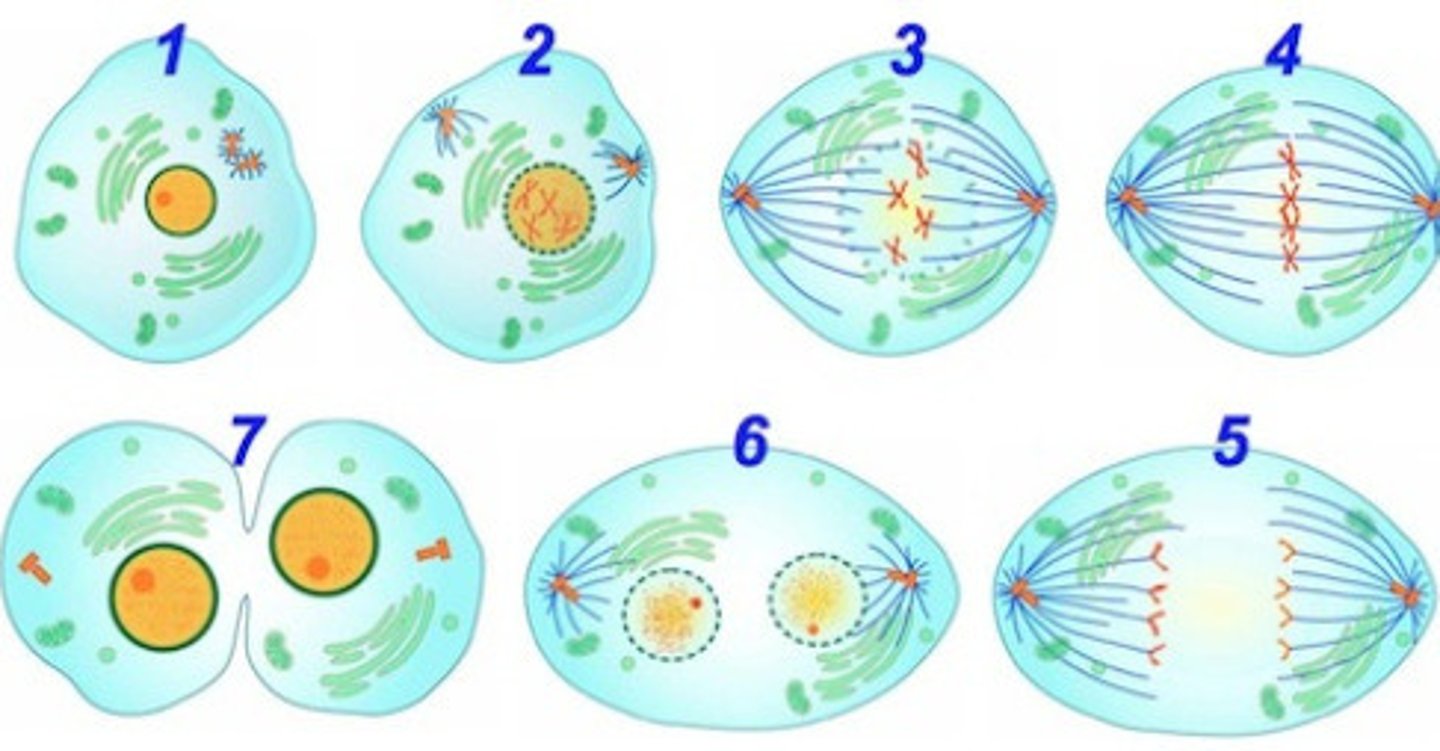
Mitosis
results in 2 cells genetically identical to the original cell. It is used for growth, repair, replacement of old cells.
Epithelium
Tightly packed cells, Polarity apical - free surface (no tissue attached)basal-attached to underlying basement membrane
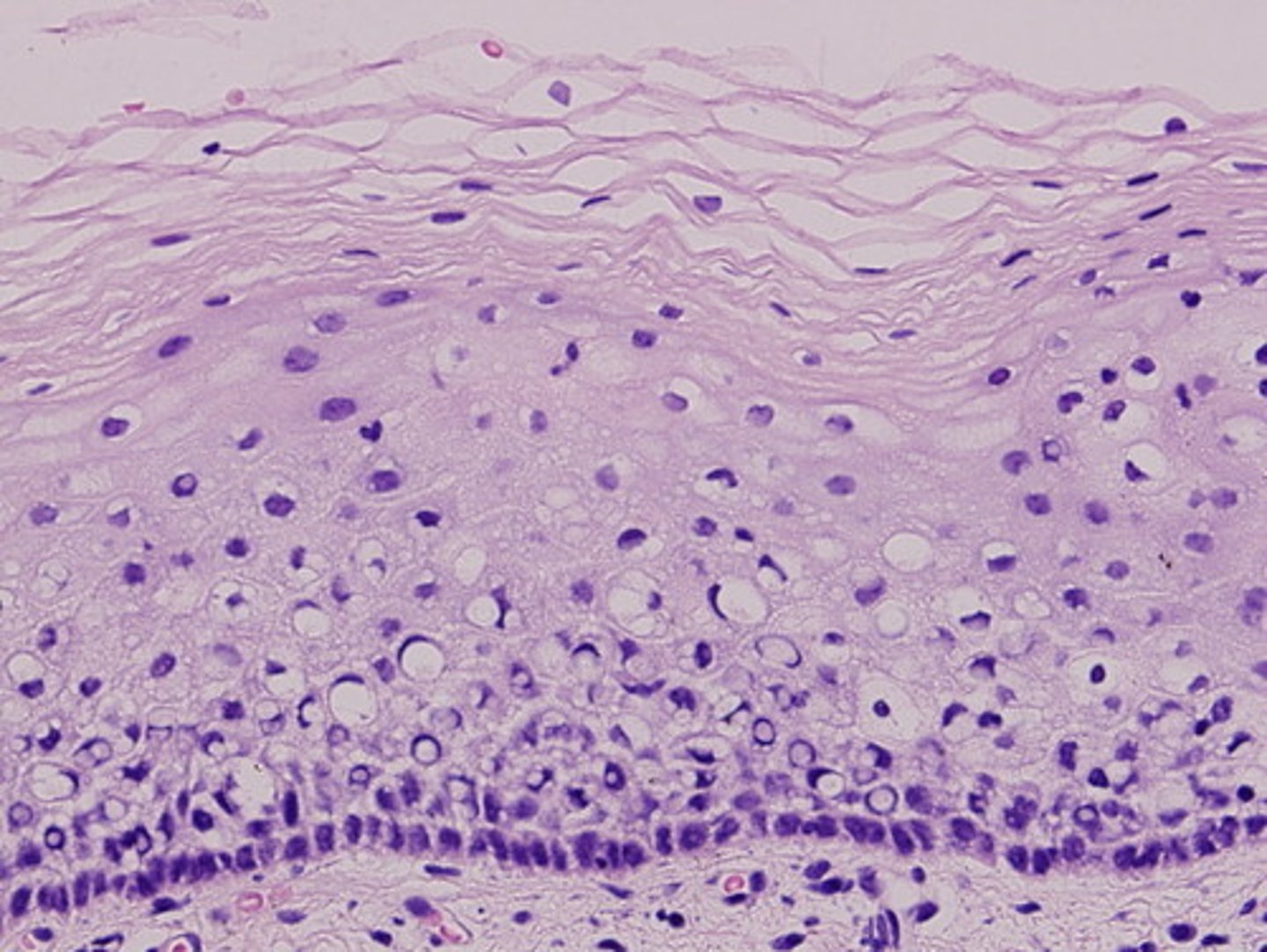
basement membrane
connective tissue that anchors and supports the epithelium
Muscle
Highly cellular ,Highly vascular with elongated, contractile cells
Classification:Smooth,Skeletal,Cardiac

Connective
Common embryonic origin
Vascularization varies widely
Matrix: contains ground substance and fibers
