Cell 220 Lecture 13 - Senses (Exam 2)
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
What are the two classes of senses?
General and Special
temperature
General
pain
General
touch
General
stretch
General
pressure
General
gustation
Special
olfaction
Special
vision
Special
equilibrium
Special
audition
Special
Stimuli are detected by…….
receptors
chemoreceptors detects
changes in chemical composition
thermoreceptors detects
temperature
photoreceptors detects
light and color
mechanoreceptors detects
touch, pressure, and vibration
nociceptors detects
tissue damage
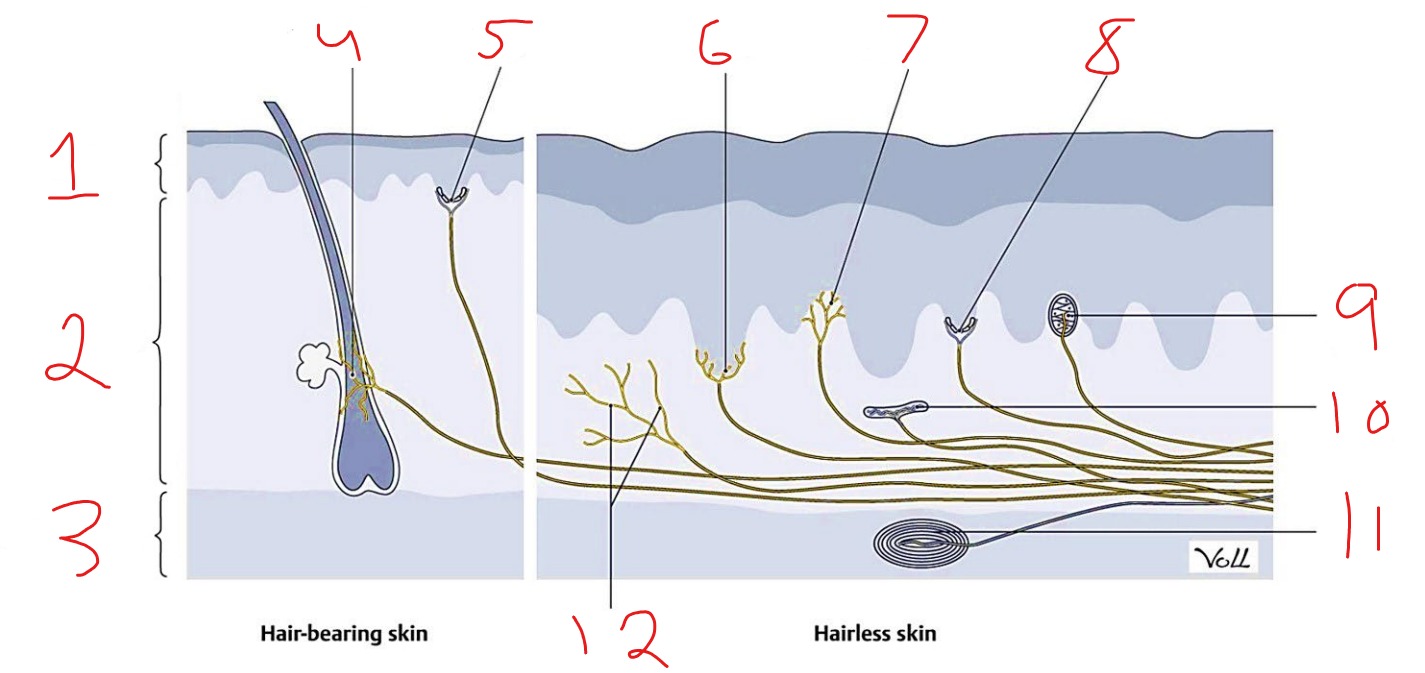
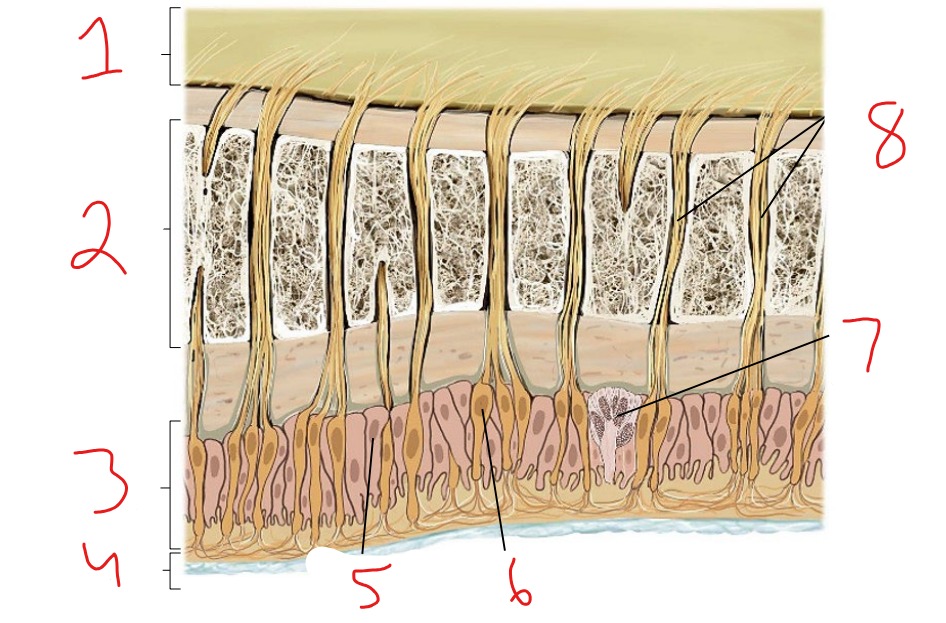
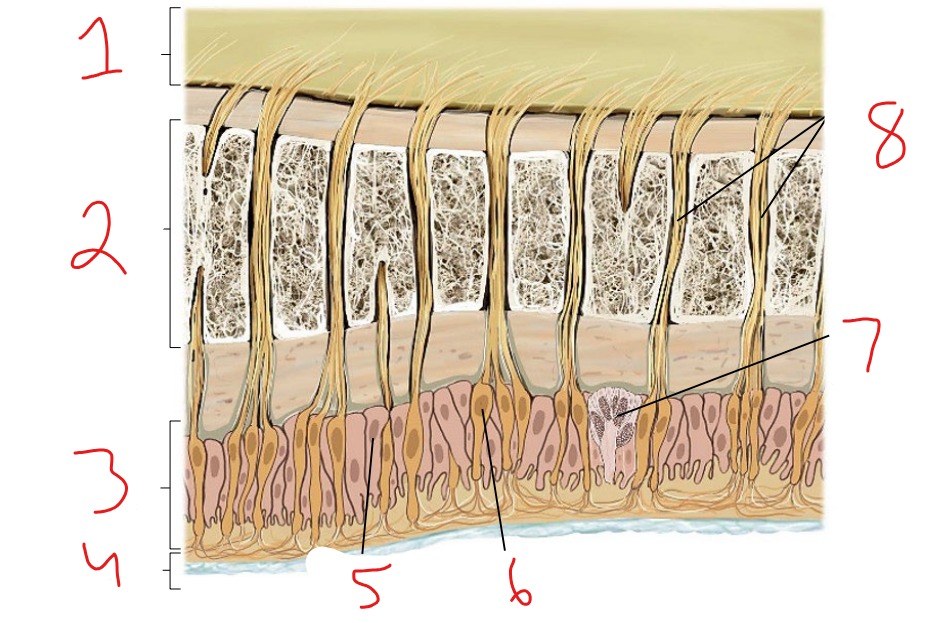
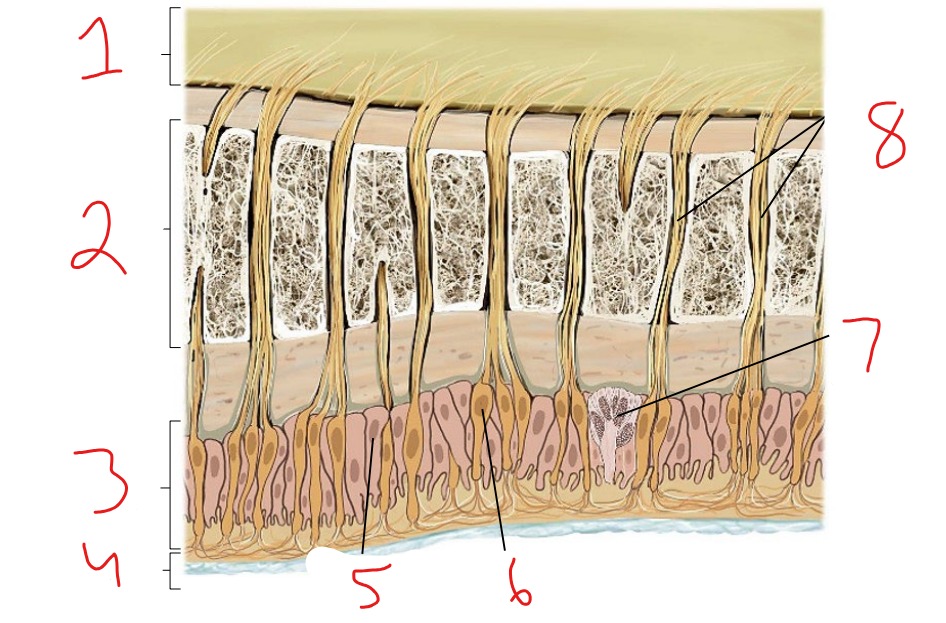
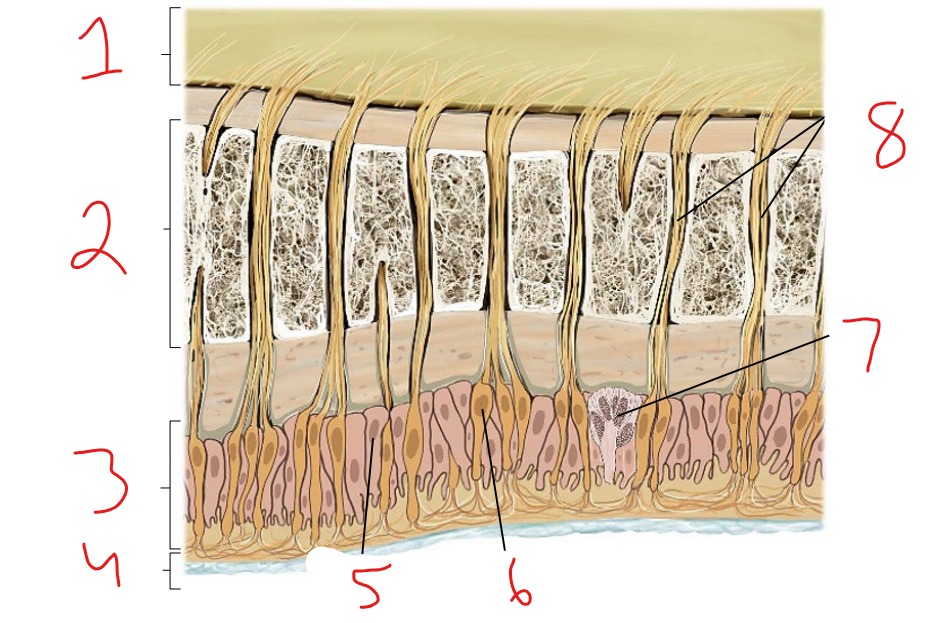
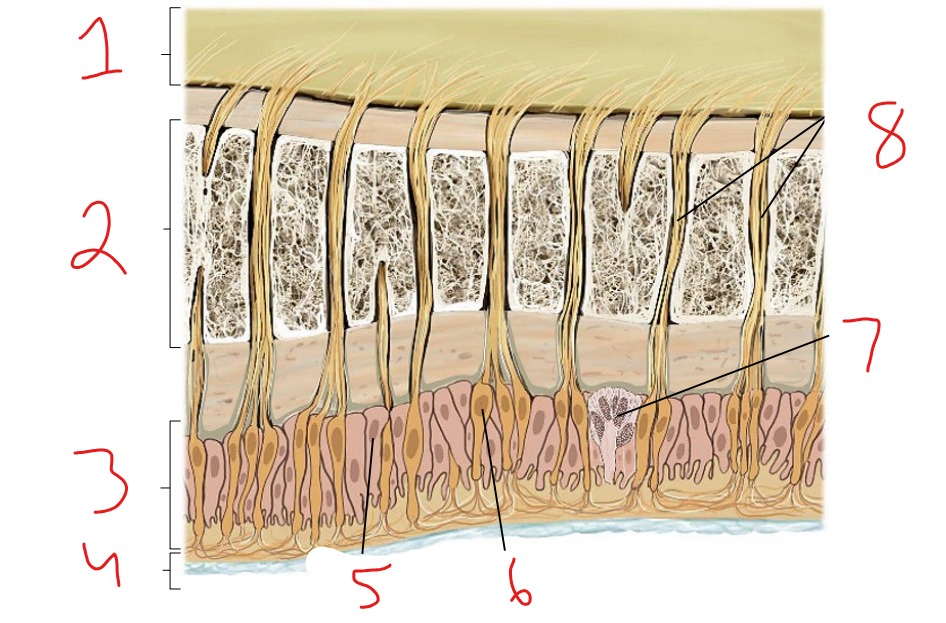
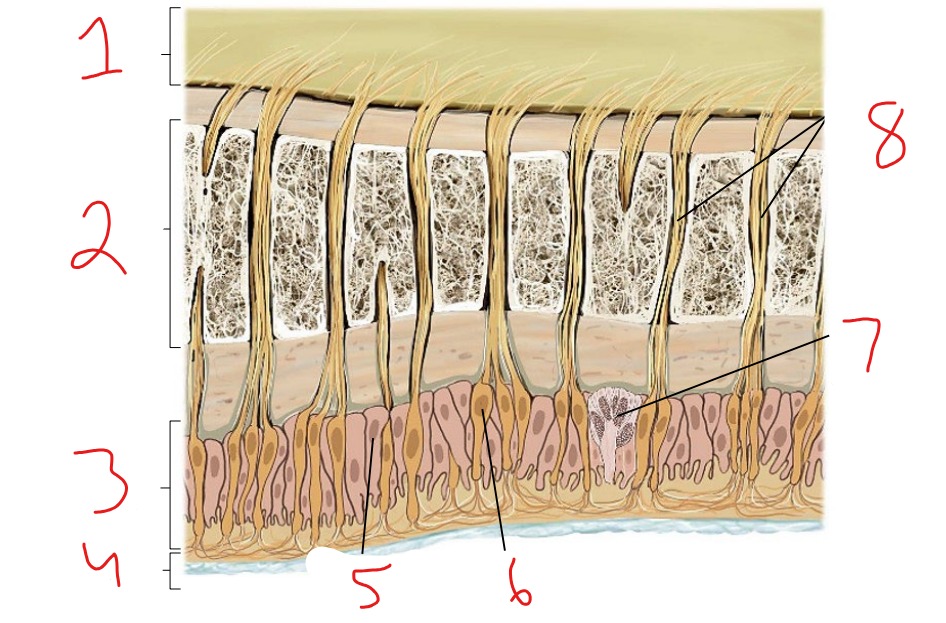
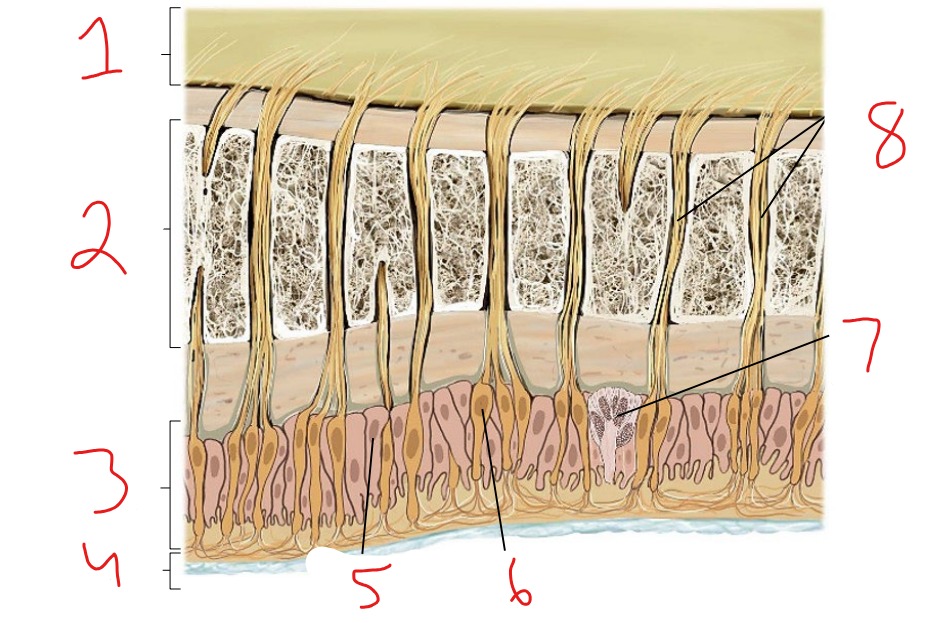
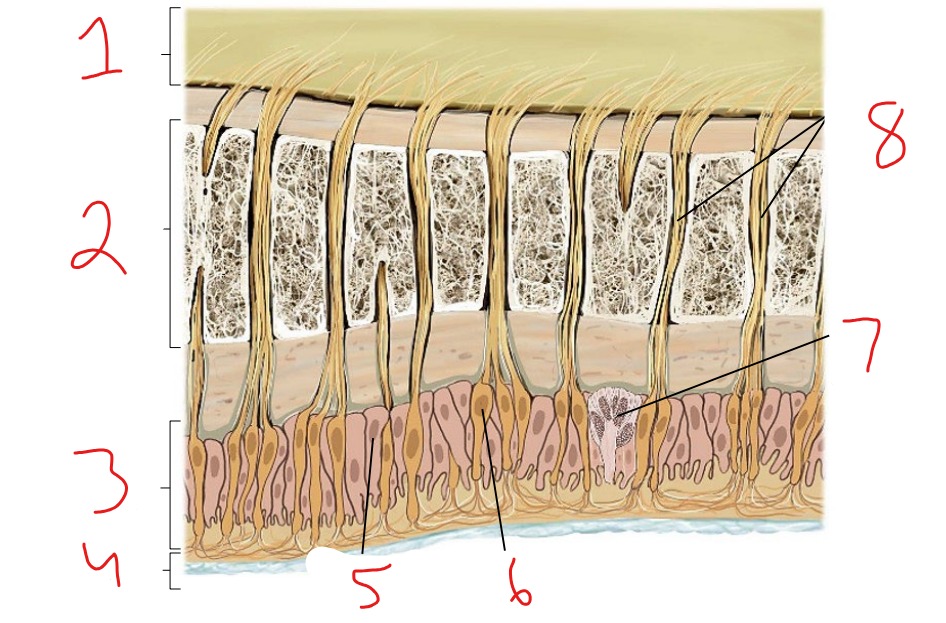
What is #1?
