Female Reproductive System Terms | Biology Chap 17 Study Set
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
female reproductive system
organs that produce and transport egg cells and secrete female hormones
what differentiates female from male (R.S)
FEMALE:
- has no continuous tubing
- most female organs start to develop in the abdomen
- most of the organs is covered by peritoneum
what similarities of the R.S. are found in both
BOTH FEMALE AND MALE
- combines with the urinary system
- production of both urinary tracts start somewhere in the abdomen
functions ; reproductive system
BOTH MALES AND FEMALES:
- produce gametes through gametogenesis
- produce hormones through steroidogenesis
- both can deliver gametes for fertilization
Functions for Female R.S. only
FUNCTIONS ONLY FOUND IN WOMEN
- perform pregnancy
- perform parturition
- perform lactation
lactation
secretion/production of milk
-----------------
- men can also perform lactation (but is very uncommon)
- if a man performs lactation its usually an indication of cancer or a tumor
Organization of reproductive systems
Divided into 3 categories
- Primary Sex organs
(gamete production)
- Accessory Sex organs
(transportation/movement of gametes)
- Secondary sex Characteristics
(physical features developed during puberty)
-----------------
Each category has its own special characteristics for both genders
female primary sex organs
- ovaries
female accessory organs
- Fallopian tube (paired)
- vestibular glands (2 pairs)
- Labia (paired)
- uterus (single)
- cervix (single)
- Vagina (single)
- Clitoris (single)
female secondary sex characteristics
↓ muscle mass
↓ skeletal mass
↓ body hair
↑ voice
↑ body deposition
↑ development of mammary glands and breasts (for lactation)
↑ wider pelvis (for pregnancy)
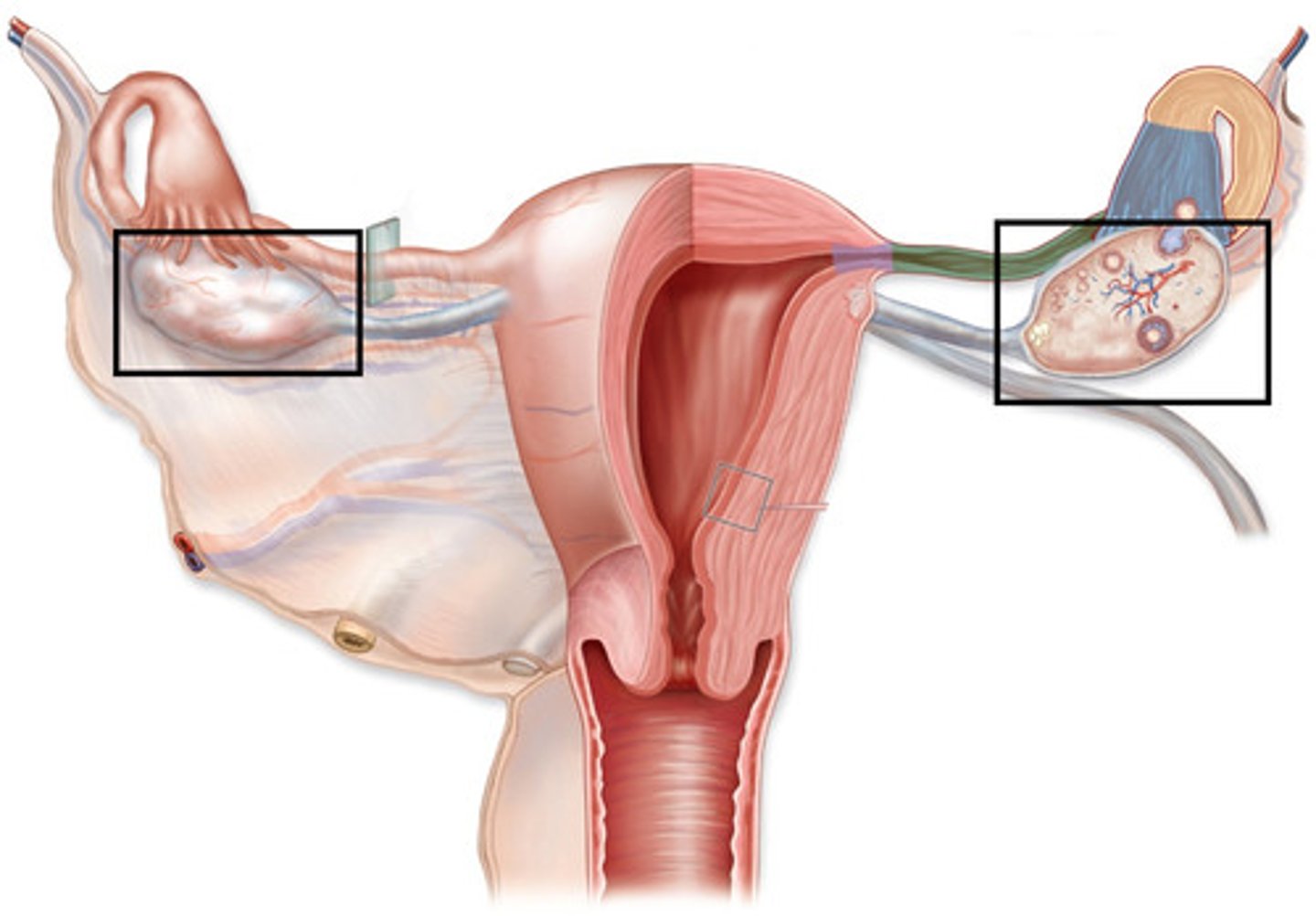
Organization + movement of the female reproductive system
(FROM START TO FINISH)
- ovaries (paired)
- fallopian (uterine) tubes (paired)
* fimbriae catches egg from ovary
- uterus
- cervix
- vagina
Fimbriae
finger or fringe like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes
- HINT: think of baseball glove
-----------------
FUNCTION:
- ___ catches the egg during ovulation release, which can be placed in the fallopian tubes to be fertilized
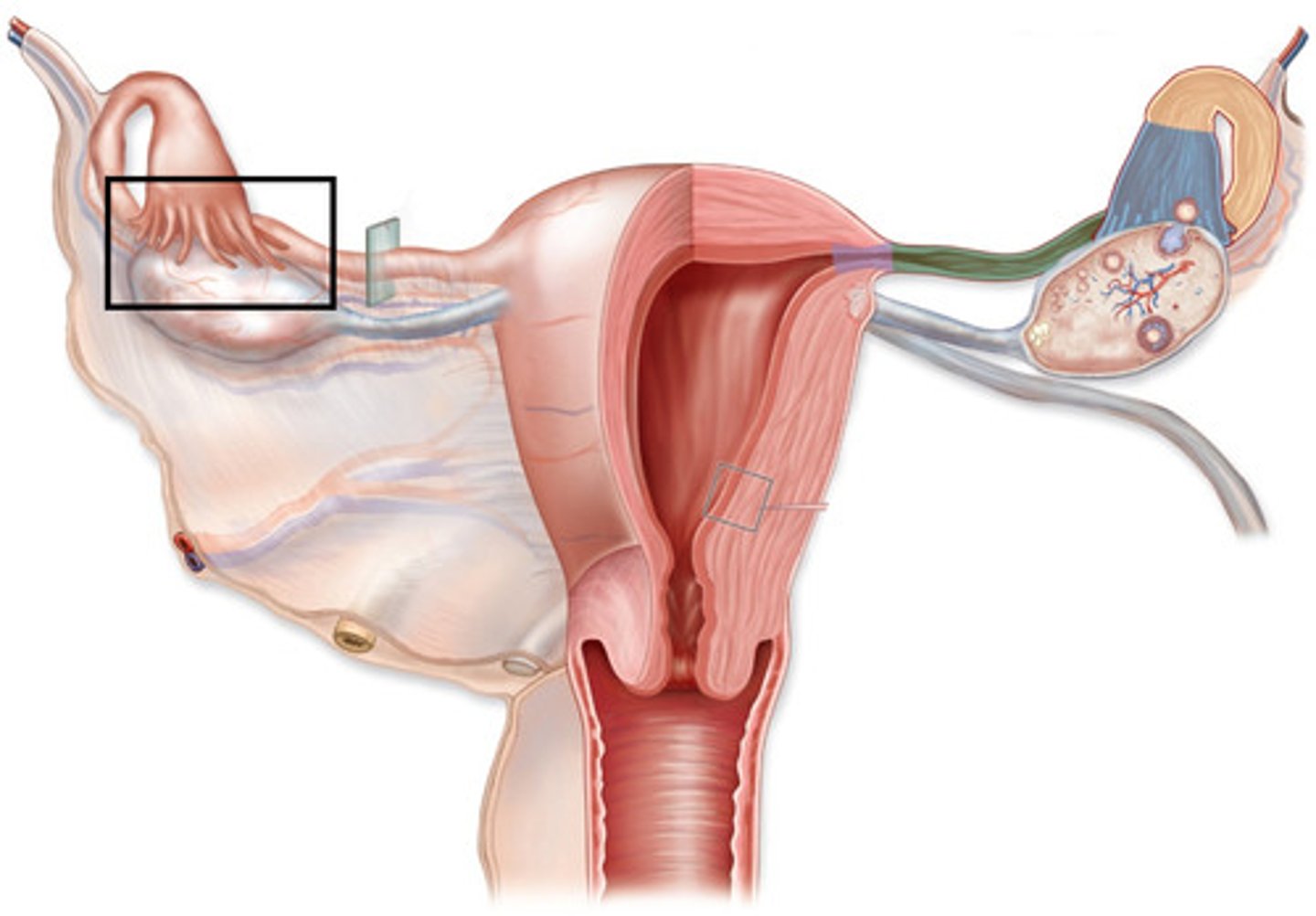
female reproductive system development
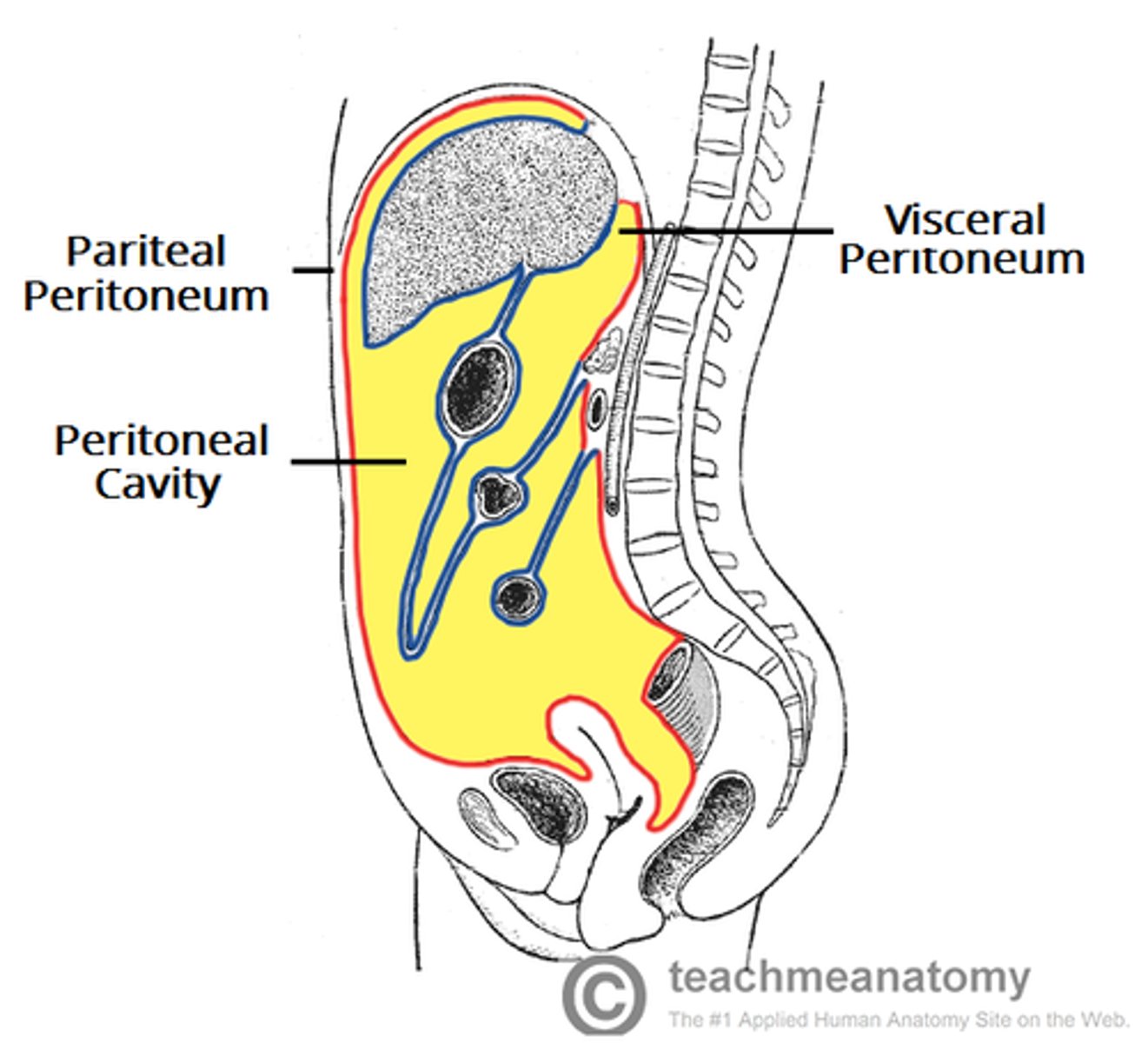
- ovaries, fallopian tubes and uterus are suspended in lower abdominal cavity by the peritoneum
- as they continue to develop a visceral peritoneum covers each of there surfaces
-----------------
similar to male
peritoneum features during development
1) some parts are retroperitioneal (behind abdominal/peritoneal cavity)
2) As they grow, a visceral peritoneum covers each surfaces
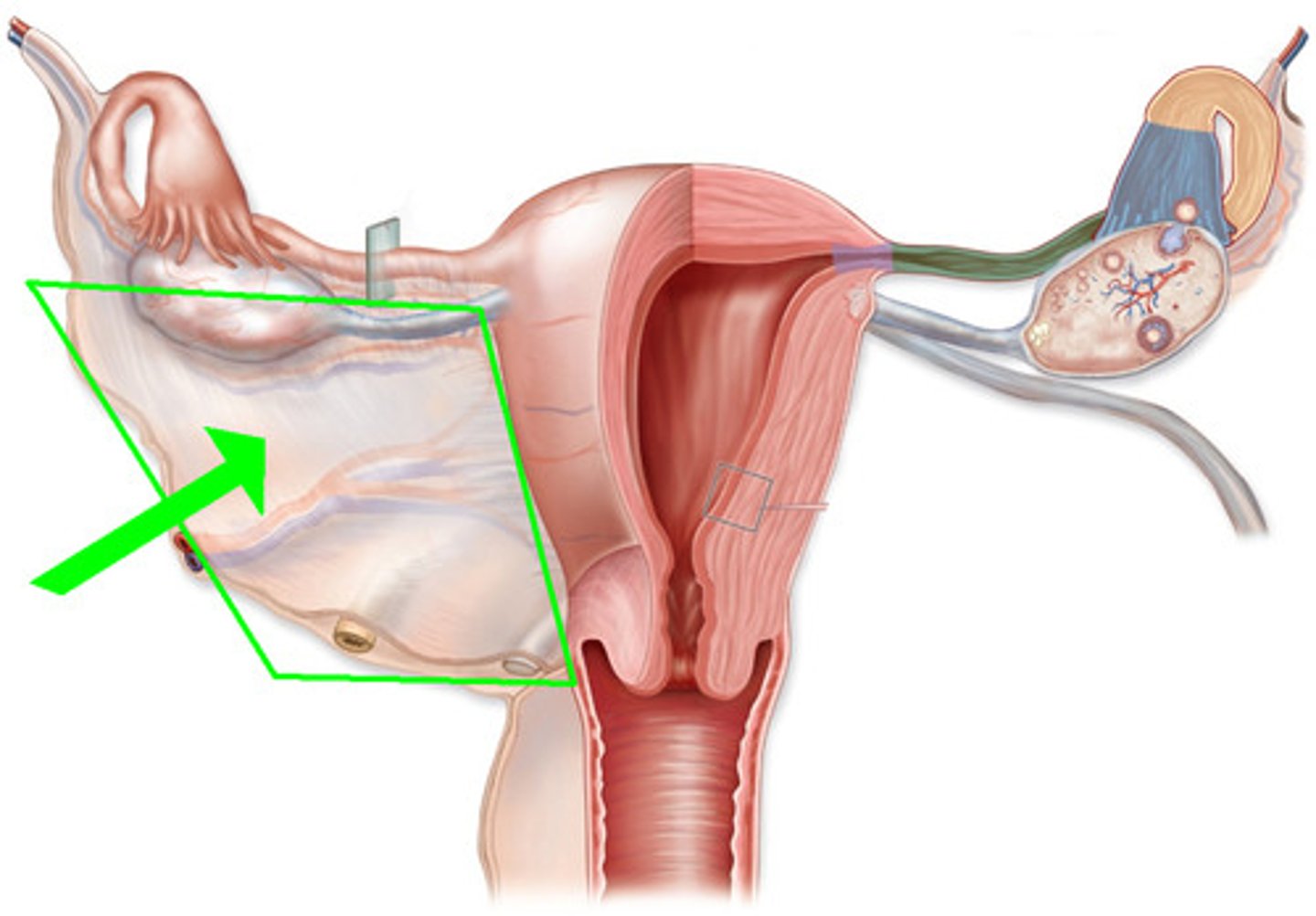
- broad ligament (posterior body wall)
broad ligament
DEFINITION
The ligament extending from the lateral margins of the uterus to the pelvic wall
-----------------
FUNCTION:
keeps the uterus centrally placed and provides stability within the pelvic cavity.
sections of broad ligament
- Mesometrium
- Mesovarium
- Mesoalpinx
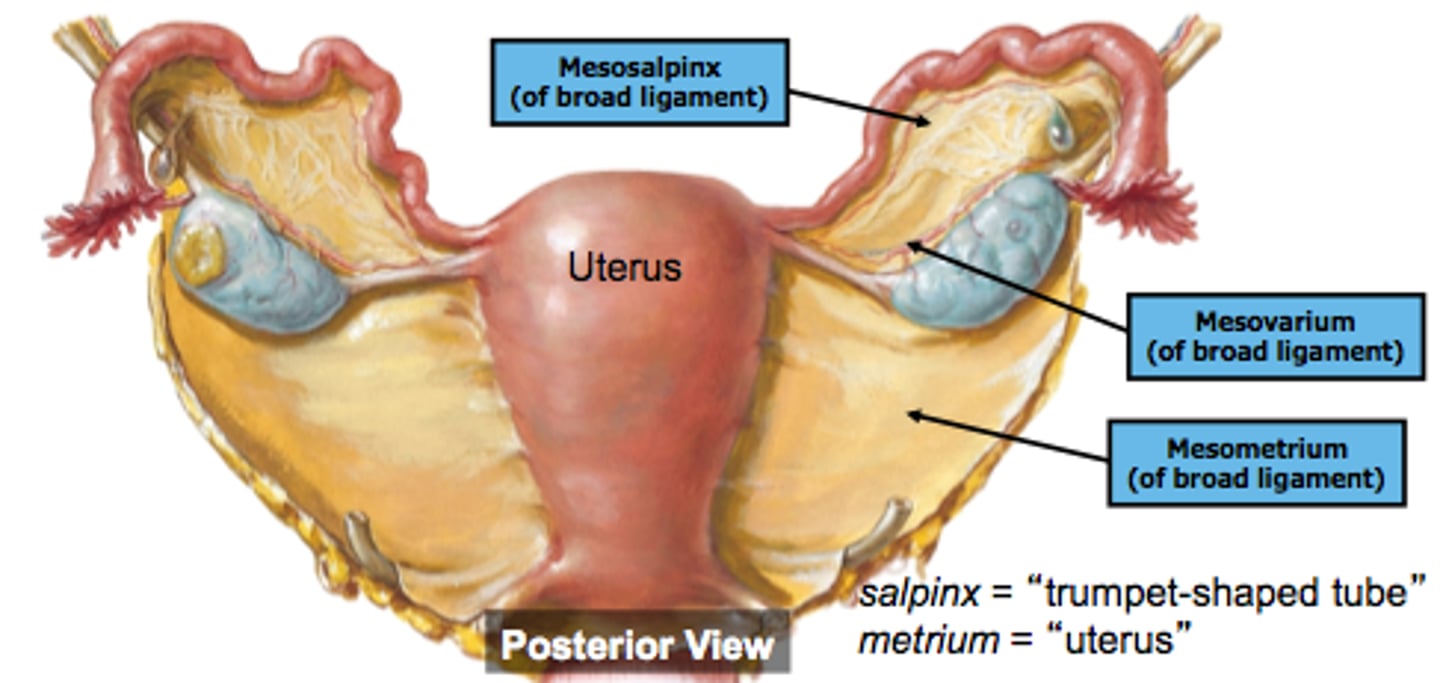
mesometrium
- section over uterus
- helps supports the uterus
mesovarian
- section thats over the ovary
- it anchors the ovary to the posterior surface of broad ligament
-----------------
- is the area where hilus and hilus cells are located
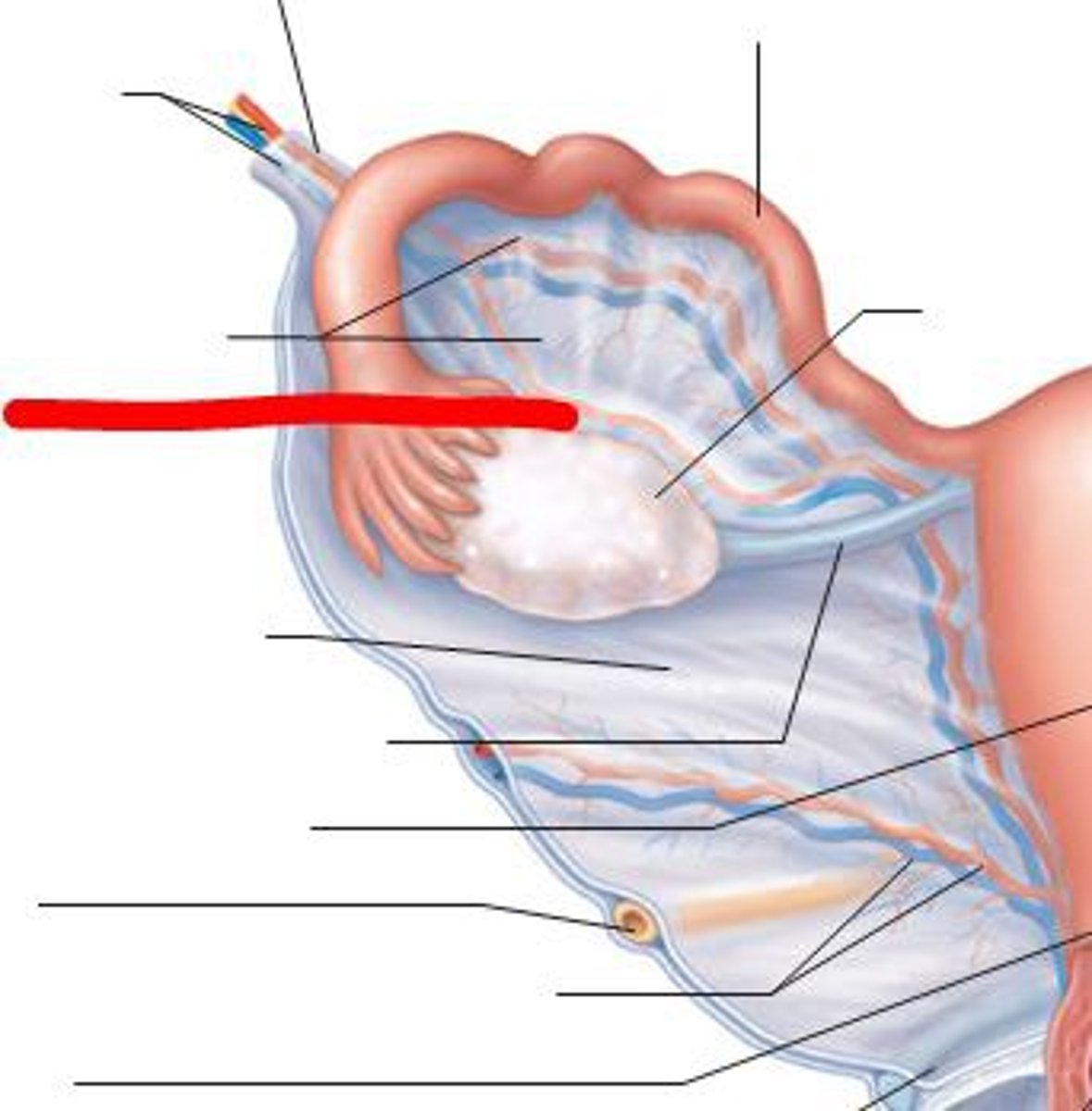
mesosalpinx
- section that over the fallopian tube
- the upper portion of the broad ligament that encloses the fallopian tubes
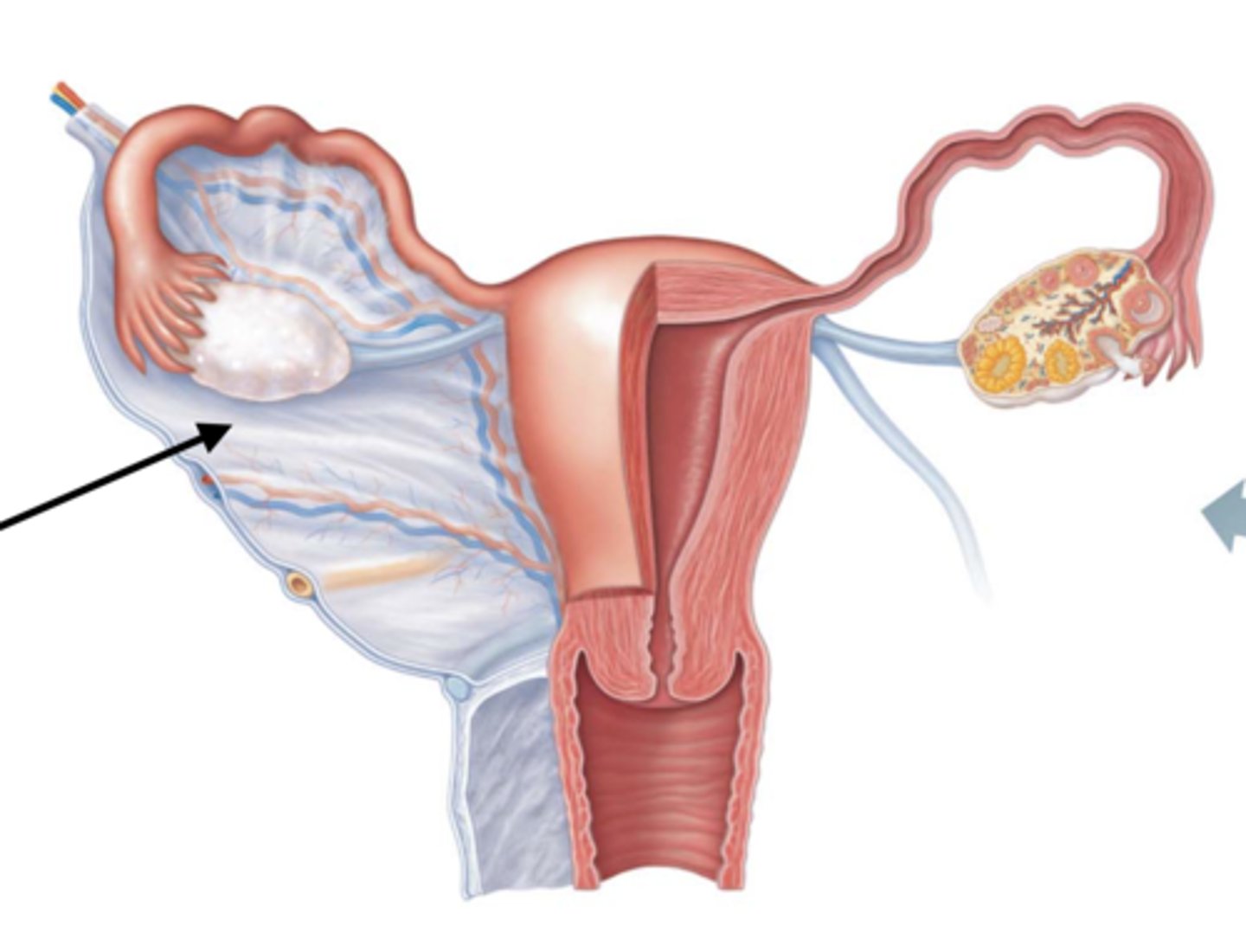
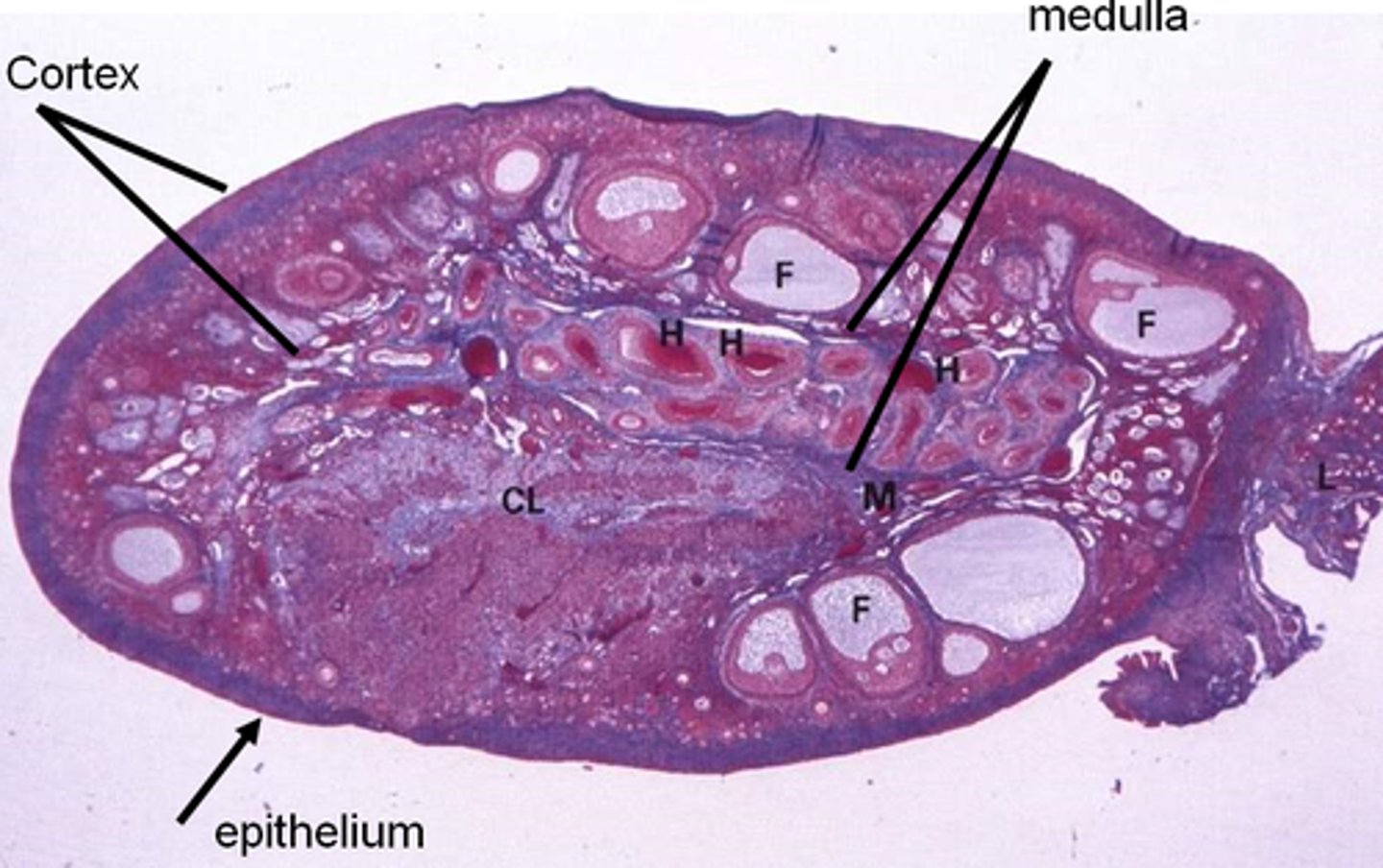