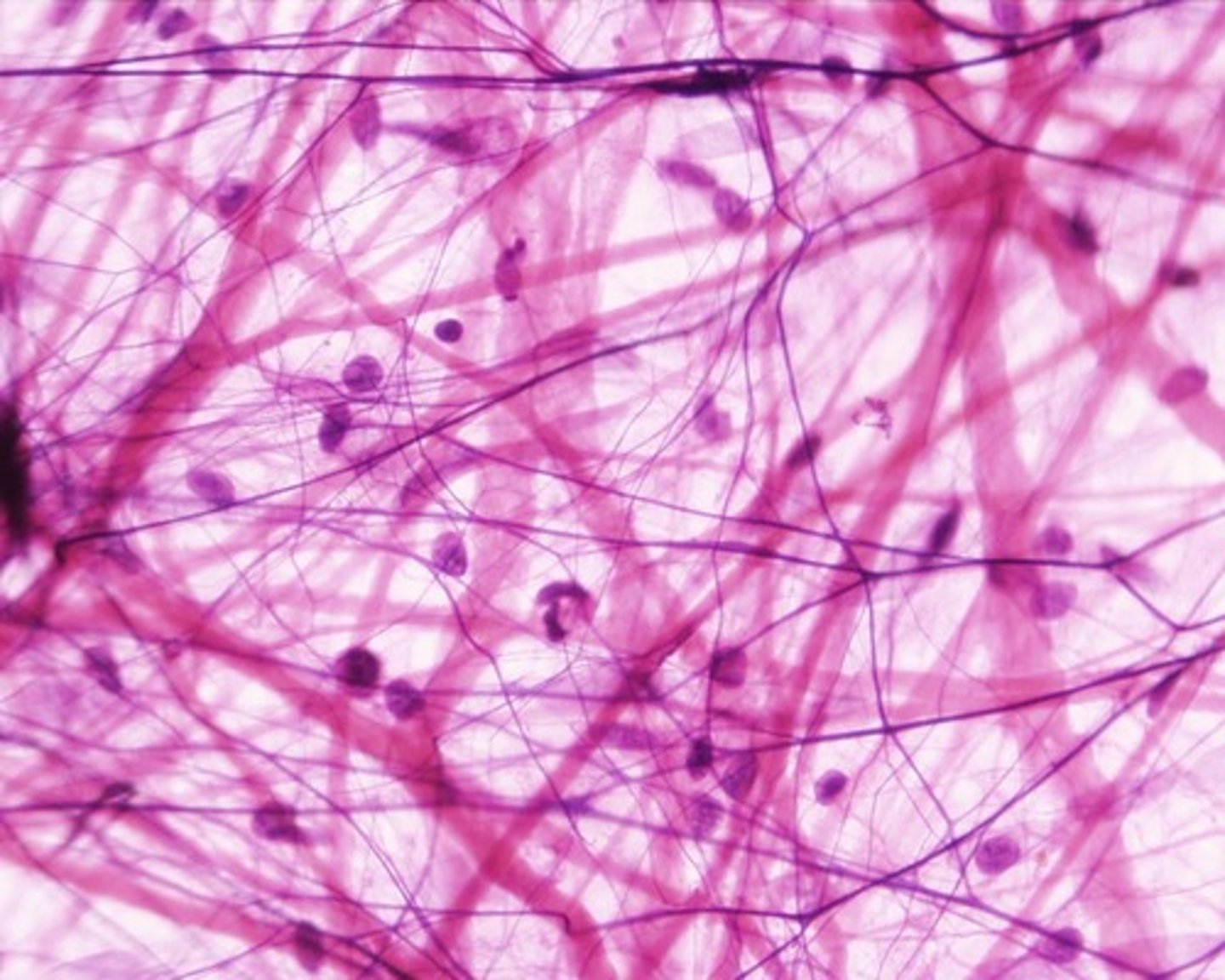
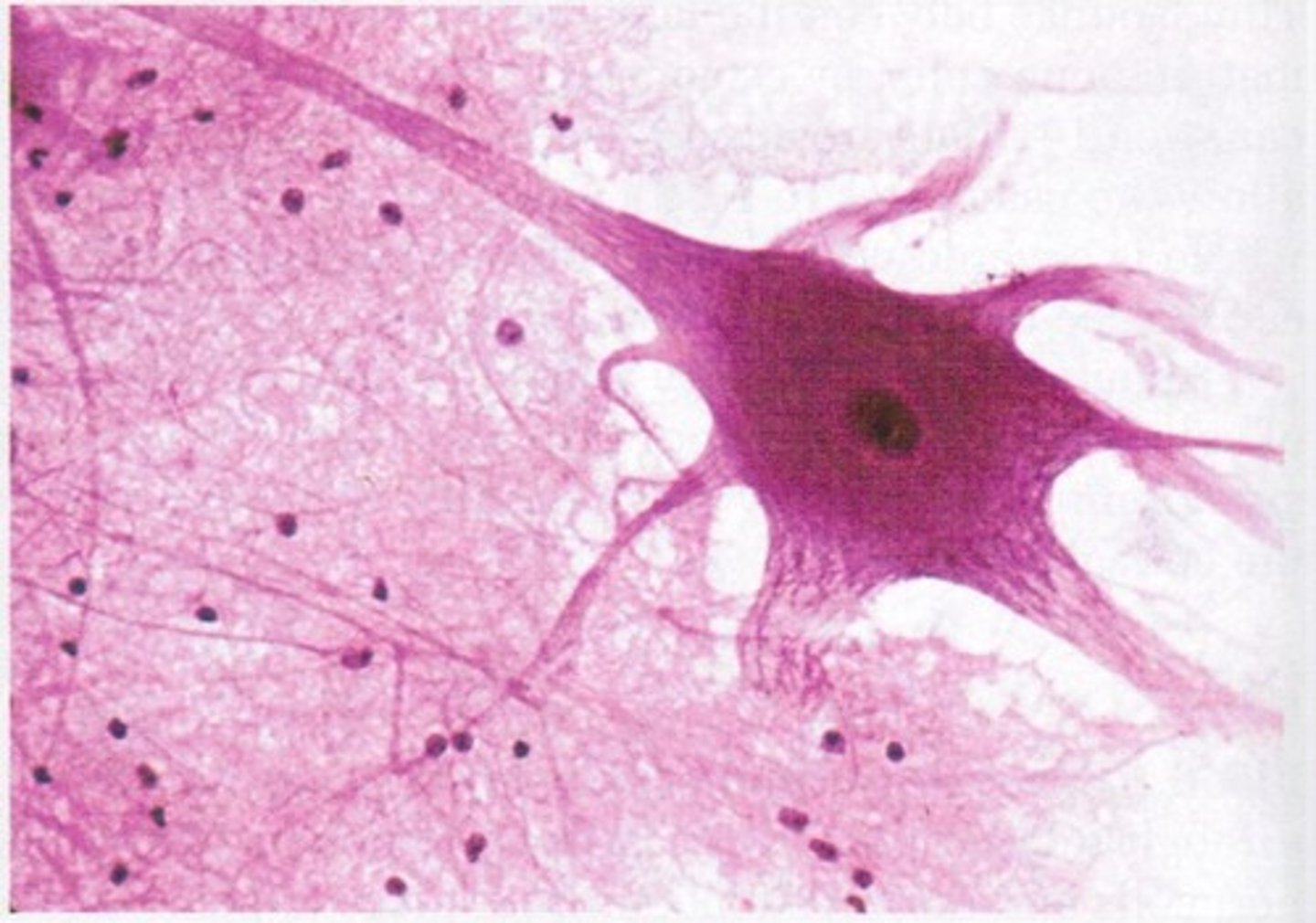
Nervous
Highly cellular, Contains neurons that conduct electrical impulses, Contains supportive cells (glial cells)
Functions of Integumentary System
Protection: chemical and physical barrier, Temperature regulation, Sensory reception, Vitamin D production, Blood reservoir, Excretion
Epidermis
keratinized stratified, squamous epithelium
Four types of cells:
Keratinocyte, Langerhans cell, Merkel cell, Melanocyte
Keratinocytes
Produce keratin and lamellar granules
Langerhans cells
Initiate immune reactions
Merkel cells
Involve touch reception
Melanocytes
