Toxicology
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
True or false: something that is non-toxic can be toxic
true
True or false: highly toxic chemicals can be life saving when given in appropriate doses
true
Explain the response curve
graphically represents the relationships between the dose of a drug and the response elicited
What is the shape of a dose response curve
sigmoidal
The reaction to the dose is known as the ______-
response
True or false: the response is independent of the dose
False
True or false: the dose-response curve may differ for different populations
true
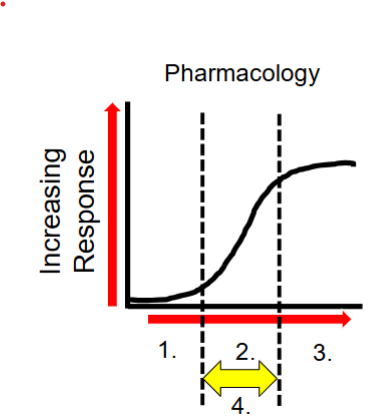
What is number 1?
low dose→ no observable response (subtherapuetic)
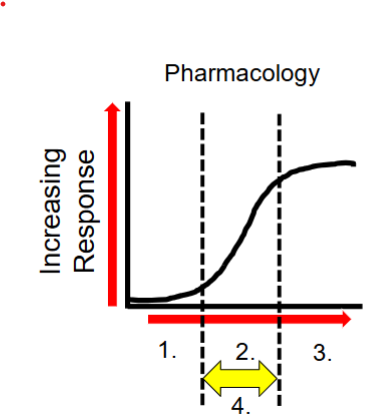
What happens at number 2?
increased dose → therapeutic response (and side effects)
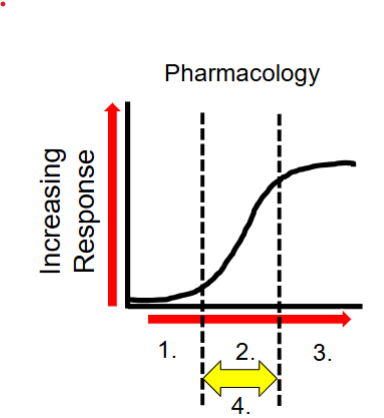
What happens at number 3?
increased dose → therapeutic dose toxicities
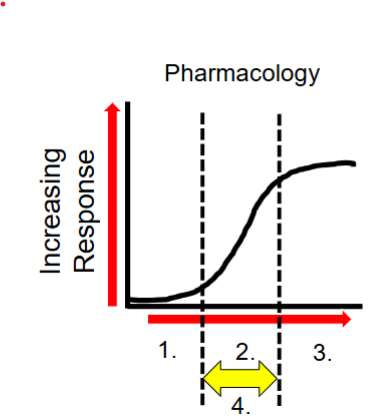
What is at number 4?
the therapeutic window
Key considerations in toxicity
routes of exposure
duration
exposure of mixtures
individual susceptibility
ADME
What are the 8 routes of exposure
oral (buccal/SL)
parenteral
topical/transdermal
rectal/vaginal
otic
ocular
nasal
inhalation
Rank the routes of exposure from most to least effic
Injection (IV) → inhalation → skin (absorption) → ingestion
(could argue between placement of skin and ingestion)
Order of efficiency
IV → inhalation → ip → im → topical → ingestion
the ability of a chemical to enter the blood
absorption
The kinetics of absorption are altered by what
concentration of the drug
What is first order kinectics
A constant proportion of the drug is eliminated per unit of time
What is zero order kinectics
constatn amount of the drug is eliminated per unit of time
Which order kinetics is a concentration-dependent process and which is independent of concentration
dependent: first order
Independent: second
storage where can lead to rapid mobilization of the fat and can rapidly increase blood concentration of mercury
adipose tissue (lipophilic compounds)
Biotransformation can result in the formation of reactive metabolites
bioactivation
what is the primary objective of metabolism
make chemicals agents more water soluble and easier to excrete (detoxification)
NAPQI is toxic to what type of cells
hepatic cells
when glucuronide sites are saturated, the body makes more what
NAPQI
How does NAC prevent Tylenol toxicity?
By increasing GSH levels
Role of glutathione
neutralize NAPQI to generate non-toxic cysteine and mercapturic acid conjugates
Overdoses on APAP depletes _____ resulting in an increase in NAQI
GSH
NAQI will start interacting with the _____ groups on proteins, especially enzymes (overdose)
SH
How are water soluble products excreted?
filtered out by the blood by kidneys and excreted into urine
how can elimination be enhanced with some toxicants
changing the pH of the urine
increasing urine flow
increased blood volume
why is drinking alcohol and taking APAP so toxic?
alcohol decreases GSH levels
alcohol (increases/decreases) CYP450?
increase
Alcohol generates (more/less) NAQI
more
Alcohol uses up liver ___
GSH
Alcohol and APAP rapidly accelerates ______
hepatic necrosis
True or false: toxicity of alcohol and APAP can be seen the day after
True
What neutralizes NAPQI
Glutathione
Alcohol (increases/decreases) CYP 450
Increases
Alcohol decreases _____
GSH levels
Which heavy metal causes CNS deficits, anemia, hypertension and reproductive toxicity?
Lead
Which heavy metal causes cardiovascular shock, peripheral neuropathy and cancer?
Arsenic
Which heavy metal is most widely stored in the fat?
Mercury
What are chelators
Treatment for metal overdose/reverse toxic effect of heavy metals on enzymes
Pros of chelation
form nontoxic complexes
From metals from soft tissues and plasma
Effective against acute poisoning
Oral therapy available
Cons of chelation
redistribution of toxic metal
Essential metal loss
No removal of metal from intracellular stores
Poor clinical recovery
Pro-oxidant effects (DTPA)
HA, nausea, increased BP
A young engineer is involved in a smelting accident and presents with rice water stools and severe GI discomfort. Which heavy metal poisoning would you diagnose the patient with?
Arsenic
Treatment for acute poisoning of arsenic and mercury
Tx of lead poisoning in junction conjunction with EDTA
Oily, colorless
Dimercaprol
While dimercaprol is great at chelating arsenic, which chelator is frequently used in its place?
Succimer bc it is water soluble and more stable
tx of poisoning by antimony
Water soluble
Well toldvrated
Doesn’t delete essential metals in body at usual doses
Succimer
A patient arrives with headaches, fatigue, and loss of appetite with weakened muscles. Which heavy metal do you predict they have been exposed to?
Lead
A small child arrives in the ER ~1 hour after ingesting tablets they had found. Their symptoms included GI distress, vomiting, epigastric pain. Metabolic acidosis and leukocytosis. WHAT DO YOU THINK THE TABLETS CONTAINED?
Iron