Epidermis
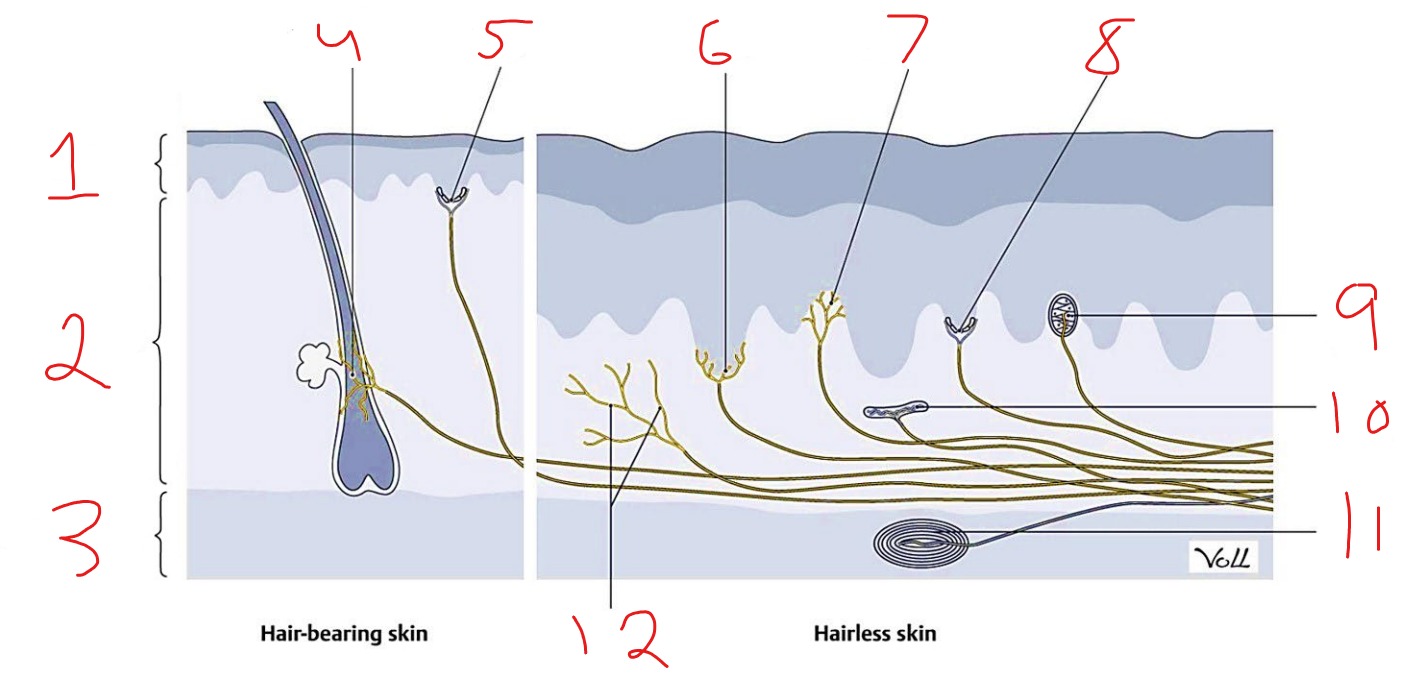
What is #2?
Dermis
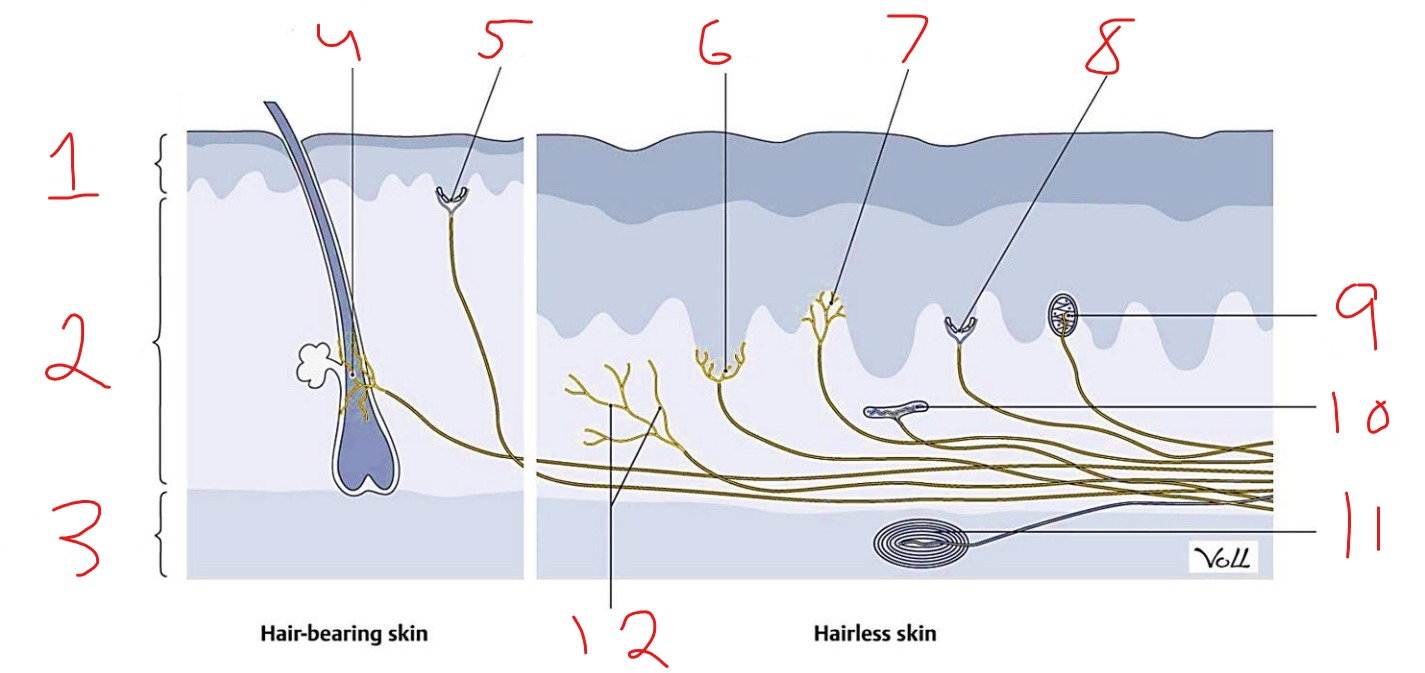
What is #3?
Subcutaneous tissue
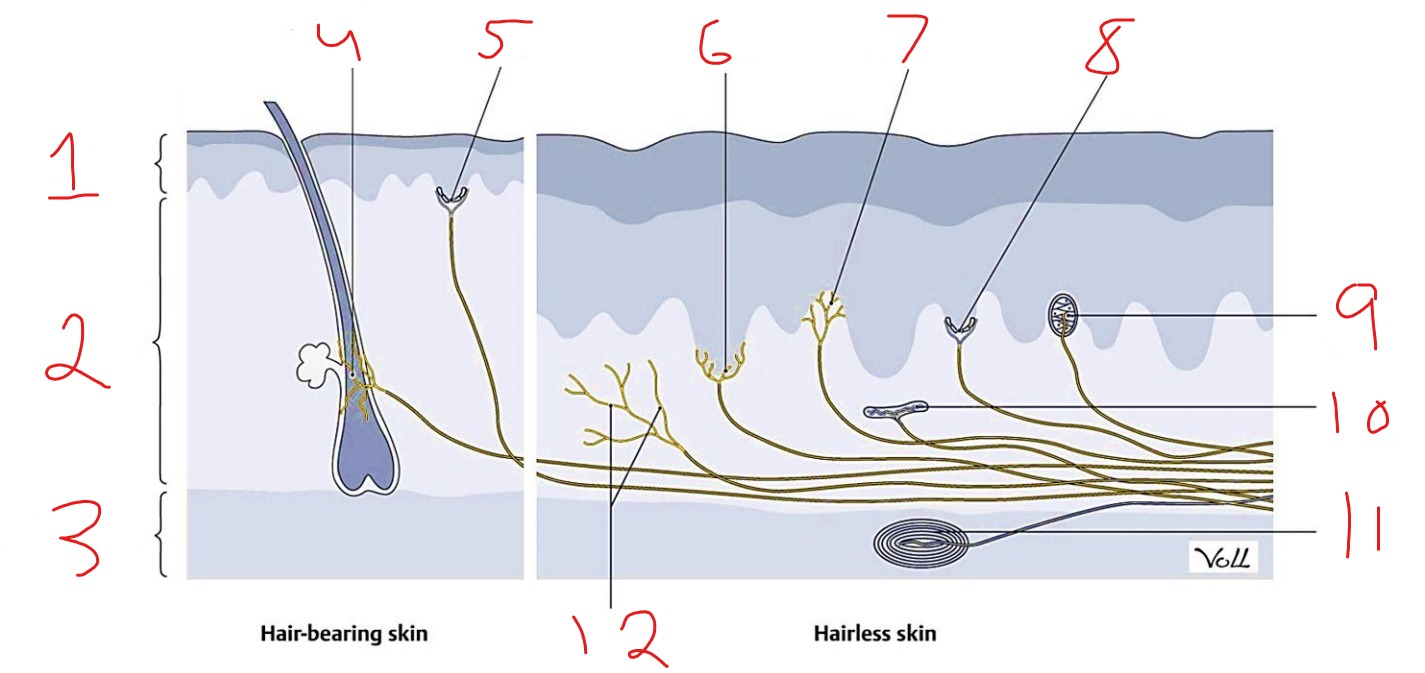
What is #4?
Hair follicle receptor
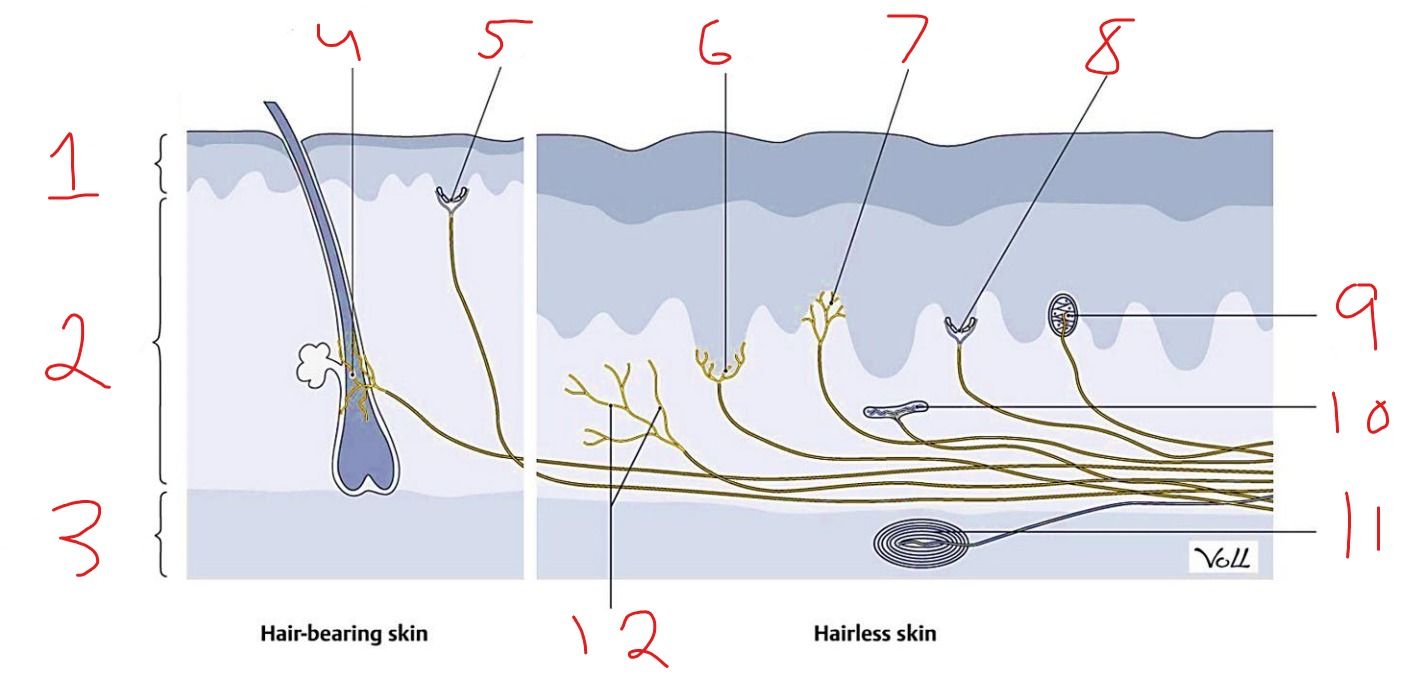
What is #5?