Produce melanin and ship it to keratinocytes
The Dermis
Connective tissue that supports the epidermis and nurtures the hypodermis
Hypodermis
(subcutaneous layer)Not part of skin, Areolar & adipose connective tissue, Anchors skin to underlying tissue, Stores fat
The Skeletal System Functions
Support, Protection, Movement, Mineral storage, Blood cell formation (red marrow), Triglyceride storage (fats are stored in yellow marrow)
Anatomy of Bones
Specialized connective tissue, Associated with cartilage, blood, and fat
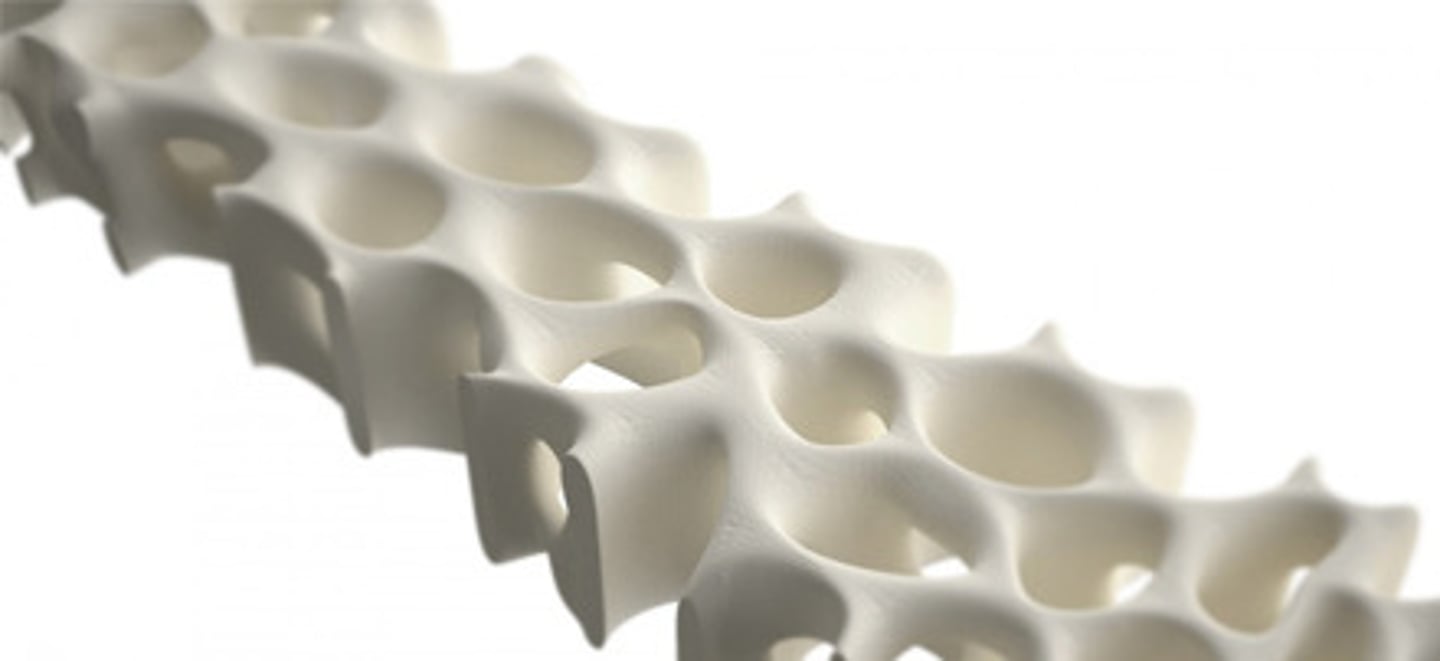
Spongy Bone
loose network of trabeculae with many spaces

Compact Bone
composed of osteons
