Organic Primer, ch 1, ch 2, ch3, and ch4
1/144
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Organic Chem test 1 Dr. Guo. One stop studying
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
Which of the following is most likely to dissolve in hexane, a nonpolar organic liquid?
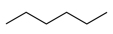 |
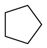
(cyclopentane) is soluble in hexane in all proportions. Cyclopentane and hexane are nonpolar molecules, with only dispersion forces between molecules. Each one has the same type of intermolecular attractions, whether as a pure substance or in a mixture. The other substances have intermolecular attractions (dipole−−dipole and hydrogen bonds for the molecules; ionic bonds in the case ofKBrKBr) that aren’t in effect when mixed with hexane.
What are the intermolecular forces between molecules in a liquid sample of sulfur trioxide, SO3?
dispersion force
No hydrogen bonding capability?
CH₂=CH₂
CH₃CH₂CH₃
Can be a hyddrogen bond acceptor but not a donor
N(CH₃)₂
CH₃C(O)CH₃
CH₃OCH₃
Can be a hydrogen bond acceptor and donor
H₂O
CH₃OH
CH₃CH₂NH₂
Rank this highest to lowest bowling point? CH3CH3, CH3CH2CH3, CH3CH2CH2CH3, CH3CH(CH3)2
CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₃ (butane) > CH₃CH(CH₃)₂ (isobutane) > CH₃CH₂CH₃ (propane) > CH₃CH₃ (ethane)
Polar or non polar? NH3, H2, CO2, CH4, HBr, BF3
Polar: NH3, HBr
Non Polar: H2, CO2, CH4, BF3
Choose the best description for the indicated bond.

This is a triple bond between two carbons in which a sigma bond arises from sp−spsp−sp overlap and two pi bonds are formed by side-to-side overlap of unhybridized pp orbitals on each carbon
The atomic number of boron is 5. The correct electronic configuration of boron is:
1s22s22p1 |
How many distinct p orbitals exist in the second electron shell, where n = 2?
3
The ________ tells us that each orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons.
Pauli exclusion principle
A node is a region of high electron density between the two atoms in a covalent bond.
False
To make it true it would be “A node is a region in an orbital where the probability of finding an electron is zero”
When filling two or more orbitals of the same energy with electrons, the electrons will go into different orbitals rather than pair up in the same orbital.
True
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called ________.
isotopes
The electron density of ________ orbitals has spherical symmetry.
s
An oxygen atom has ________ valence electrons.
6
Which element in the second row of the periodic table has six valence electrons and a valence of two?
oxygen
Orbitals which are equal in energy are referred to as ________.
degenerate
In a carbon atom, the 2s and 2p orbitals are equal in energy.
False The 2s orbital is lower in energy than the 2p orbitals.
The element with the electronic configuration 1s22s22p63s1 is ________.
sodium
A carbon-hydrogen bond in ethane (CH3CH3) is best described a ________.
essentially nonpolar
The electronegativity of elements on the periodic table increases going ________ a column and to the ________ in each row.
up, right
Within a given row of the periodic table, electronegativity typically increases left to right across the row.
true
Which of the following molecules contains a polar covalent bond?
CH3Cl |
Covalent bonds may be polar or nonpolar. What property of the atoms forming a given bond determines this?
electronegativity
The compound methylamine, CH3NH2, contains a C-N bond. In this bond, which of the following best describes the charge on the carbon atom?
slightly positive
The formal charge on oxygen in dimethyl ether, CH3OCH3, is ________.
0
For most compounds in which a nitrogen atom bears no formal charge, the valence of this nitrogen atom is ________.
3
Which of the following are correct Lewis structures, including formal charges, for nitric acid, HNO3?