Ovary
the female primary sex organ
that held in place by dense fibrous CT to the uterus
-----------------
FEATURES:
- contains a continuous simple cuboidal germinal epithelium thats continious with the mesothelium of the peritoneal peritonium
Organization of the ovary
SUPERFICIAL
- contains a continuous simple cuboidal germinal epithelium that wraps around the whole ovary
- may appear simple squamous
(its continuous with the mesothelium of the peritoneal peritoneum)
-----------------
DEEP
- contains a dense irregular/ fibrous CT layer called tunica albuginea
- contains a ovarian cortex and medulla
Overian cortex
cellular filler space filled with a mixture of follicles and stroma (parenchyma cells, and CT fibers)
- located below the tunica albuginea
-----------------
FEATURES:
- nuclei is usually found higher
- contains weird alveolar dense CT
- is usually populated with lots of cells
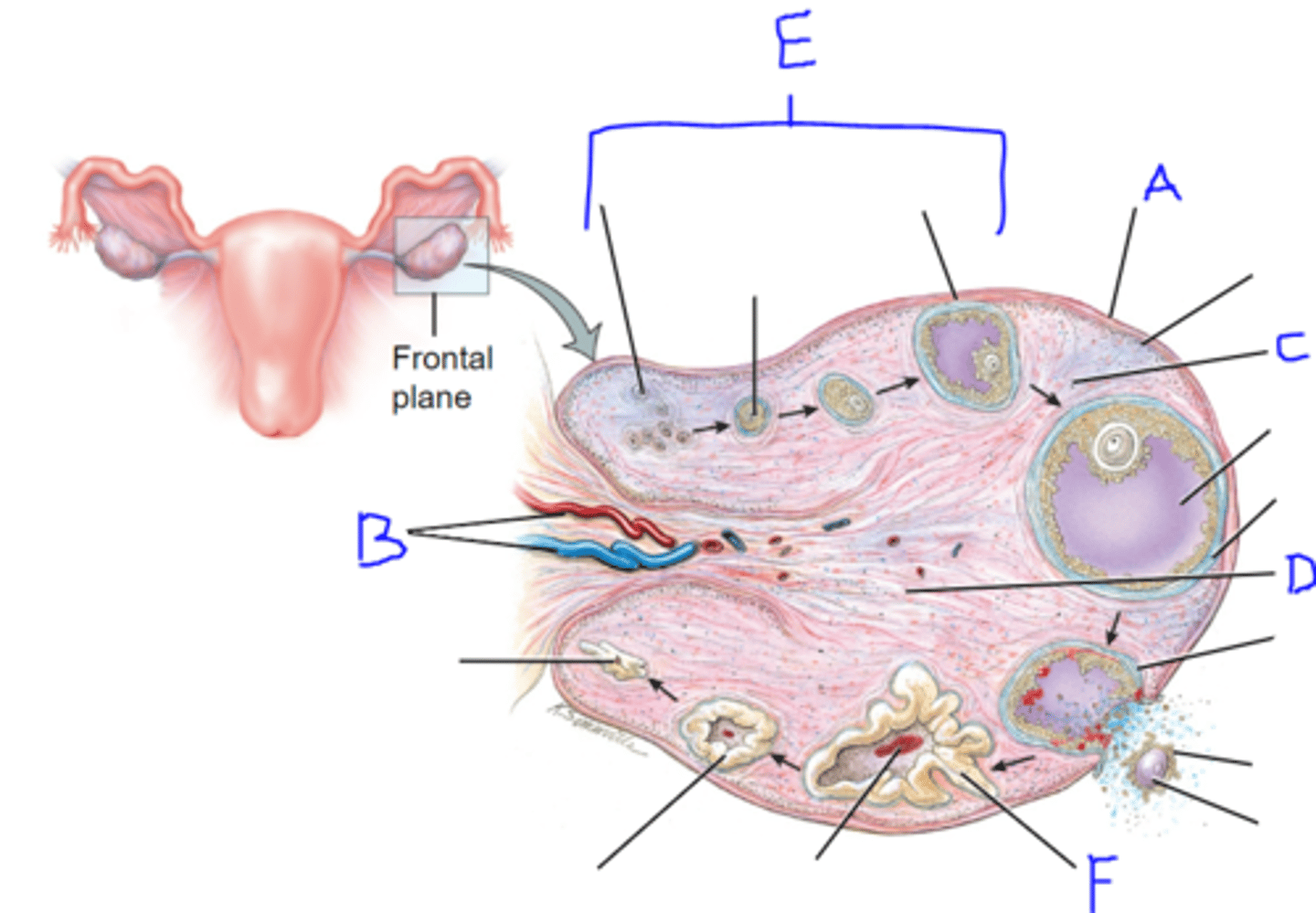
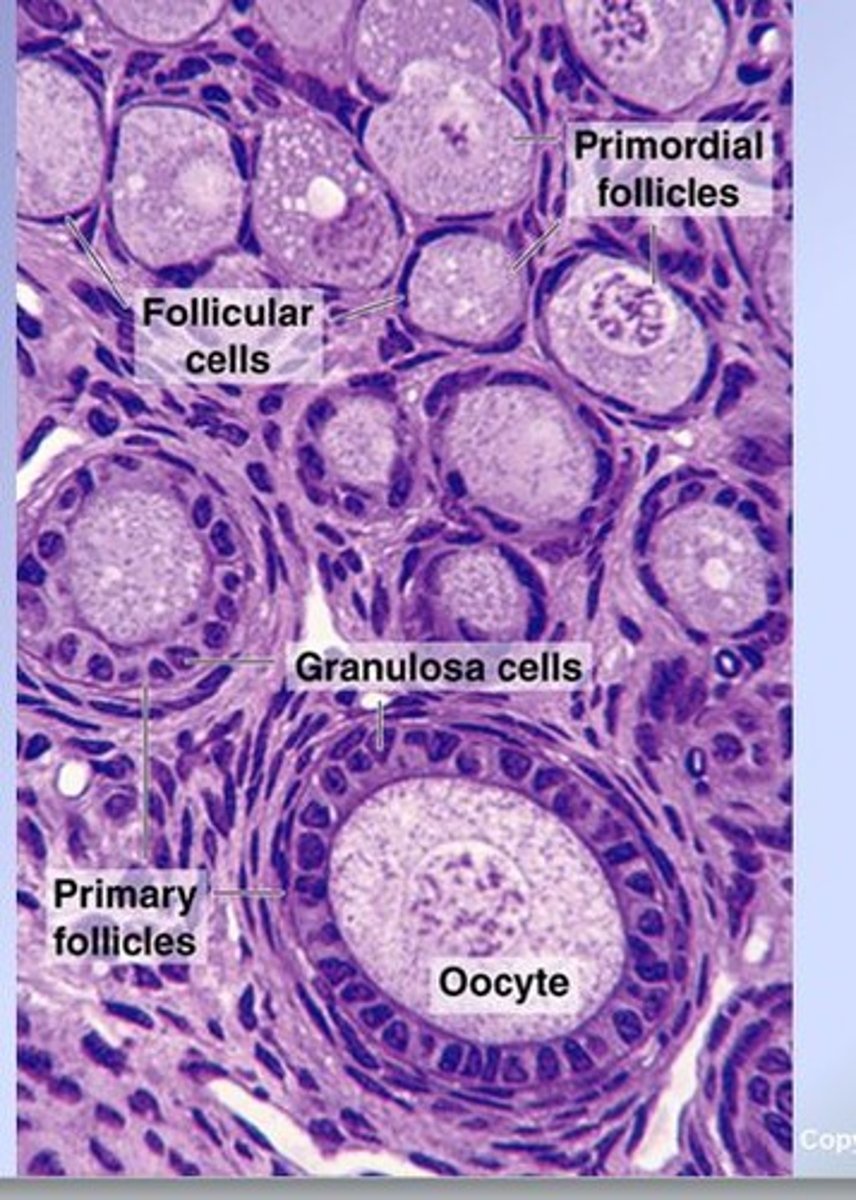
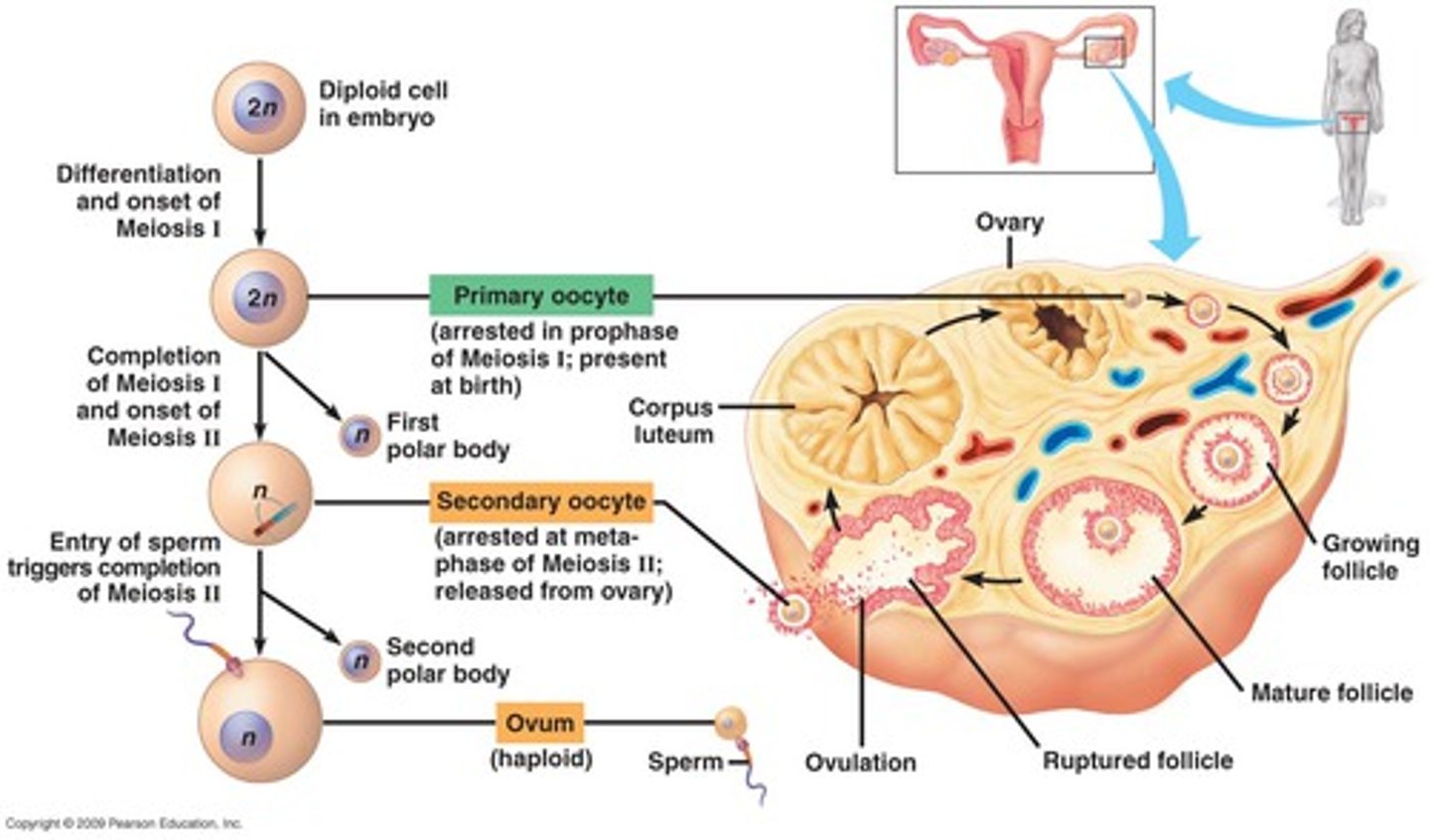
follicle development in ovary (PRE-DEVELOPMENT)
FROM BEGINNING TO MATURE
1) primordial follicle
2) primary follicle
- no antrum present
3) secondary follicle
- antrum present
4) Graafian follicle (MATURED)
- antrum surrounds ovum
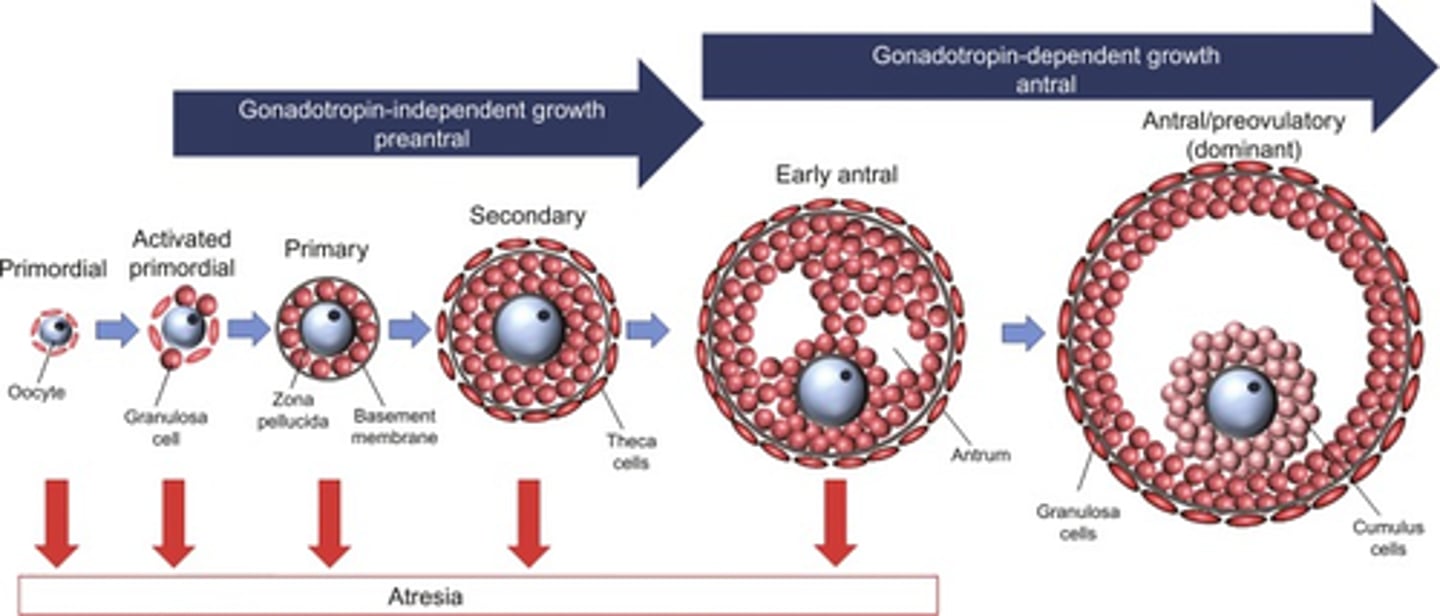
primordial follicle (pre-ovulatory)
FEATURES:
- contains 1 primary oocyte
- surrounded by simple squamous epithelium
- surrounded by follicle cells
-----------------
WHEN DOES IT OCCUR:
Follicular phase: (Ovarian C.)
- can become Corpus atretica
Menses phase: (Uterine C.)
primary follicle (pre-ovulatory)
KEY FEATURES:
- oocyte surrounded by simple/stratified cuboidal epithelium (changes during growth)
- contains a small antrum (w/ antral follicular fluid)
- contains Thecal layers w/ blood vessels
(glandular theca interna)
(muscular theca externa)
- NO ANTRUM PRESENT
-----------------
WHEN DOES IT OCCUR:
Follicular phase: (Ovarian C.)
- can become Corpus atretica
Proliferative phase: (Uterine C.)
primary follicle (PHASE 1-3 OOCYTE DEVELOPMENT)
FEATURES ARE DIVIDED INTO PHASES AS THEY GET BIGGER
-----------------
PHASE 1: Smaller Primary Follicle
- oocyte is surrounded by simple cuboidal epithelium
- oocyte starts to get bigger
-----------------
PHASE 2: Medium-Sized Primary Follicle
- oocyte gets bigger
- epithelium changes to stratified cuboidal
- Granulosa cells develop inside the follicle
- Theca Cells develop outside of follicle
-----------------
PHASE 3: Big primary follicle
- oocytes get bigger
- antrum starts to develop with antral follicular fluid flowing inside
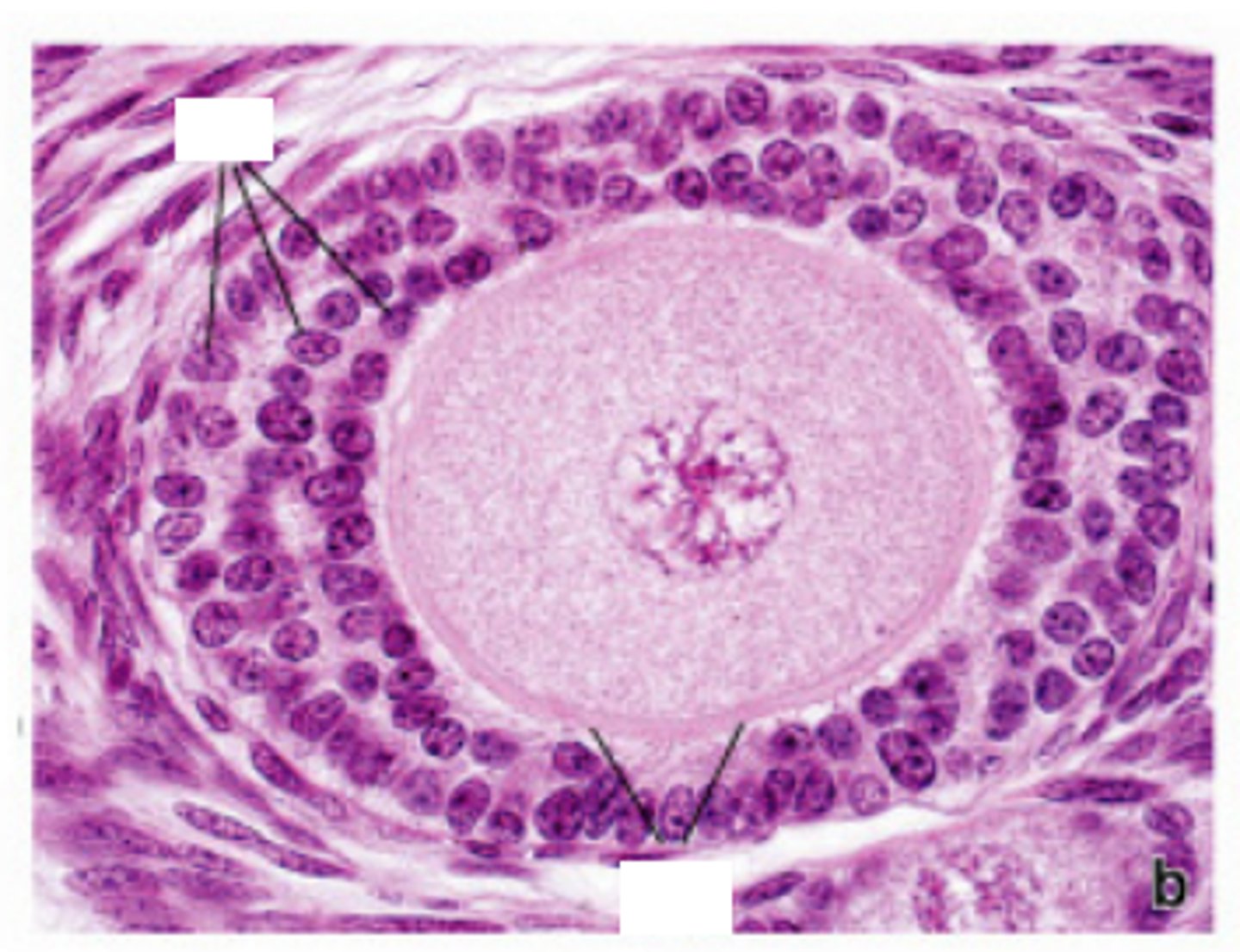
secondary follicle (pre-ovulatory)
a continuation of primary follicle development
-----------------
KEY FEATURES
- oocyte surrounded by stratified cuboidal epithelium
- contains a larger antrum (w/follicular fluid)
- follicular cells (increase of granulosa cells)
-----------------
WHEN DOES IT OCCUR
Follicular phase (Ovarian C.)
- can become a Corpus atretica
Proliferative phase (Uterine C)
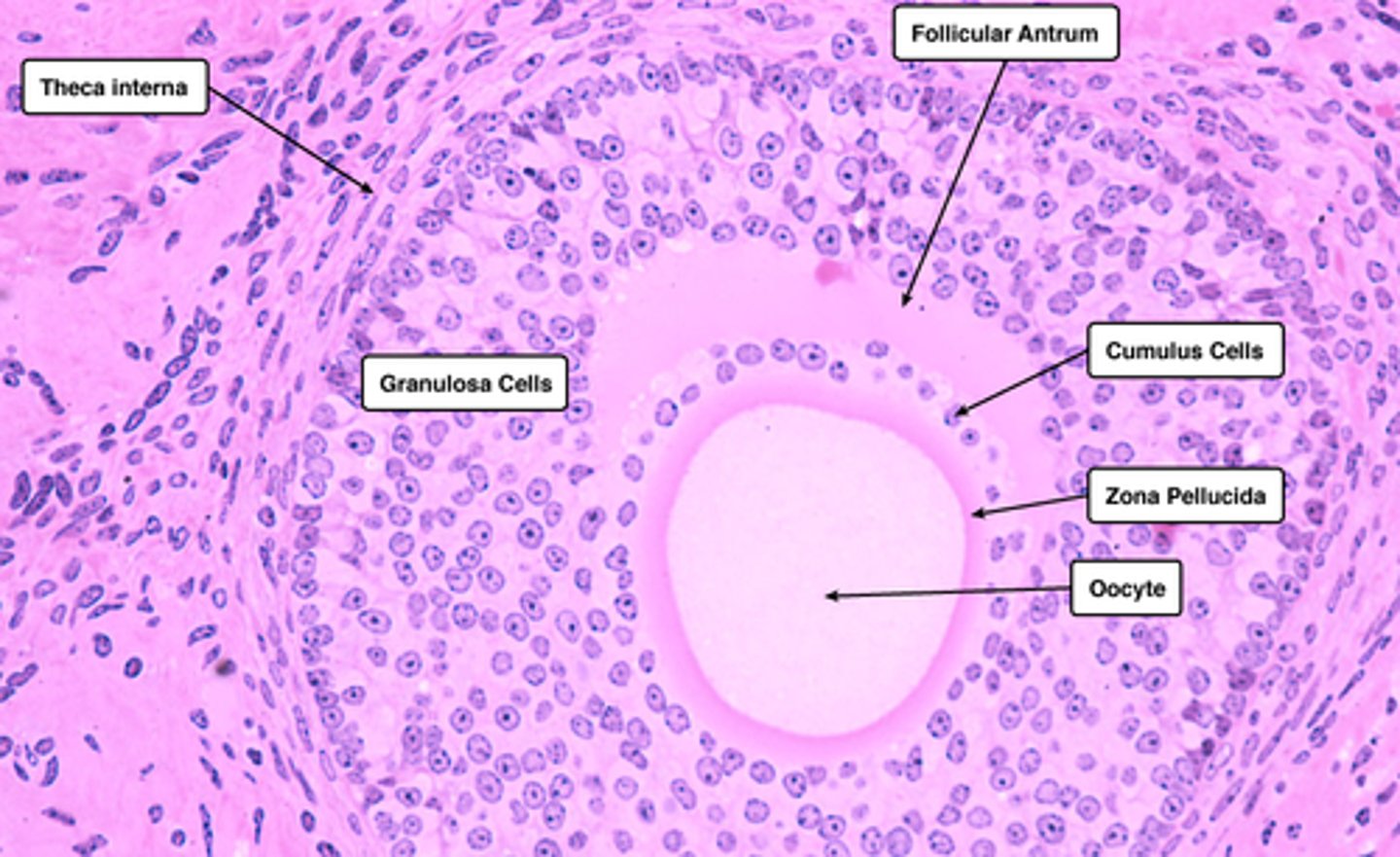
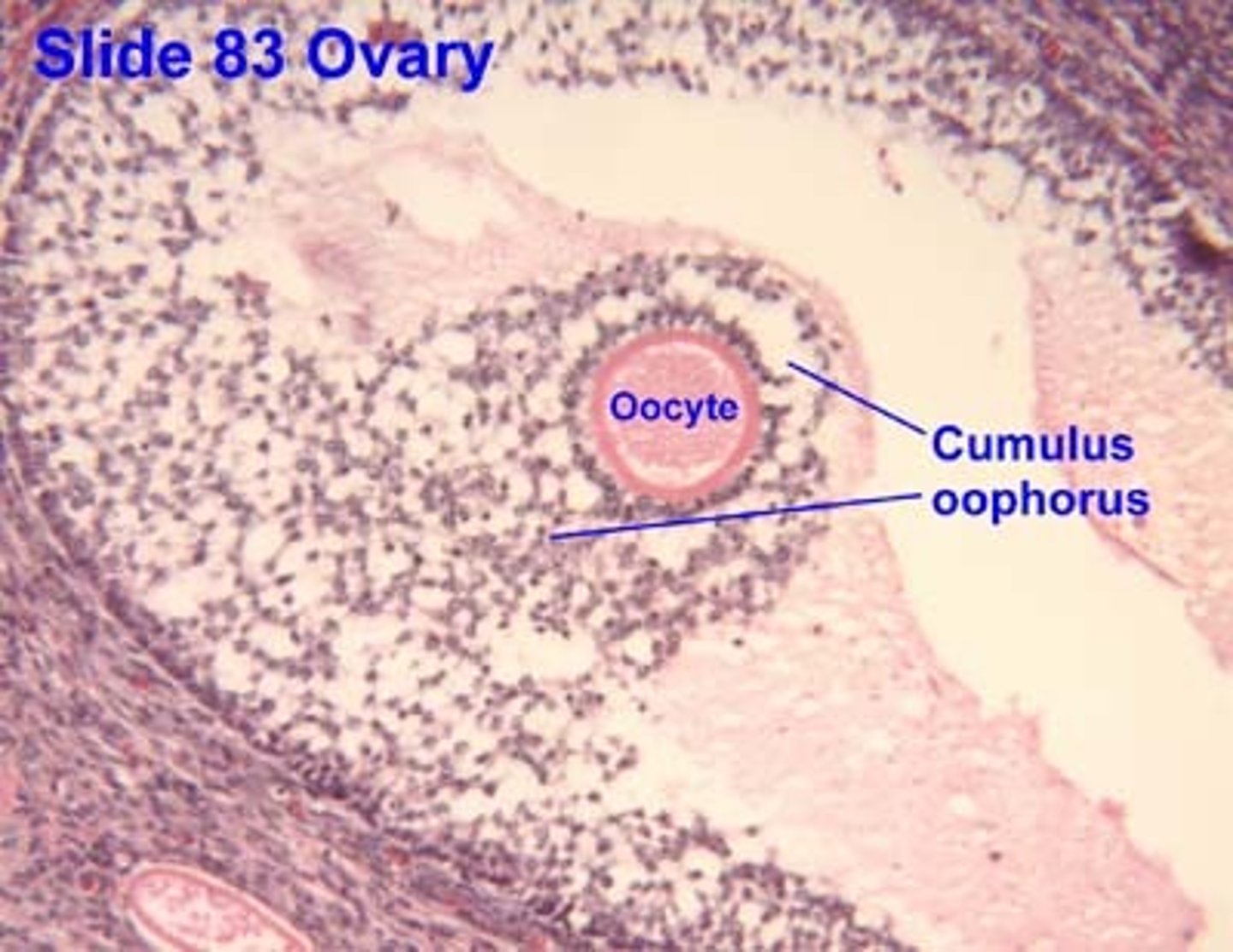
cumulus oophorus (secondary follicle)
a mound of granulosa cells on one side of the antrum that covers the oocyte and secures it to the follicular wall
-----------------
- "thin neck"
zona pellucida (secondary follicle)
A thick, transparent coating rich in glycoproteins that surrounds a primary oocyte.
-----------------
- thin covering that covers oocyte
-----------------
- Forms between granulosa cells and primary oocytes (an amorphous glycoprotein layer)
corona radiata (secondary follicle)
Outer layer of cells surrounding the oocyte.
- These cells are secreted by follicle cells.
