5 - Profiling and Classification
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
why use classification?
theoretical development
guides assessment practices
guides treatment practices
why not use classification?
important individual differences may be obscured
categorizations often seen as pejorative
humans have a strong tendency to _____
categorize
better to use this natural inclination than ignore it
issues where classification may be relevant
level of risk
institutional housing decisions
degree of supervision required
offender needs
treatment inclusion
are between-group differences theoretically informative?
yes
developmental trajectories and risk factors can help identify later problems
circumstantial risk management post-release
Chaiken and Chaiken study
8 dimensions based on past crimes yields 256 possible combinations, but 10 of those accounted for 59% of inmates
leaves some people unclassified
doesn’t guarantee clinical differences between groups
lots of combos
Megargee’s good system criteria (7)
comprehensive
unambiguous
statistically reliable
type distinctions are valid
sensitive to individual changes
treatment relevant
economical to apply
systems based on ________ rather than impressions fair better
cohesive personality / criminogenic theory
most attention now is on ____ _____ systems
empirically derived
most testable and accurate
impressionistic system
an individual, or group, think they recognize a pattern or type among some members of a clinical/institutional sample
no theory or method of measurement
essential features identified after the fact
prognostic is poor
ex., DSM-5
problems with DSM-5 as an impressionistic system
many NOS categories
systematic disagreements (ex., schizoaffective vs. schizophrenic)
many personality disorders go hand in hand
predictions are circular
assumes discontinuity among personality disorders (which is untrue)
discrete taxons
theoretically derived systems
stem from a developmental or personality theory
relates specific attributes or points of maturation to antisocial behaviour
measure instruments draw heavily on concepts central to theory
introduces significant bias
conceptual level (example of theoretically derived system)
based on ability to adopt other perspectives
attempts to tap reasoning process more so than outcome
incomplete sentences task
responsivity principle
delivering treatment in a way that is tailored to the individual and meaningful to them to maximize effectiveness
used in both impressionistic and theoretically derived systems
ex., lower conceptual level = more behaviourally oriented interventions
empirically derived classifications
internet data used to profile you
based on two statistical techniques
cluster analysis
factor analysis
cluster analysis
numerical taxonomy
groups subjects according to level of similarity as measured by variables selected by the researcher
ex., MMPI based scheme
factor analysis
correlational
good for reducing a large number of variables to a smaller number
may help identify “underlying dimensions” like when 1-2 variables are responsible for the others
ex., Hewitt and Jenkins 4-factor solution
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory
most commonly used clinical personality measure (cluster analysis)
1200 convict profiles yielded 10 types
classifies almost all profiles (96%)
results replicated
characteristic criminal based on MMPI
able, 17%
elevated psychopathy (4) and mania (9)
problems with MMPI
predictive accuracy in question, poor correspondence between MMPI and MMPI-2 profiles
high scale overlap (characteristics are not orthogonal)
are 10 groups really needed?
profile derivation was atheoretical, results may not be unique to instrument
Hewitt & Jenkins 4-factor solution
example of factor analysis
4 factors
unsocialized aggressive behaviour (UA)
poor prognosis
LCP
socialized delinquency (SD)
better prognosis
AL
over-inhibited (OI)
more likely mentally ill
phuscial deficiency
less interpretable
profiling
used to describe serial offenders, high premium to catch as they are likely to offend again
collection of related techniques:
psychological profiling
criminal personality profiling
criminal behaviour profiling
investigative profiling
criminal investigative analysis
goal of profiling
describe perpetrators in order to narrow the investigative field
profiling sources of information
autopsy results
victim verbal reports
examination of crime scenes / photos
test and interview data (psychological profiling only)
criminal profiling
relies heavily on intuition
first attempts in WWII to predict military beahviour of enemy officers
directs attention of investigators to most likely subjects
akin to interpreting personality profile
makes general assertions
works best with frankly ill and highly sadistic individuals
_____ of police psychologists express discomfort with profiling
70%
two reasons
constitutional concerns, is it inappropriate to profile based on race etc.