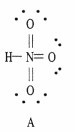 | 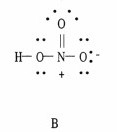 | 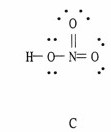 |
B only
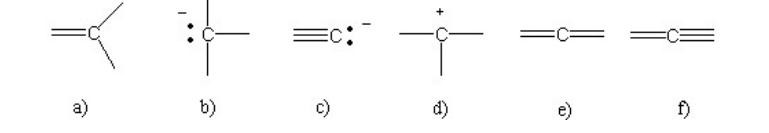
Which of the following bonding patterns of carbon is not allowed in the formation of an organic compound?
f
Which of the following compounds are covalent compounds?
KCl |
CF4 |
NH3 |
both KCl and CF4 |
both CF4 and NH3 |
both CF4 and NH3 |
When a negatively charged species is most appropriately depicted as a hybrid of several resonance forms, the negative charge present is considered to be rapidly moving between the resonance forms bearing the formal negative charge.
False
The negative charge does not literally move back and forth between resonance structures.
Instead, the real molecule is a resonance hybrid, meaning the electron density (including the negative charge) is delocalized or spread out over the entire structure simultaneously.
Resonance forms are just different ways of drawing the same molecule, not actual rapidly interconverting structures.
So, the charge is delocalized, not rapidly shifting between forms
When a molecule can best be represented as a series of resonance forms, each of these forms always contributes to the same degree in the hybrid.
False
Not all resonance forms contribute equally to the resonance hybrid. Some forms are more stable or significant than others, so they contribute more.
Which of the following structures (a-d) is another resonance structure
of the following organic molecule?
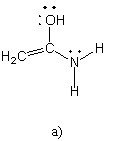 | 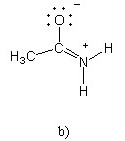 | 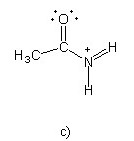 | 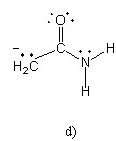 |
B
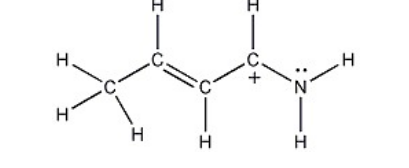
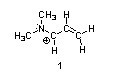
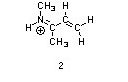
One resonance structure of a cation is shown. Provide the other reasonable resonance structures.
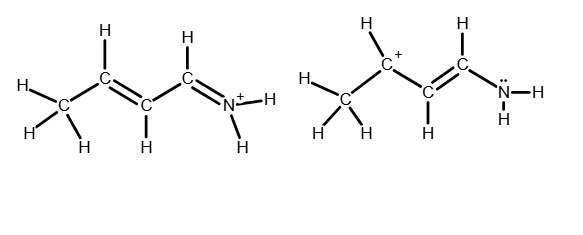
Draw the important resonance forms of:
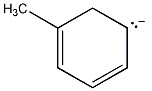
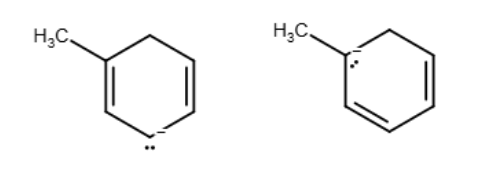
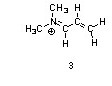
Structures ________, shown below, are resonance structures, and structure ________ is the major contributor to the overall resonance hybrid.
 |  |  |
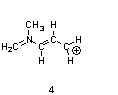 | 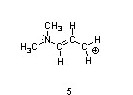 | 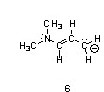 |
1,3,5:3
Draw a line-angle formula for (CH3)2CHCH2CH2NH2.
Draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds), Atoms, and Advanced Template toolbars. The single bond is active by default.
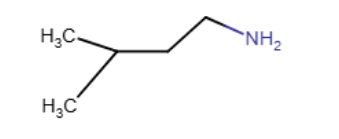
The Lewis structure of trimethylamine is shown below. Draw the condensed structural formula which corresponds to this Lewis structure.