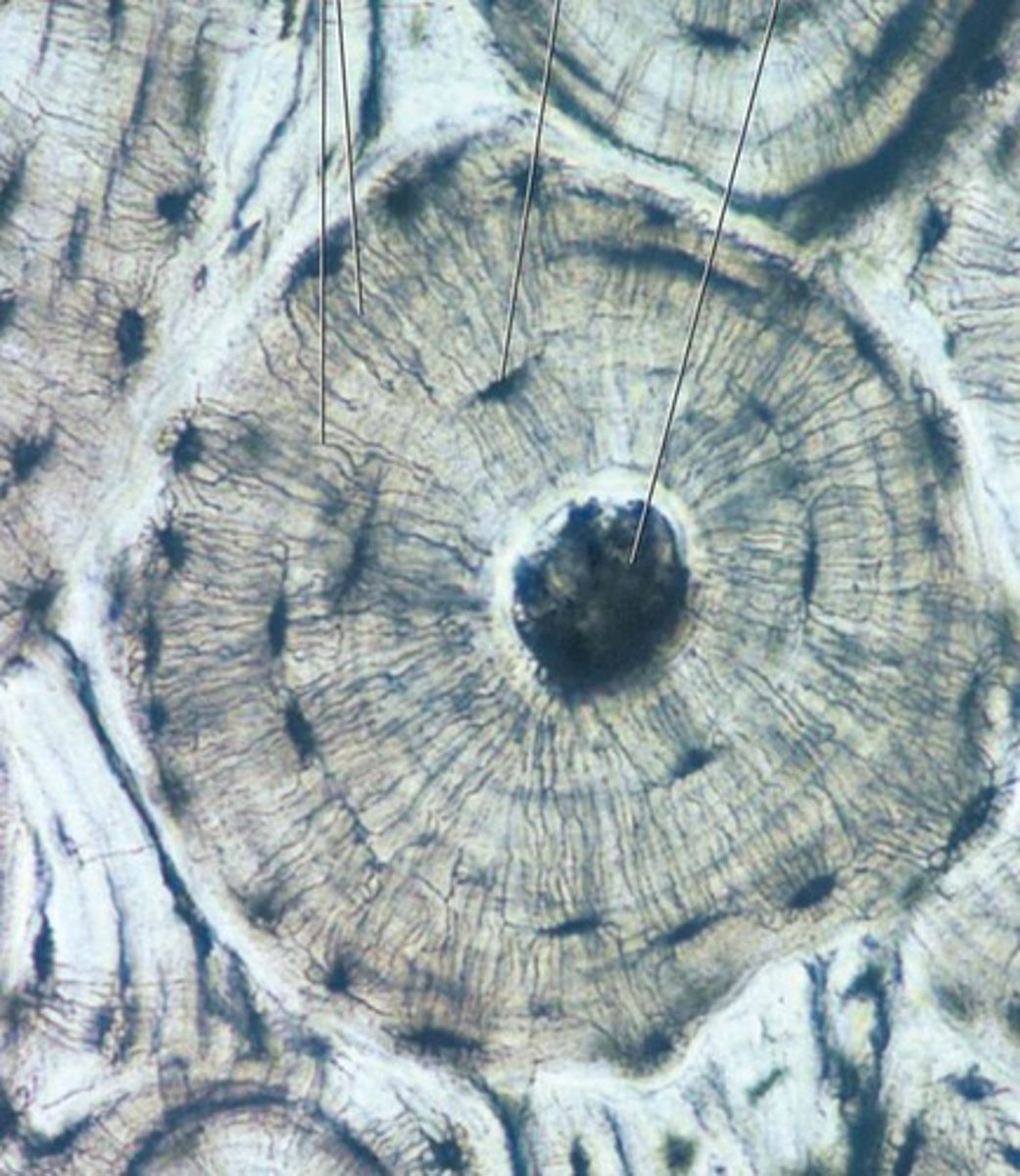
Long Bones
Ex: humerus
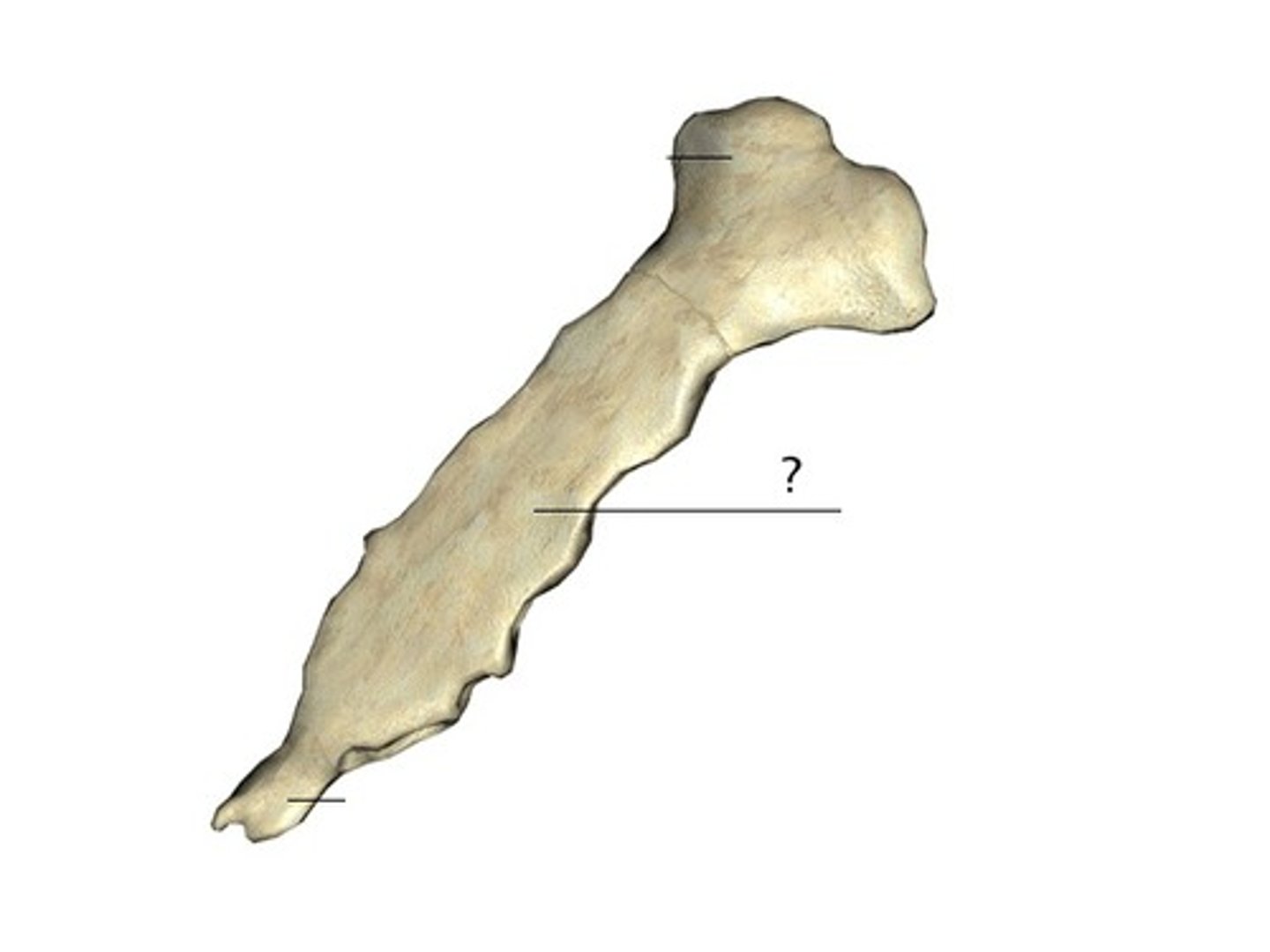
Short Bones
Ex: Trapezoid, wrist bone

Flat Bone
Ex: Sternum
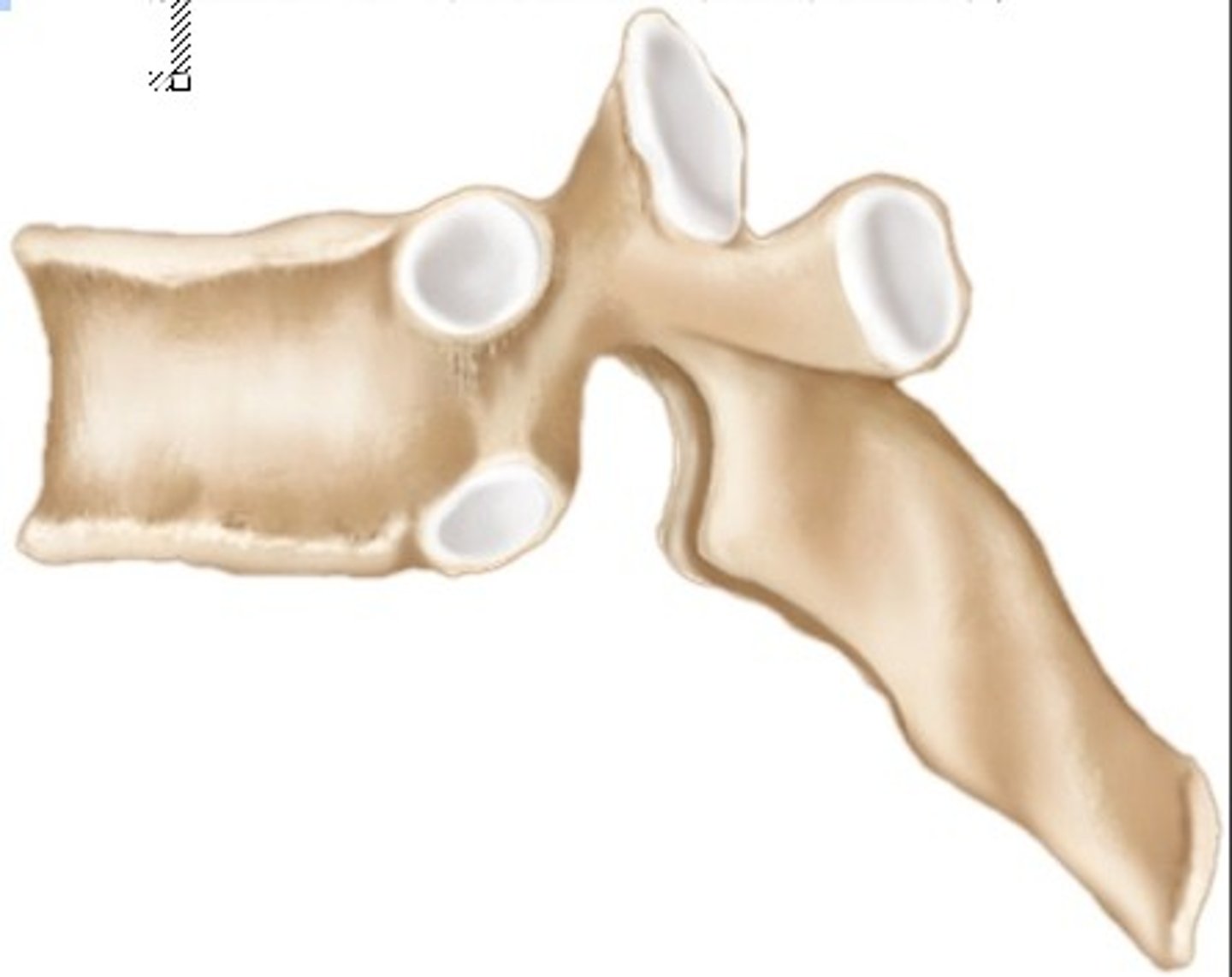
Irregular Bone
Ex: Vertebra
Sesamoid Bone
Ex: Patella

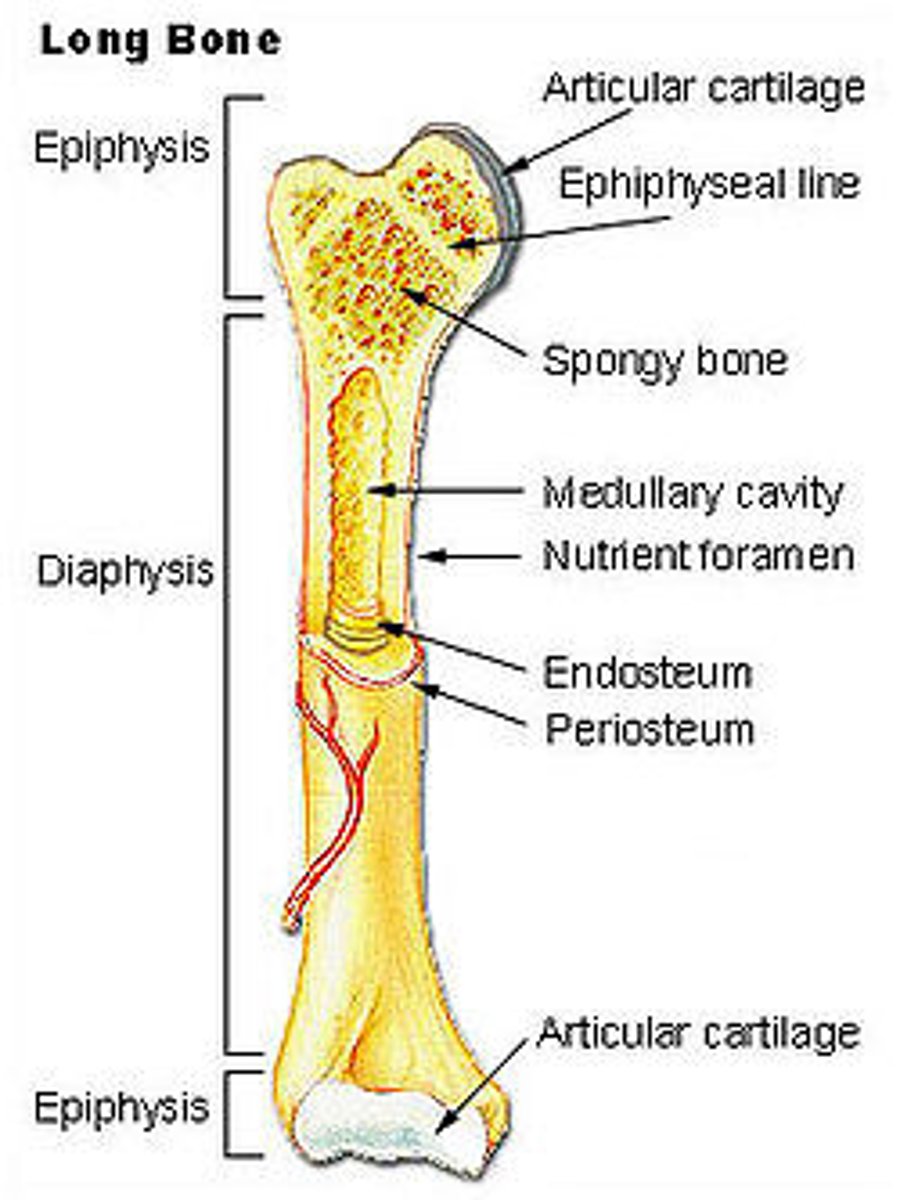
Gross Anatomy of the long bone
Diaphysis, Epiphysis, Periosteum, Endosteum
Diaphysis
compact; yellow marrow cavity
Epiphysis
external compact bone,internal spongy bone, has red marrow
Periosteum
covers the external surfaces
Endosteum
covers the inner surfaces
Blood Calcium Homeostasis
Calcium homeostasis of blood: 9-11 mg/100ml.