Tactile disk
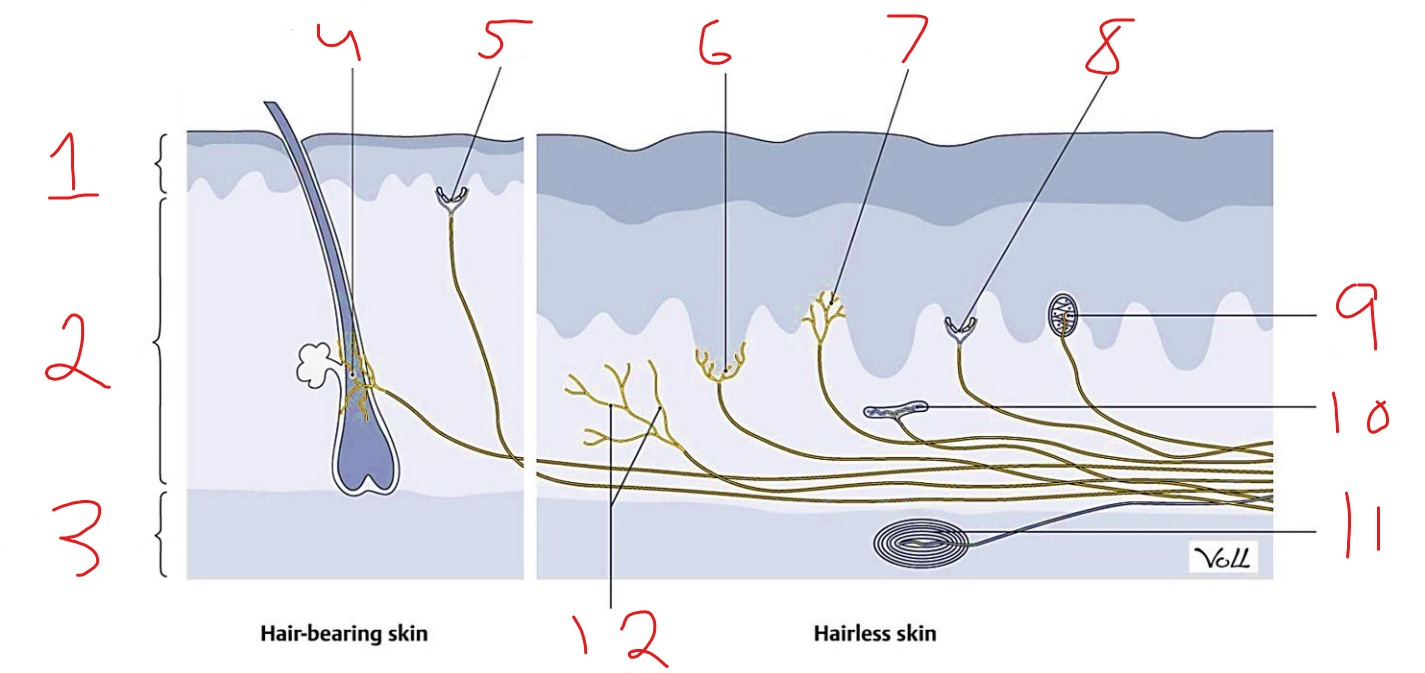
What is #6?
Heat receptor, nociceptor
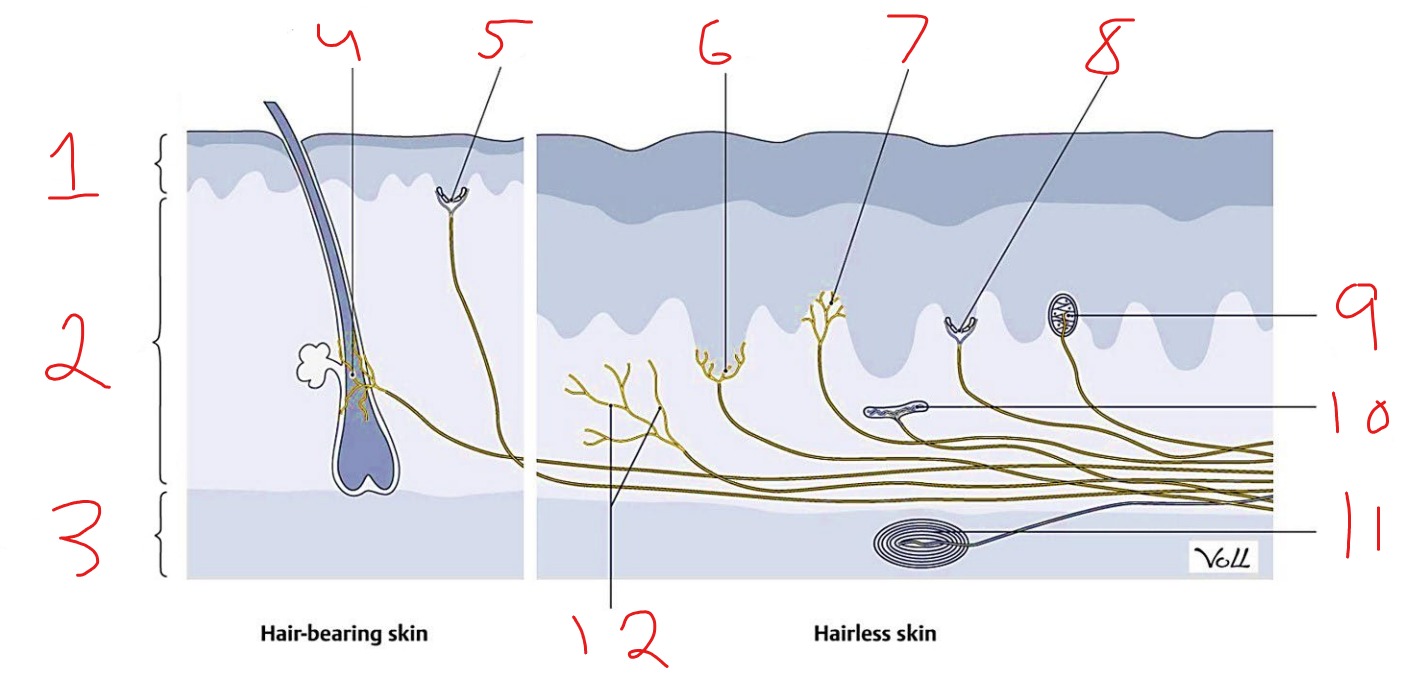
What is #7?
Cold receptor, nociceptor
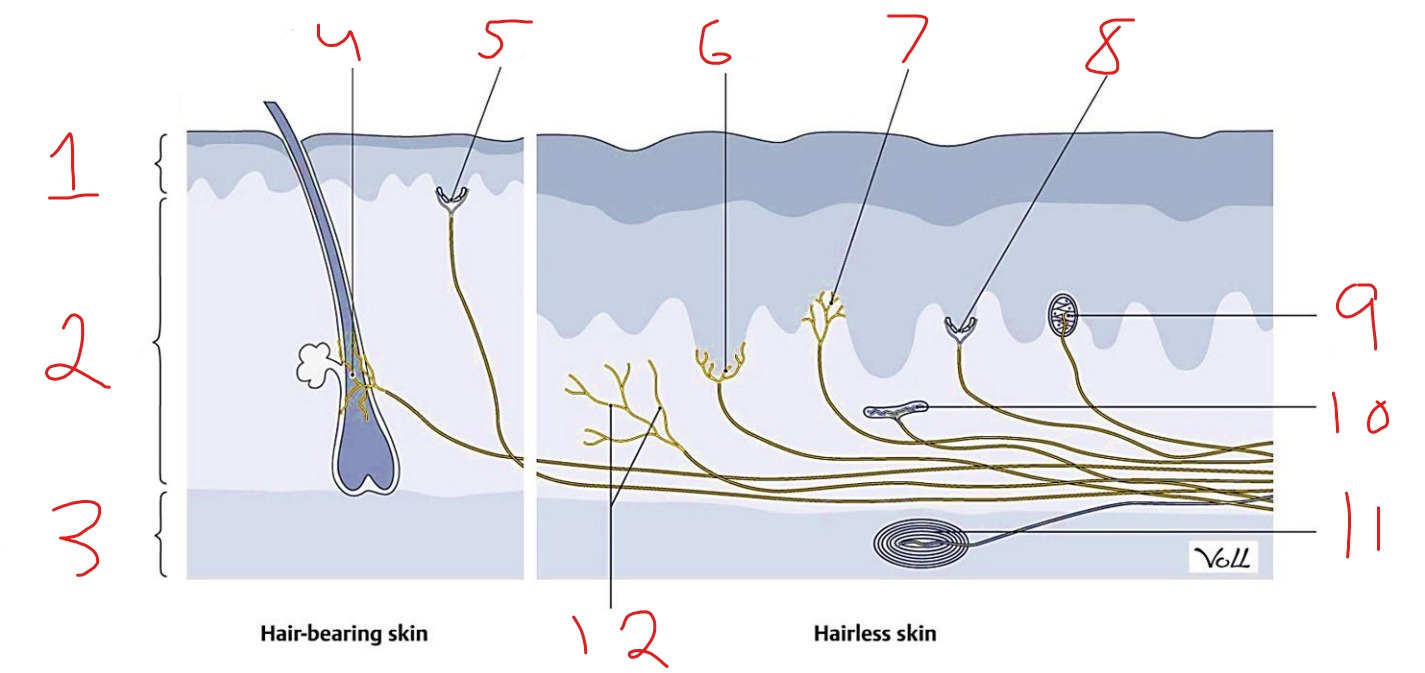
What is #8?