-----------------
- membranous granulosa that covers the oocyte
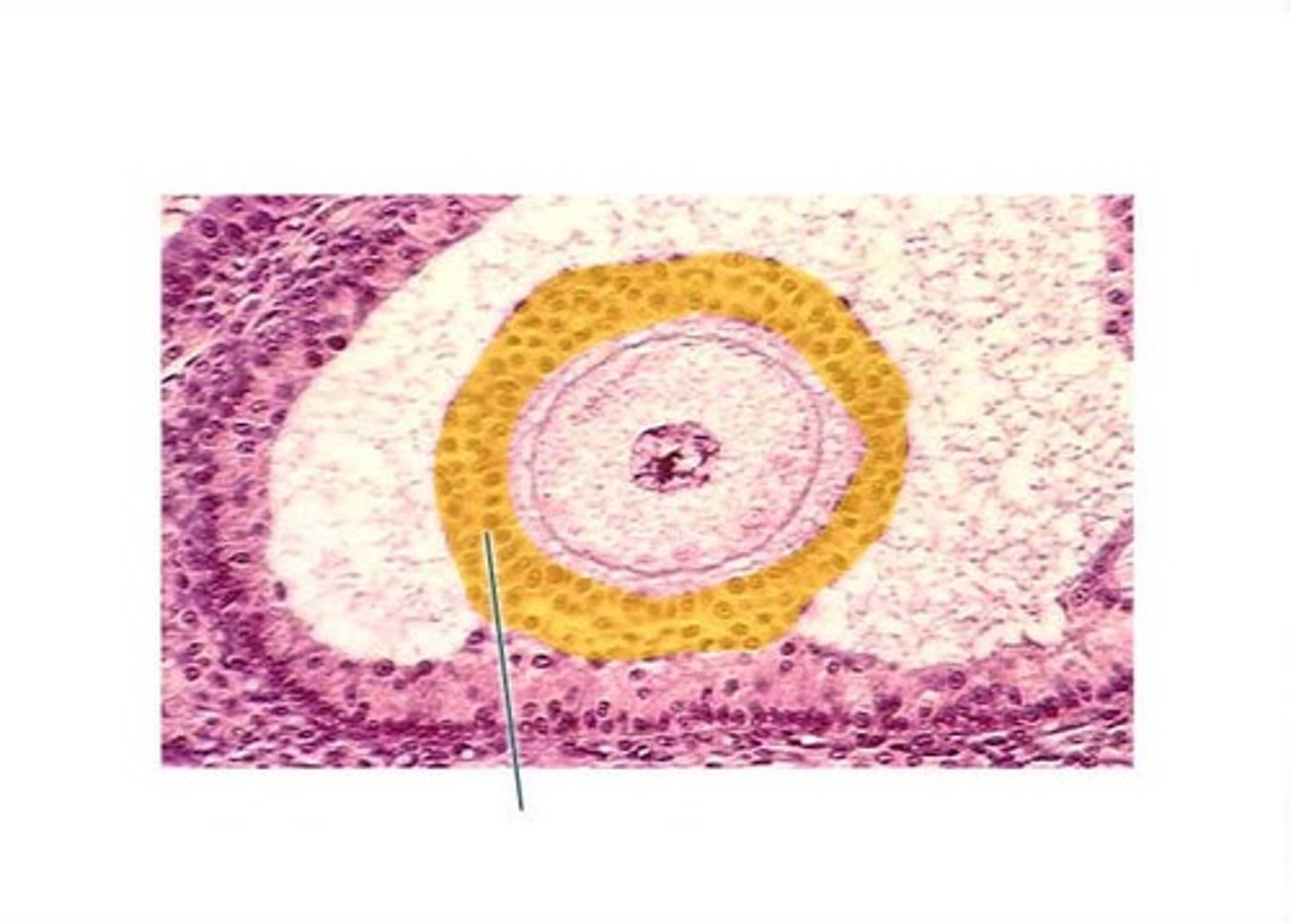
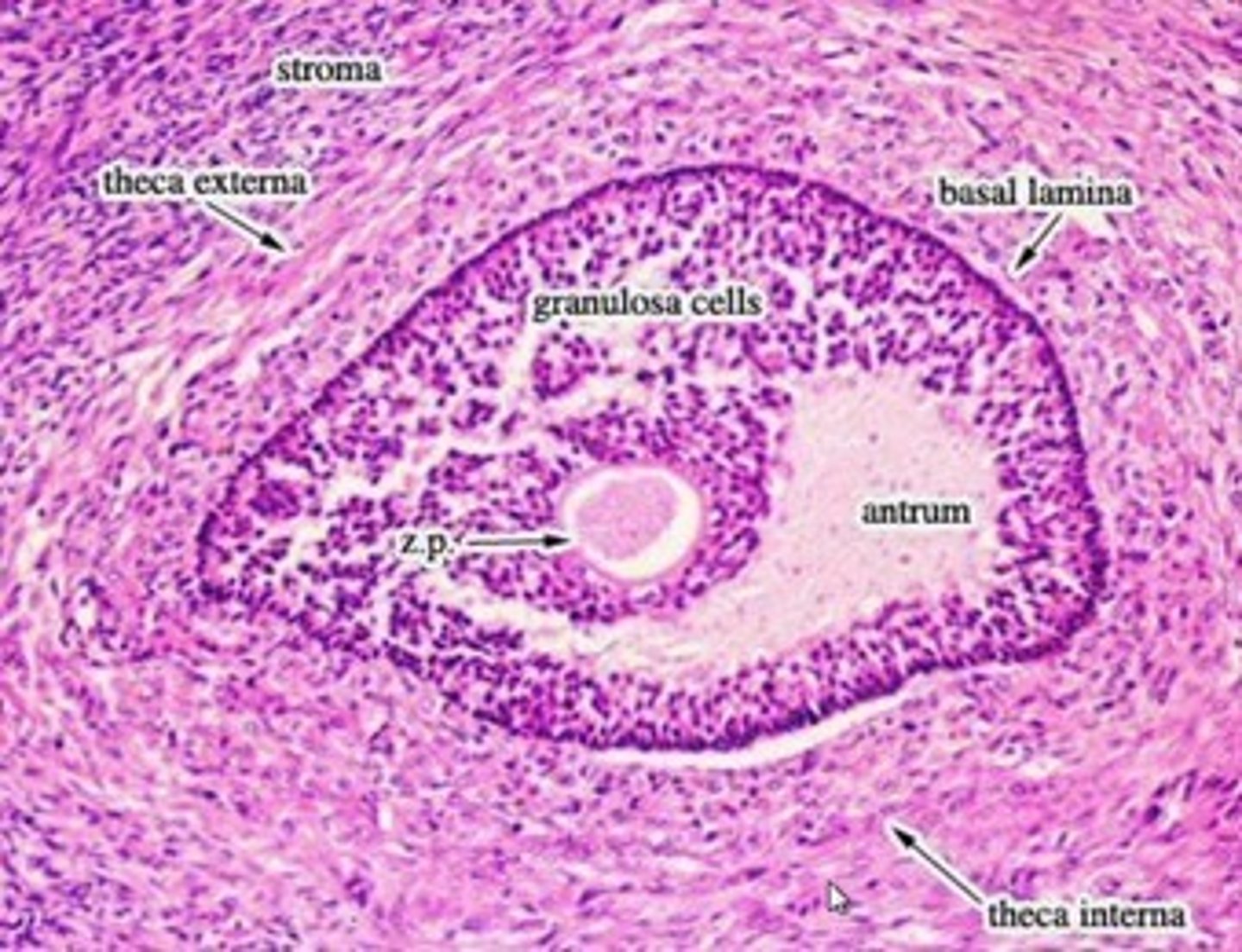
Graafian follicle (mature) (pre-ovulatory)
mature follicle
- antrum expands making a crest (surrounds the ovum)
-----------------
FEATURES:
- bigger antrum
- theca layers present (interna + externa)
- granulosa present
- cumulus oophorus present
- zona pelucida present
-----------------
WHEN DOES IT OCCUR
Follicular phase (Ovarian C.)
Proliferative Phase (Uterine C.)
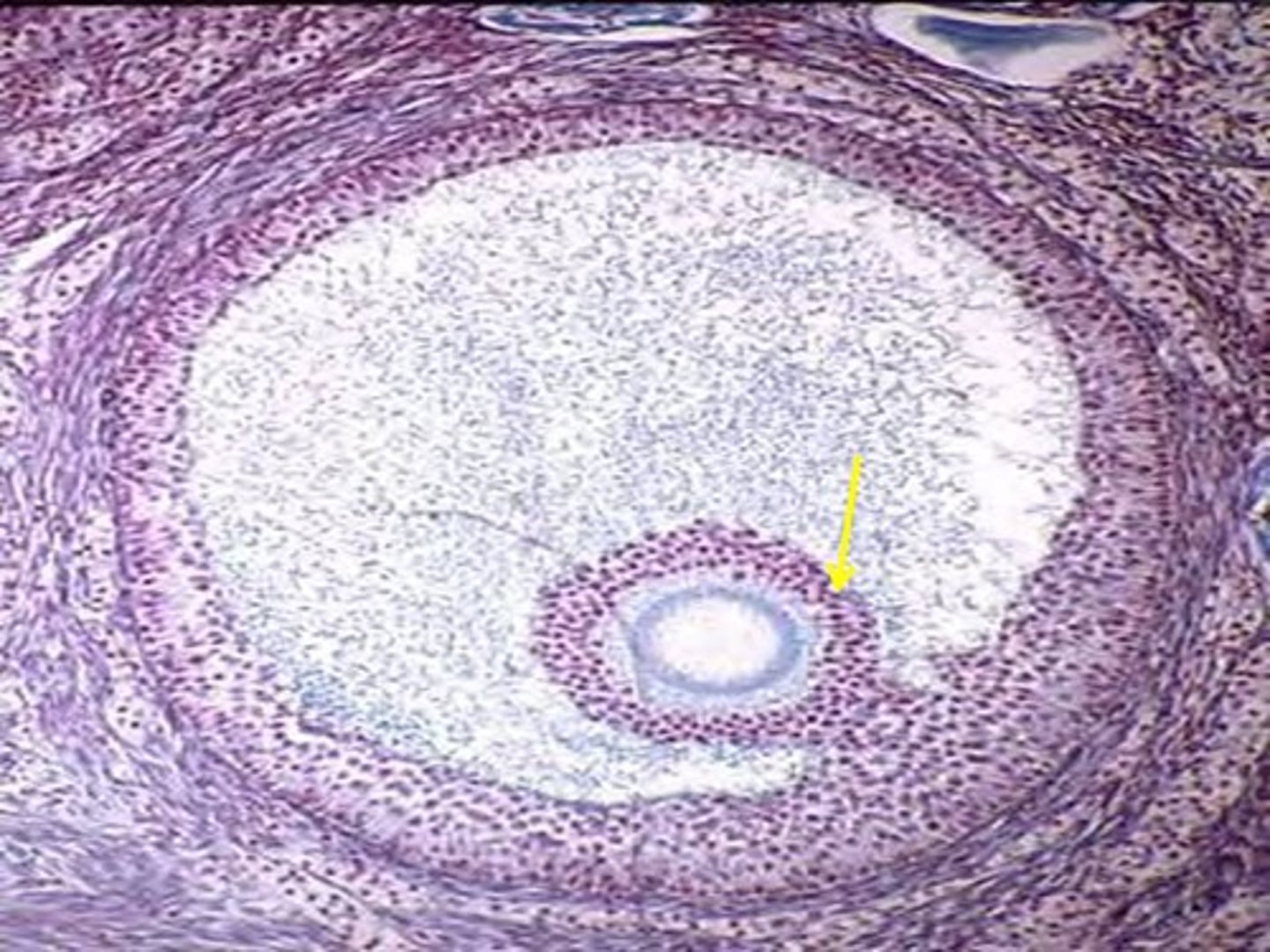
What does a Graafian follicle do/WHEN DOES IT OCCUR
Graafian follicle ruptures and releases the ovum during:
- Ovulation phase (near end of Follicular phase) Ovarian C.
- Proliferative phase (Uterine C.)
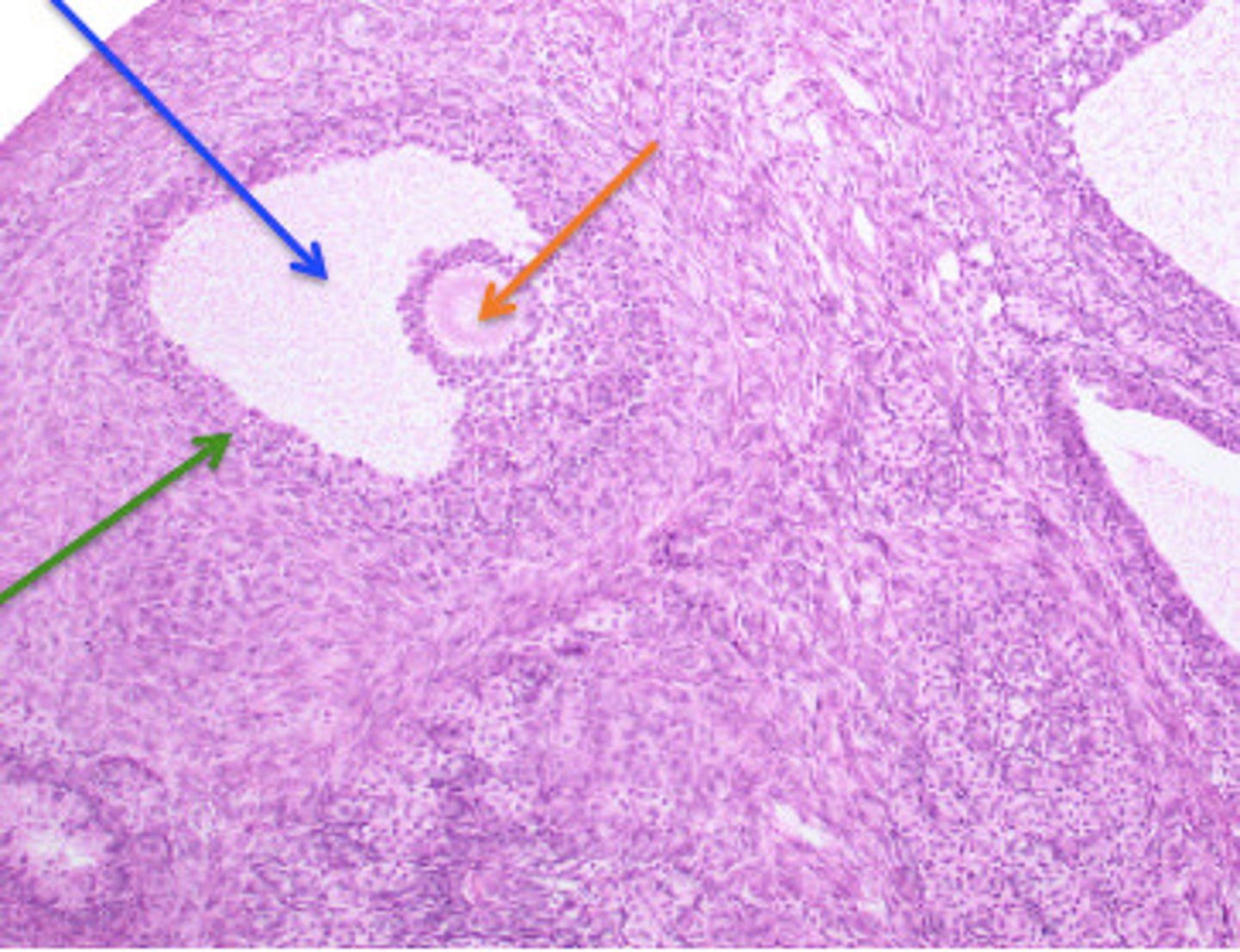
post ovulatory (follicle development)
Occurs when the ovulatory follicle is released
-----------------
FROM BEGINNING TO DEATH
1) corpus hemorrhagicum
2) corpus luteum
3) corpus albicans
4) corpus atretica
Corpus Hermorrhagicum (post ovulatory)
the blood filled remnant of the ovarian follicle immediately after ovulation
- its where the luteal phase starts
-----------------
BOOK VER.
- its under the influence of LH
- follicle cells that are remaining in the ovary fold inward on themselves
- antrum fills with blood to form ___
-----------------
WHEN DOES IT OCCUR
Luteal phase (Ovarian C.)
Secretory phase (Uterine C.)
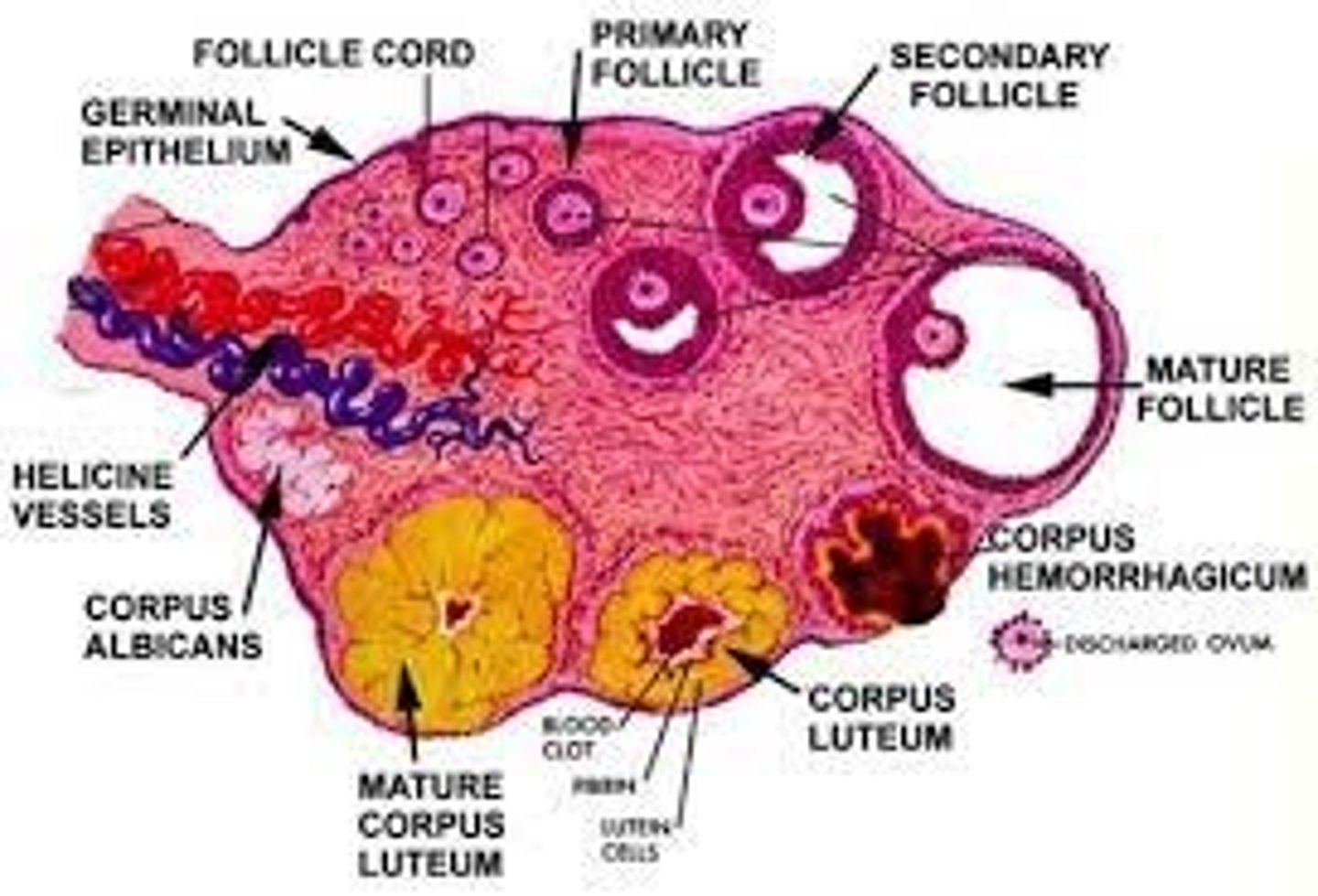
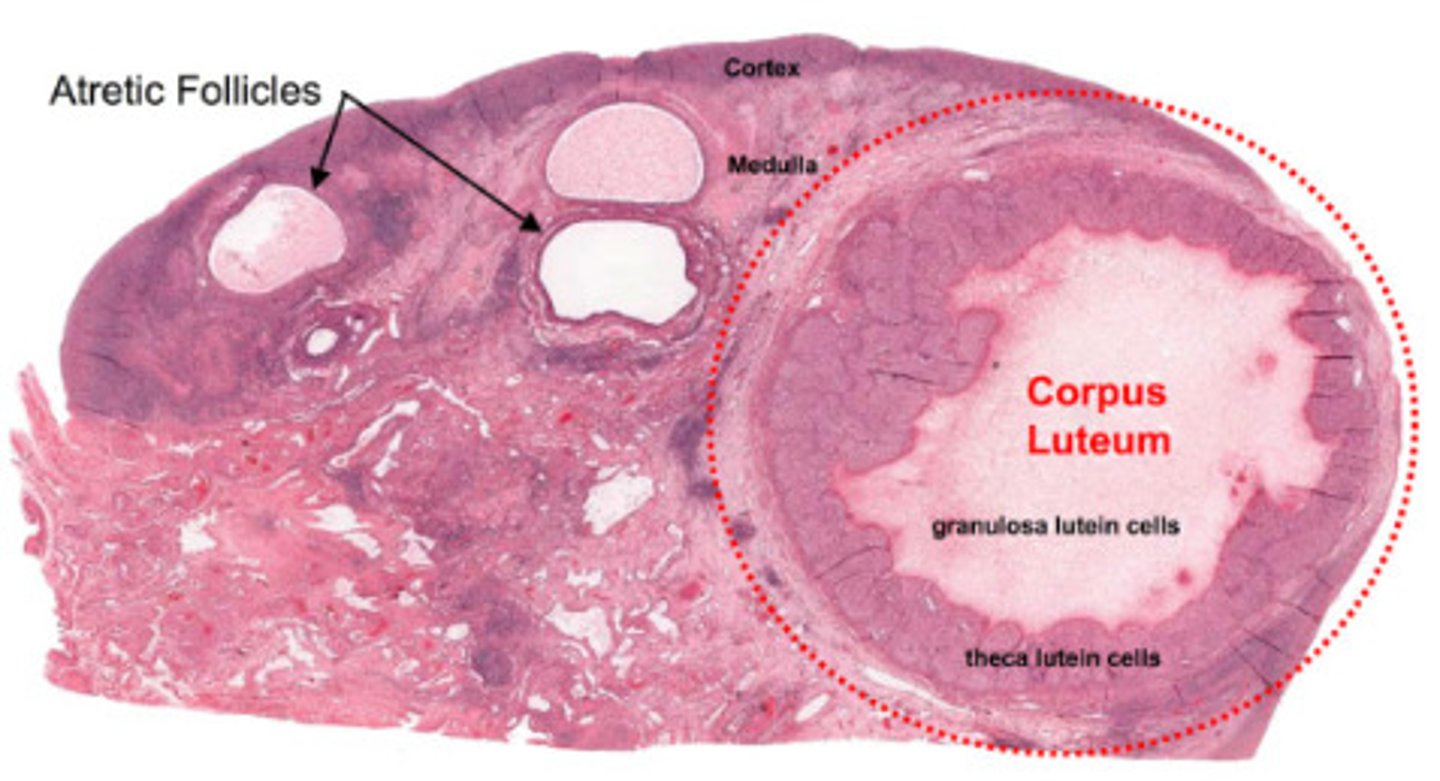
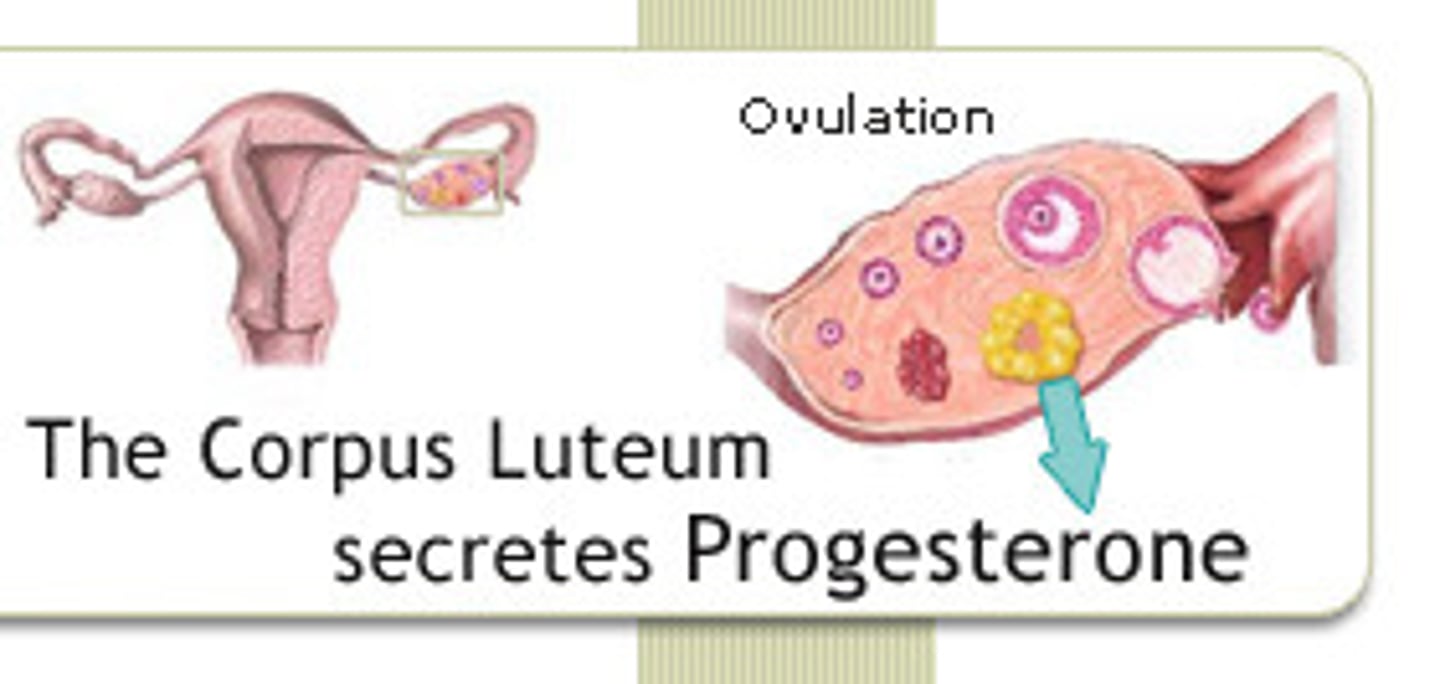
corpus luteum (post ovulatory)
a highly vascularized empty ovarian follicle (Derived from granulosa cells)
- area that secretes progesterone, estrogen and inhibin to prepare the uterine lining for receiving an embryo
-----------------
FEATURES:
- contains a yellow body
- highly vascularized
- maintenance of a uterine environment that allows for implementation and pregnancy
-----------------
WHEN DOES IT OCCUR
Luteal phase (Ovarian C.)
Secretory phase (Uterine C.)
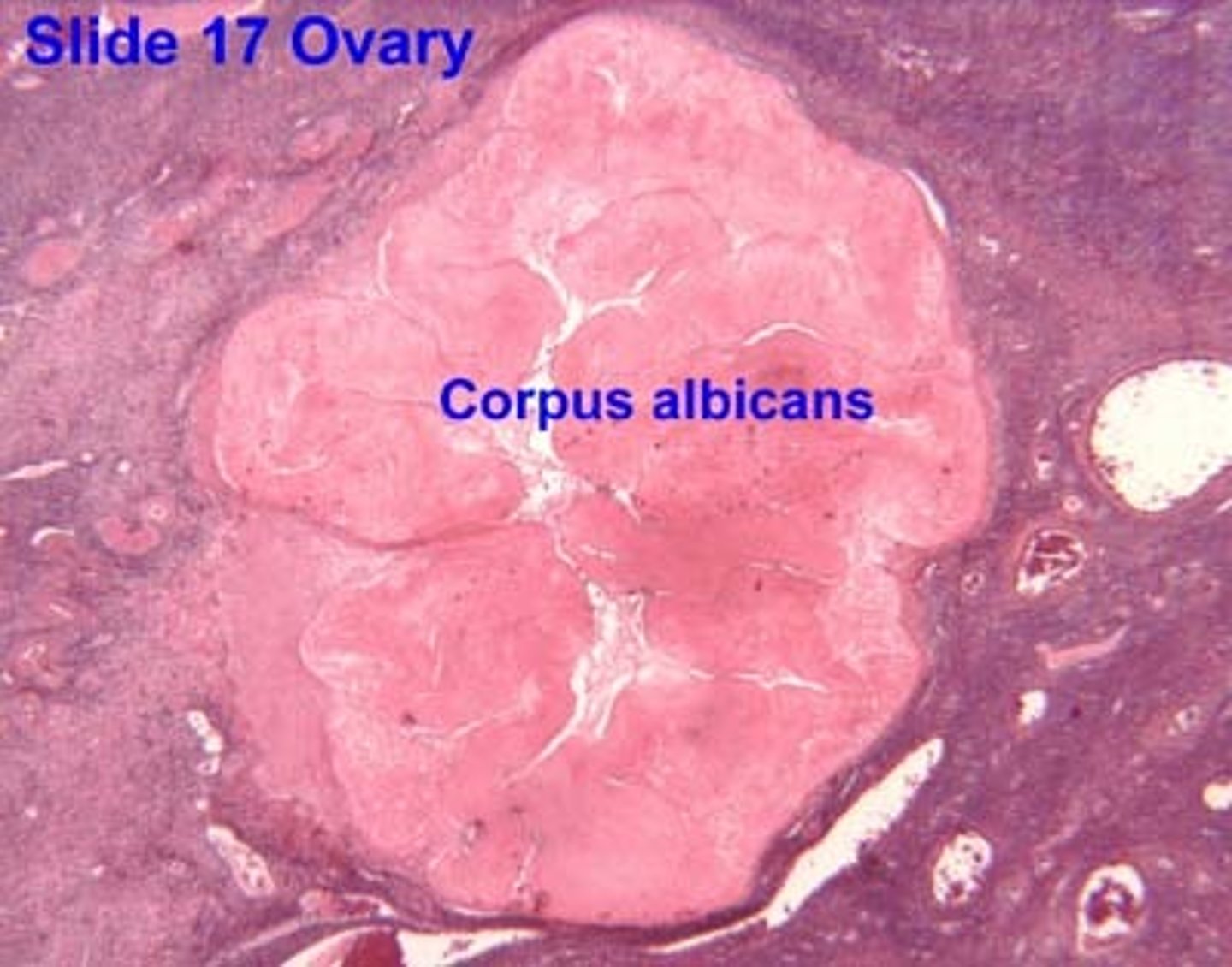
corpus albicans (post ovulatory)
a disintegrated corpus luteum that leads to the follicles death
- contains scar tissue w/ fibroblasts
-----------------
BOOK VER.
- a failed fertilization due to the death of the corpus of lutein cells
- becomes replaced with fibroblasts that form scar tissue called ___
-----------------
WHEN DOES IT OCCUR
Luteal phase (Ovarian C.)
Secretory phase (Uterine C.)