Rising blood Ca2+ levels
-The thyroid gland secretes calcitonin
-Calcitonin stimulates calcium salt deposit in bone
Falling blood Ca2+ levels
-Parathyroid glands release parathyroid hormone PTH
-Osteoclasts degrade bone matrix and release Ca2+ into the blood
Axial skeleton
Skull, Sternum, Rib cage, Vertebral Column
Appendicular skeleton
Pectoral Girdle (Clavicle, Scapula), Upper limbs (Humerus, Ulna, Radius, Carpals, Metacarpals, phalanges),Pelvic Girdle, Lower Limbs(Femur, Patella, Tibia, Fibula, Tarsals, Metatarsals, Phalanges)
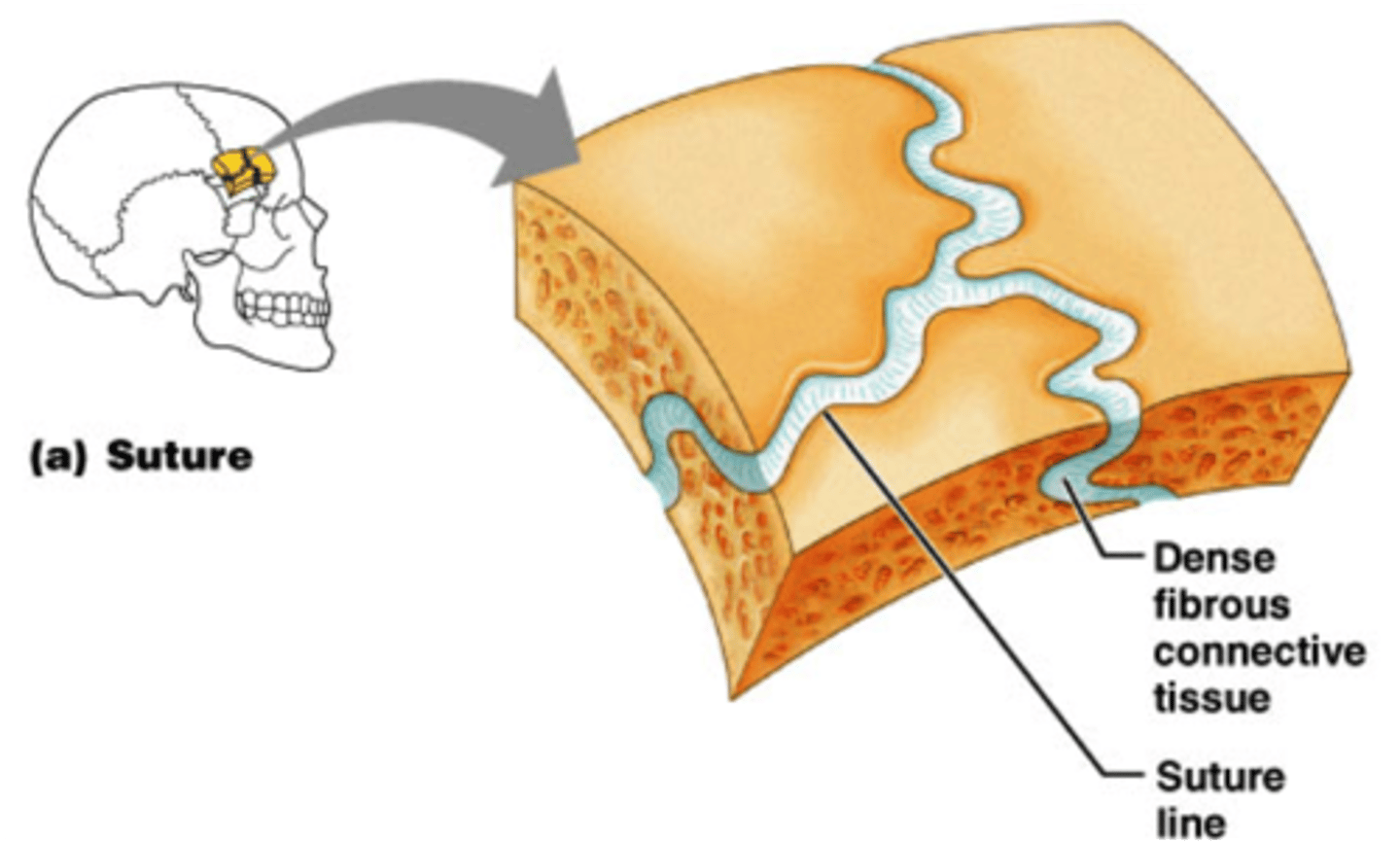
Fibrous joints
connected by fibrous c.t., no cavity present
Cartilaginous joints