Merkel cell-axon complex
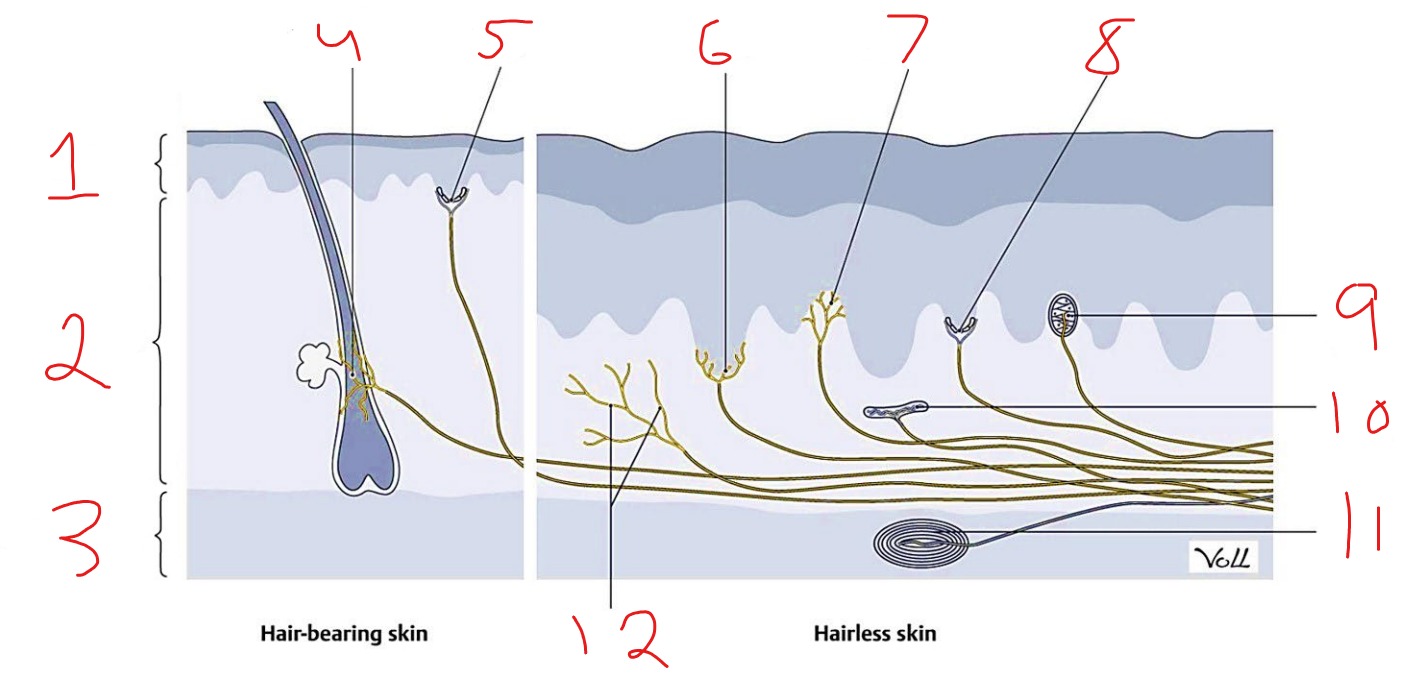
What is #9?
Meissner corpuscle
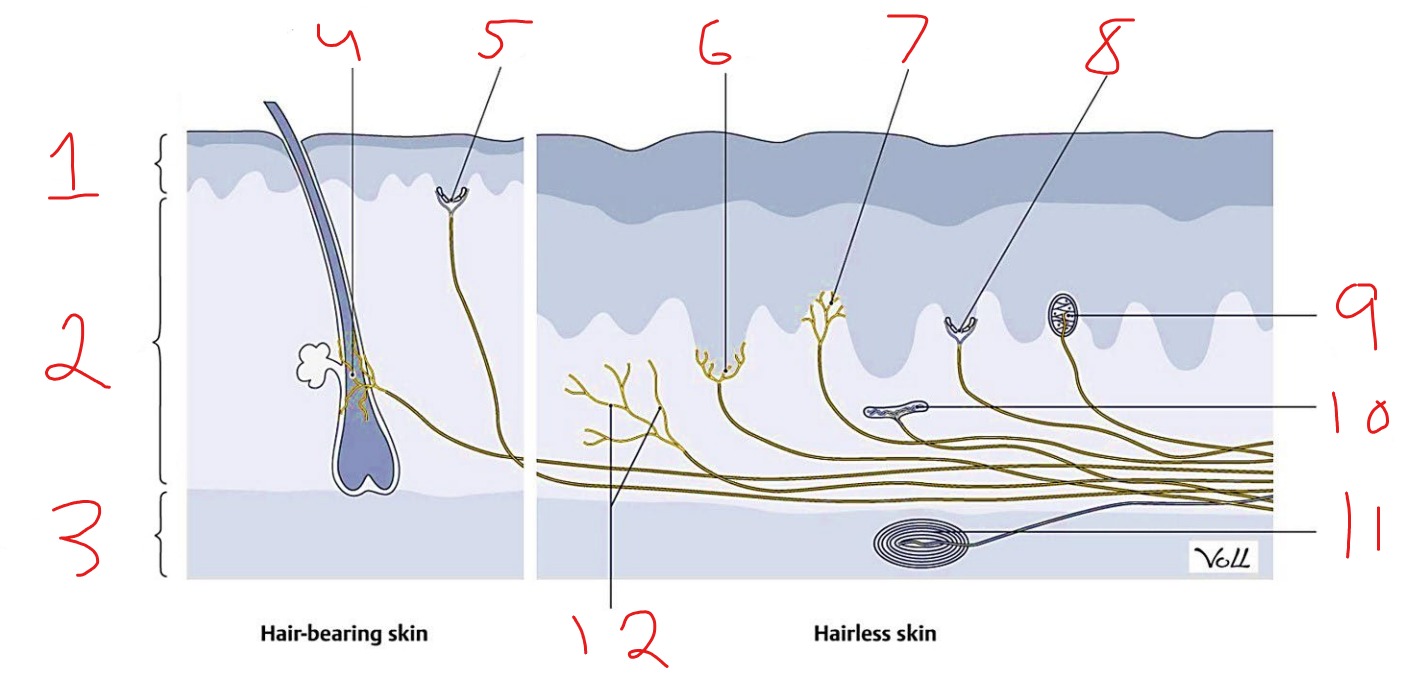
What is #10?
Ruffini corpuscle
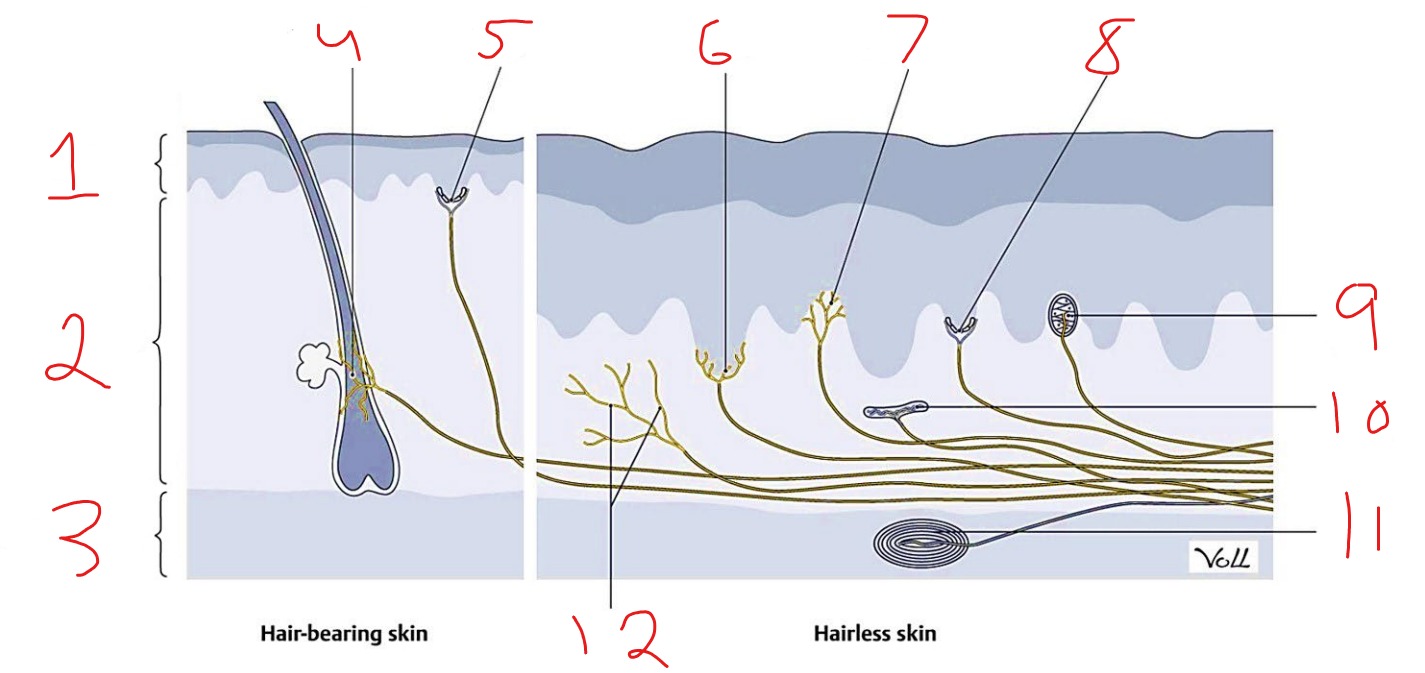
What is #11?