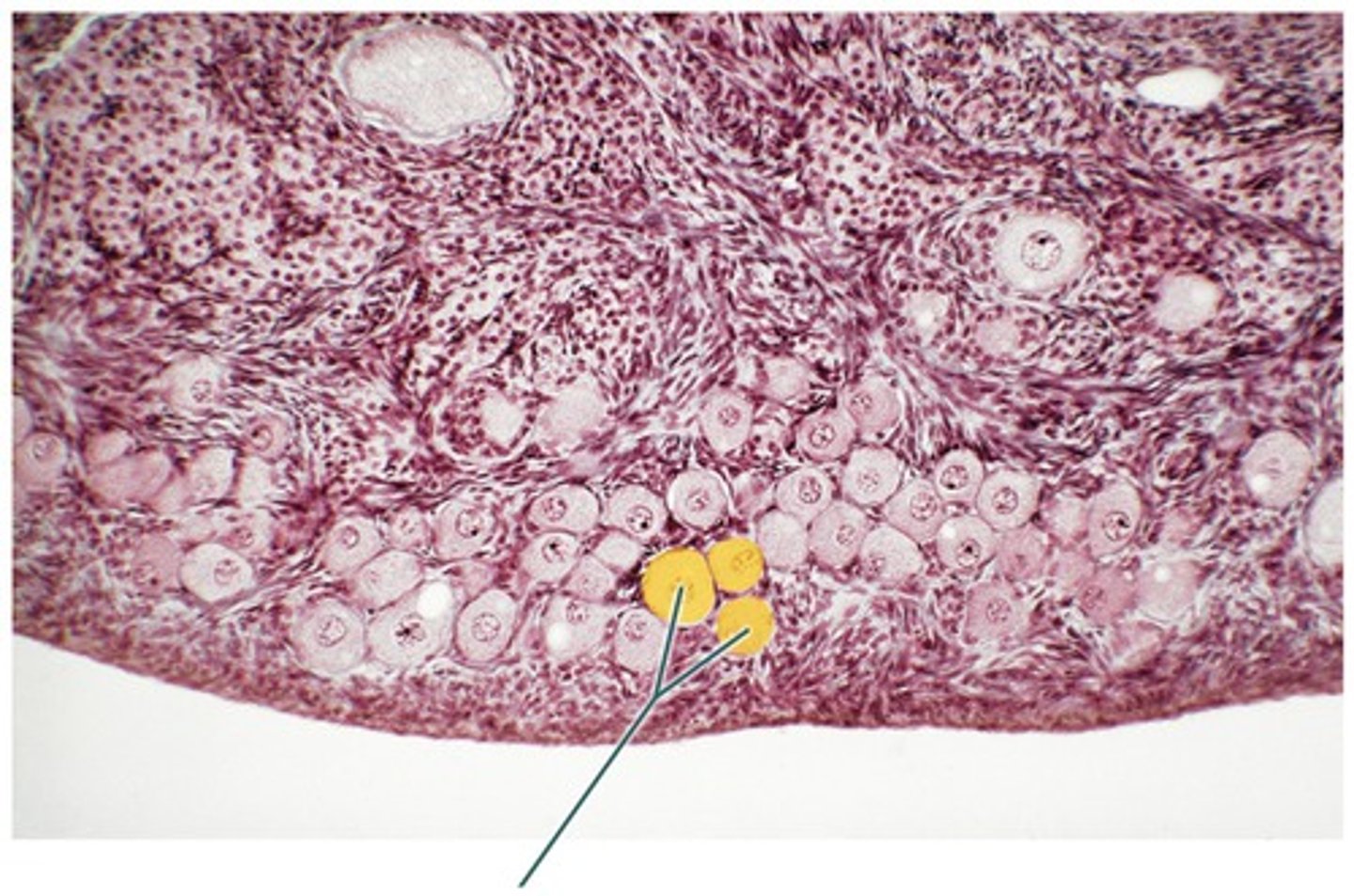
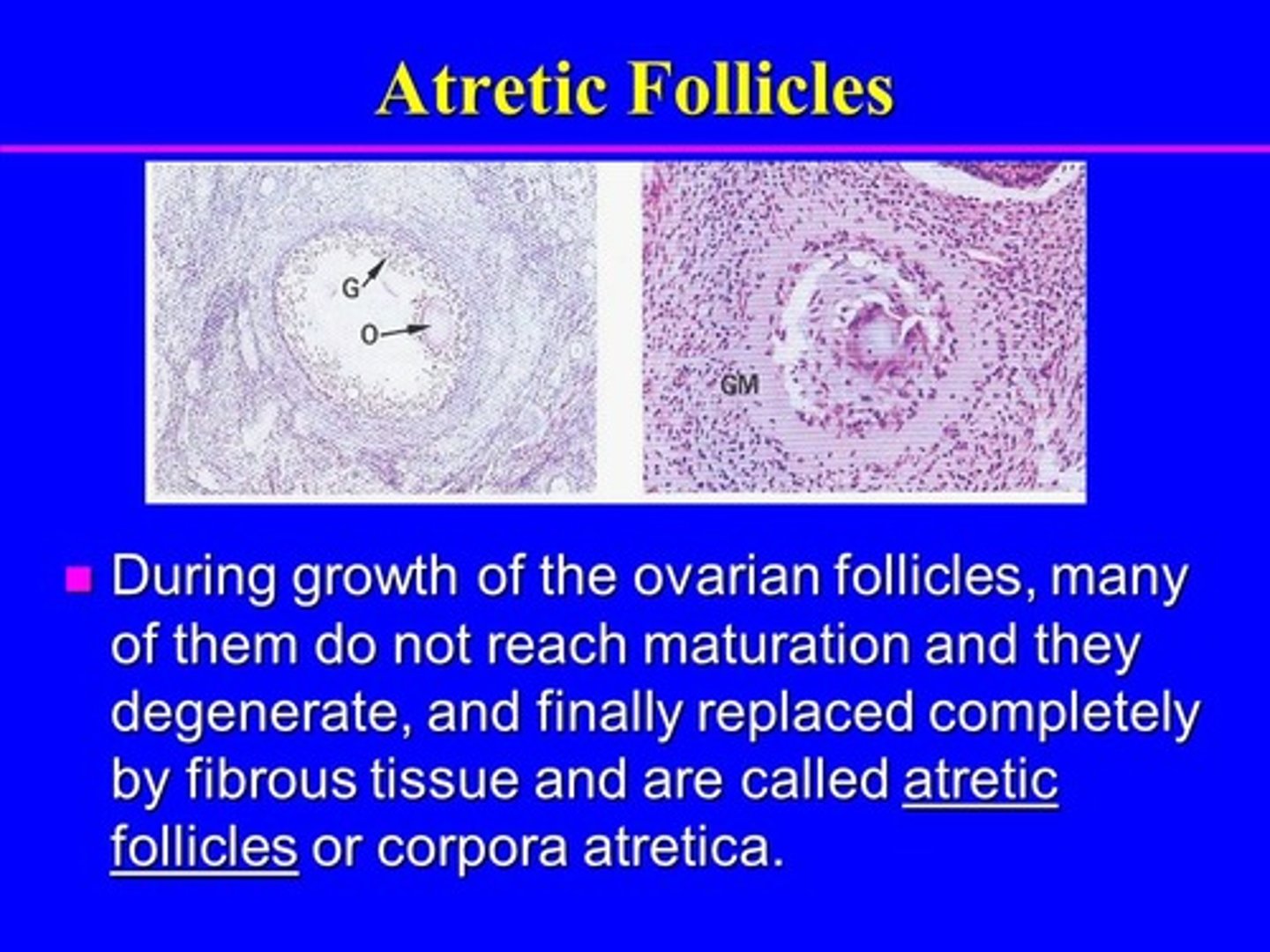
corpus atretica
shrinkage of the ANY follicle that results in a "more purposeful death"
-----------------
can happen any follicle from the process of primordial to secondary follicles
-----------------
WHEN DOES IT OCCUR
Follicular phase (Ovarian C.)
Meses + Proliferative (Uterine C.)
follicle cells
- theca cells
- granulosa cells
- follicular antrum
theca cells
estrogen-producing cells in a maturing ovarian follicle
- are produced outside the ovarian follicle
-----------------
FEATURES
- they are under the influence of FSH
- are usually found in primary and secondary follicles (during development)
Theca layers
- theca interna
- theca externa
-----------------
usually present in
- primary follicle
- secondary follicle
- Graafian follicle
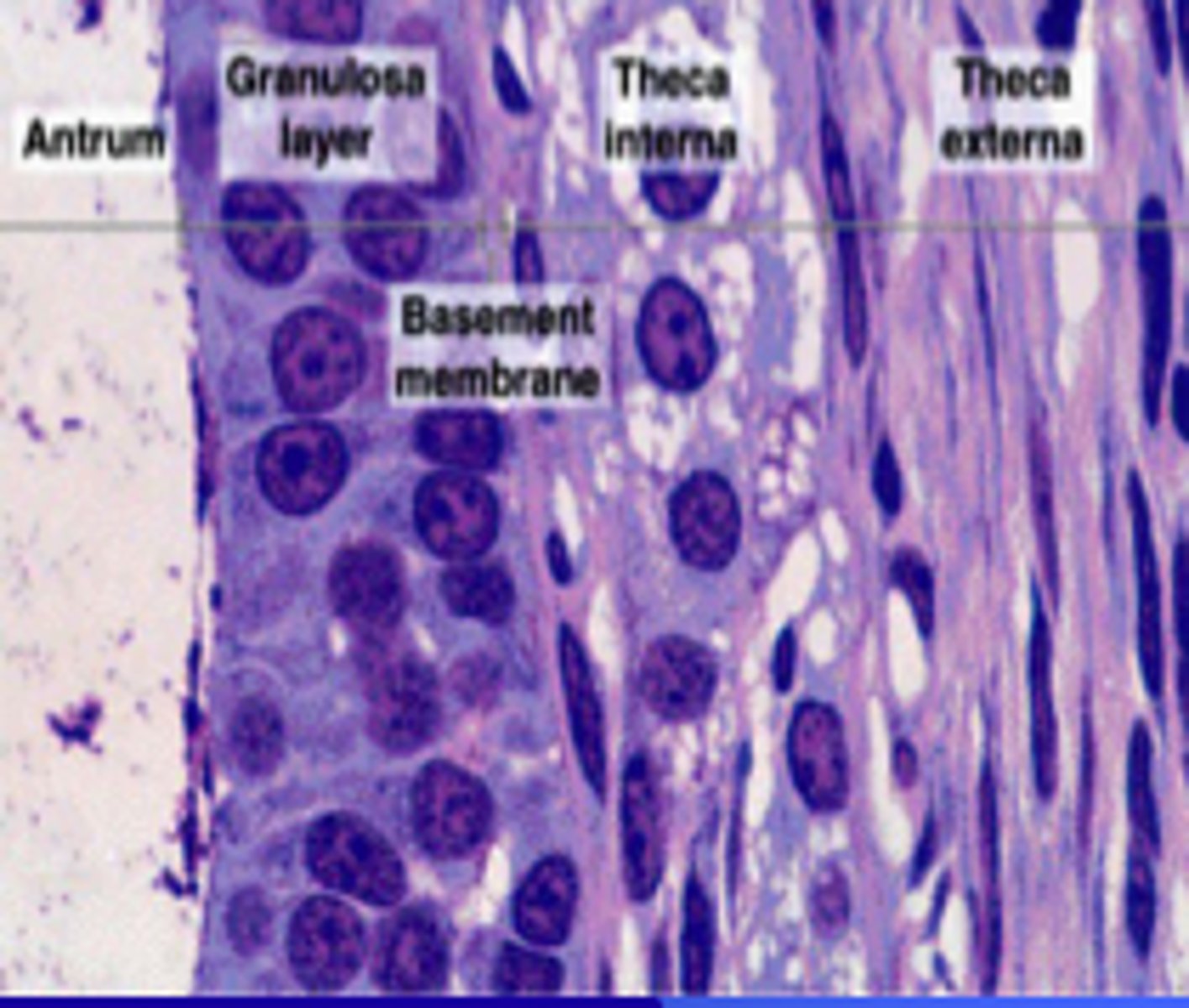
theca interna
a richly vascularized layer that contains a flattened spindle-shaped cells that produce androgens
(primarily progesterone)
-----------------
- glandular w/ capillaries
theca externa
a highly fibrous layer that contains collagen fibers
-----------------
- muscular layer
granulosa cells
cells that are formed during the development of the secondary follicle
- cells that surround the zona pellucida
-----------------
FEATURES
- majority of there cells surround the oocyte/ovum within (inside) the follicle
- secrete estrogen during the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle (before ovulation)
- cells that transition from simple cuboidal and stratified cupoidal
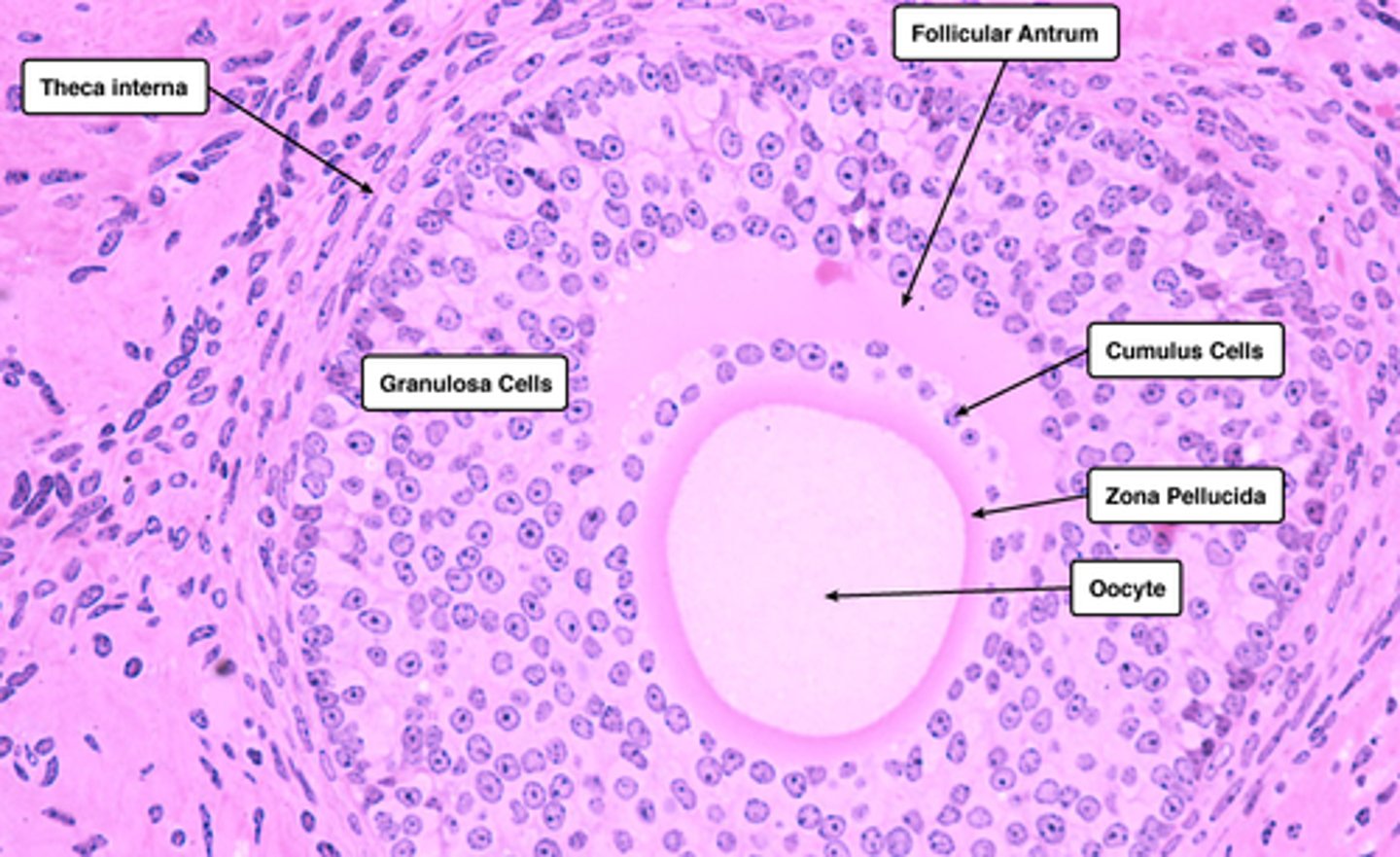
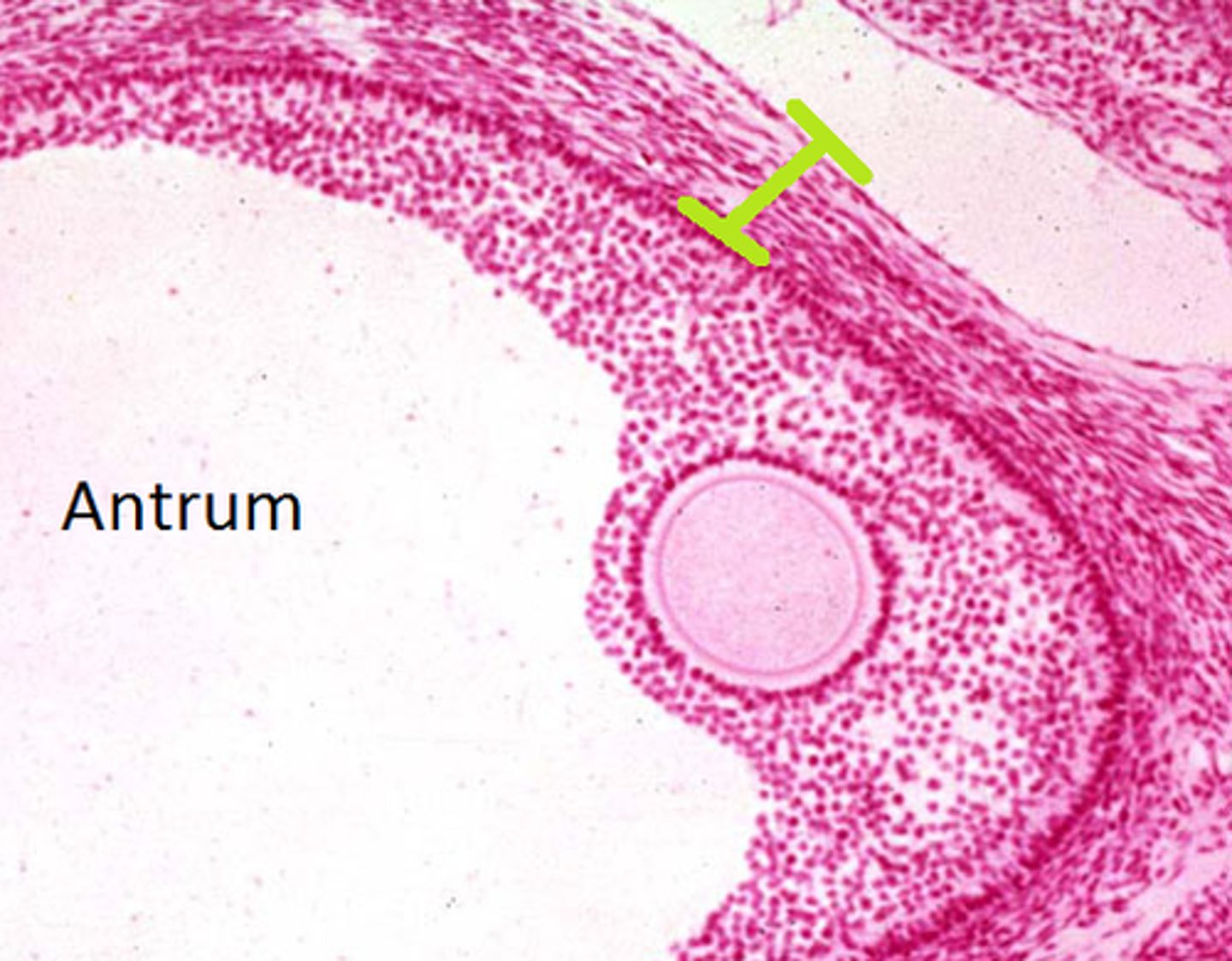
Follicular Antrum
the portion of an ovarian follicle filled with follicular fluid
-----------------
FEATURES:
- continuously gets bigger and eventually wraps around the oocyte (from secondary => Graafian)
-----------------
picture= blue arrow
gamete (egg) development
FROM START TO FINISH
- oogonium/oogonia
- primary oocyte
- secondary oocyte
- ovum
oogonium
Diploid cell in the ovary capable of undergoing meiosis (replication of it self) to produce an egg cell
-----------------
- is only found in the embryo (before birth)
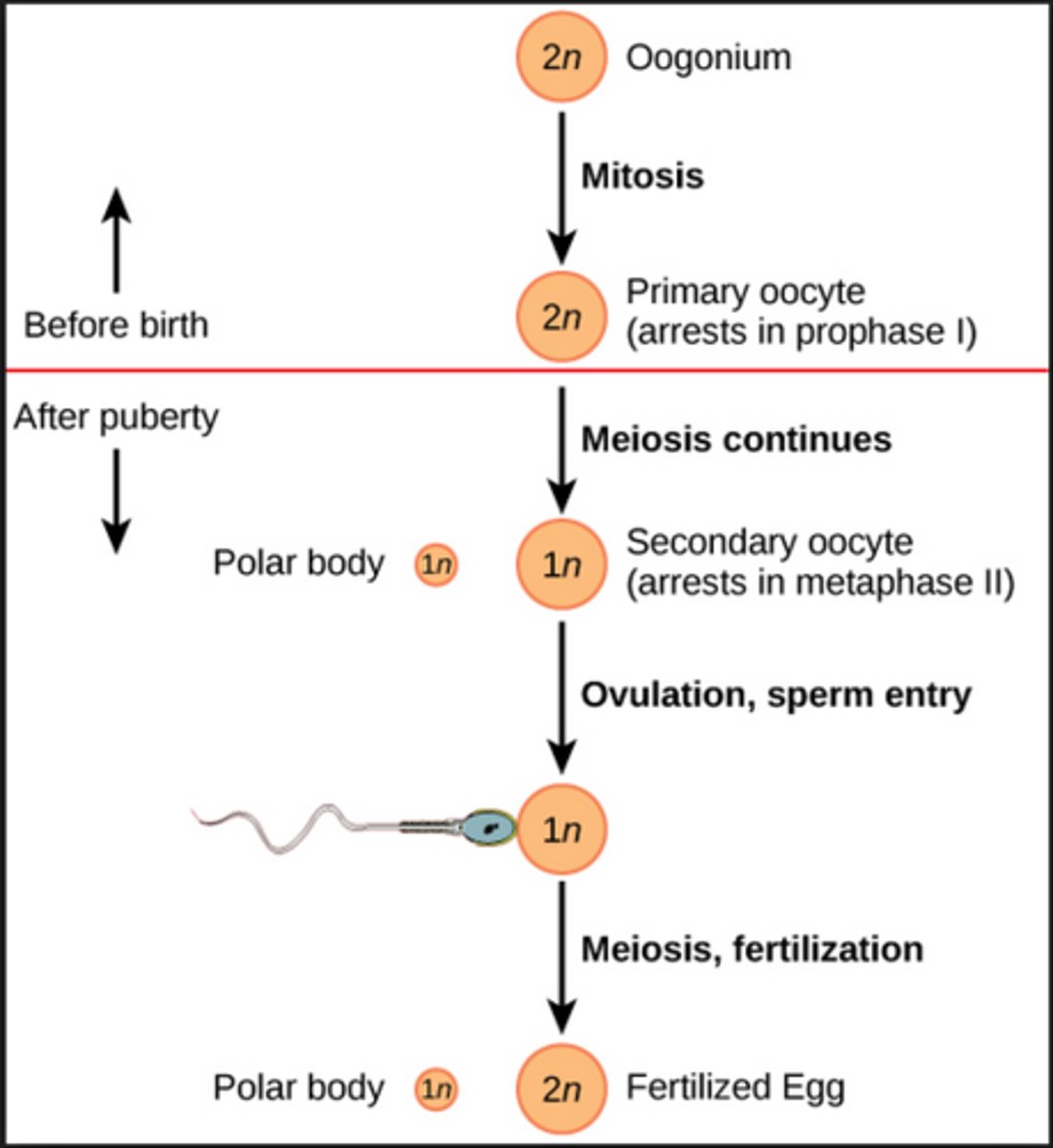
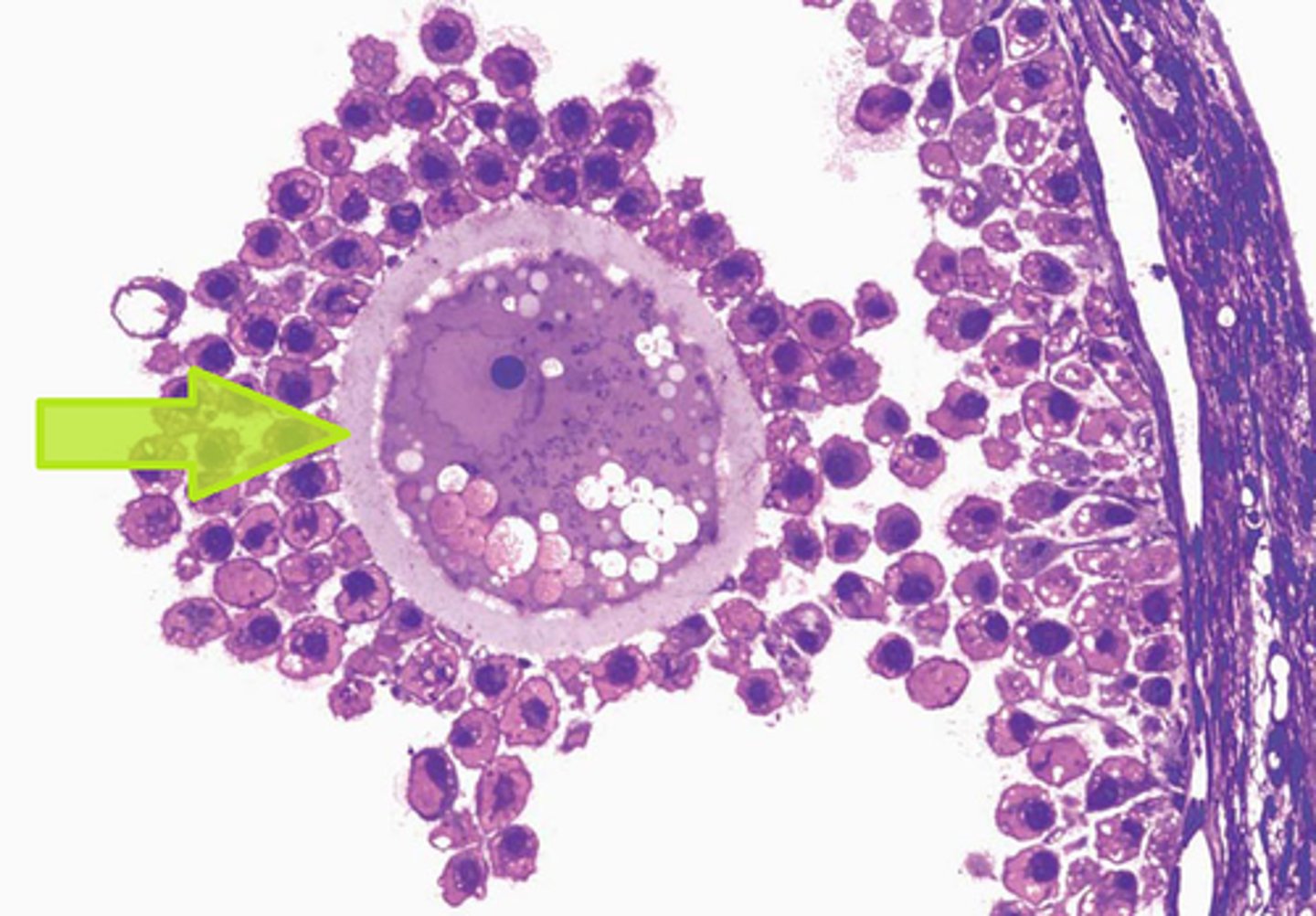
primary oocyte
a diploid cell that divides to form the polar body and the secondary oocyte
-----------------
FEATURES:
- has a large ,"eccentric" (abnormal) nucleus
- has NO ANTRUM
- as it develops the epithelium enlarges and becomes granulosa cells
-----------------
Frozen/rested in (meiosis I to prophase I)
Zona pellucida (RECAP)
forms between the granulosa cells and primary oocytes
secondary oocyte
a haploid cell that undergoes the second meiotic division
- yields a haploid polar body and a haploid egg cell
- remains in this state until fertilization
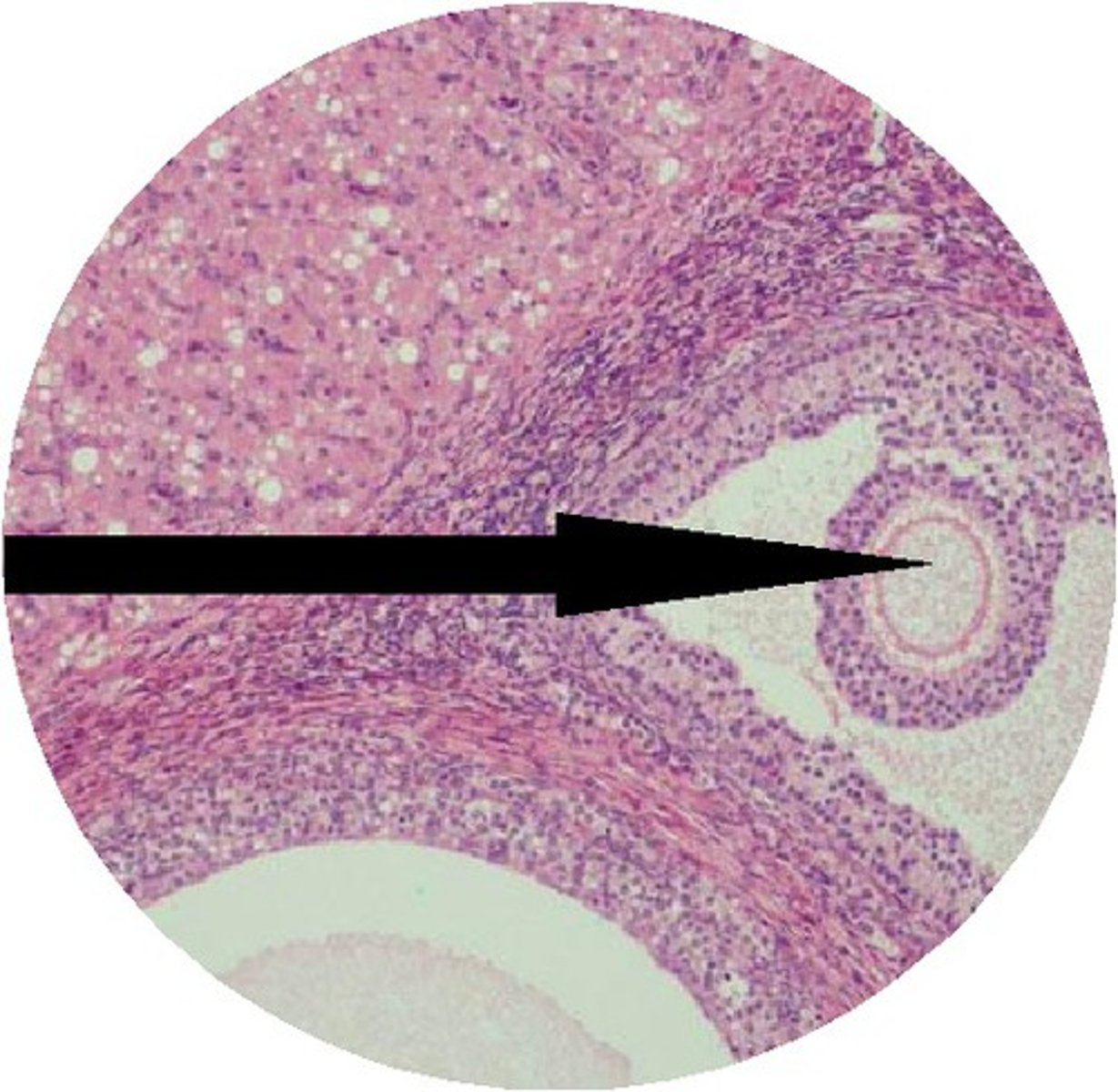
ovum
A mature egg cell
- only after ovulation and sperm contact
-----------------
- continues to develop until a sperm cell comes in contact with the ___
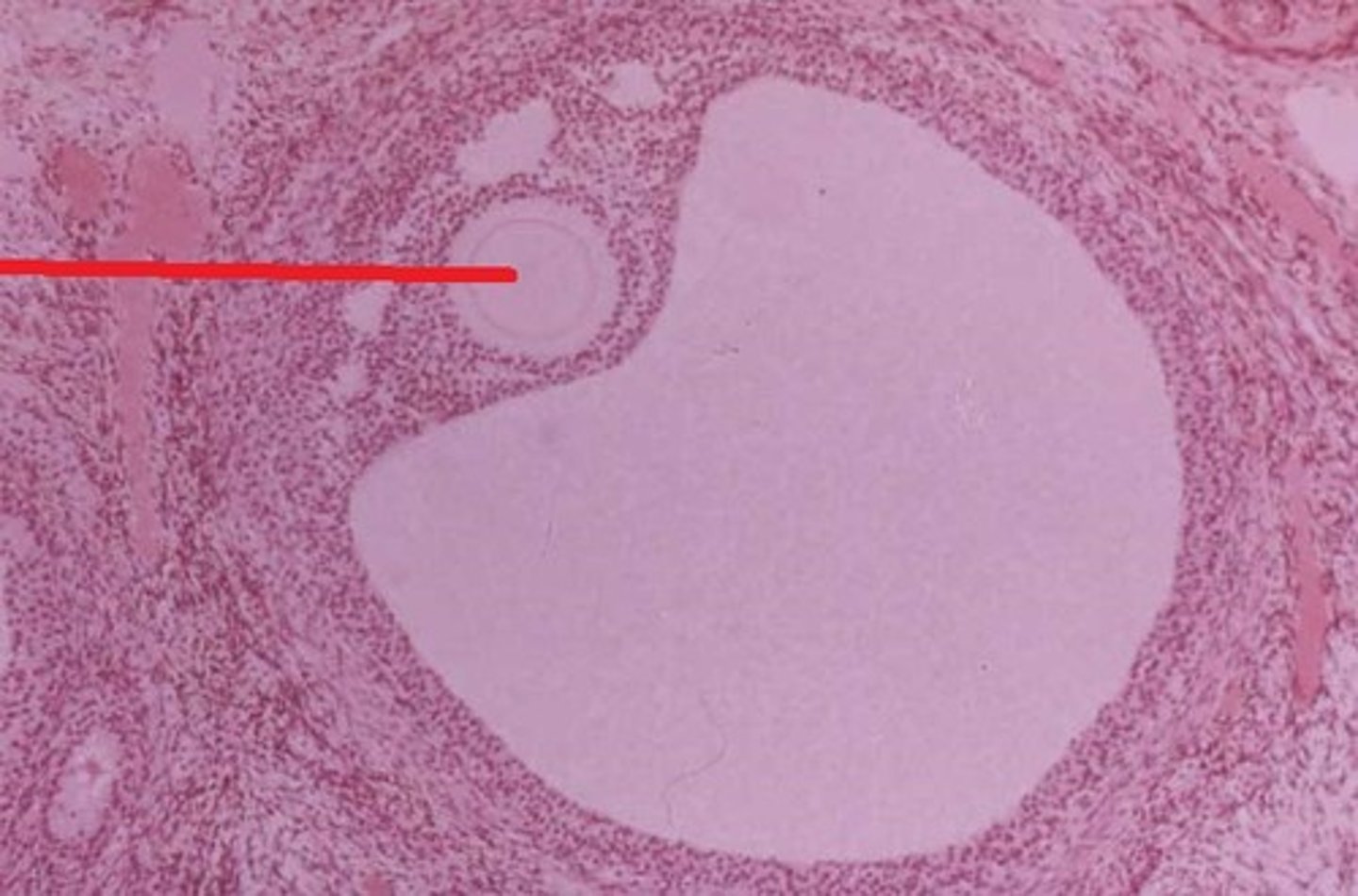
steroid synthesis
FROM START TO FINISH
1) theca Interna develops granulosa cells
2) granulosa cells create hormones:
- estradiol (estrogen)
- progesterone (progestin)
estrogen
- Female sex hormone that stimulates growth of primary and secondary sex organs
- inhibits FSH
Progesterone
- stimulates development of endometrium
- promotes development of mammary glands
- inhibits FSH
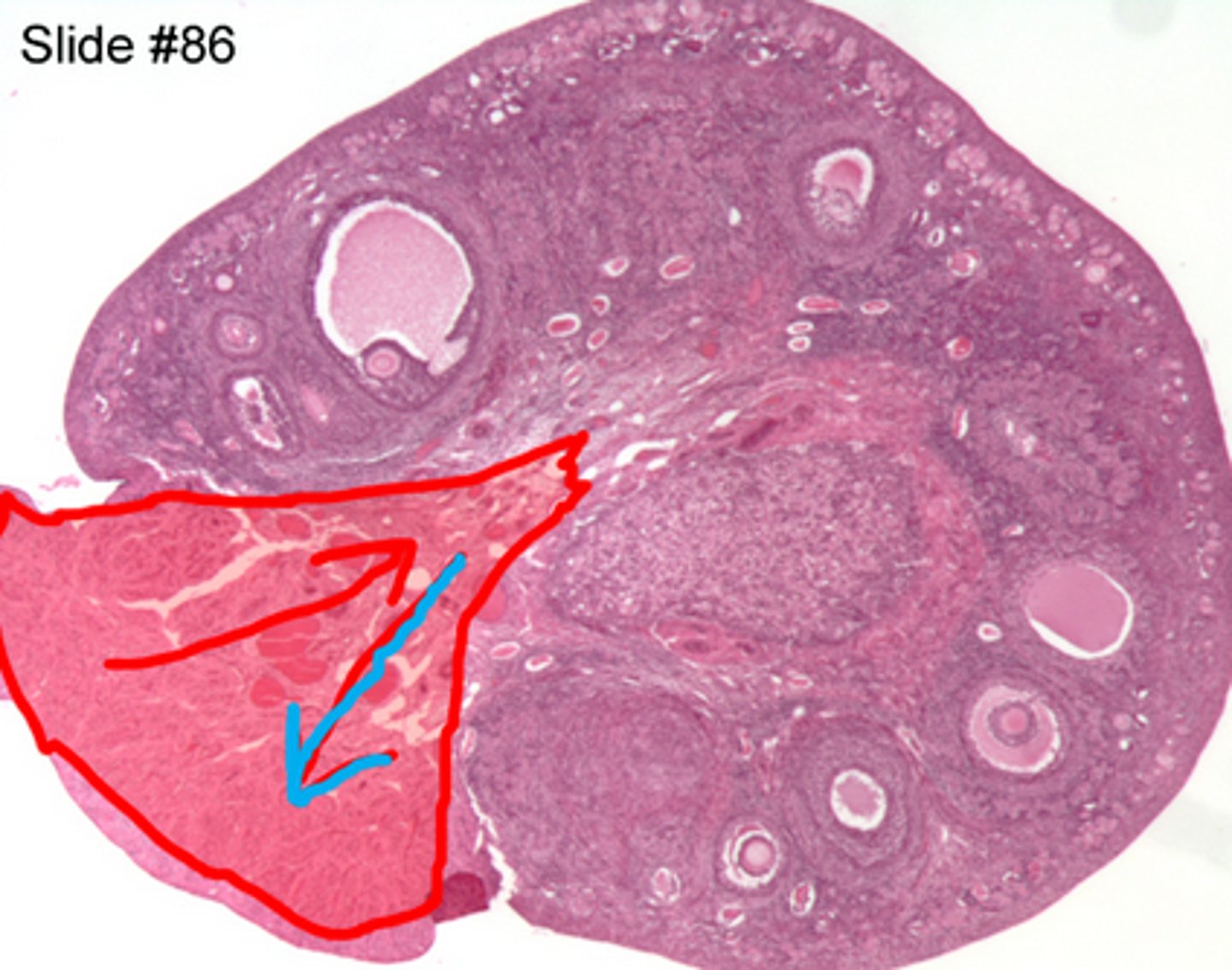
ovarian medulla
A highly vascular stroma in the center of the ovary that's continuous with the hilum
-----------------
FEATURES:
- contains loose fibrous CT
- blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves are present (making it vascular)
What cells are present in the ovarian medulla?