connected by cartilage, No cavity present
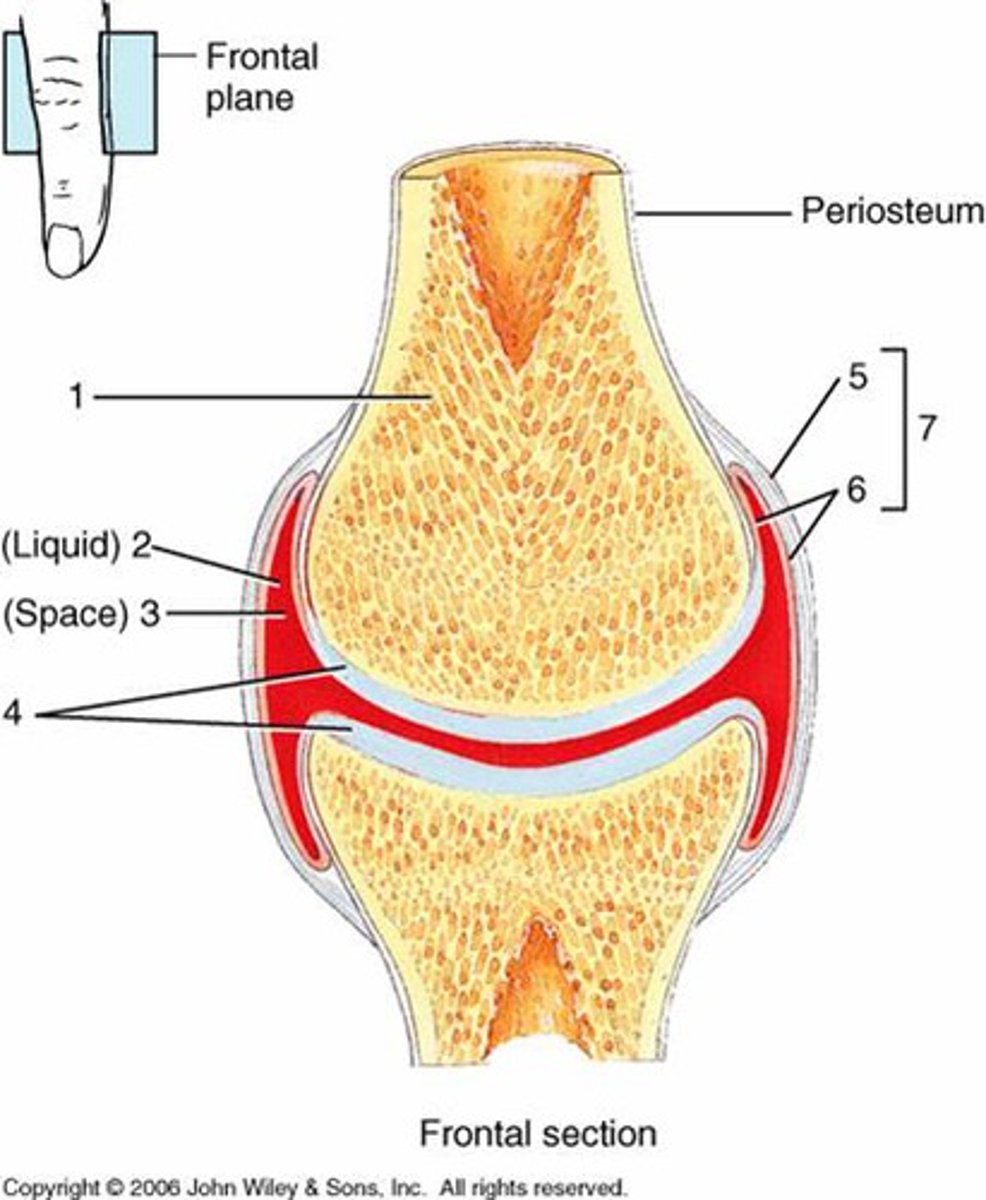
Synovial joints
fluid filled cavity present, most common
The Muscular System Functions
Movement, Maintaining posture, Stabilizing the joints, Temperature homeostasis, Regulate movement of substances between compartments
Skeletal
attached to bones voluntary control striated limited regeneration
Cardiac
in heart walls, involuntary , striated, no regeneration
Smooth
in the walls of the, hollow organs, involuntary, not striated, fast regeneration
Endomysium
surrounds each individual muscle fiber
Perimysium
endomysium wrapped muscle fibers are grouped into fascicle
Epimysium