Pacinian corpuscle
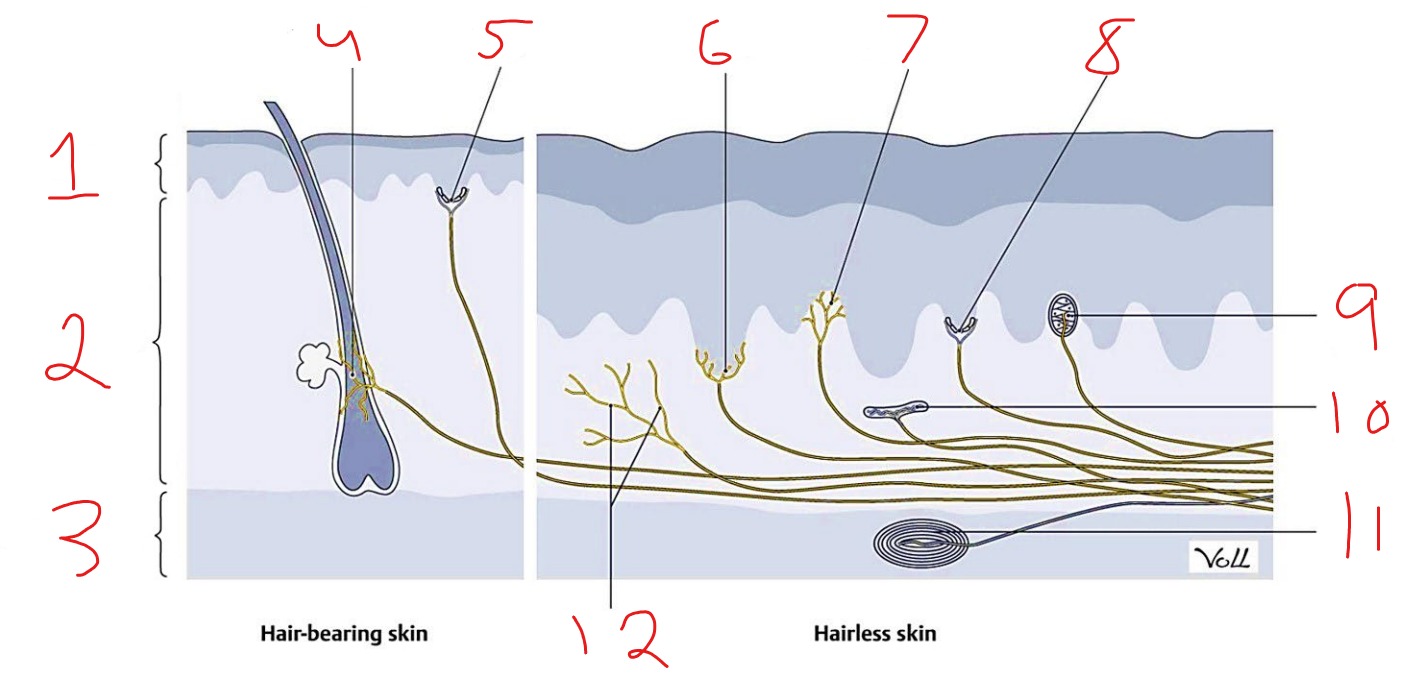
What is #12?
Free nerve ending
Proprioceptors: Muscle spindles detect
muscle stretch
Proprioceptors: Golgi tendon organs detect
tendon stretch
Filiform
anterior 2/3 tongue
Fungiform
anterior 2/3 tongue
Circumvallate
back of tongue, largest
Foliate
lateral tongue
Facial nerve:
anterior 2/3 of tongue
Glossopharyngeal nerve:
posterior 1/3 of tongue
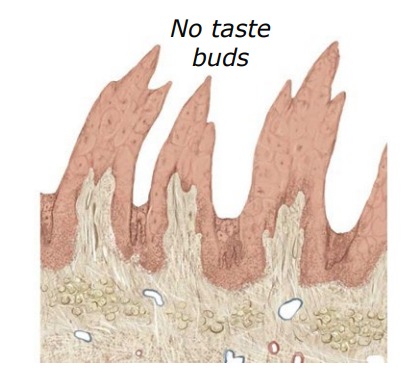
What is this?
Filiform papillae
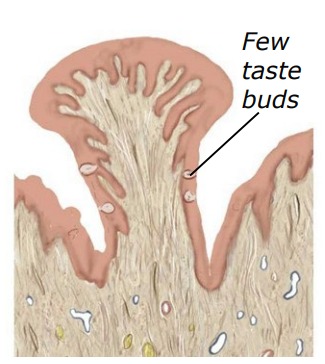
What is this?
Fungiform papillae

What is this?
Filiform and fungiform papillae
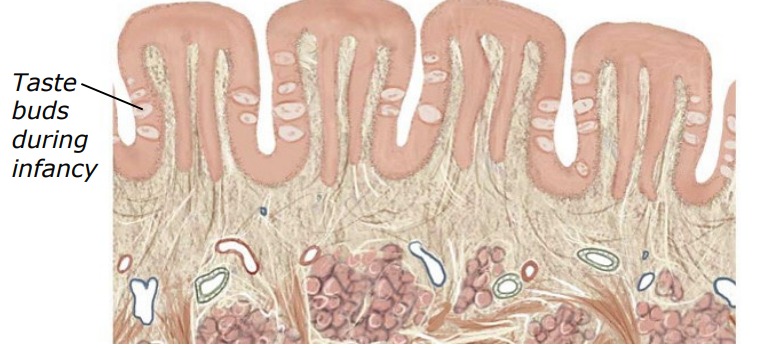
What is this?
Foliate papillae
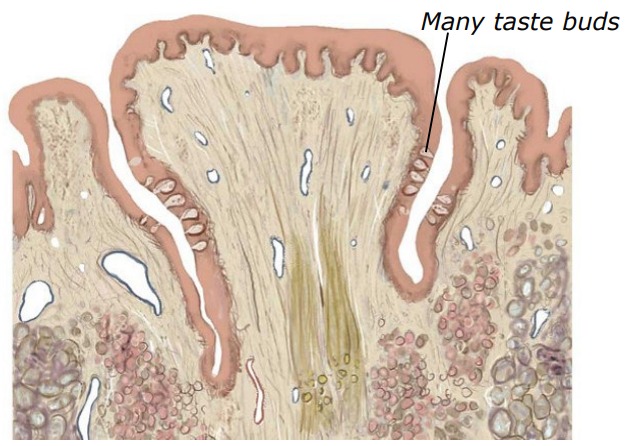
What is this?
Circumvallate papillae
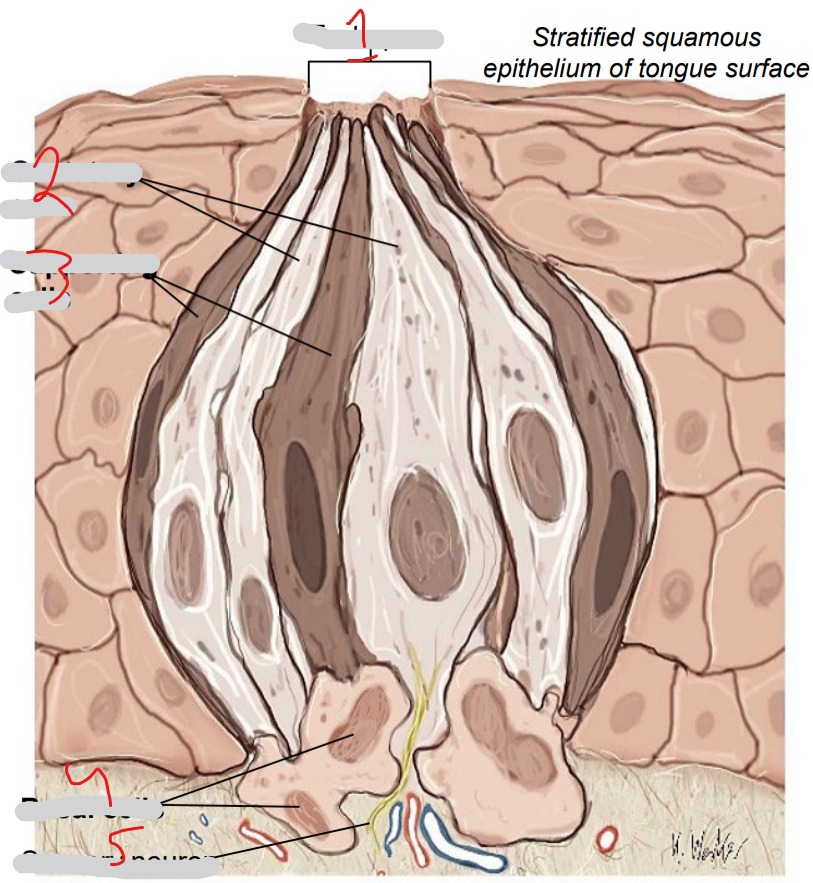
What is #1?