- Fibroblasts
- epithelioid Hilus cells
(produce androgens)
- macrophages
- lymphocytes
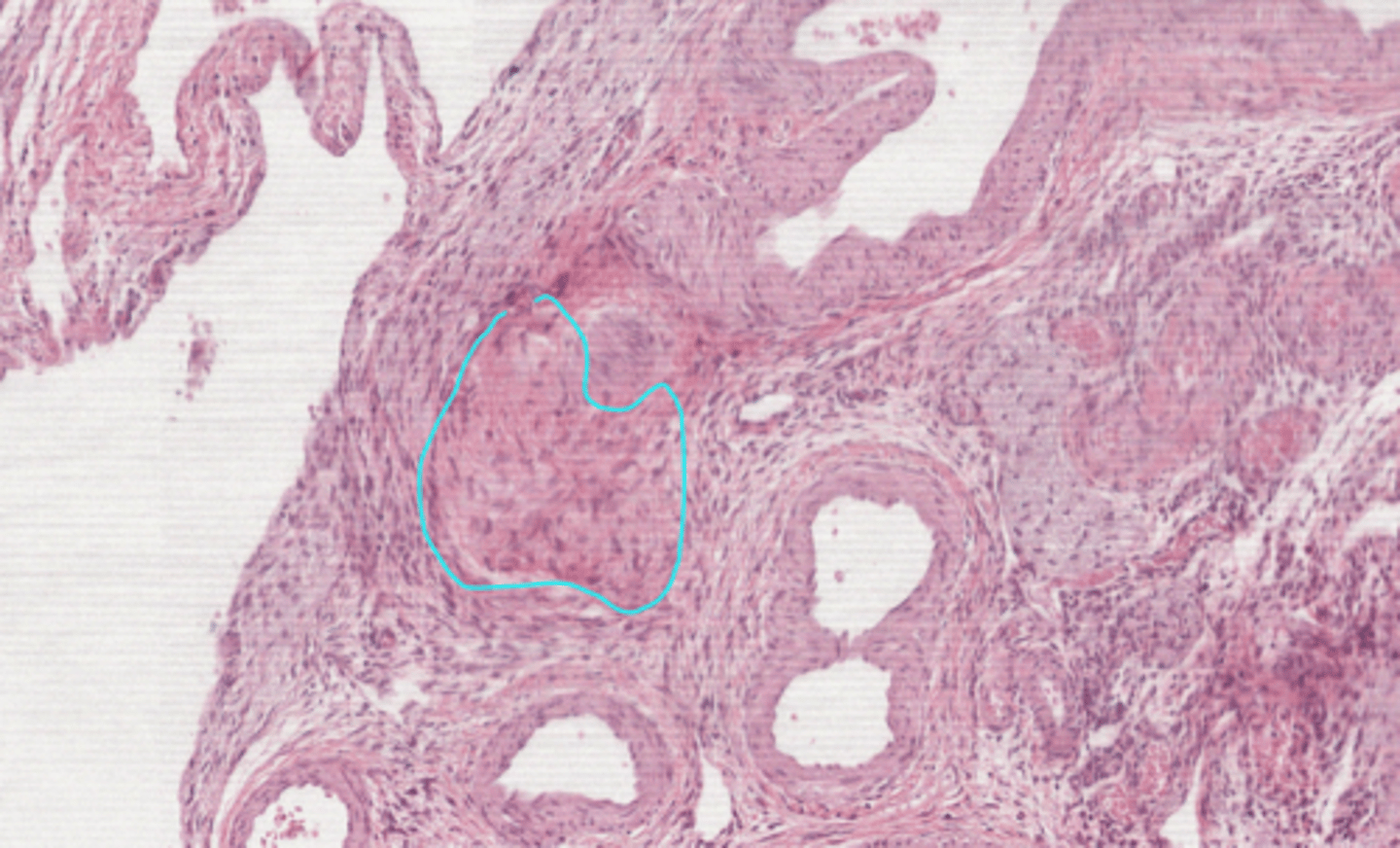
ovarian hilum
space inside the mesovearium where the broad ligament supports the ovary
- its the area where blood vessels and nerves enter (similar to the kidney)
-----------------
FEATURES:
- contains epithelioid hilus cells
epithelioid hilus cells
cells that produce androgens
- they look similar to Leydig cells of the testes
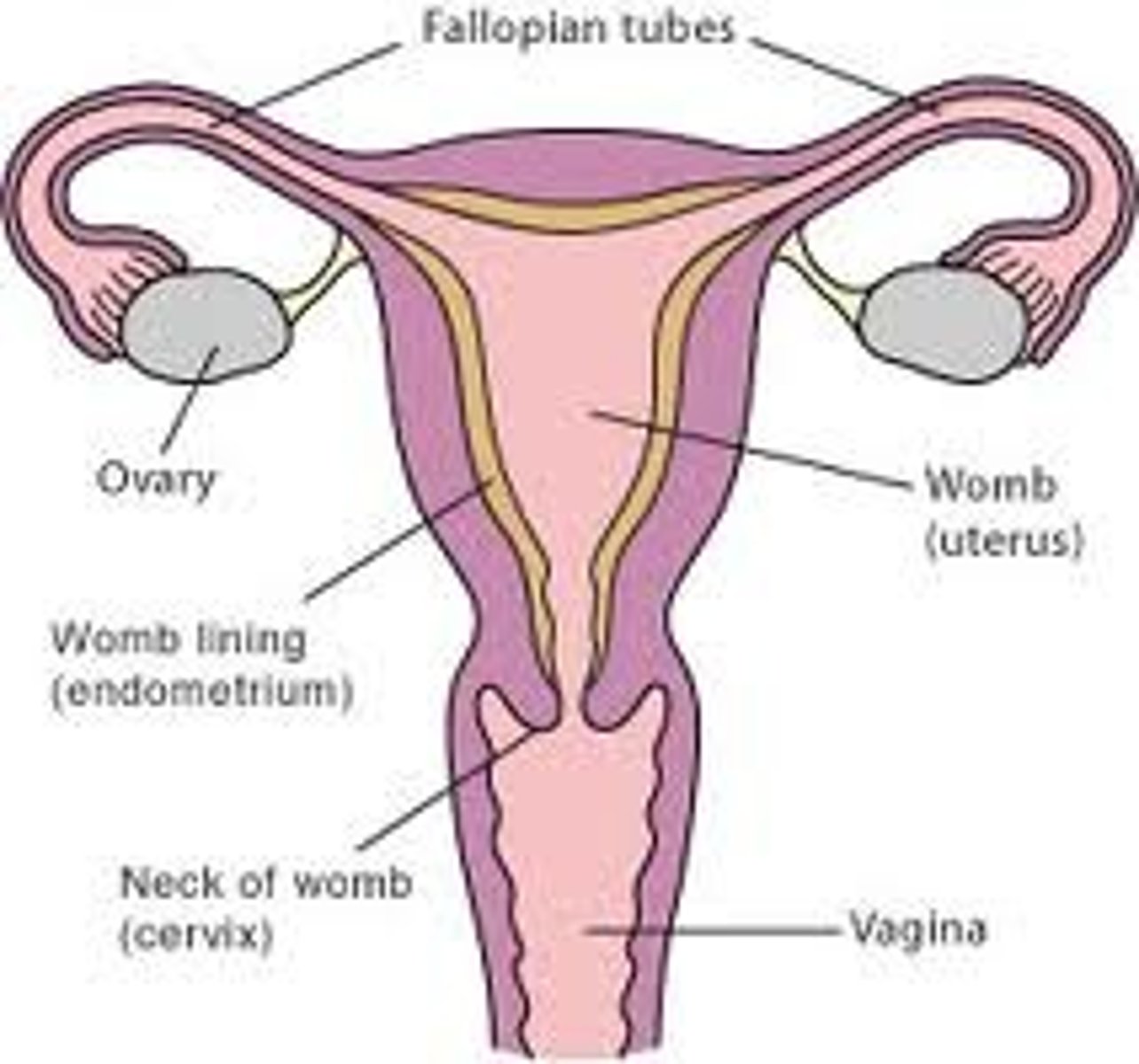
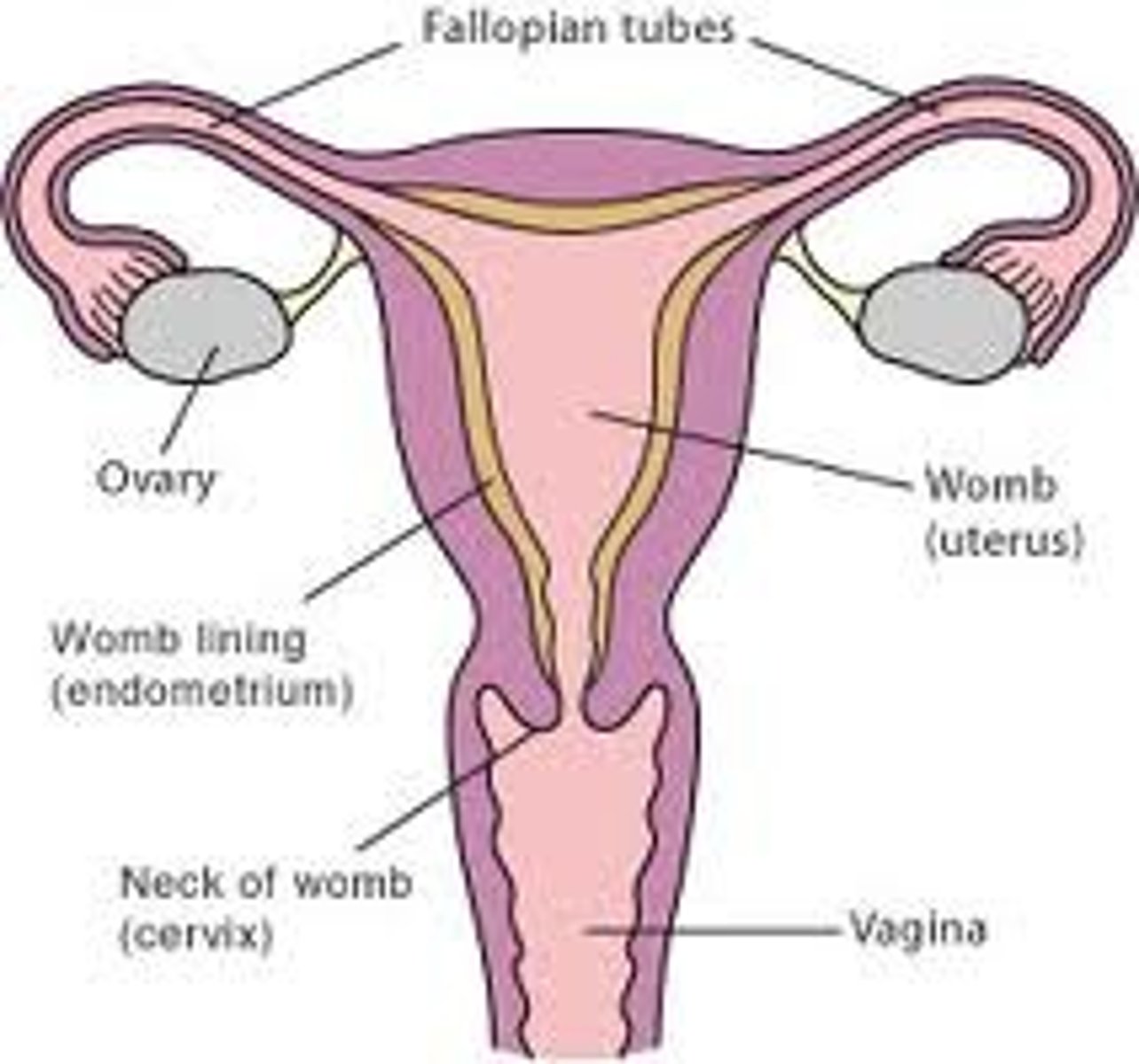
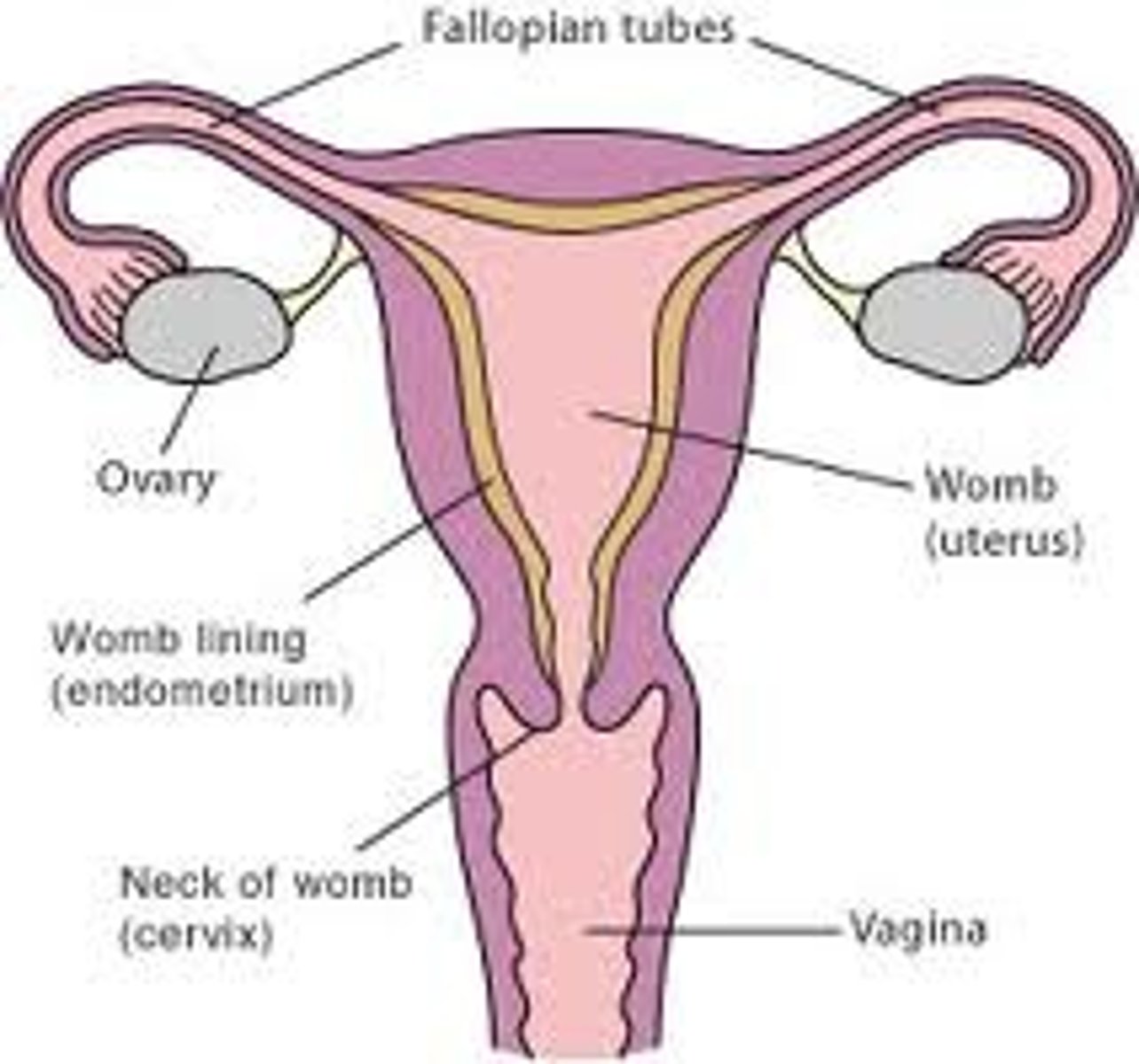
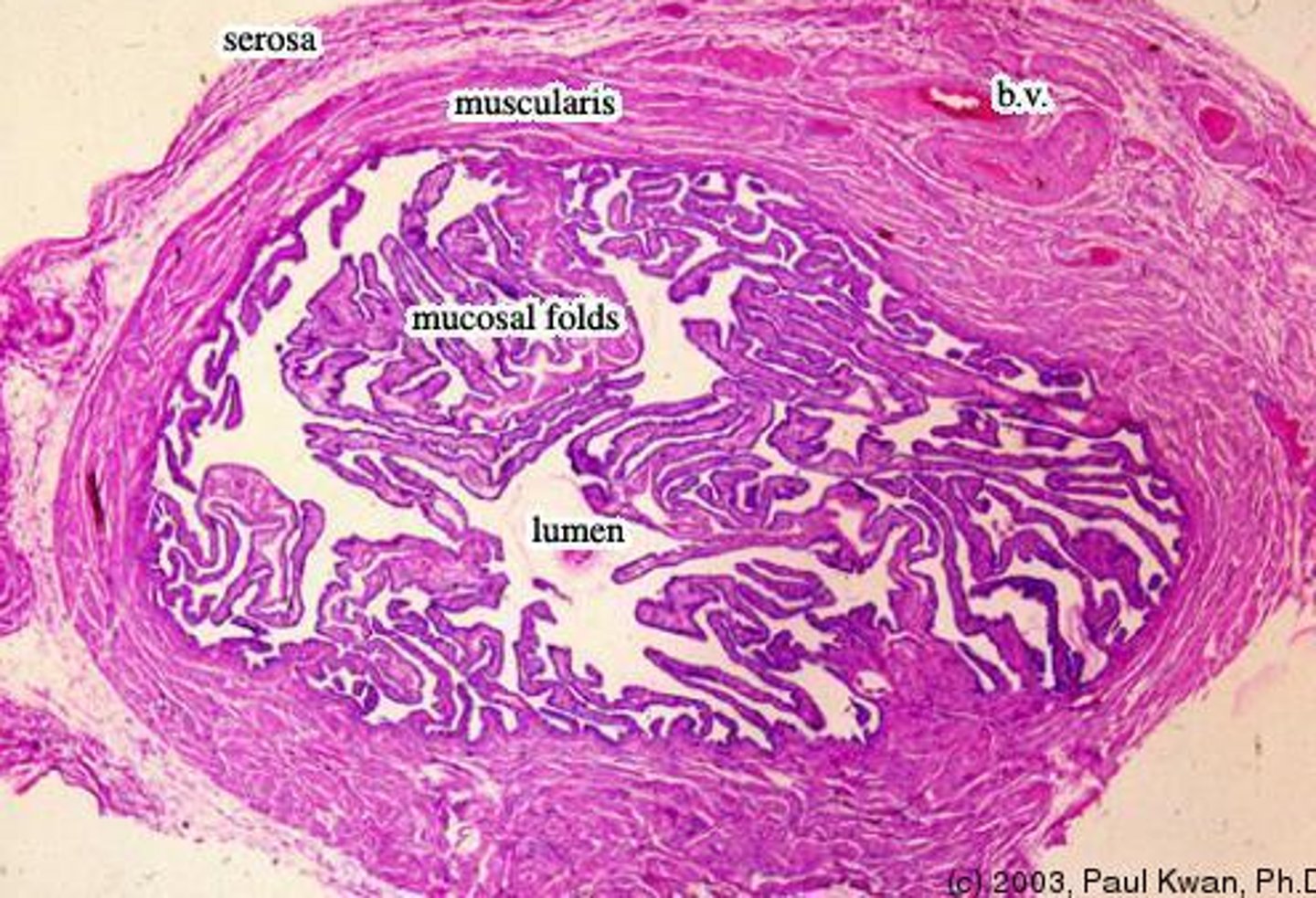
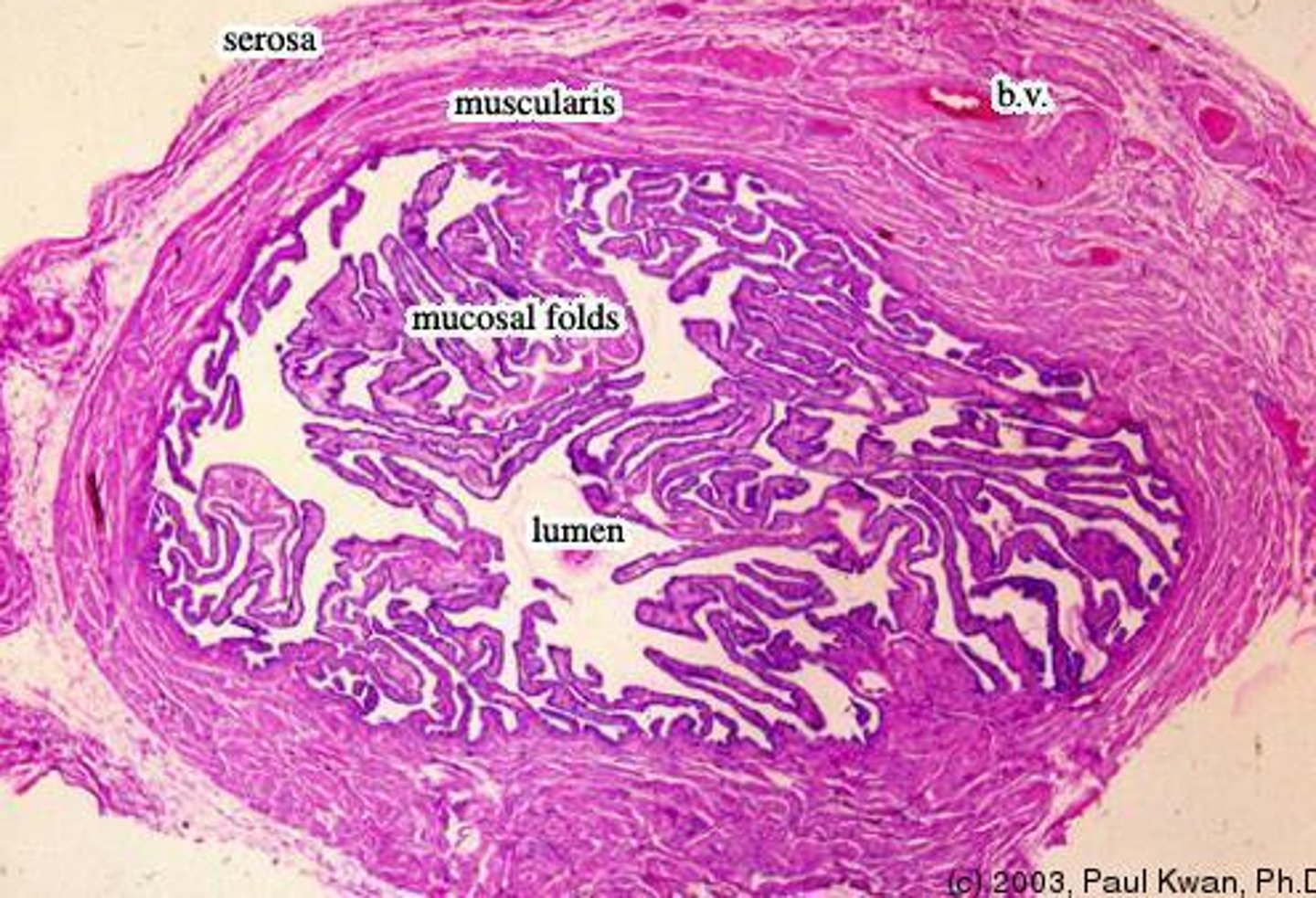
fallopian tubes (oviducts)
tubes that carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus
- its the area where fertilization usually occur
-----------------
LINING DIVIDED INTO 3 SECTIONS
- mucosa
- muscularis externa
- serosa (mesoalpinx)
Mucosa of fallopian tubes
FEATURES
- forms longitudinal folds which are branched in the ampulla
- are lined with simple columnar epithelum
- contains ciliated cells and peg cells
- the lamina propria is loose CT
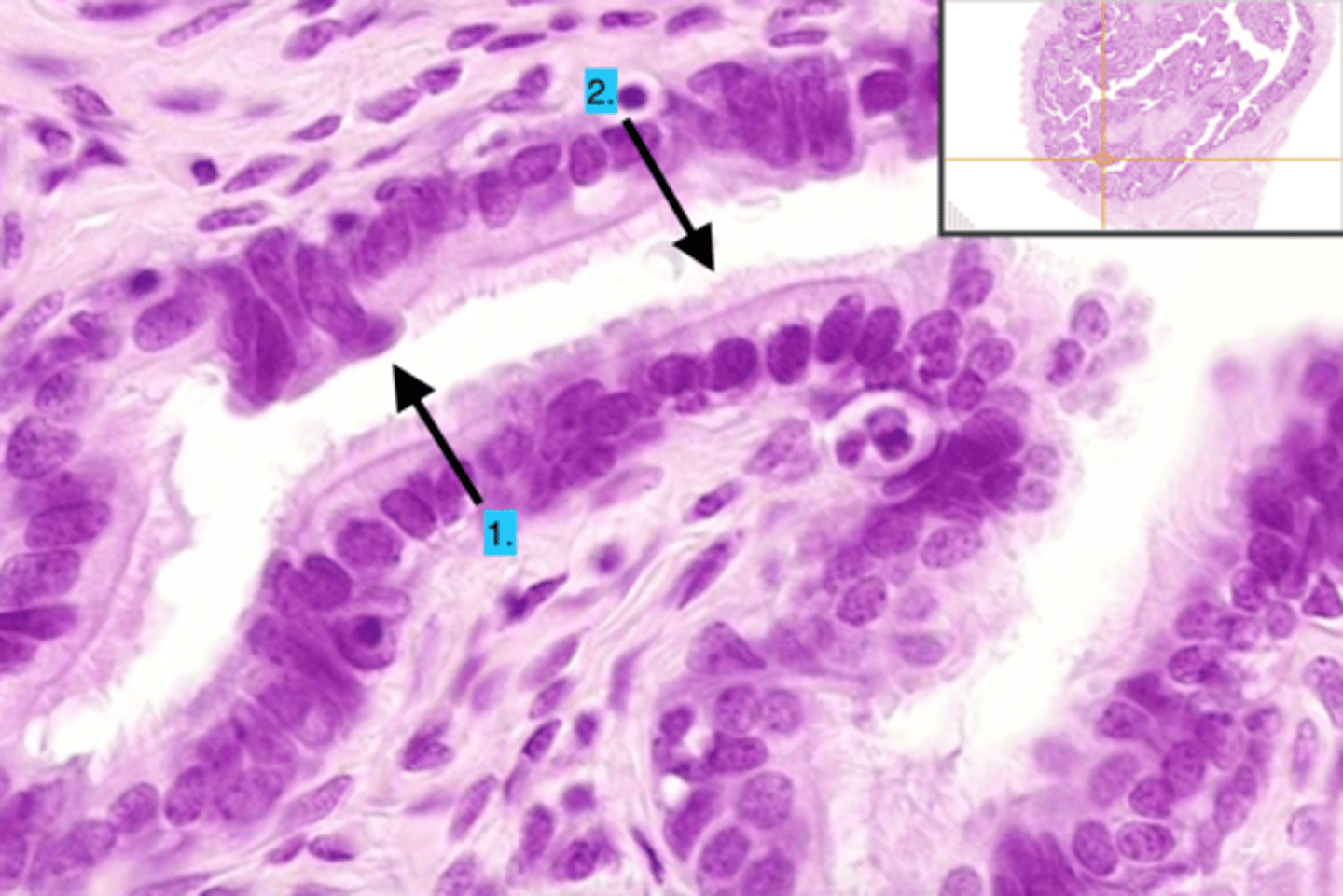
ciliated cells (fallopian tube)
help facilitate the movment of the egg
- also helps with fluid movement secreted by peg cells to the uterus
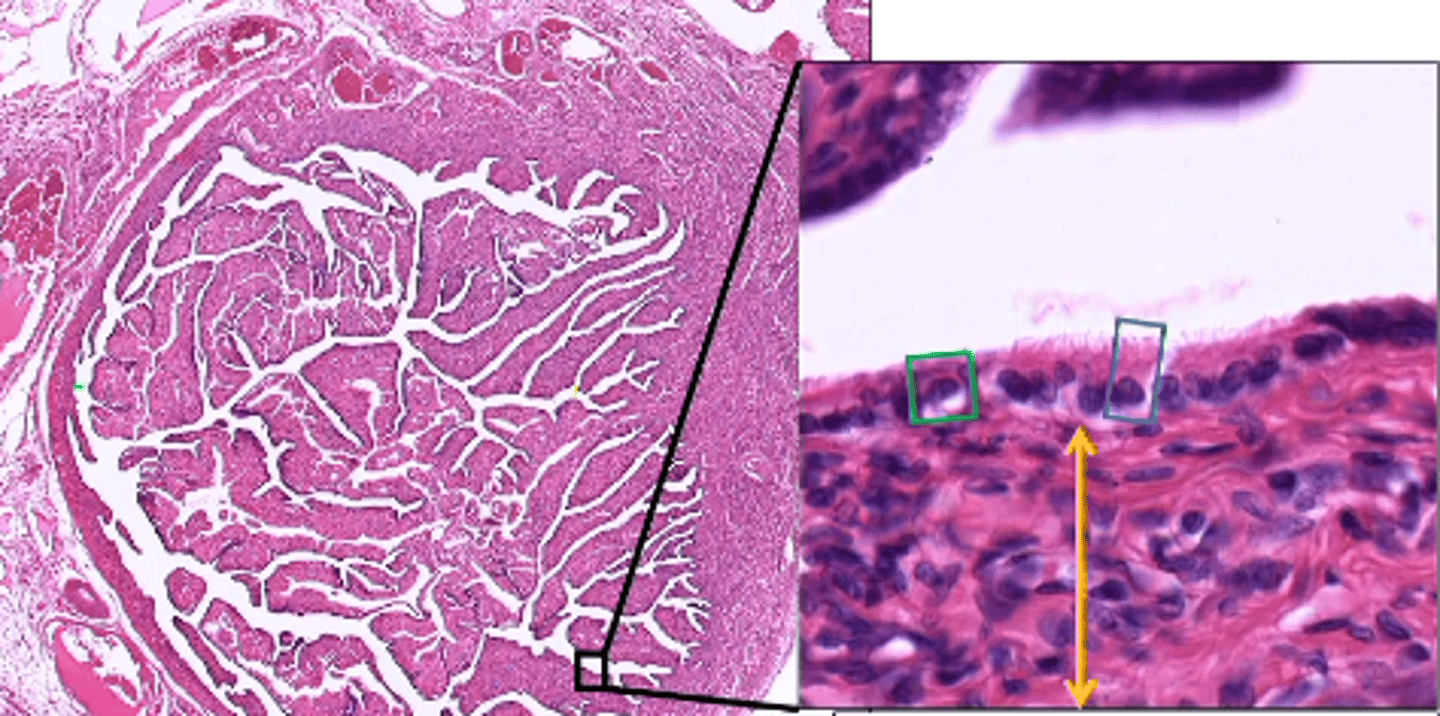
peg cells (fallopian tube)
cells that secrete a fluid providing nourishment for the ovum
- fluid movement is assisted by ciliated cells in the fallopian tube
-----------------
FLUID MOVEMENT:
- apical membrane pushing out => secret fluid
Muscularis of fallopian tube
contains 2 layers both composed of smooth muscle
- inner circular layer
- outer longitudinal layer
Serosa of fallopian tube
layer of the fallopian tube that can be also referred to as the mesosalpinx ("broad ligament of the fallopian tube")
-----------------
FEATURES:
- superficially its composed of simple squamous epithelium