not good enough of science basis
profiling is more of an ____ than a science
art
<___ of profile cases are solved
50%
partly because profiling only for the most challenging cases
Pinizotto and Finkel findings of profiling accuracy study
found that trained profilers did only slightly better with sex offender profiling, but no better with violent offenders than police detectives, non-forensic psychologists, and university undergrads
reconstructive psychological autopsy (psychological autopsy)
post mortem descriptions based on a known offender
intended to add to profiling database
attempts to address historically dynamic features, not just static
psychological profiling
begins with known perp
findings added to database
test selection is critical
one relevant test is of greater value than many irrelevant tests
geographic profiling
based on analysis and prediction of movement patterns, highly statistical
uses Rigel Analyst software or Dragnet software
uses distance decay functions based on the journey to crime model
yields jeopardy surface (level of risk in certain location)
probability based on minimizing the mean distance from all known crime sites attributed to that offender
paradigm
way of doing something, viewpoint, perspective
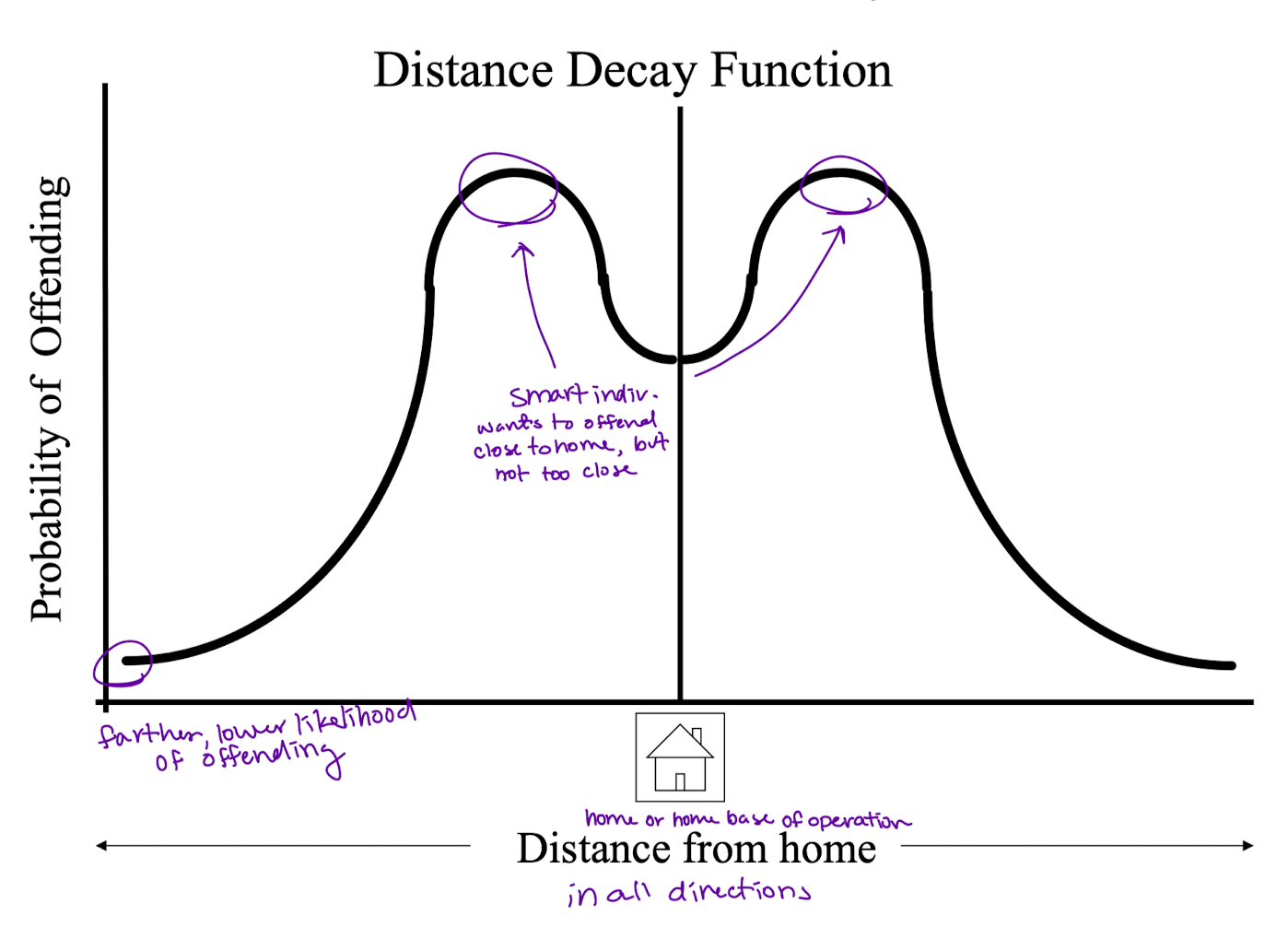
distance decay function
graph of distance from home compared to probability of offending, peaks on all sides of home a bit away
rasterization
used to determine the lowest distance that their home base is likely to be based on all the crime locations
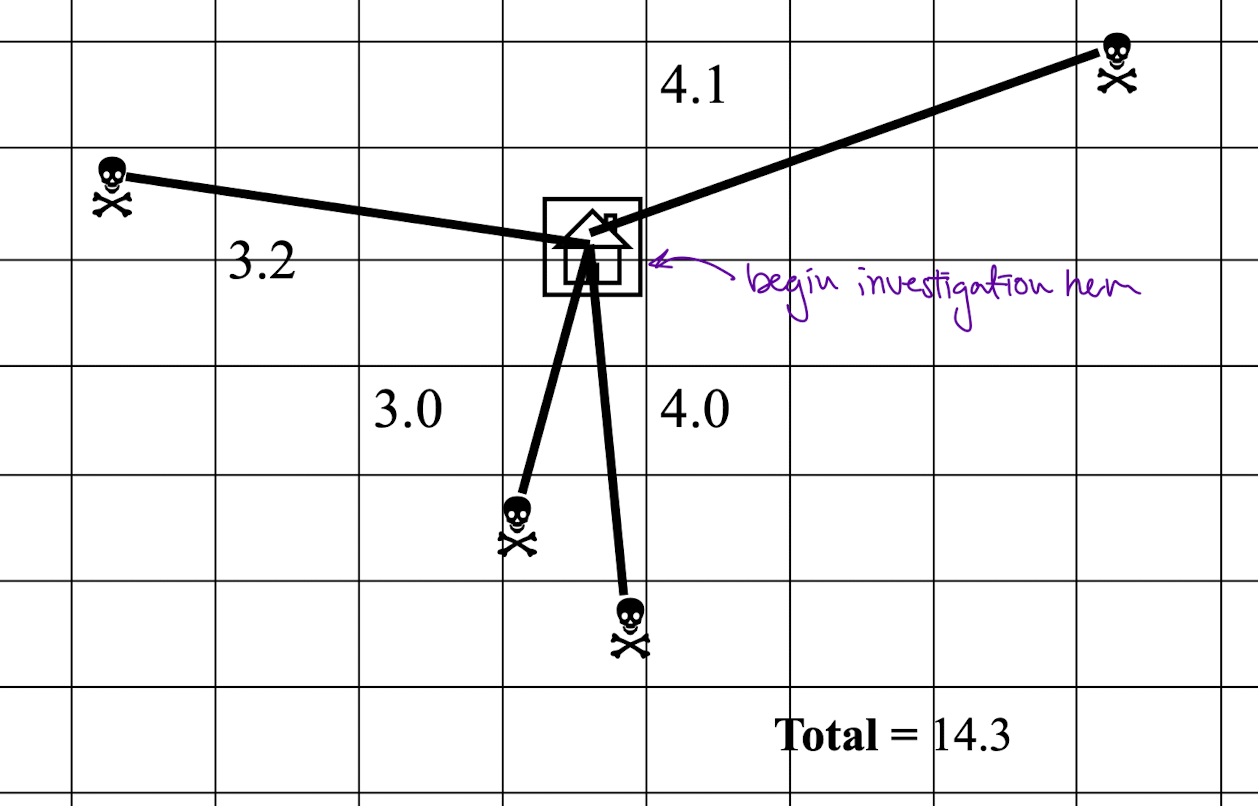
jeopardy surface
elevated points on the map have highest probabilities of home base
Rossmo’s minimal criteria for profiling
minimum 3 years experience investigating interpersonal crime
“superior” investigative skill
case linkage analysis
joint probability, multiplying aspects of crime to see if they were committed by same person
canter’s circle hypothesis
serial offender’s home base most likely to be located within a circle defined by the two most distance crime scenes
works best for small areas
architectural psychologist
Canter
give people advice on designing businesses based on flow of human traffic
a prediction, will this Starbucks stay in business here?
