particle-size-reduction
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Why is particle size important in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
It affects material handling (e.g. flowability) and biopharmaceutical properties such as dissolution and bioavailability.
How does comminution (particle size reduction) affect drug dissolution and bioavailability?
It increases surface area, leading to a higher dissolution rate and potentially increased bioavailability if absorption is dissolution-limited.
Why is particle size critical for inhaled and transported pharmaceuticals?
It determines lung deposition site for inhaled drugs and increases bulk density, improving transport efficiency.
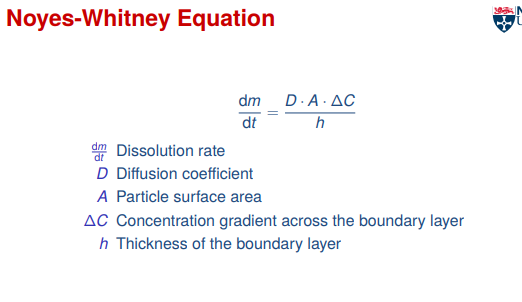
noyes whitney requation
Dissolution rate ∝ surface area of the drug
Increased by smaller particle size
Increased by higher diffusion coefficient
Increased by greater concentration gradient
what is milling?
A mechanical process used to reduce particle size of solid materials
Achieved by impact, compression, attrition, or shear forces
Increases surface area, improving dissolution rate
Improves flowability and uniform mixing in manufacturing

What is a cutter mill and how does it work?
Uses rotating and stationary knives to cut particles
Produces coarse particle size reduction
Screen retains particles until the desired size is achieved
What is a hammer mill and how does it work?
Hammers radiate from a central rotating shaft
Particles are struck at high velocity
Causes brittle fracture of most materials
What is a runner mill and how does it operate? edg and end
Based on pestle and mortar (manual or mechanised)
Edge runner mill: grinding occurs at the edge of a rotating wheel
End runner mill: grinding occurs under the flat base of the rotating wheel
What is a roller mill and how does it work?
Uses two rotating rollers (or one rotating, one stationary)
Particles are crushed as they pass through the roller gap
Speed difference between rollers introduces shearing action
What is a ball mill and how does it reduce particle size?
A:
Hollow rotating drum partially filled (≈30–50%) with mill balls
Rotation speed and feed volume are critical
Balls are lifted by centrifugal force
Avalanche (cascading) effect causes impact and attrition, reducing particle size
What is a vibration mill and how does it work?
Mill chamber is ~80% filled with milling balls
Vibration causes frequent impacts between balls and particles
Produces fine particle size reduction
What is a pin mill and how does it reduce particle size?
Consists of two discs with closely positioned pins
Size reduction occurs by impact when particles collide with pins
Also by attrition/shear between opposing pins
What is a fluid energy mill and how does it reduce particle size?
Uses high-velocity air injected into a toroidal milling chamber
Particles are suspended in turbulent airflow
Size reduction occurs by particle–particle and particle–wall collisions
What is Griffith’s theory of brittle fracture?
Materials contain microscopic cracks (flaws)
During comminution, applied energy concentrates at crack tips
When energy exceeds bond strength, the crack ruptures and propagates
How do cracks propagate according to Griffith’s theory, and how do tough materials differ?
Cracks spread through weak regions with many flaws
Elastic energy redistributes, concentrating at other cracks
Causes a cascade effect → rapid brittle fracture
Tough materials show ductile fracture with slower crack growth
What is deformation and how does it affect fracture?
Deformation dissipates applied energy that might otherwise cause fracture
Energy used in deformation is not available for crack propagation
Therefore, deformation can reduce brittle fracture
What is the difference between elastic and plastic deformation?
Elastic deformation: reversible; material returns to original shape when stress is removed
All materials show some elastic deformation
Plastic deformation: irreversible; permanent shape change
What is hardness and how is it measured?
Hardness is the ability of a material to resist plastic deformation
Measured in N m⁻² or using the Mohs’ scale (ordinal)
On the Mohs’ scale: Diamond = 10, stainless steel ≈ 5
Measured using hardness testers (e.g. Brinell, Vickers)
ow does hardness affect comminution?
Hard materials are more difficult to comminute
Require more energy for size reduction
Can cause wear of milling equipment parts