- deeper its composed of fibrous CT
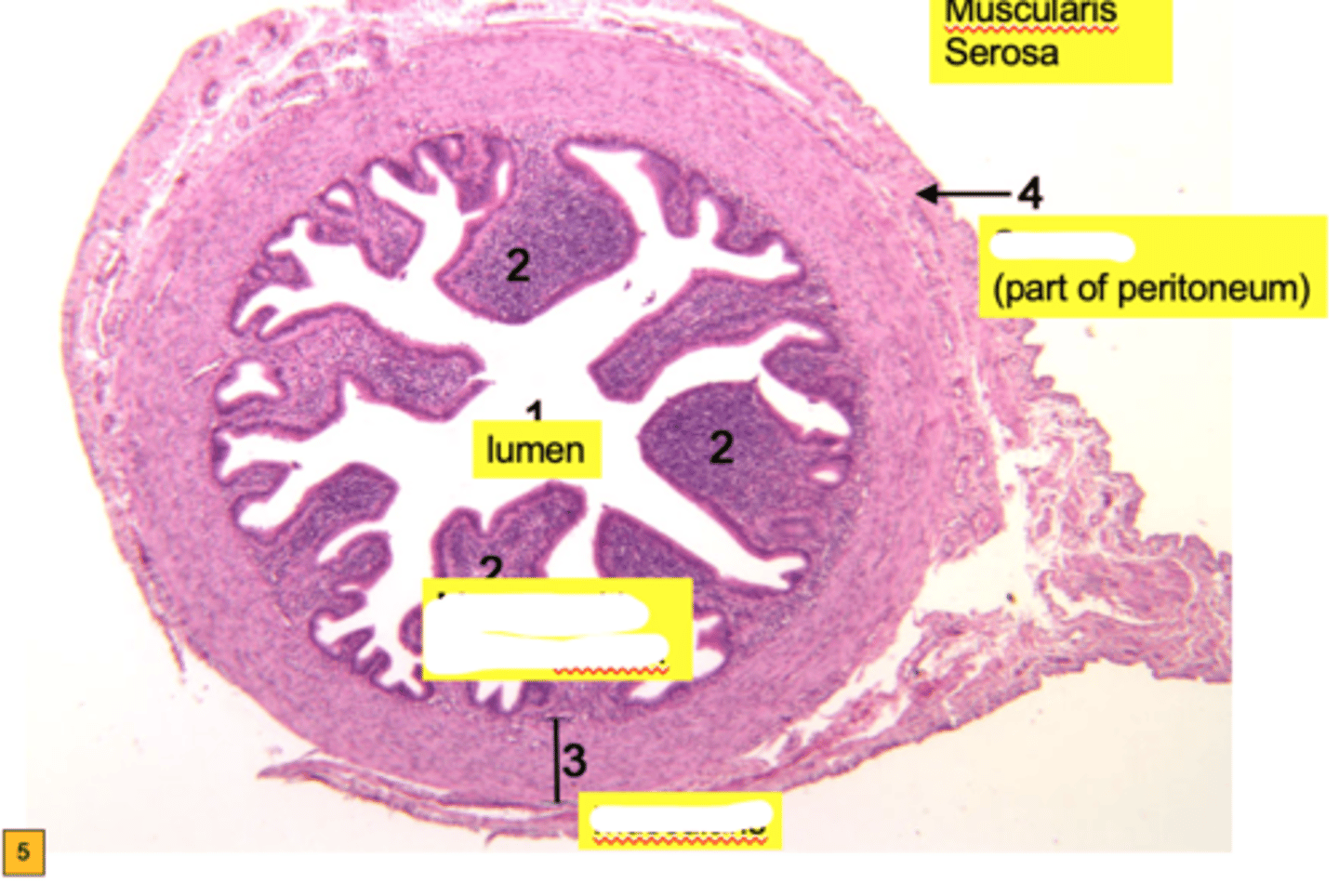
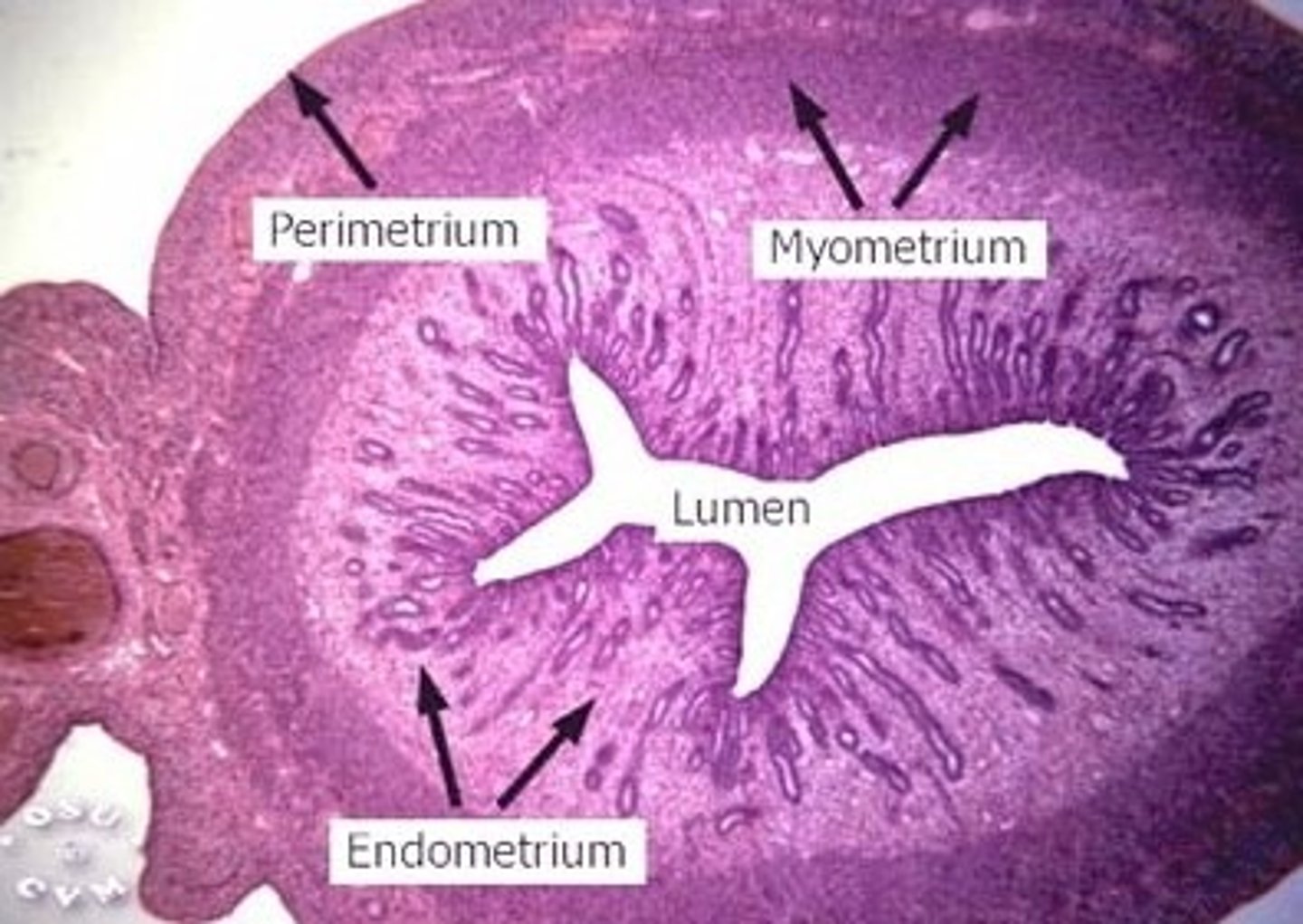
uterus
Female (pear shaped) organ used to house the developing fetus.
- contains 3 regions (body, fundus, and cervix)
- located in the pelvic cavity
-----------------
FEATURES
- contains 3 regions (body, fundus, and cervix)
-----------------
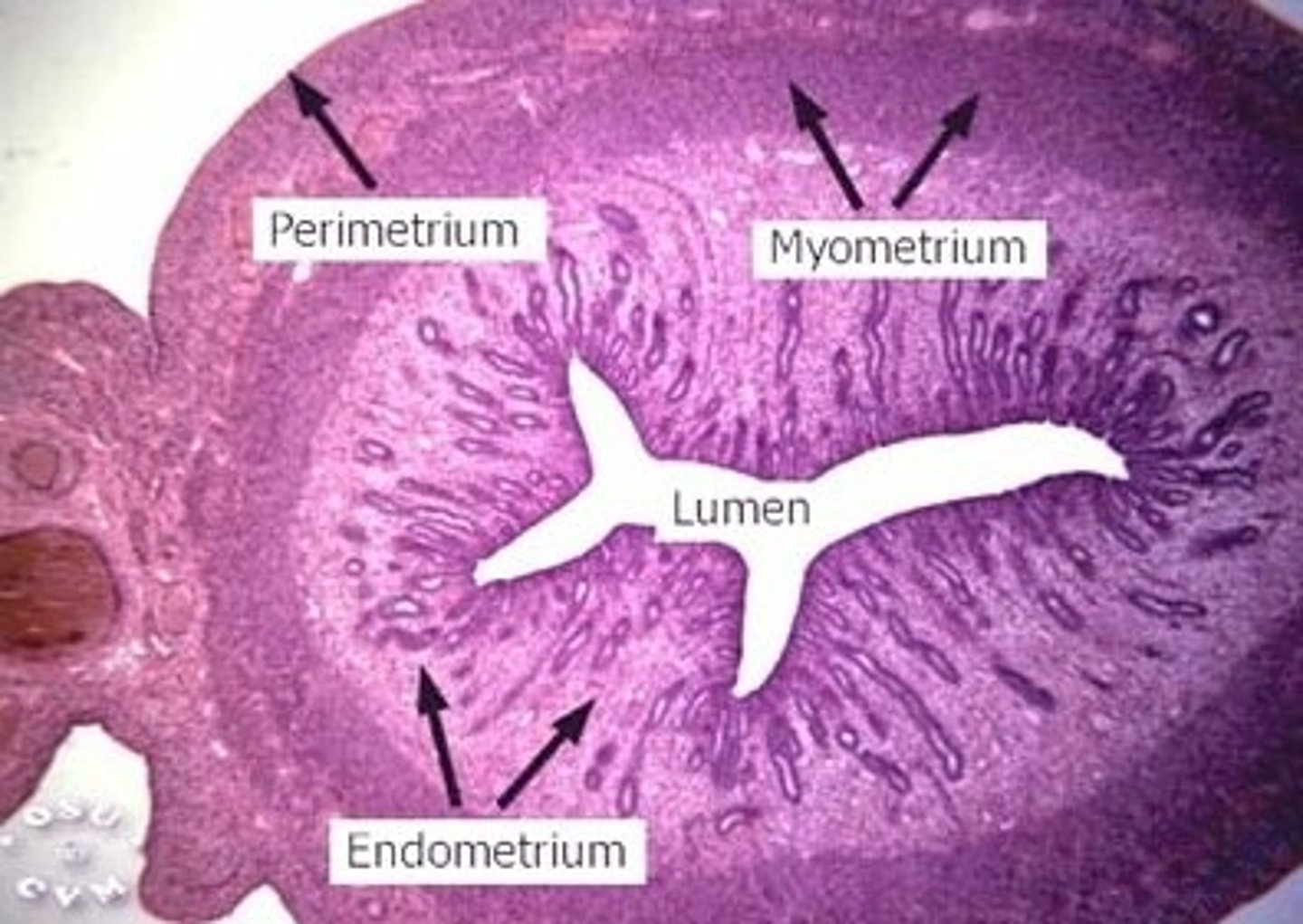
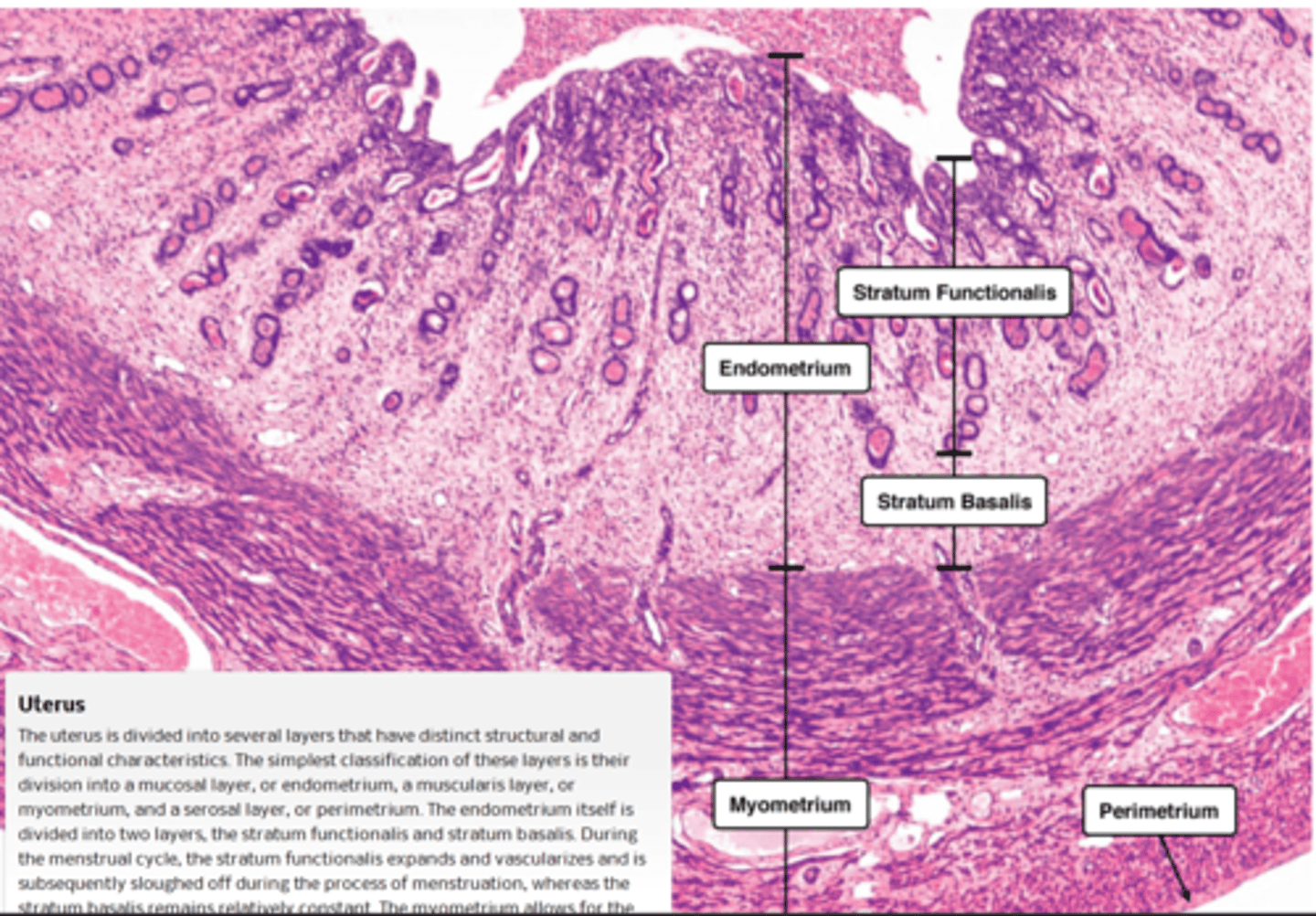
3 MAJOR LAYERS (FROM INNER TO OUTER)
- endometrium
- myometrium
- perimetrium or adventitia
endometrium of uterus
inner layer of the uterus
-----------------
FEATURES:
- composed of simple columnar epithelium
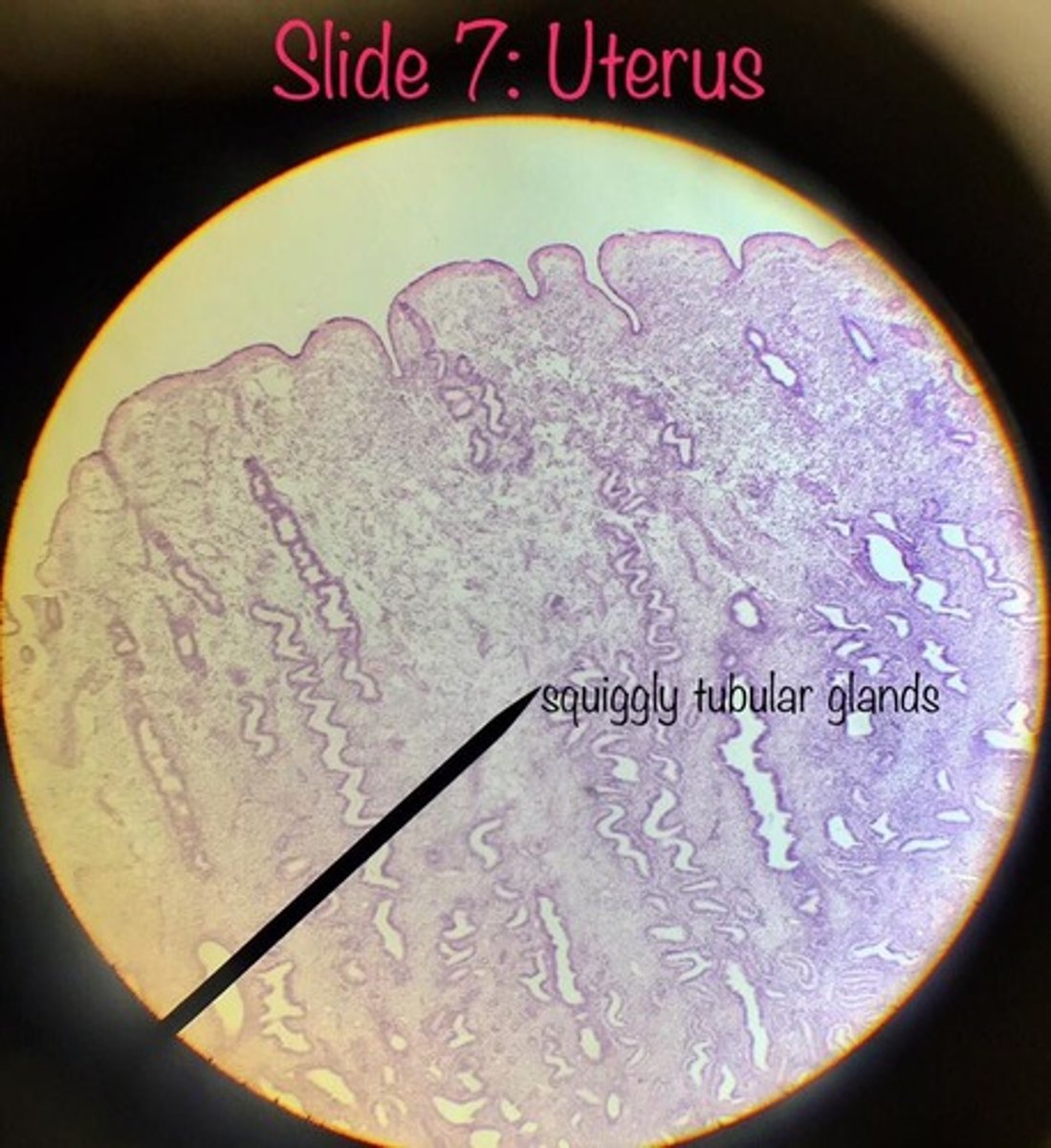
- contains a simple tubular uterine glands
- contains an underlying stroma that's divided into 2 sections
simple tubular uterine glands (uterus) STUG
FUNCTION:
- glands that secrete glycogen
-----------------
depending on which layer on the stroma the tubular glands are either seen straight (basalis) or coiled (functinalis)
Underlying stroma
composed of 2 sections:
- stratum basalis
- stratum functionalis
-----------------
FEATURES:
- contains lots of blood vessels
- contains either coiled or straight simple tubular uterine glands
stratum basalis (endometrium)
a permanent layer that builds the functional layer after each menstruation
-----------------
FEATURES:
- arteries go straight up
- contains straight STUG
-----------------
- "located next to/below the myometrium" (theres no submucosa between them)
- doesn't change shape during the ovarian cycle
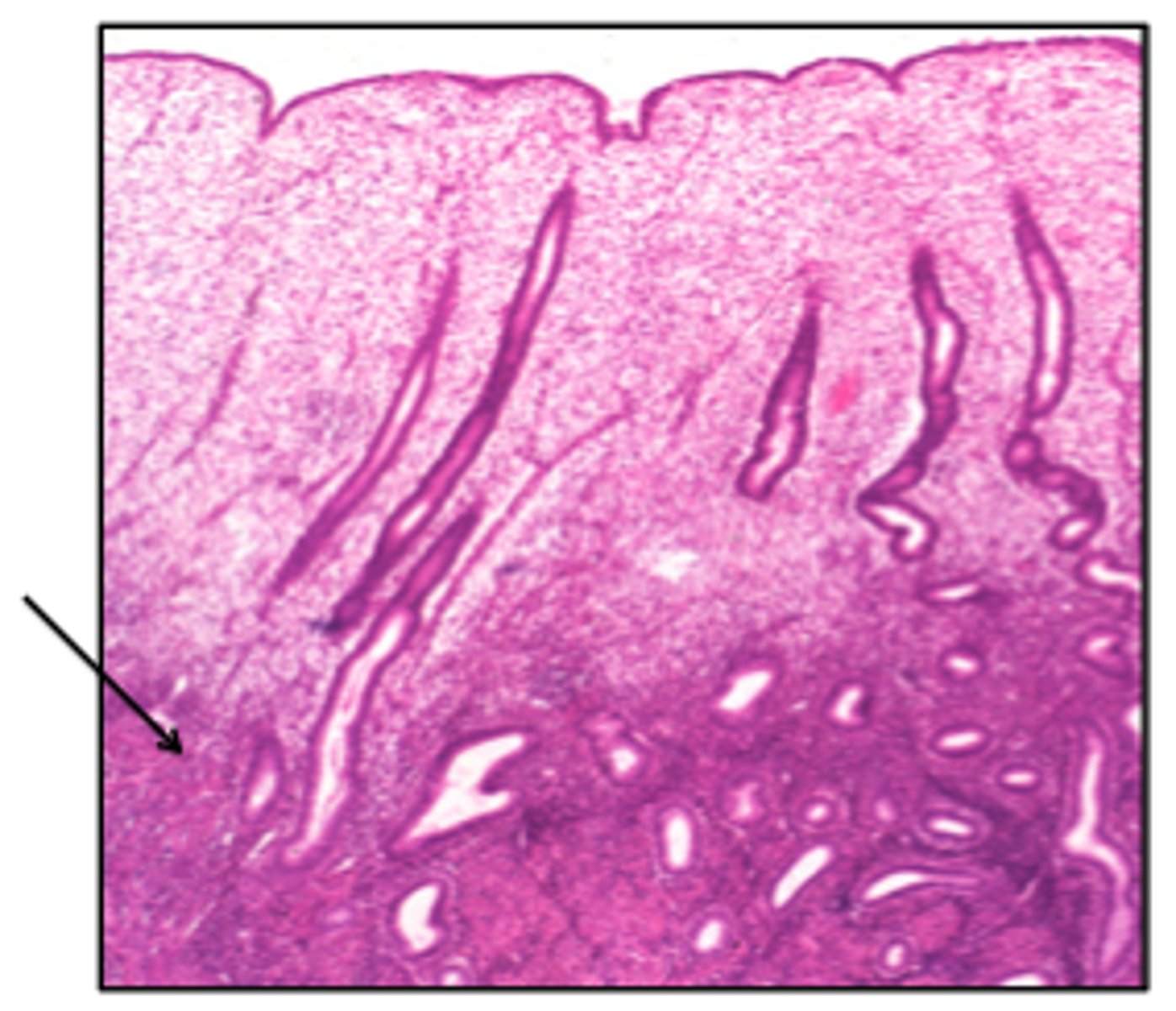
stratum functionalis (endometrium)
layer that lines the uterine cavity and eventually sloughs off during mesturation
-----------------
FEATURES:
- contains spiral/coiled arteries
- contains coiled STUG
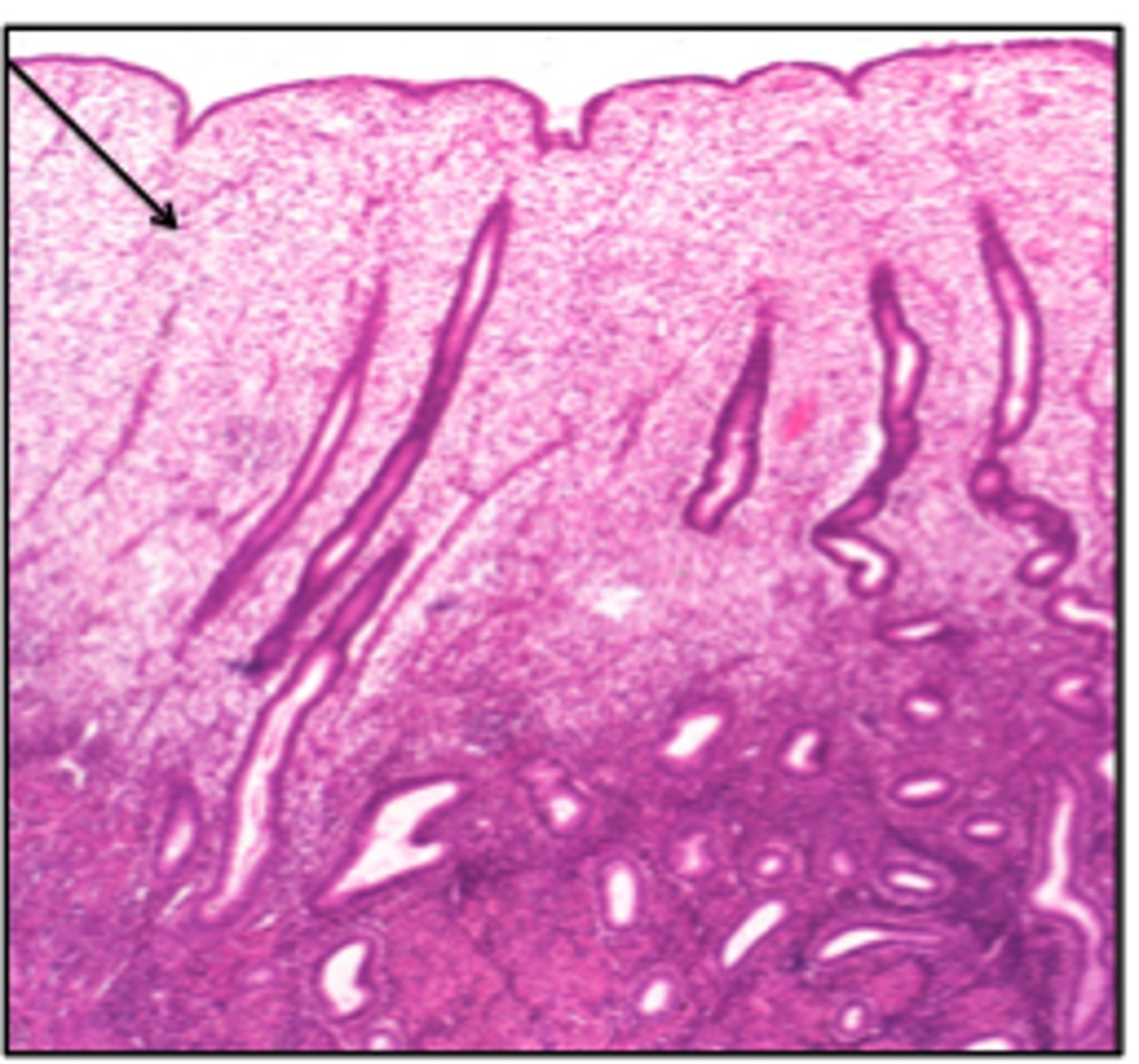
Stratum functionalis during proliferative phase
during the proliferative phase the stratum functionalis starts/continues to grow.