Taste pore
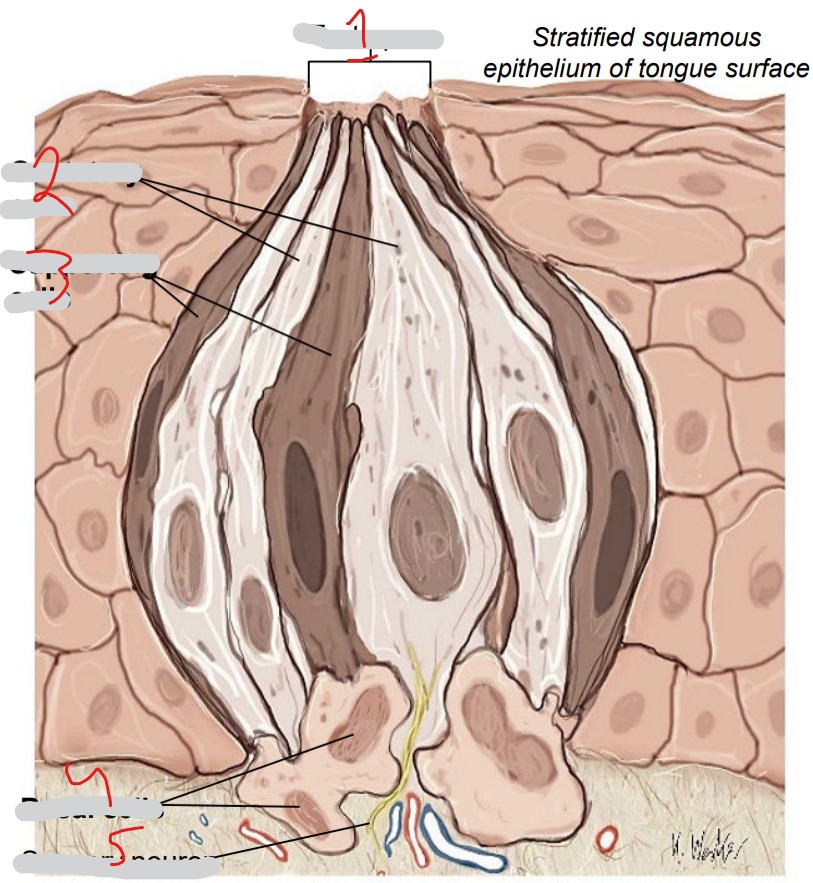
What is #2?
Gustatory cells
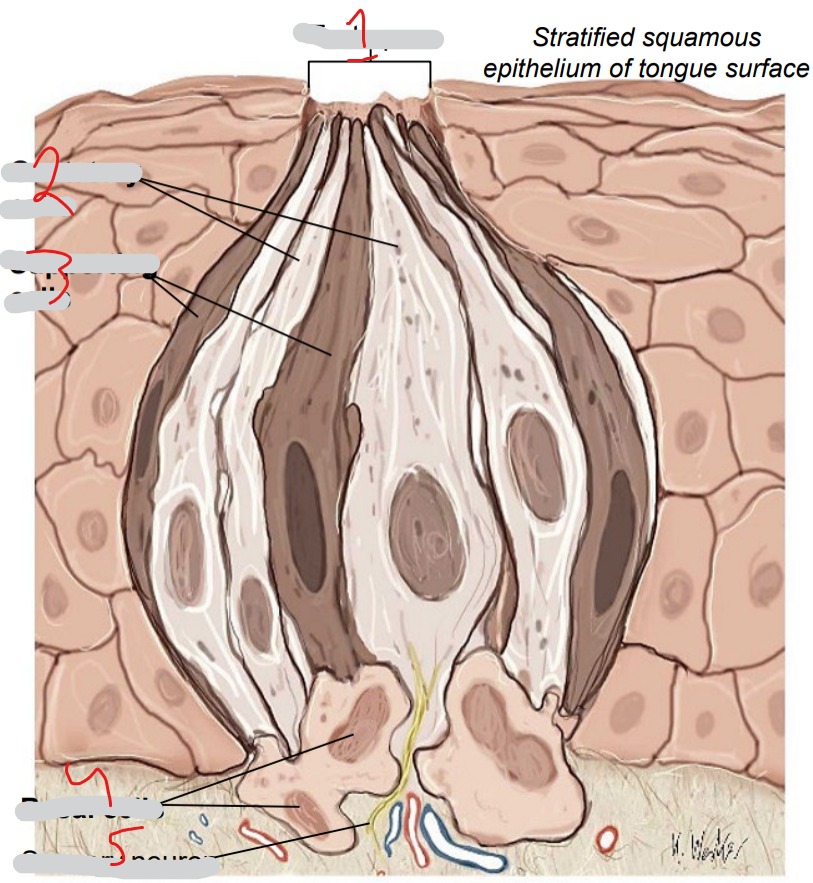
What is #3?
Supporting cells
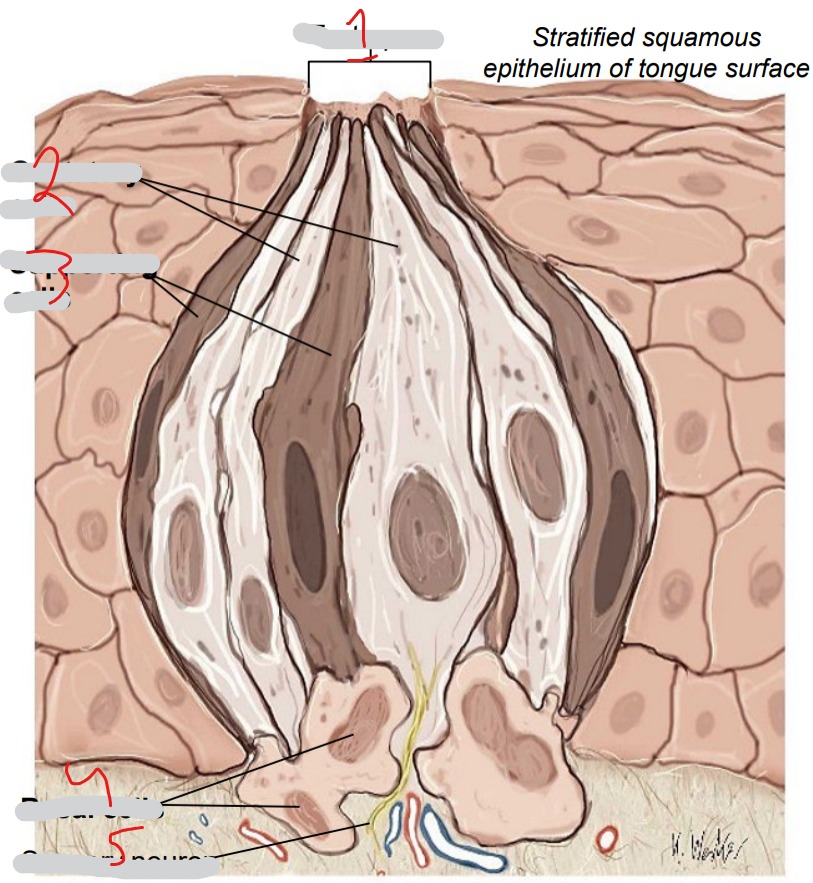
What is #4?
Basal cells
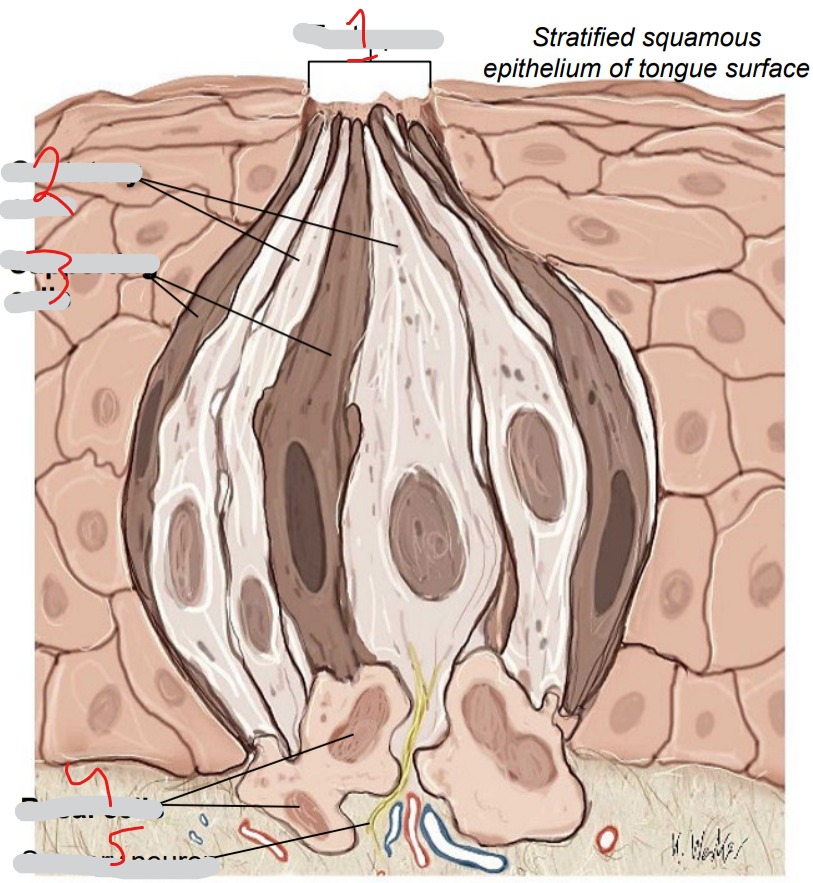
What is #5?
Sensory neuron
Gustatory cells
Chemoreceptors. Respond to five basic tastes (salty, sour, sweet, bitter, umami). Replaced every 7-10 days
Basal cells
Immature cells, replace other two cell types
What is #1?
Olfactory bulb
What is #2?
Cribriform plate
What is #3?
Olfactory epithelium
What is #4?
Mucus layer
What is #5?
Supporting cell
What is #6?
Olfactory receptor neuron
What is #7?
Olfactory gland
What is #8?
Axons of CN I
What are the olfactory receptor neurons?
Chemoreceptors, bipolar neurons
Olfaction
Thousands of chemical stimuli can be recognized by the olfactory receptor cells
What do the eyebrows, eyelashes, and eyelids (palpebrae) do?
Prevent foreign objects from contacting the eye
What does conjunctiva do?
Covers eye’s anterior surface and internal eyelid surface
Vitreous chamber is filled with
Vitreous humor
What makes up the fibrous tunic?
Sclera, Cornea
What makes up the vascular tunic?
Choroid, Ciliary body, Suspensory ligaments, Iris
What makes up the neural tunic?