connective tissue that surrounds the whole muscle
Origin
attachment to bone that does not move during contraction
Insertion
attachment to bone that moves during contraction
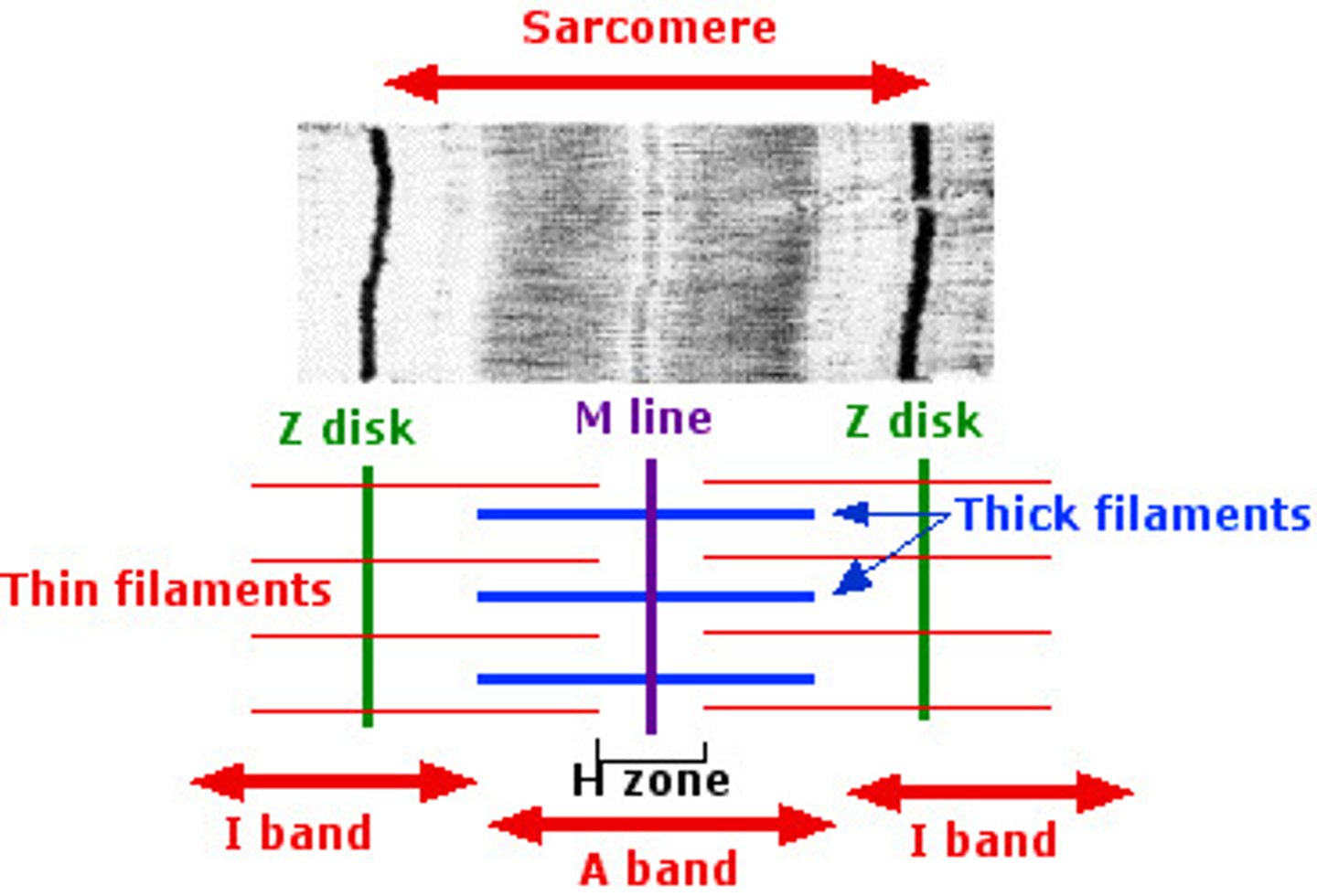
Myofibril
Rod-like structures that fill the cell
Contain bundles of proteins that
compose the contractile units
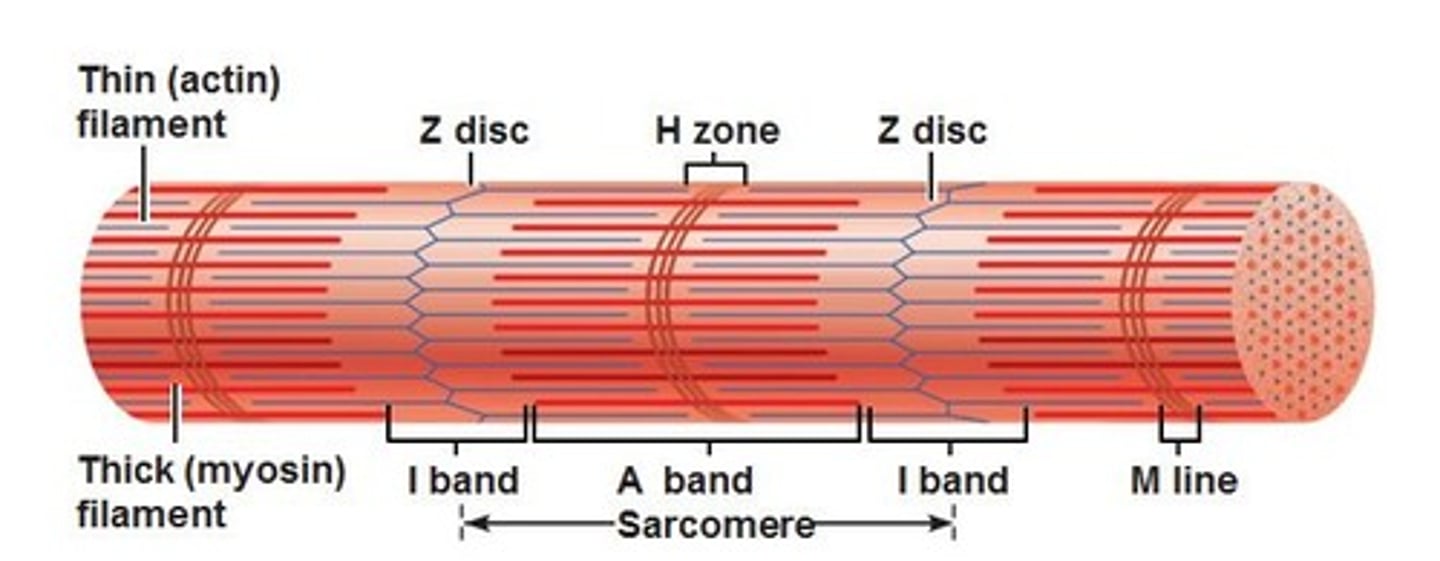
Thick and Thin Filaments
The proteins of the myofibrils
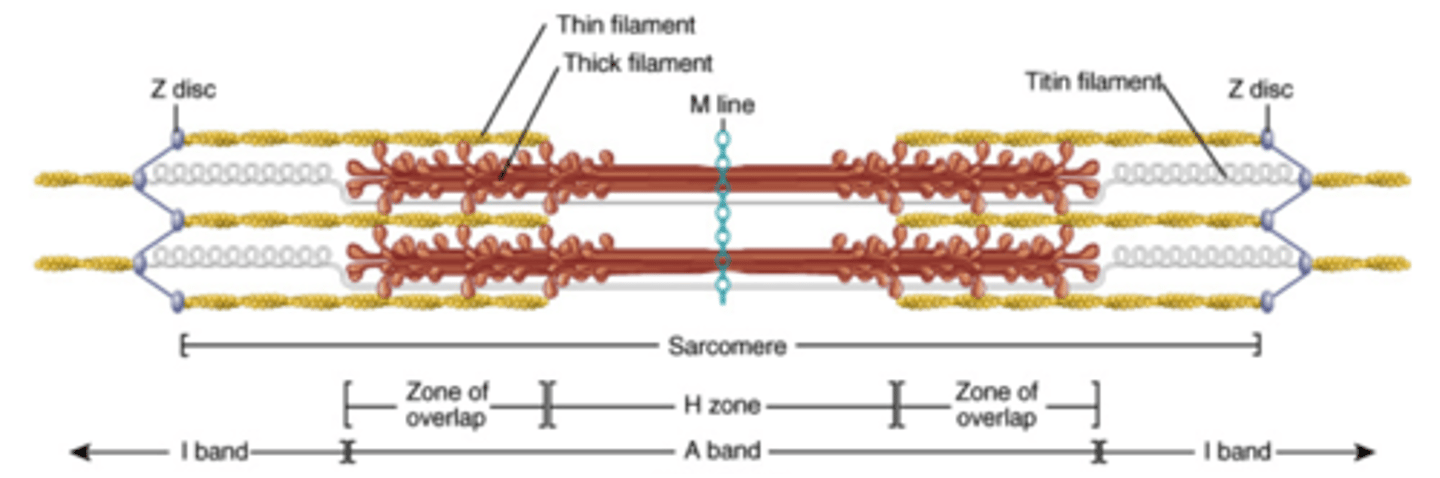
Sarcomere
The contractile units formed by the thick and thin filaments of the myofibril
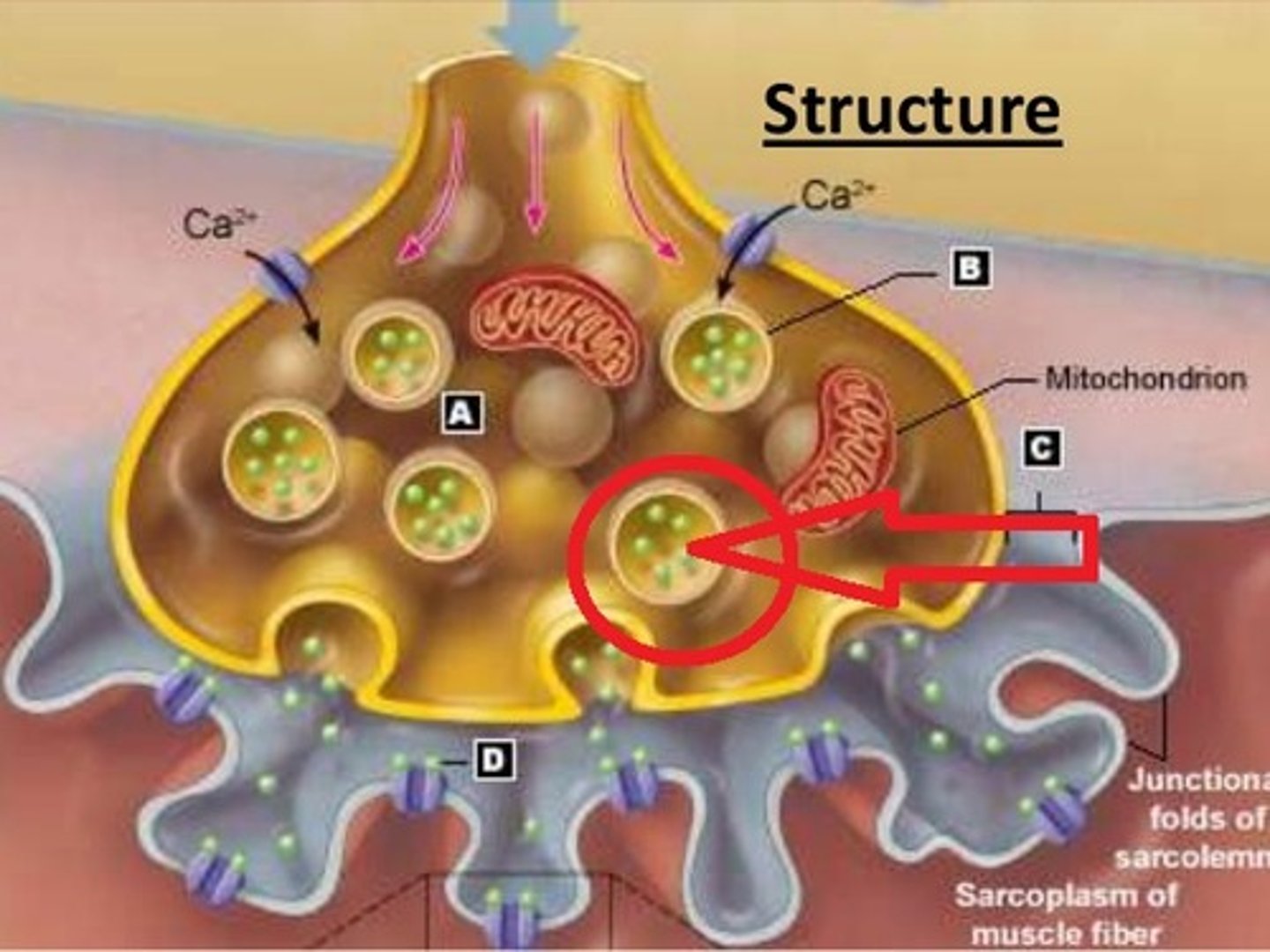
Neuromuscular Junction
-Neuron's axon end bulb filled with vesicles of acetylcholine (ACh)