-----------------
WHAT IS IT DEPENDENT ON?
- estrogen (stimulates growth)
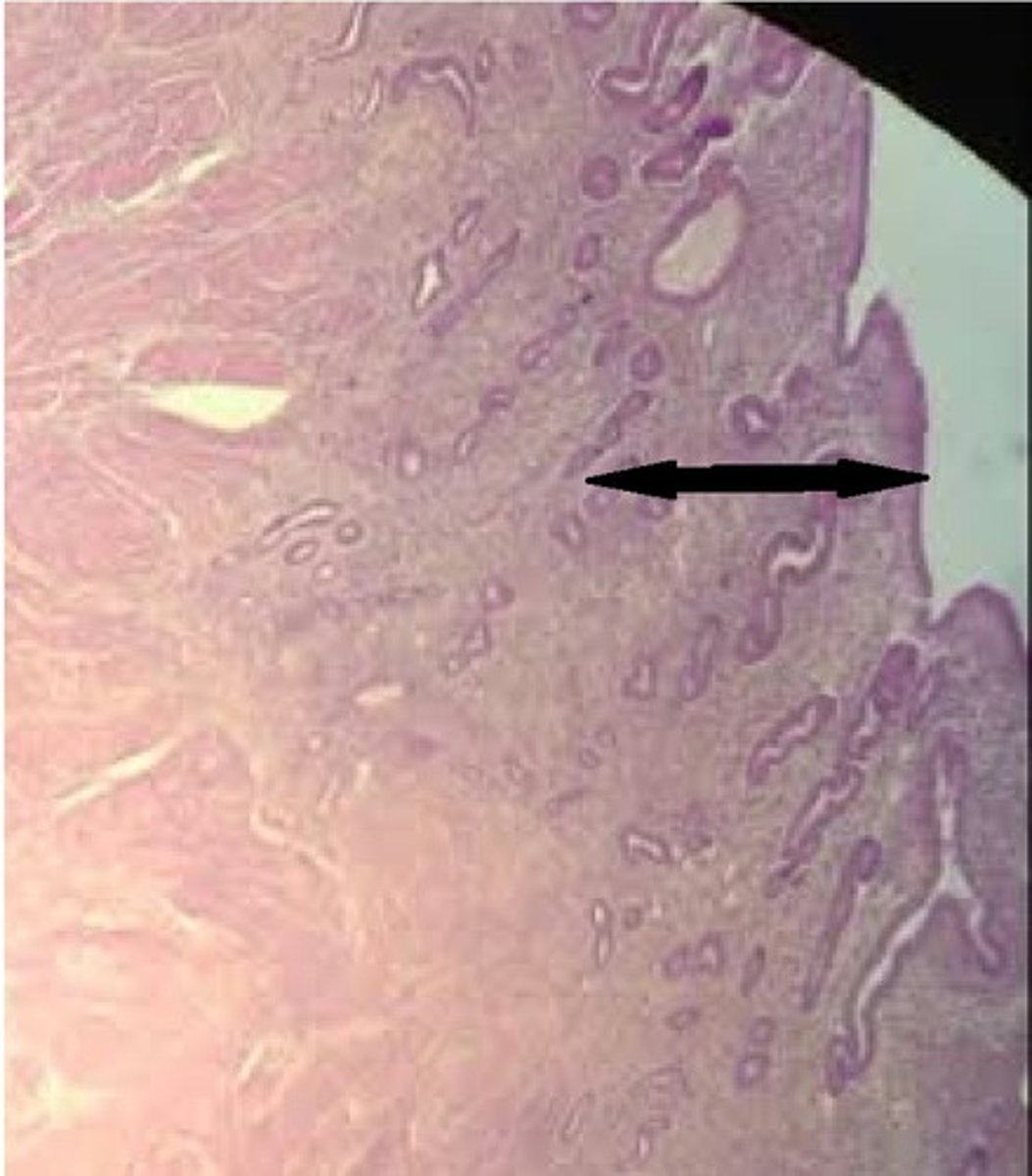
secretory phase (stratum functionalis)
happens after ovulation (release of the egg)
- progesterone makes more gland secretion and blood flow
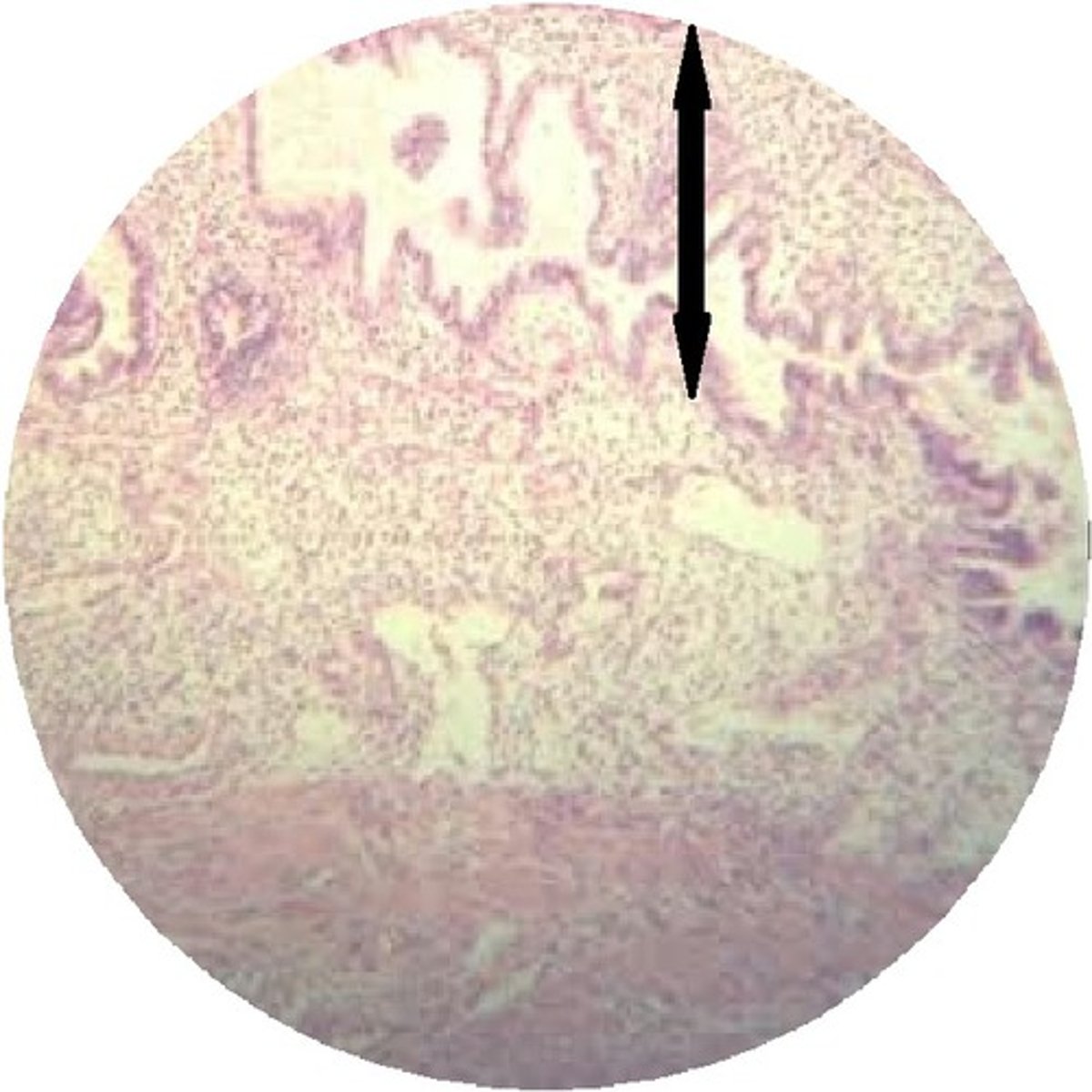
hormone changes (stratum functionalis)
during menses (uterine cycle) there are no more hormones as everything disintegrates
-----------------
- can change through different phases
ex: if not pregnant the stratum functionalis sloughs off after 14 days
myometrium (uterus)
the thick wall/middle layer of the uterus consisting of smooth muscle and connective tissue
- contains 3 indistinct layers
-----------------
3 LAYERS:
- inner longitudinal
- middle circular
- outer longitudinal
stratum vasculare (SV)
the middle layer of the myometrium that sits between the muscle layers of the myometrium
-----------------
FEATURES
- thickest layer and has interlaced circularly oriented smooth muscle
- contains numerous amounts of blood vessels and lymphatics
-----------------
WHERE CAN IT BE FOUND?
inner Long.
- SV
middle Circ.
- SV
- outer Long.
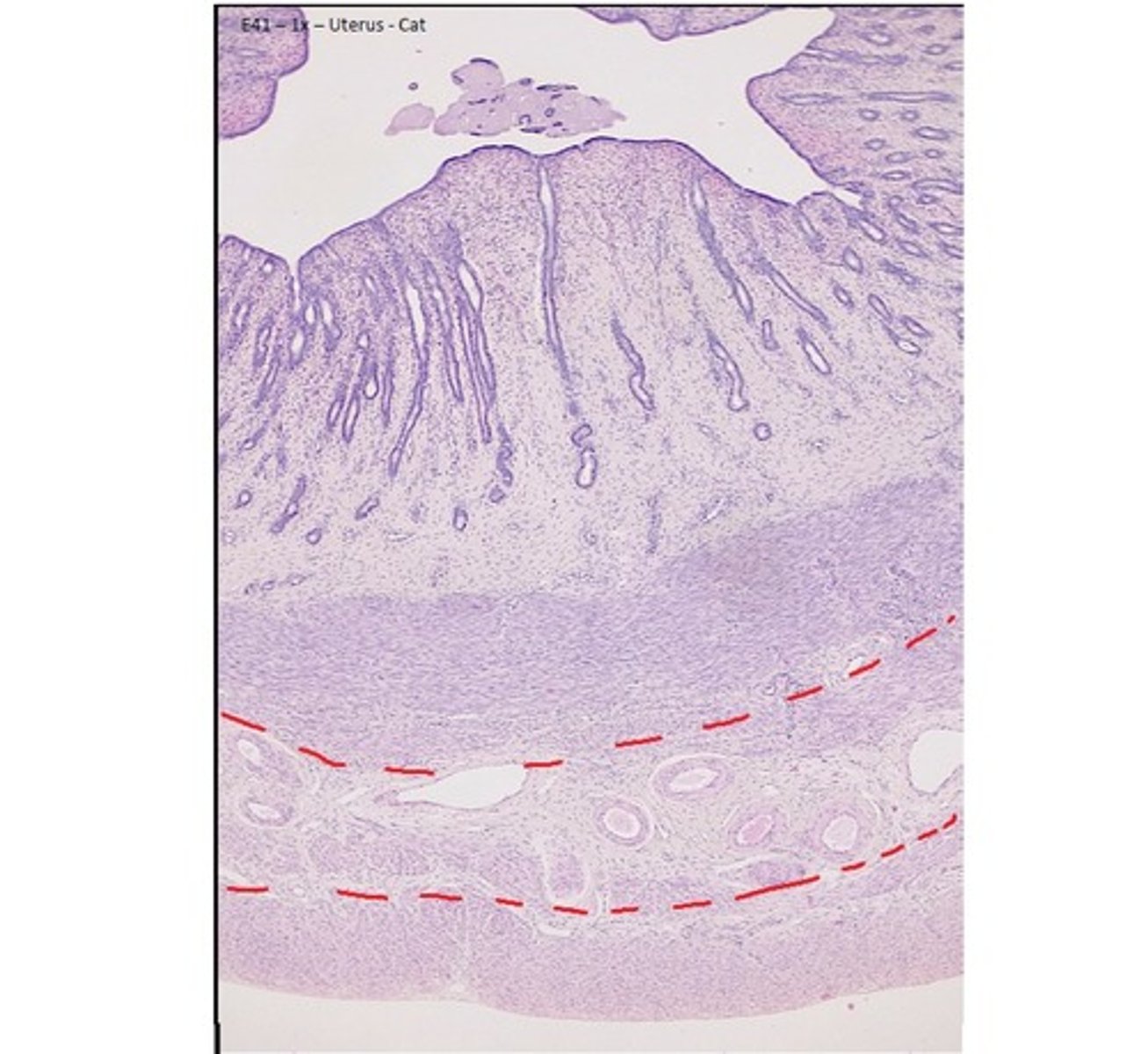
perimetrium or adventitia (uterus)
the outer thin surface layer of the fundus and body of the uterus
-----------------
- OUTER SURFACE: is covered with serosa (parietal peritoneum)
- INNER/REMAINDER: is covered with fibrous adventitia
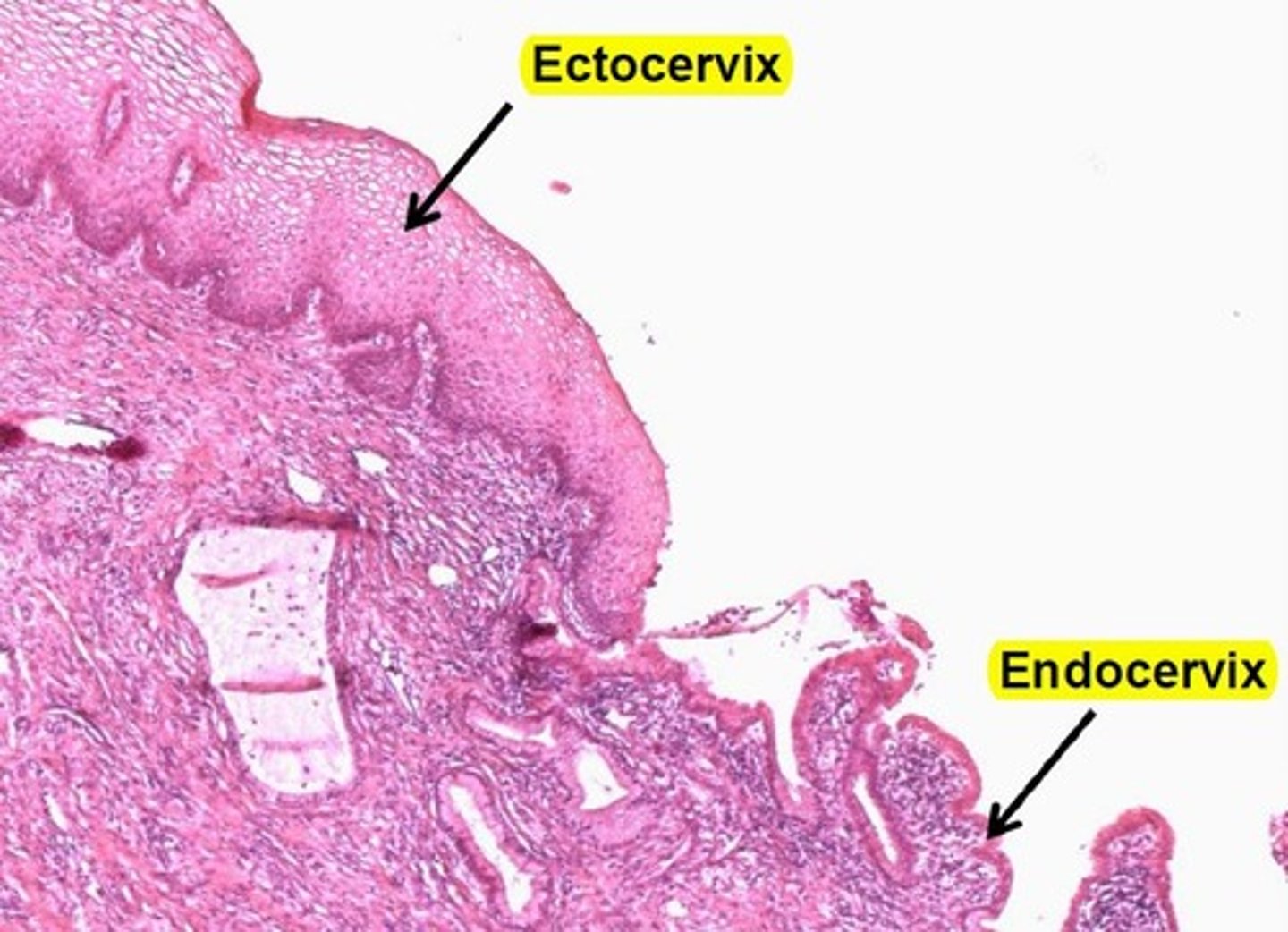
uterine cervix
the lower narrow end of the uterus that forms a canal between the uterus and vagina
- contains an undelying cervical epithlia made of CT fibers and lots of Smooth muscle cells
-----------------
DIVIDED INTO 2 SECTIONS:
- Endocervix
- Ectocervix
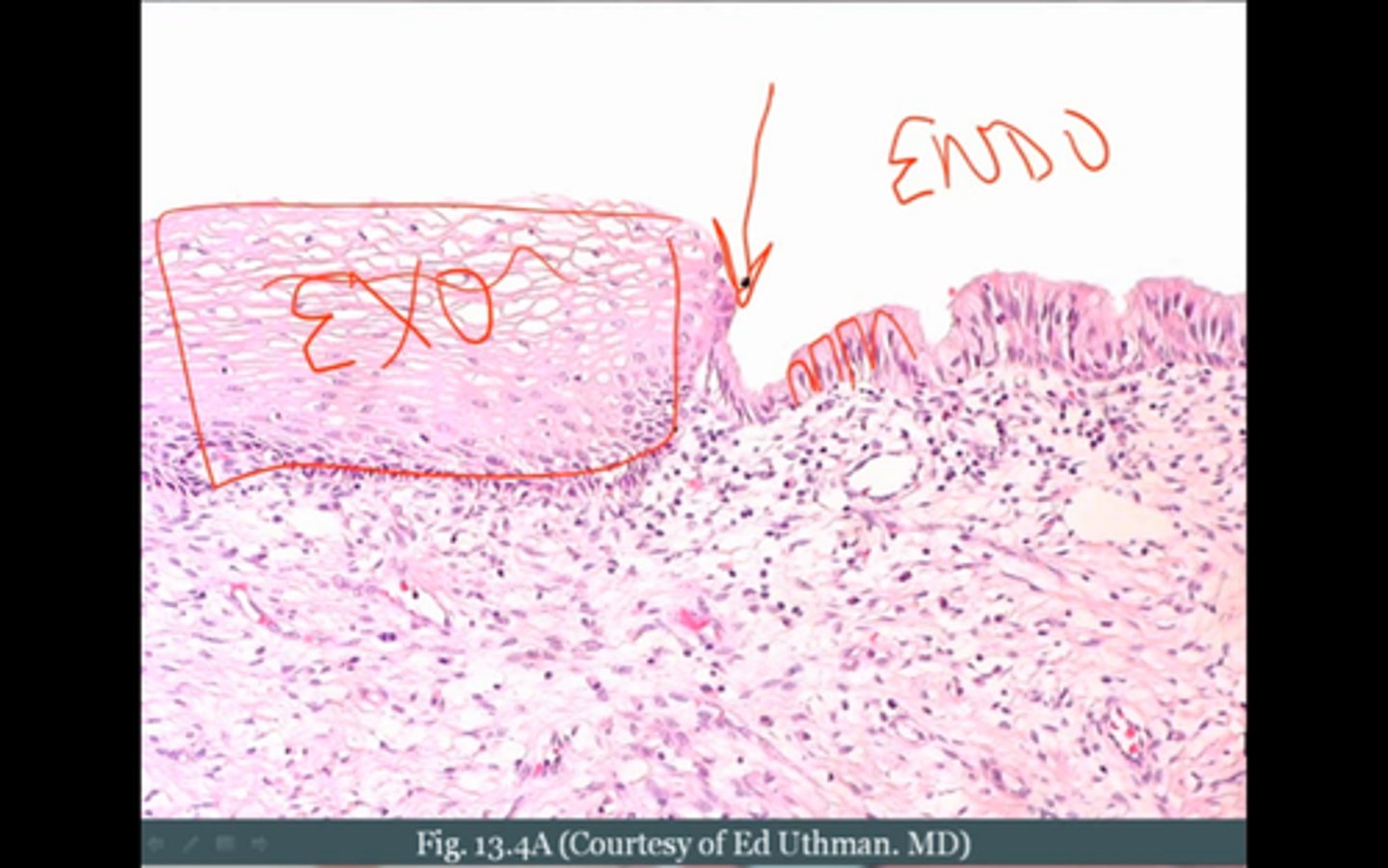
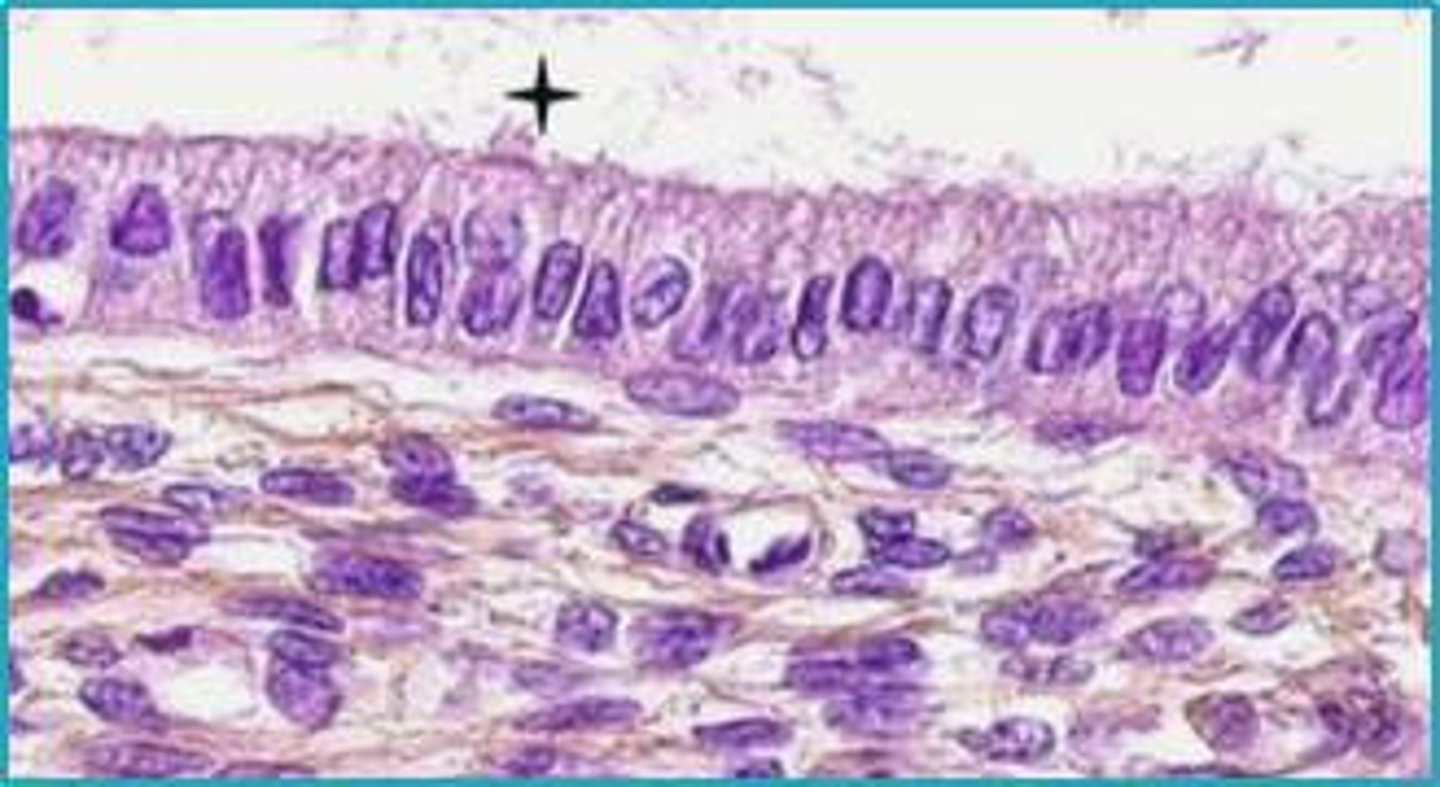
Endocervix (Cervix)
the mucous membrane lining the cervical canal
-----------------
FEATURES:
- contains simple columnar mucosa
- cells secrete cervical mucus
- some cells may be ciliated
- contains reserve cells
Ectocervix
the part of the cervix that projects into the vagina and is lined with non- keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