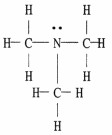
(CH3)3N |
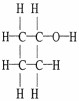
The Lewis structure of pentane is shown below. Draw the condensed structural formula which corresponds to this Lewis structure.
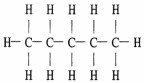
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
How many carbon atoms are present in the molecule shown?
10
Which of the following condensed formulas represents the same compound as the line-angle structure shown?
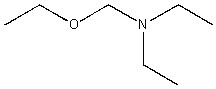
CH3CH2OCH2N(CH2CH3)2
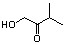
ndicate the line-angle structure that corresponds to the condensed structure, HOCH2C(O)CH(CH3)2.
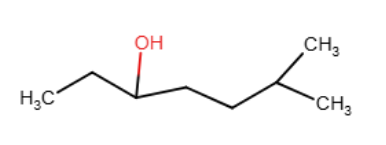
Provide the line-angle formula for the alcohol CH3CH2CH(OH)CH2CH2CH(CH3)2.
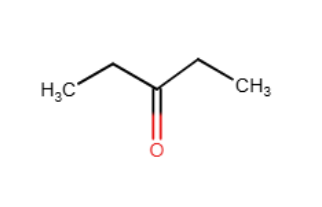
Provide the line-angle formula (skeletal structure) for (CH3CH2)2C=O.
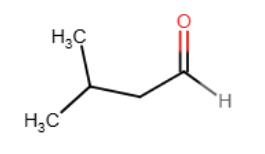
Provide the line-angle formula (skeletal structure) for (CH3)2CHCH2CHO.
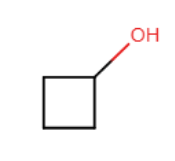
Draw an acceptable line-angle formula for cyclobutanol (shown below).
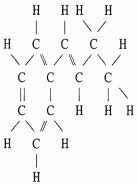
Draw an acceptable line-angle formula for the compound shown below.
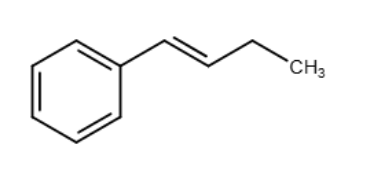
Which of the following condensed formulas correctly represents the line-angle structure shown below?
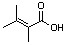
(CH3)2CC(CH3)CO2H
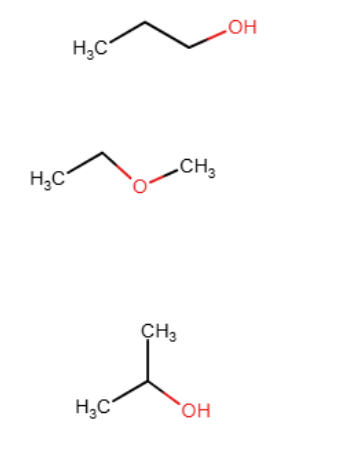
Draw the line-angle formula for three compounds with molecular formula C3H8O
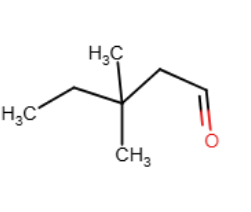
Provide the line-angle formula for CH3CH2C(CH3)2CH2CHO
How many hydrogen atoms are present in the molecule shown?
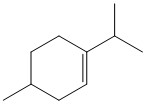
18
What is the molecular formula for the molecule shown?
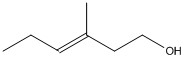
C7H14O
A molecule of acetylene (C2H2) has a ________ geometry and a molecular dipole moment that is ________.
linear, zero
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Induced dipole interactions are usually stronger than dipole-dipole interactions |
B) Polar solutes tend to be more soluble in nonpolar solvents |
C) All polar molecules are capable of hydrogen bond formation |
D) Higher molecular dipole values (μ) are associated with nonpolar molecules |
E) The polarity of a molecule is dependent on its three-dimensional structure |
E
Which one of the molecules shown below has no net molecular dipole moment?
