OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS
1/10
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are the 4 pathways for the oxidation of fatty acids?
Beta-Oxidation (major)
Peroxisomal Oxidation
Alpha-Oxidation
ω oxidation
What is β oxidation?
It is a catabolic reaction that occurs during fasting as oxidation of acyl CoA to acetyl CoA where 2 carbon atoms are serially split off from carboxyl end of fatty acids.
Why is it called β oxidation?
•It is called β-oxidation because the oxidation starts at the β carbon atom of fatty acids.
Location of β oxidation?
Tissues – liver, muscle, renal cortex, adrenal medulla, heart, etc.
Intracellular site – mitochondria
What are the 3 stages of β oxidation?
1. Activation of fatty acids
2. Transport of fatty acyl coA into mitochondria
3.Degradation (β-oxidation reactions)
Explain The 3 stages?
Activation of Fatty Acid
At the cytoplasm, fatty acids are activated to form Fatty Acyl CoA by the enzyme thiokinase (acyl CoA synthetase).
Between the carboxyl group of the fatty acid and the thiol group of coenzyme A (CoA-SH) creates a thioester bond.
Fatty Acid + CoASH ————————> Fatty acyl CoA.
This process uses 2 molecules of ATP.
Explain the 3 stages?
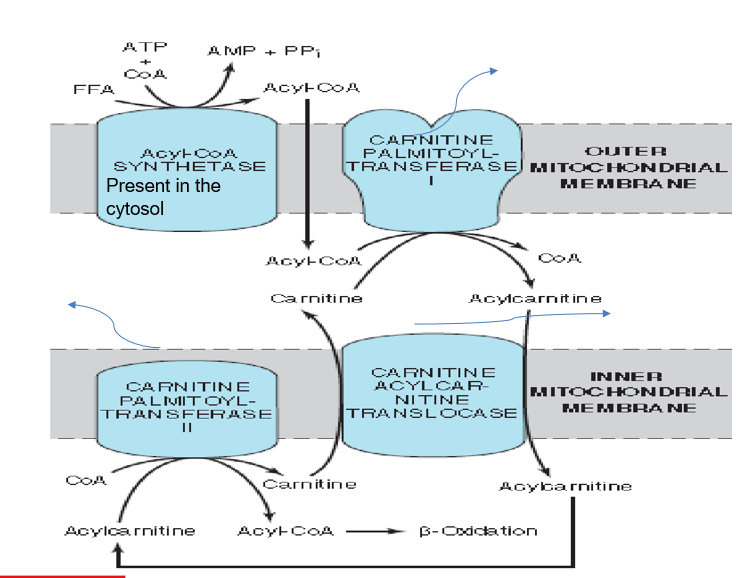
Transport of fatty acyl CoA into mitochondria using Carnitine Shuttle:
β oxidation occurs in the mitochondria and the fatty acids are present in the cystol.
The fatty acid in the cystol will be acted on an enzyme known as THIOKINASE where it utilizes ATP and CoASH and essentially adds a CoA group to the FFA and activates it and forms fatty acyl CoA.
In the outer membrane of the mitochondria, an enzyme CPT1 is present. This enzyme will remove the CoASH group and add a carnitine group forming acylcarnitine.
The acyl carnitine then moves pass the inner mitochondrial membrane by the enzyme CACT (Carnitine-acylcarnitine Translocase).
In the mitochondrial matrix, the enzyme CPT2 converts acylcarnitine to Acyl CoA and carnitine is regenerated.
Reactions of β oxidation?
It is a cyclical process. There are 4 reactions:
1.Oxidation
2.Hydration
3.Reoxidation
4.Thiolytic cleavage
End products of β oxidation?
Even No. of C atoms: Acetyl CoA
Odd No. of C atoms: Acetyl CoA and propionyl CoA
Propionyl CoA can be converted to succinyl CoA which condenses with glycine to sunthesize heamoglobin
ENERGETICS OF β oxidation of Palmitic Acid (16 C) ?
-2 ATP used in Fatty acid Synthesis.
Finding no. of Acetyl CoA = (16/2) = 8 Acetyl CoA produced.
No. of cycles (n-1) = (8-1) = 7 rounds
1 cycle of β-oxidation produces 4 ATP. Therefore, 7 cycles produces 28 ATP.
A total of 8 acetyl CoA are produced; each one enters
TCA cycle and gives 10 ATP. 8 X 10 ATP = 80 ATP
Net Total = (28 + 80) - 2 = 106 ATP in total
List 5 biomedical Importance of β oxidation?
Carnitine Deficiency: Occurs in infants. Results in hypoglycemia, raised plasma fatty acid, muscle weakness and lipid accumulation.
Hepatic CPT I Deficiency: hypoglycaemia and low plasma ketone bodies.
Muscle CPT2 Deficiency: muscle weakness and myoglobinuria.
Dicarboxylic Aciduria
Refsum’s Disease : caused by inherited defect in α-oxidation that allows accumulation of phytanic acid.
Zellweger’s Syndrome: due to inherited deficiency of peroxisomes. Affects brain, liver and kidney.