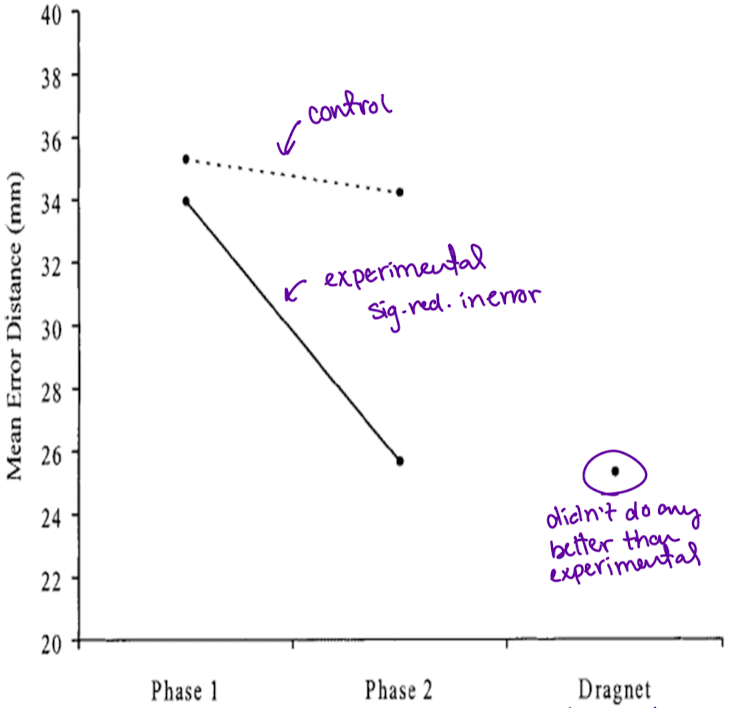
Snook’s circle hypothesis study
undergrads given circle hypothesis instructions saw a significant decrease in their error
found no advantage to using Dragnet over the circle hypothesis experimental group
conclusion: neither extensive experience or a computer is necessary to profile
three classes of crime scene features
modus operandi
signature
staging
modus operandi
the way the violent act was committed, follows same pattern of human behaviour
time, place, weapon, victim characteristics, type of crime, location, method of entry
refined over time and with practice, MO becomes stable eventually as processes become automated
can also de-evolve to become sloppy and less patterned
signature (calling card, personation)
features extra to the crime itself
may become highly ritualized
pattern of mutilation or property destruction, taking trophies, leaving something behind, notes/writing, positon of body, burning body
may provide more info than an unstable MO
staging
alteration to the crime scene after the crime was committed
may not have been done by assailant
ex., family making suicide look like murder
offender may attempt to psychologically undo, or reverse the act
particularly in acts of passion
classifications of crime scenes
organized
disorganzed
mixed
organized crime scene
evidence of planning to eliminate obstacles
reduces chances of detection
allows greater specification of victim characteristics
may become cocky
abduction, murder, disposal usually not in same locations
disorganized crime scene
reflects work of more impuslive, less intelligent criminal
crimes in angry, hihgly aroused state
no movement of evidence (including body) from crime scene
victims more random
mixed crime scene
features of both organized and disorganized
usually means poorly planned crime fell apart, encountering unexpected resistance
Turvey said most crime scenes exist along a _____ of classification, not a dichotomoy
continuum
what features Turvey thinks should be considered for crime scenes
point of contact
primary scene
secondary scene
point of contact
where the perp first had contact with the victim
primary scene
place where something criminal took place for the first time
secondary scene
place where the actual large crime took place
there may also be intermediate scenes and the dumpsite scene
method of approach
how the assailant will approach the victim
mainly for rapists
may reveal information about relationship to victim
blitz
surpise
con
blitz
(method of approach)
limits opportunity to work out a defense resulting in injurious physical assault
surprise
(method of approach)
laying in wait for the victim, having knowledge of their schedule
can turn a 2nd degree into 1st degree murder
con
(method of approach)
employs a ruse, may involve repeated contacts over time
hunting strategies
involve looking for a victim, greater movement for the perp than just method of approach
hunter
poacher
troller
trapper
hunter
(hunting strategy)
goes out and gets a victim fairly close to home (31%)
geoprofiling most effective for them
distance decay function
poacher
(hunting strategy)
goes into another town or city, doesn’t operate from home (54%)
fewer victims
still have a base of operation
troller
(hunting strategy)
crimes of opportunity, victims are encountered while other routine tasks are carried out (11%)
trapper
(hunting strategy)
lure/trick victims to a location where the perp has control (1%)
attack strategies (Rossmo)
raptor
stalker
ambusher
raptor
(attack strategies)
attack is immediate upon location of victim (79%)
serial predators
stalker
(attack strategies)
watches, follows, waits to catch victim in a vulnerable, off-guard state (<1%)
ambusher
(attack strategies)
always works close to home or another prepared and familiar location (21%)
types of motives
revenge, financial gain, jealousy, power, non-sadistic or sadistic sexual gratification, insanity, self-defense