H2C=CH2 |
CH2Cl2 |
CH2O |
CH3OH |
CH3Cl |
H2C=CH2
Which one of the molecules shown below has a net molecular dipole moment?
BeCl2 |
CO2 |
CCl4 |
CH3CCl3 |
CH3CCl3
Does 1,1-dichloroethene (Cl2C=CH2) have a net molecular dipole moment?
Yes, 1,1-dichloroethene has a net molecular dipole moment.
Show the direction of the Cl3H molecular dipole moment in the chloroform molecule.
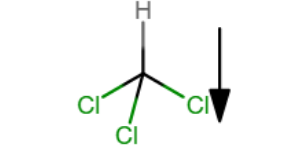
Which sequence ranks the following isomers in order of increasing boiling points?
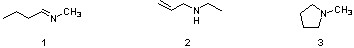
3<1<2
Which of the following has the highest boiling point?
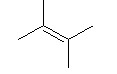 |
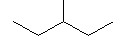 |
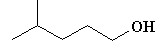 |
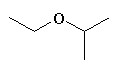 |
 |
The one with the OH at the end
What intermolecular forces are present among molecules in dimethyl ether, CH3OCH3?
both London dispersion forces and dipole-dipole forces
Which of the molecules below can hydrogen bond to another of the same compound?
(CH3CH2)2CHOH
What intermolecular attractions exist in a pure sample of methylthiol, CH3SH?
dipole-dipole attractions |
London dispersion forces |
Which of the molecules below has the higher boiling point?
CH3CH2CH2OH or CH3CH2OCH3
CH3CH2CH2OH
Which of the molecules below has the higher boiling point?
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 or (CH3)2CHCH2CH3
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
Which of the molecules below has the higher boiling point?
(CH3)3N or CH3CH2CH2NH2
CH3CH2CH2NH2
The compounds below are base pairs used to form supramolecular polymers (Org. Lett. 2011, 240). They are held together by three intermolecular hydrogen bonds and each contains one intramolecular hydrogen bond. Which atom in structure B forms a hydrogen bond with the circled hydrogen in structure A?
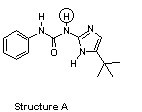 | 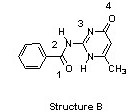 |
3
Which compound is more soluble in water?
(CH3)2NH or CH3CH2CH3
(CH3)2NH
Which compound is more soluble in water?
CH3OCH3 or CH3CH2OH
CH3CH2OH
Does the C-O bond in methanol (CH3OH) possess an individual bond dipole moment?
Yes, the C-O bond in methanol has an individual bond dipole moment.
Draw the structure of the isomeric form of 1,2-dichloroethene (CHCl-CHCl) which has no net dipole moment.
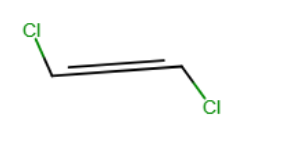
Which functional groups below indicate the presence of two atoms connected by a triple bond?
both alkyne and nitrile
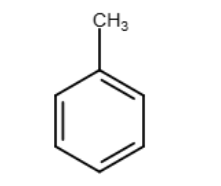
Provide the structure of an aromatic compound with seven carbon atoms.
Dopamine is shown below. What functional group, or structural element is not present in this compound?
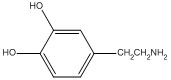
carboxyl
Which of the following functional groups is not present in the HIV protease inhibitor drug called Saquinavir?
amine |
ketone |
aromatic |
amide |
alcohol |
Ketone
Which functional group occurs more than two times in the structure of the HIV protease inhibitor drug called Saquinavir?
ketone |
amine |
alkene |
amide |
carboxylic acid |
amide
Which molecule below is an alkene?