-Impulse causes release of ACh into synaptic cleft
-ACh binds to receptors on muscle cell's motor end plate causing contraction
Axon terminal of a motor neuron
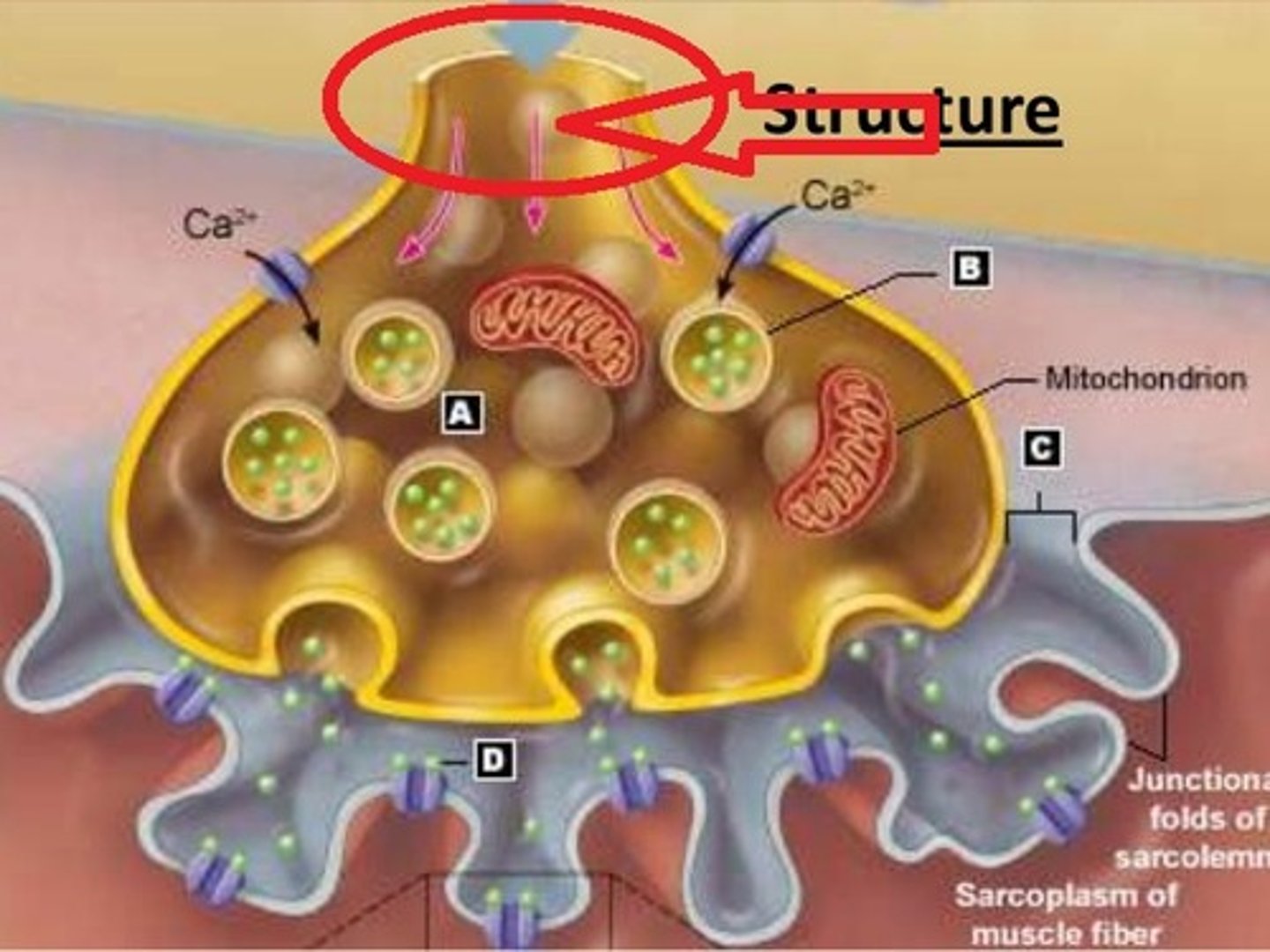
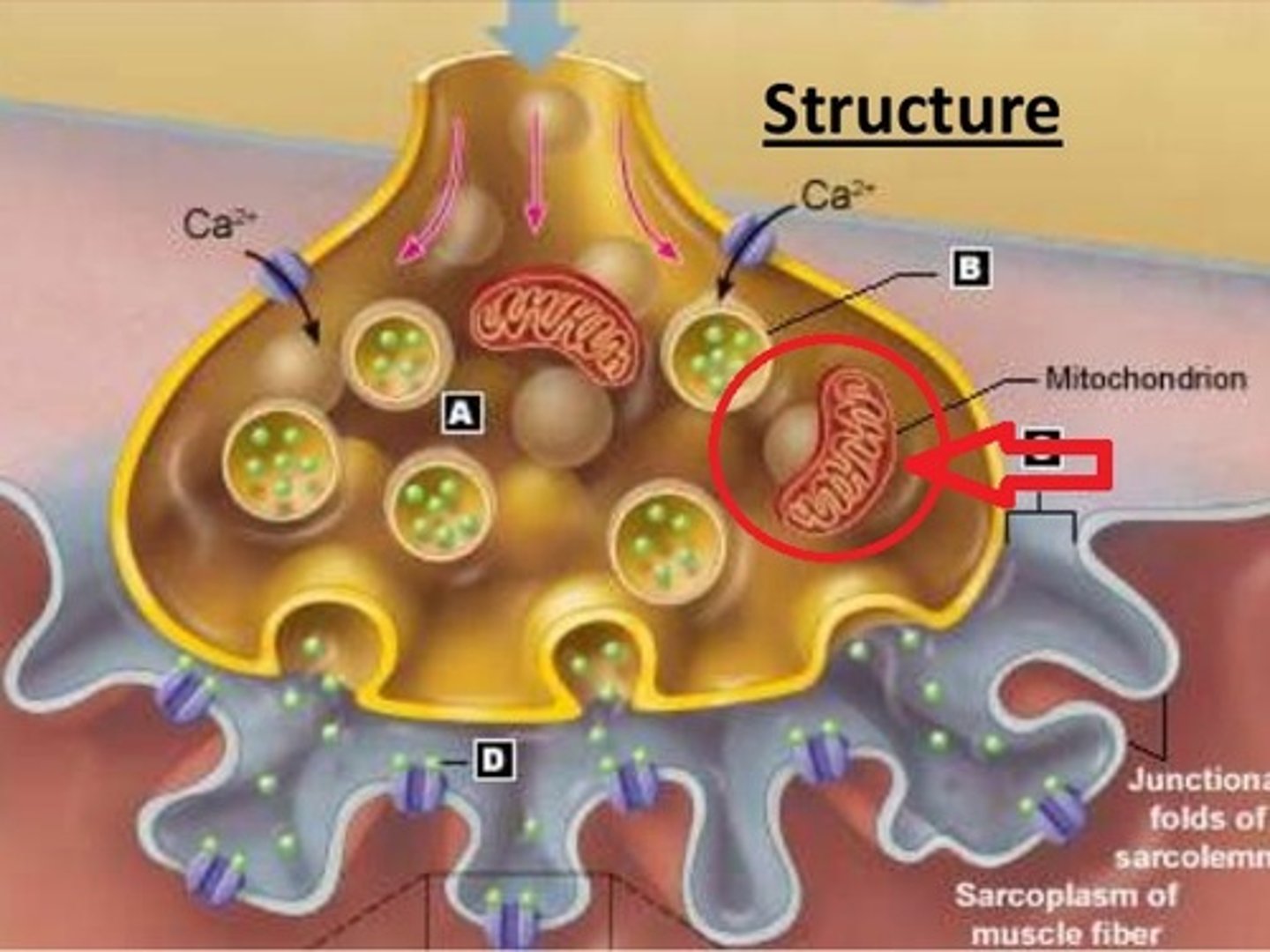
Mitochondrion
Synaptic Cleft
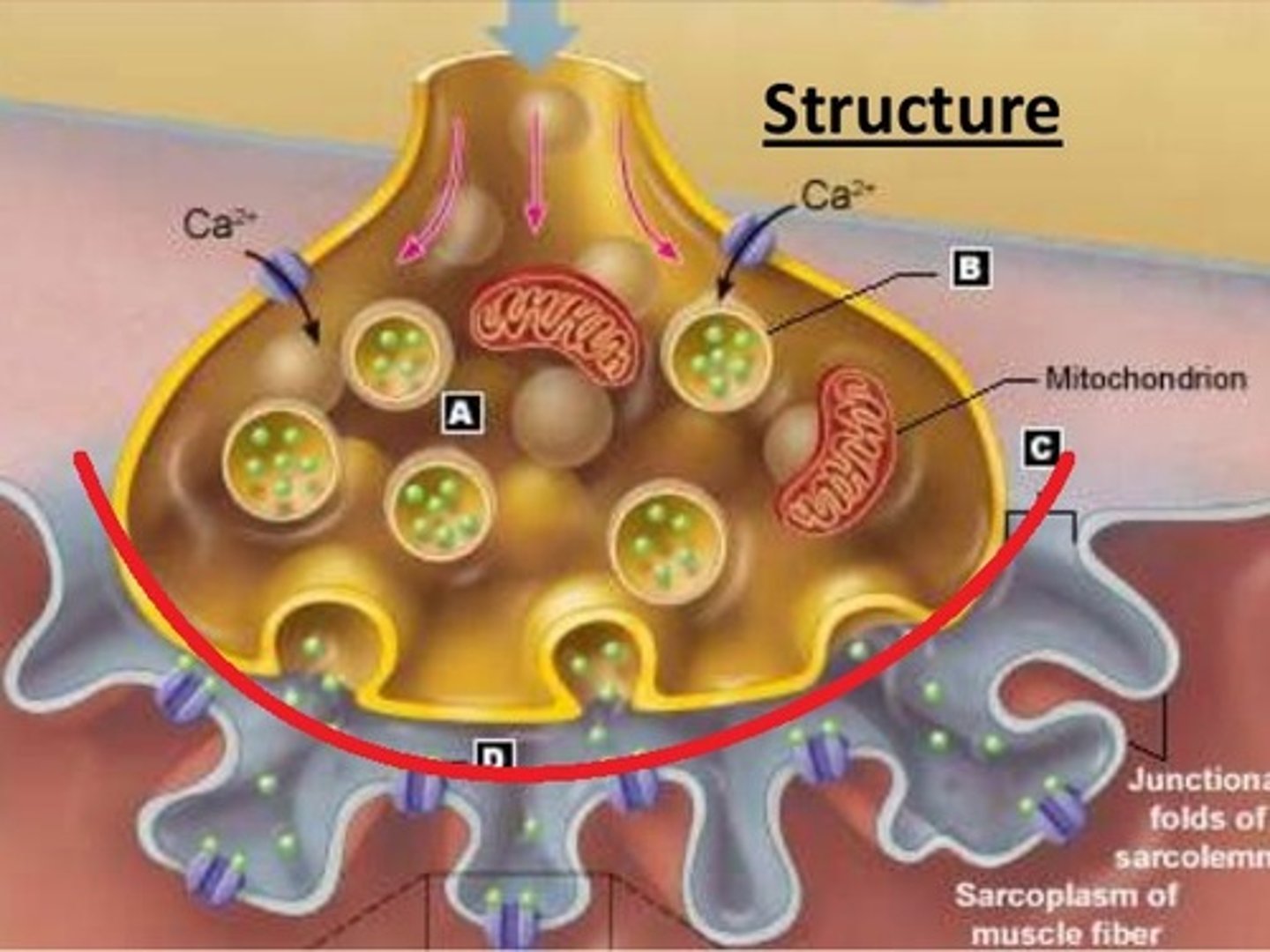
Junctional Folds fo the Scarolemma at the moter end plate
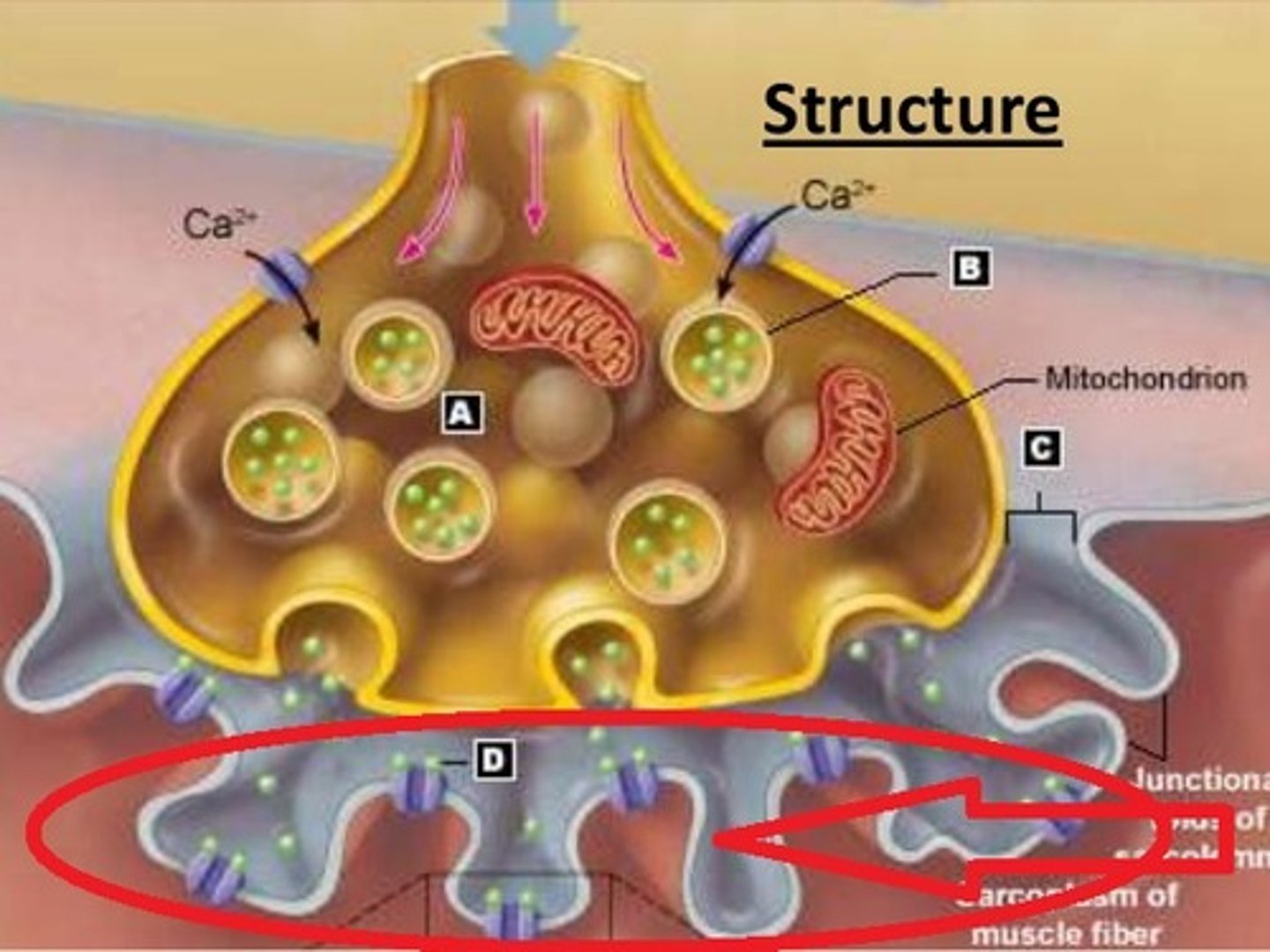
Synaptic Vesicle
Agonist
primary mover, the muscle that is contracting
Antagonist
stretches when the agonist is contracting
Synergist
muscles that assist primary mover and/or stabilizes a joint during a contraction