follicular phase (ovarian cycle)
period of follicle growth
(lasts to about 1-14 days)
- progesterone is low
- estrogen starts to rise
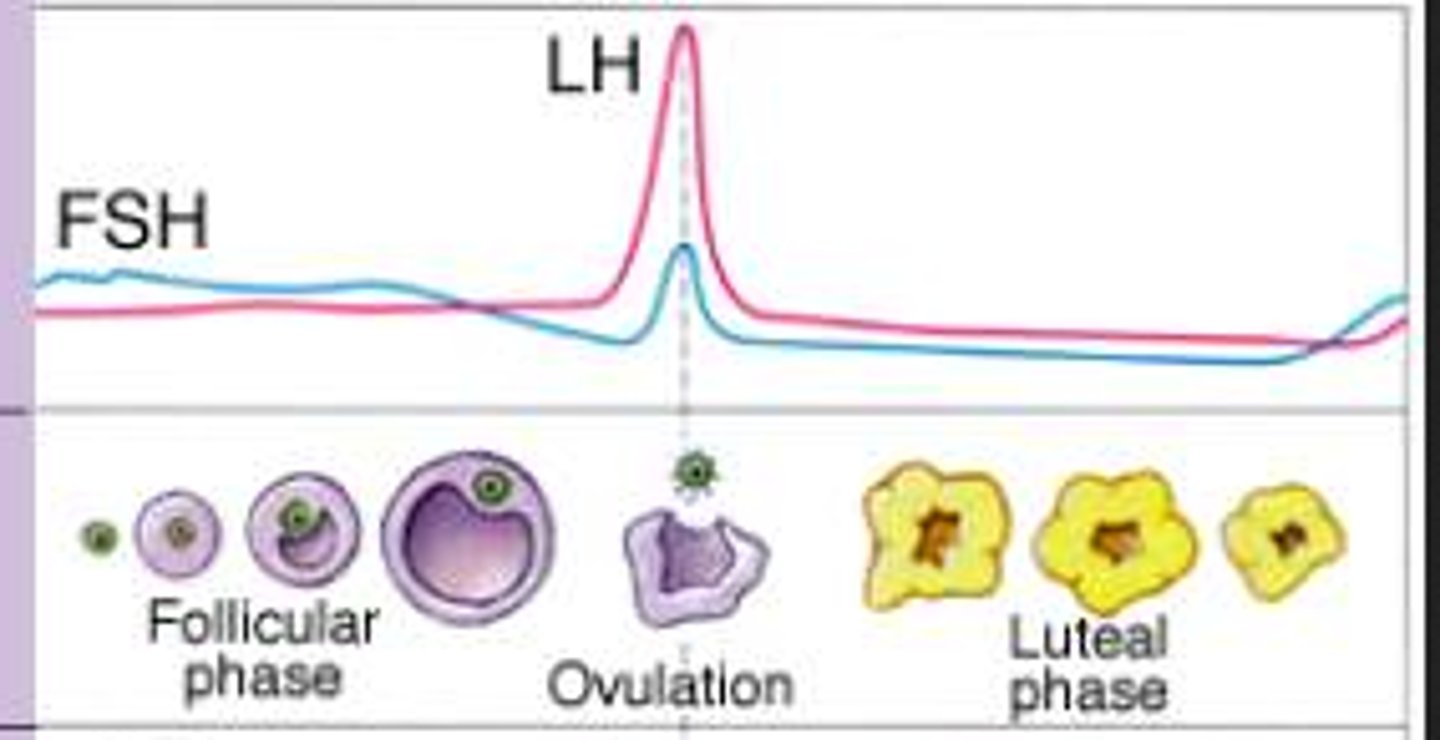
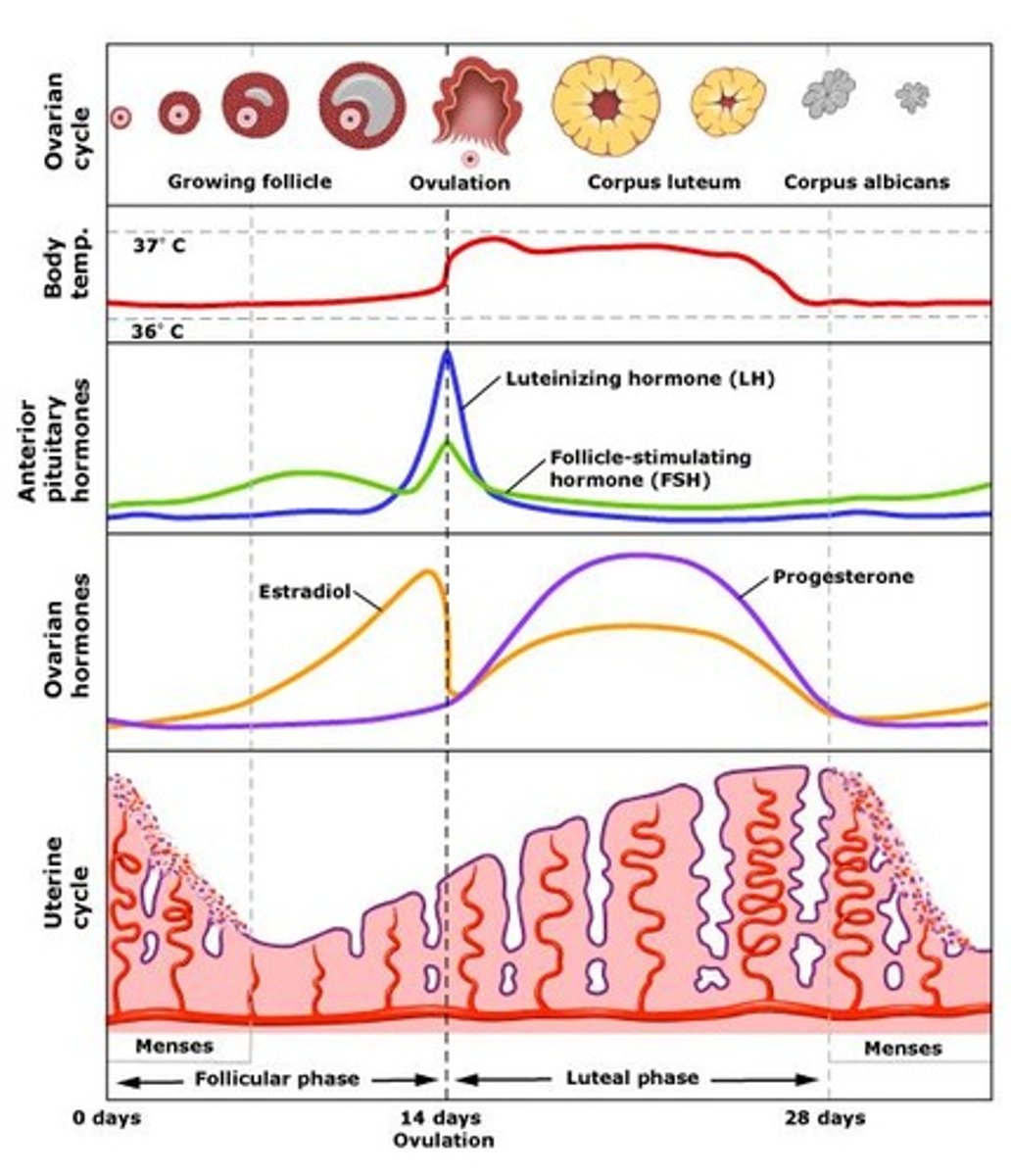
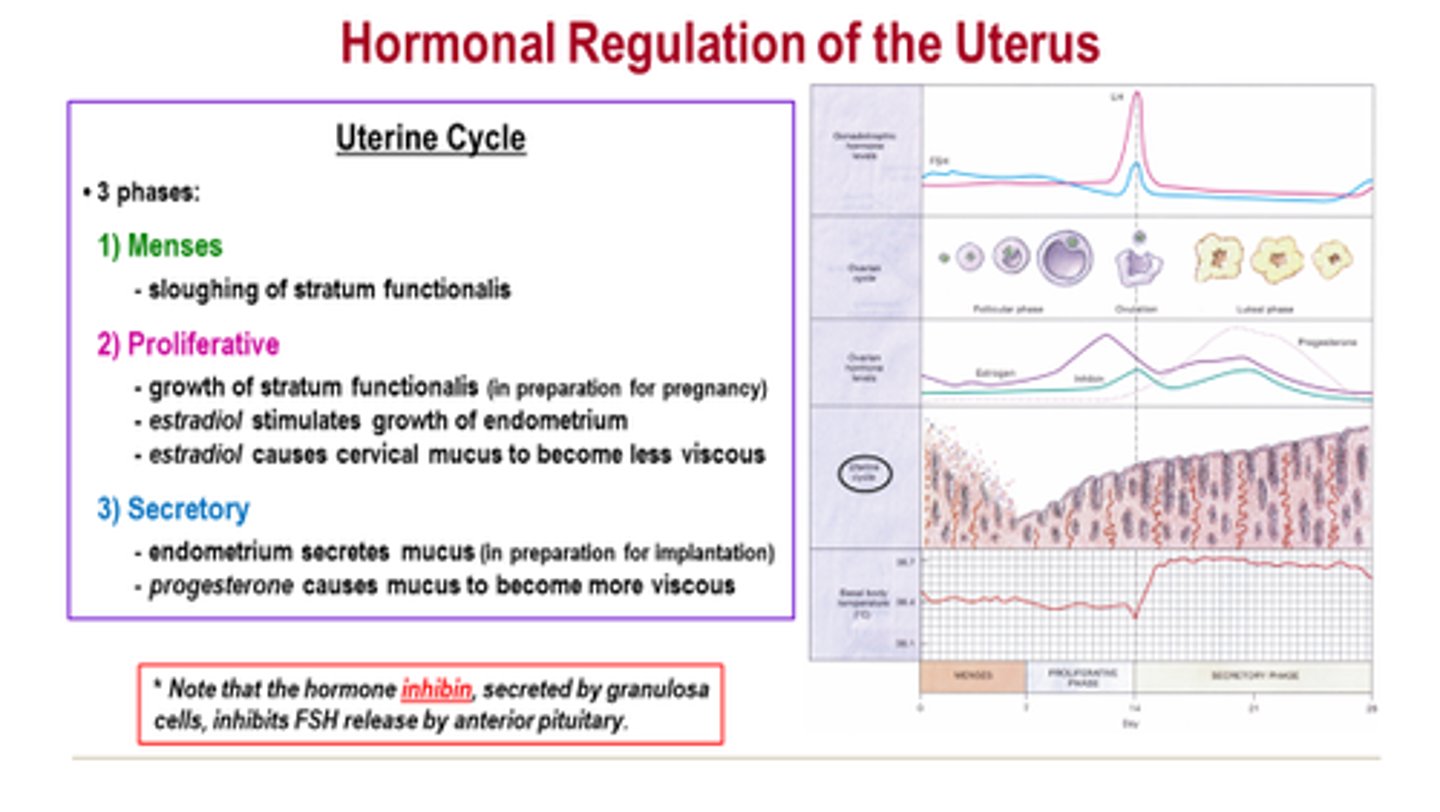
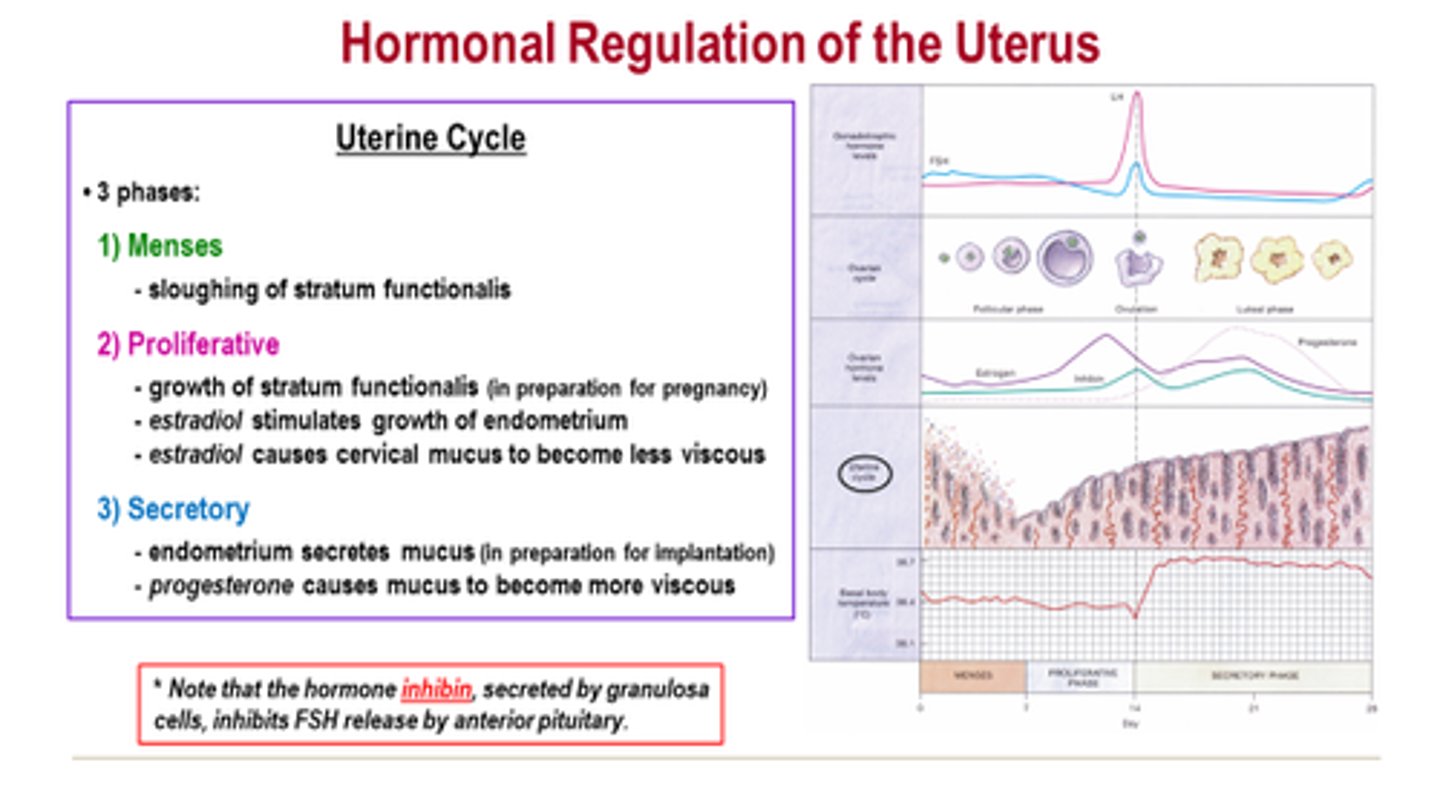
ovarian cycle
The 28 days of the menstrual cycle correlate with the development of the ovary.
-----------------
Has three subphases
- follicular phase
- ovulation phase
- luteal phase
-----------------
this cycle is in line with the uterine cycle (happens at the same time)
ovulation phase (ovarian cycle)
period where ovulation occurs
(occurs instantly)
- estrogen levels are high
- Luteinizing hormone (LH) levels are high
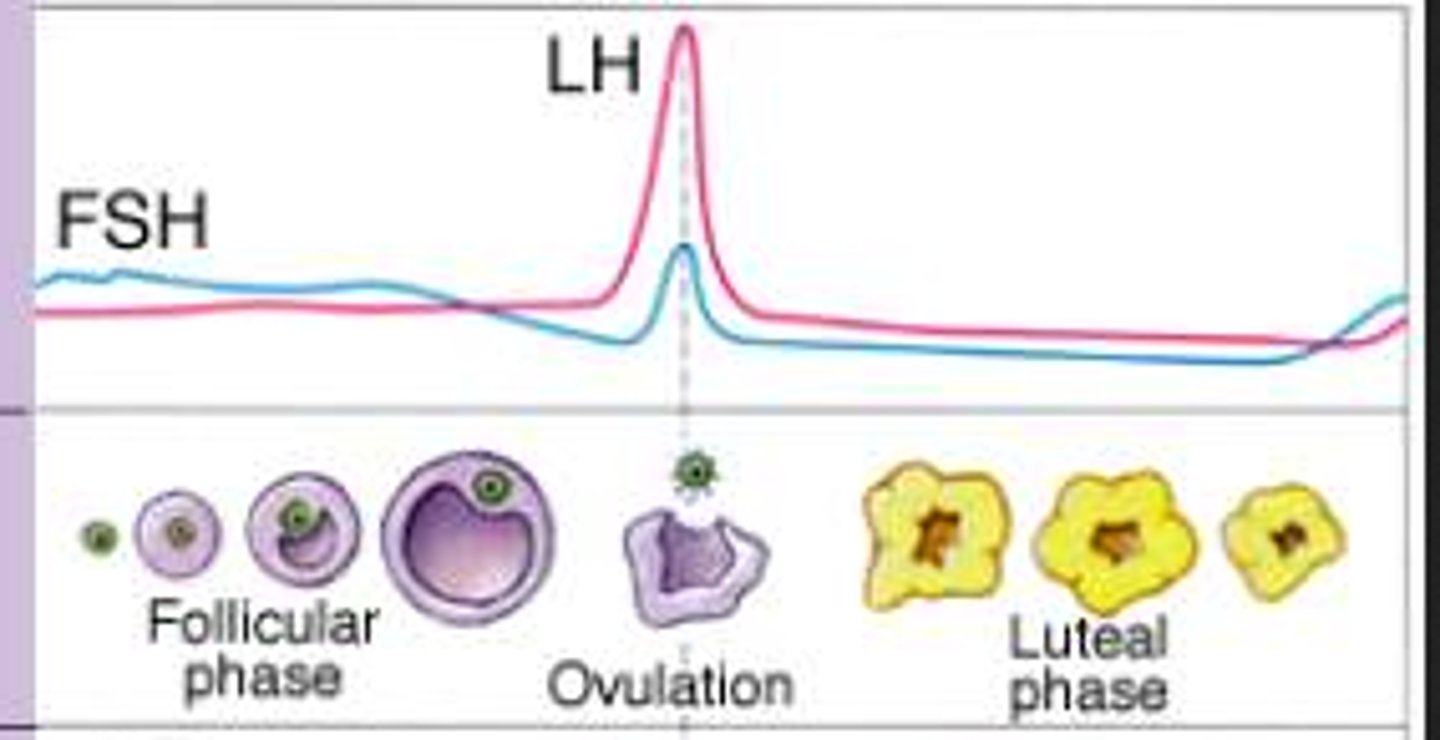
Leuteal phase (ovarian cycle)
the period when an egg travels from the ovary to the uterus
- it's the phase where sperm comes in contact with the egg (in the uterine lining) and where pregnancy occurs
-----------------
occurs after the ovulation phase and takes about another 14 days
-----------------
- Estrogen levels are high (but not as high as compared to ovulation phase)
- Progesterone levels are very high
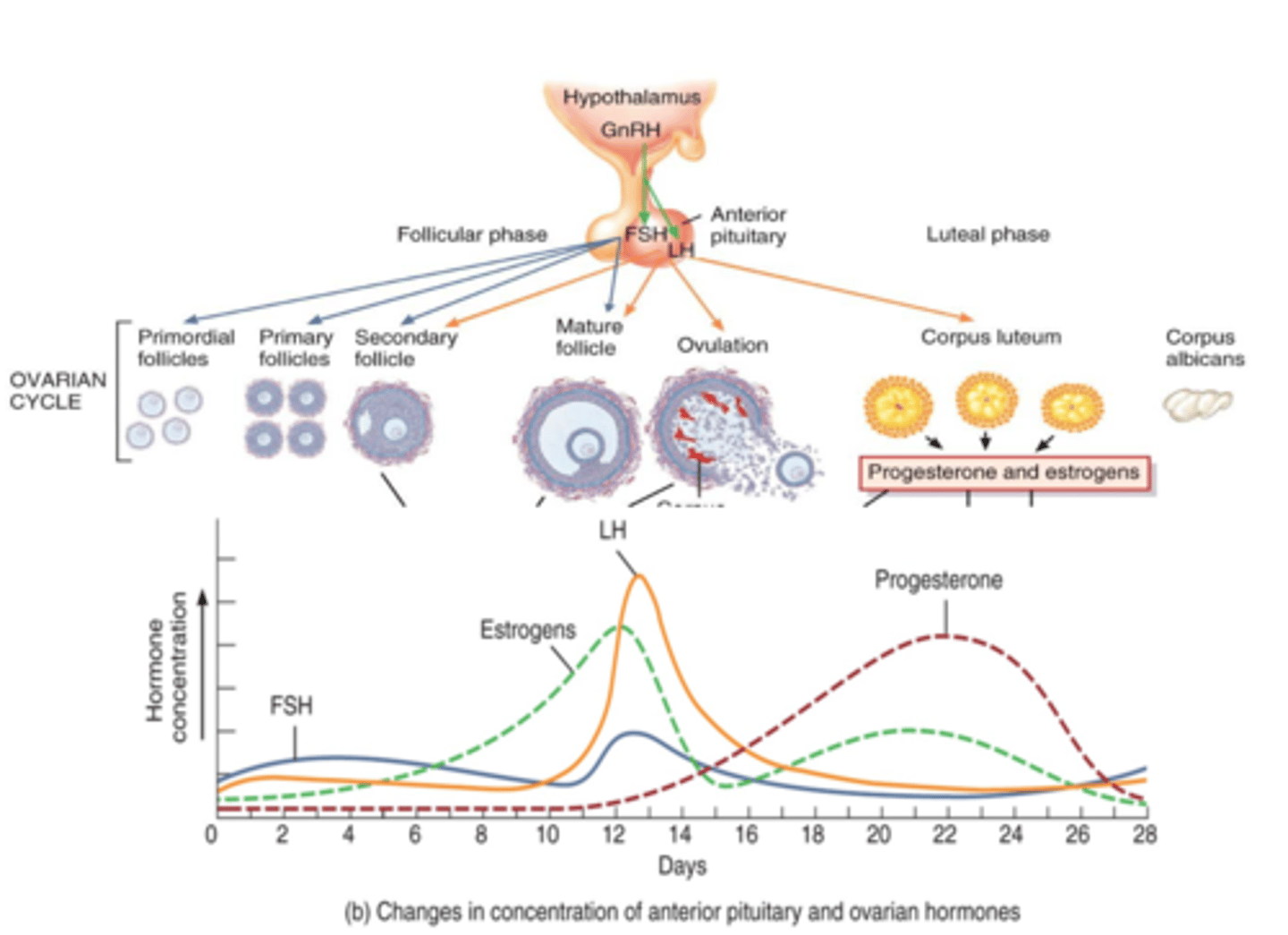
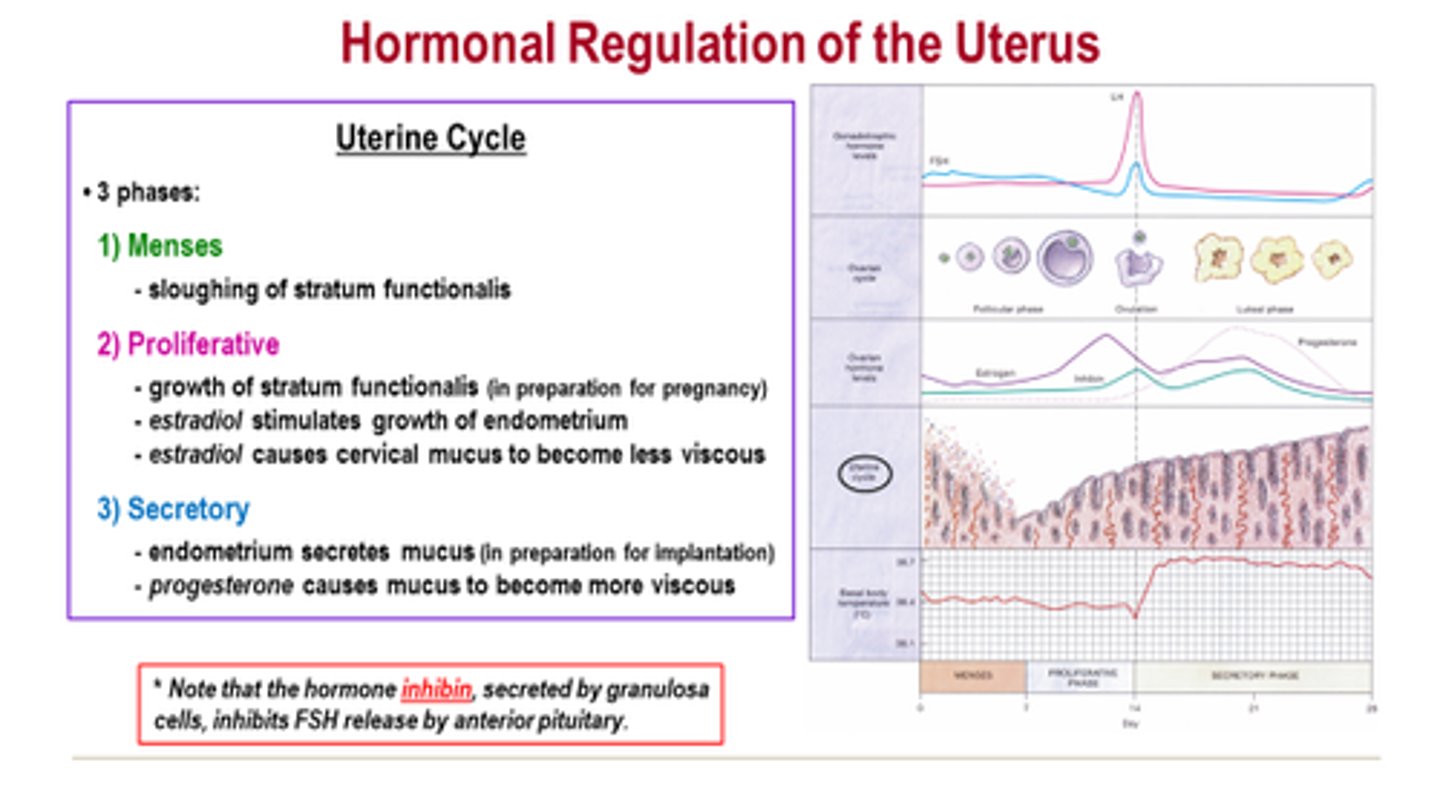
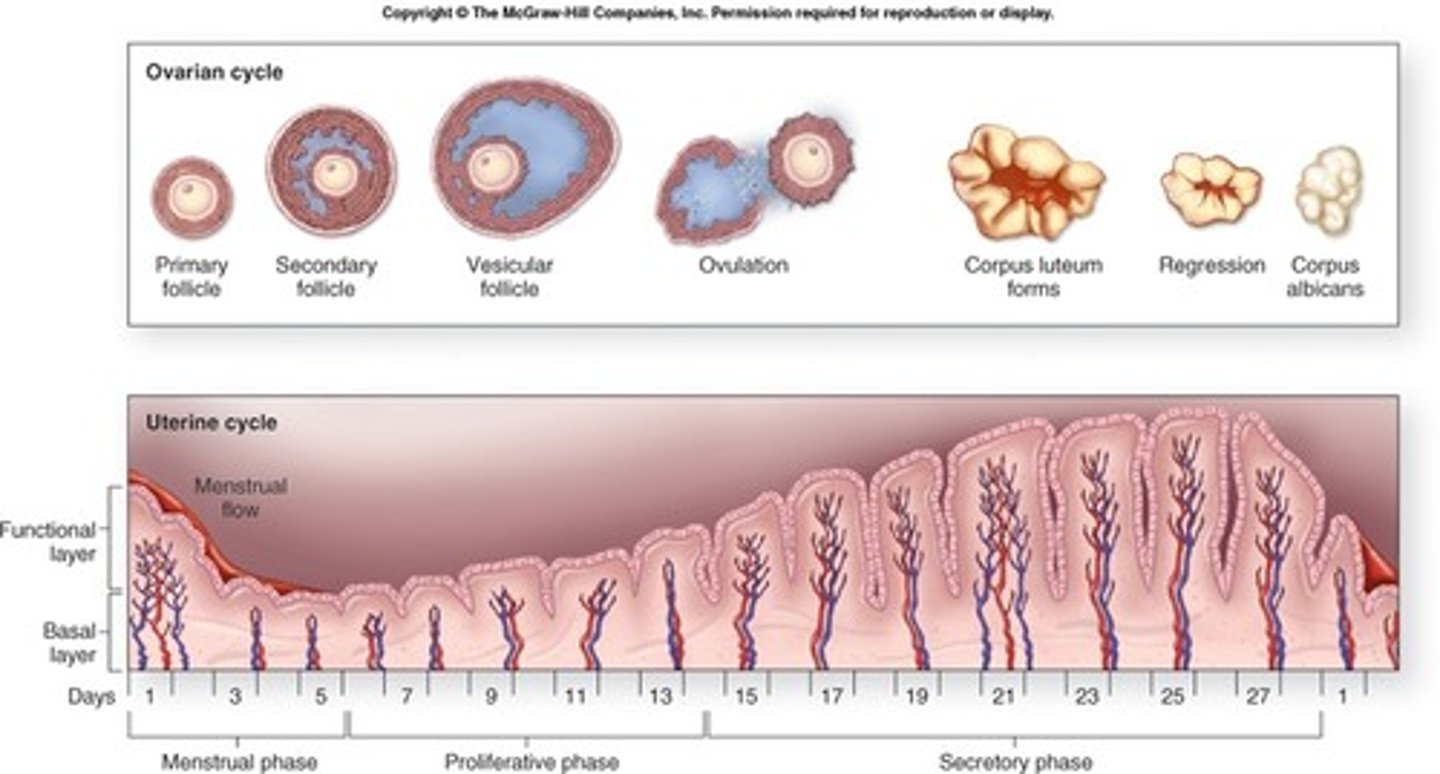
uterine cycle
The cycle that prepares the uterus for the growth of an embryo.
(takes about 28 days)
-----------------
DIVIDED INTO 3 PHASES
- meses phase
- proliferative phase
- secretory phase
-----------------
this cycle is in line with the ovarian cycle (happens at the same time)
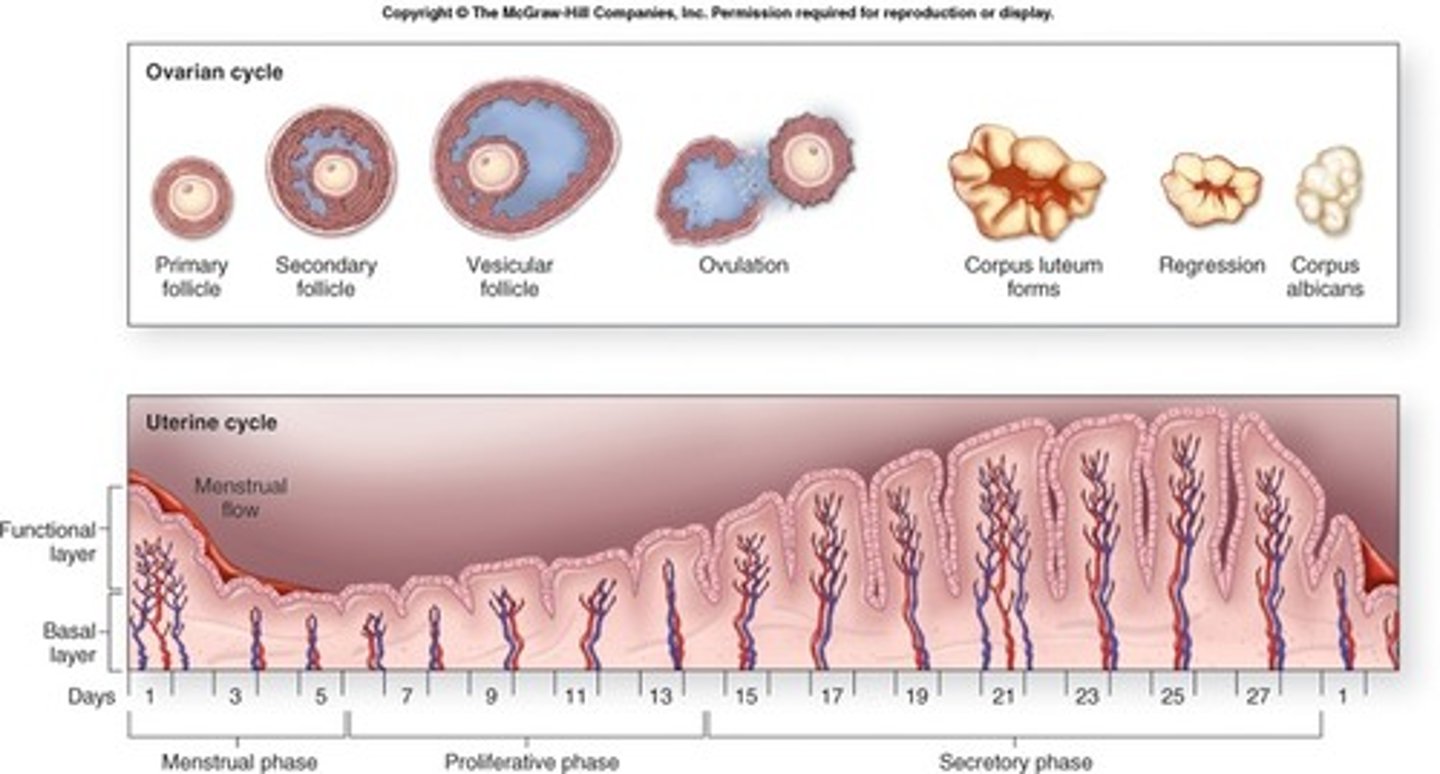
menses phase (uterine cycle)
myometrium contracts and endometrium detaches
-----------------
(takes about 5 days)
- Estrogen and progesterone levels are low
Proliferative phase (uterine cycle)
refers to the estrogen-induced thickening of the endometrium
-----------------
(takes about 9 days)
- estrogen levels start to rise
- progesterone levels are low
secretory phase (uterine cycle)
is the endometrial response to progesterone
-----------------
(takes about 14 days)
- estrogen levels are high
- progesterone levels are VERY high