(CH3)2CHCH2NH2 |
(CH3)2C=CH2 |
CH3CH2CH2CO2H |
(CH3)2CHCH2OH |
CH3CH2OCH2CH3 |
(CH3)2C=CH2
Which of the molecules below is an ester?
HC≡CCH3 |
CH3OCH2CH2CH3 |
CH3CH2CH(CH3)2 |
CH3COOCH3 |
CH3COOH |
CH3COOCH3
Which of the functional groups below contain a hydroxyl group as a part of their structure?
aldehyde |
amine |
carboxylic acid |
alcohol |
both alcohol and carboxylic acid |
both alcohol and carboxylic acid
Which of the class of organic compound below contains a carbonyl group as a part of its structure?
aldehyde |
ester |
carboxylic acid |
ketone |
all of the above |
all of the above
Which of the following does not contain a carbonyl group?
carboxylic acid |
ketone |
aldehyde |
ester |
ether |
ether
Anisole, the compound shown below, is an example of ________.
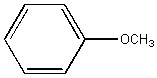
an ether
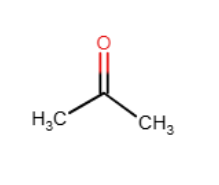
Acetone is a ketone that contains three carbon atoms. Provide its structure.
What is the name of the characteristic functional group found in the molecule CH3CH2COOH?
ester group |
carboxyl group |
carbonyl group |
hydroxyl group |
carboxyl group
Which molecule below is an ether?
CH3CH2CH2CO2H |
(CH3)2CHCH2NH2 |
(CH3)2C=CH2 |
(CH3)2CHCH2OH |
CH3CH2OCH2CH3 |
CH3CH2OCH2CH3
Which of the molecules below can be properly called an amine?
CH3COOH |
CH3CH2CH2NO2 |
CH3CH2NHCH3 |
CH3CN |
CH3CH2CH2OH |
CH3CH2NHCH3 |
Which of the statements below accurately describe(s) alkanes?
Alkanes belong to the class of unsaturated hydrocarbons. |
Alkanes are hydrocarbons which contain only single bonds. |
Alkanes are the simplest and least reactive class of organic compounds. |
Statements"Alkanes are hydrocarbons which contain only single bonds" and "Alkanes belong to the class of unsaturated hydrocarbons" are correct |
Statements "Alkanes are hydrocarbons which contain only single bonds" and "Alkanes are the simplest and least reactive class of organic compounds" are correct |
Statements "Alkanes are hydrocarbons which contain only single bonds" and "Alkanes are the simplest and least reactive class of organic compounds" are correct
Which of the following types of hydrocarbons is(are) saturated?
alkanes |
alkenes |
aromatics |
alkynes |
All of the above are saturated. |
alkanes
If a hydrocarbon has no double or triple bonds, it is said to be ________.
saturated
If an acyclic alkane hydrocarbon contains n carbon atoms, how many hydrogen atoms must it also contain?
2n + 2
How many methylene groups are present in 2,4-dimethylhexane?
2
How many secondary (2°) carbons are found in 5-ethyl-3,3,4-trimethylheptane?
3
Provide an acceptable name for (CH3CH2CH2)3CH.
4-propylheptane
Provide the name of the compound below.
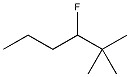
3-fluoro-2,2-dimethylhexane
Provide the name of the compound below.
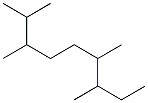
2,3,6,7-tetramethylnonane
Provide an acceptable name for the alkane shown below.
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
Hexane
Provide an acceptable name for the alkane shown below.
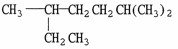
2,5-dimethylheptane
Draw an acceptable structure for 3-ethyl-3-methylhexane.

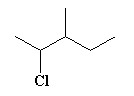
Name the haloalkane shown.
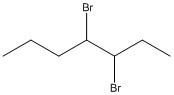
3,4-dibromoheptane