Retina and photoreceptors
Rods
(function in dim light, don’t provide sharp vision or color vision, more numerous than cones)
Cones
(operate best in bright light, provide high acuity color vision)
Fovea centralis
(contains only cones, maximal visual acuity)
Optic disc
(contains no rods or cones, axons exit eye, blind spot)
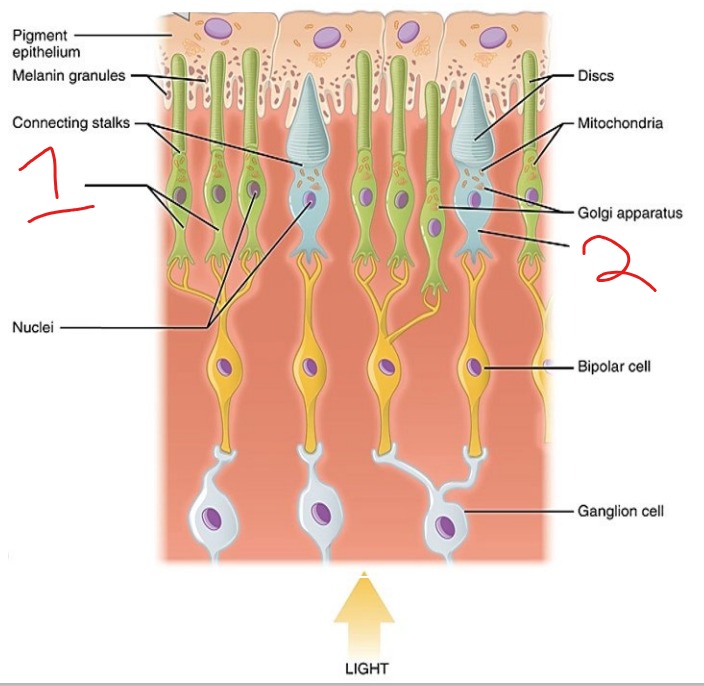
What is #1?
Rods
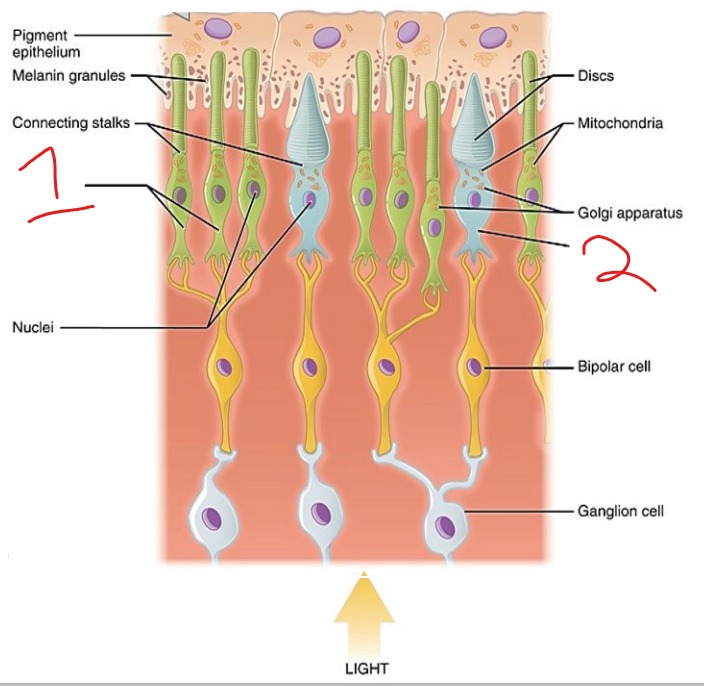
What is #2?
Cone
Macular Degeneration
area around fovea degenerates
Cataracts
(cloudy lens)
Glaucoma
(high pressure in eye hurts optic nerve)
Auricle
External Ear
External auditory canal
External Ear
Ceruminous glands
External Ear
Tympanic Membrane
External Ear
What produces cerumen?
Ceruminous glands
Earwax impedes microorganism growth
Ceruminous glands
Ossicles: Malleus Incus Stapes
Middle Ear Structures
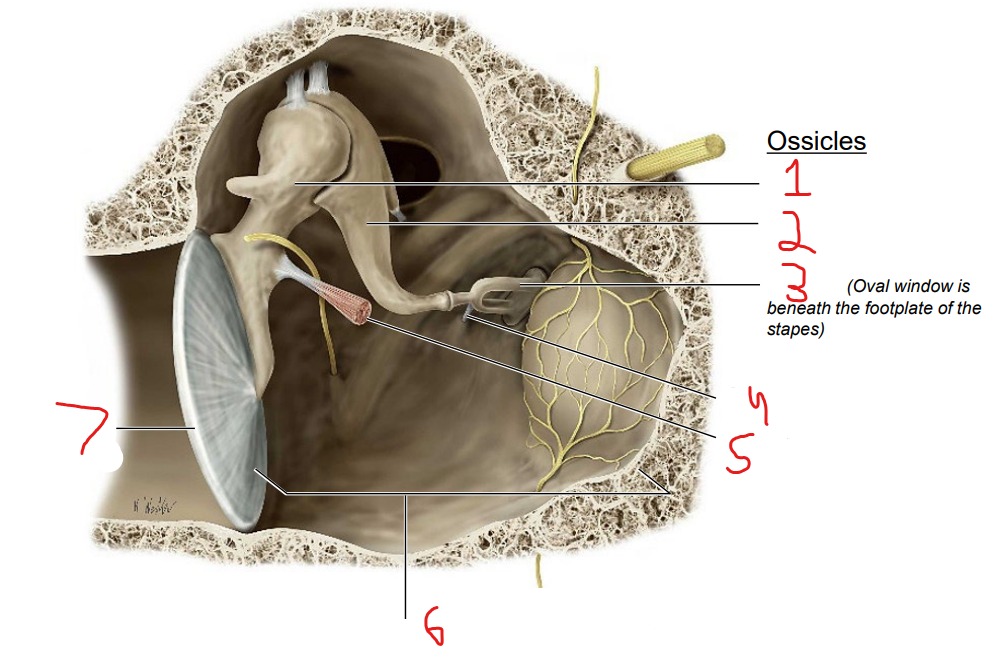
What is #1?
Malleus
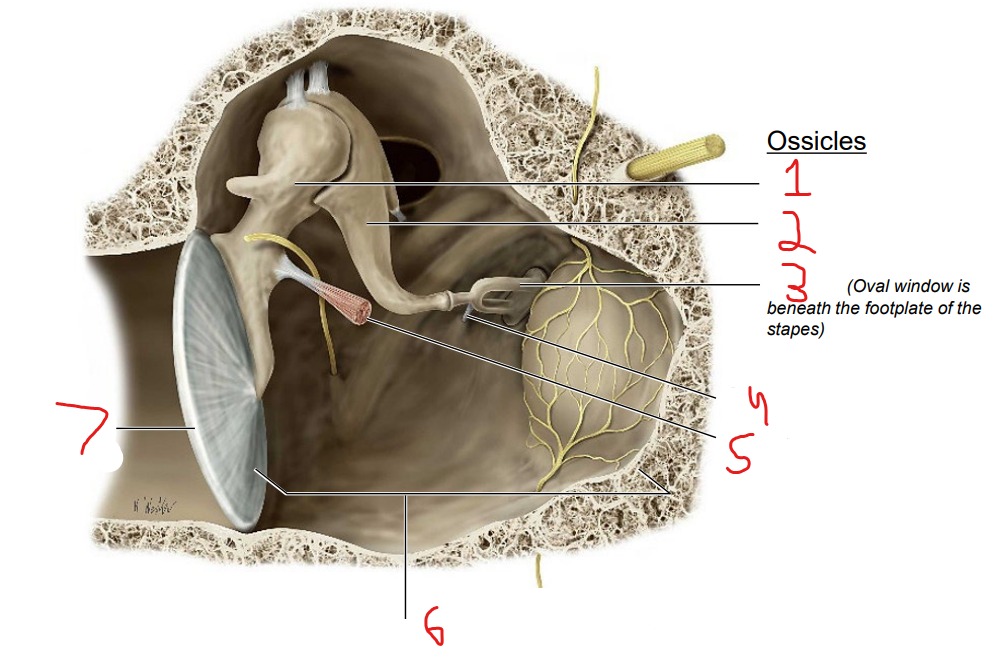
What is #2?
Incus
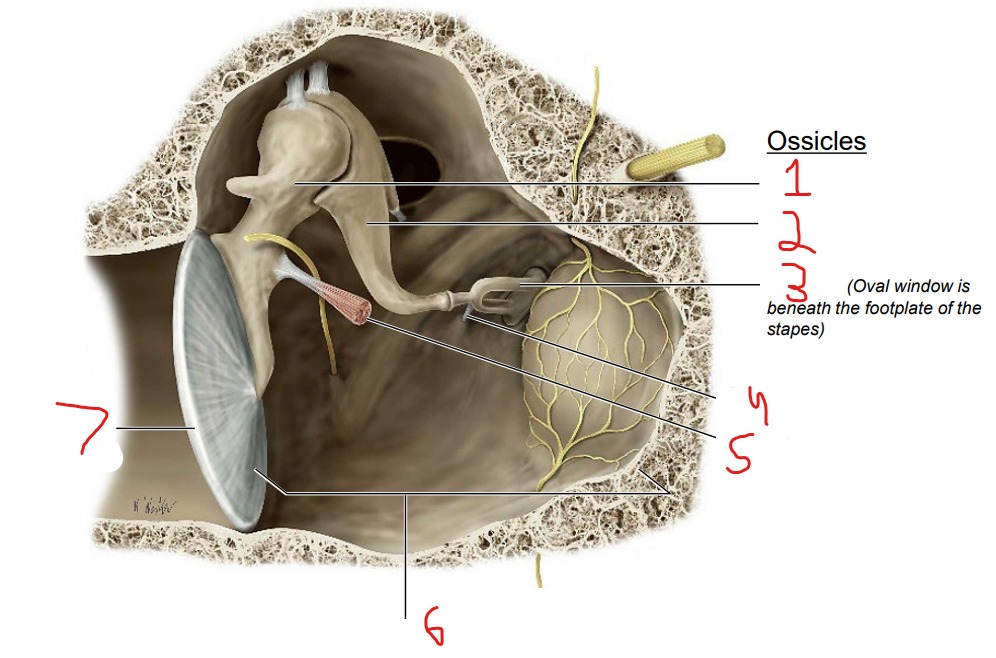
What is #3?
Stapes
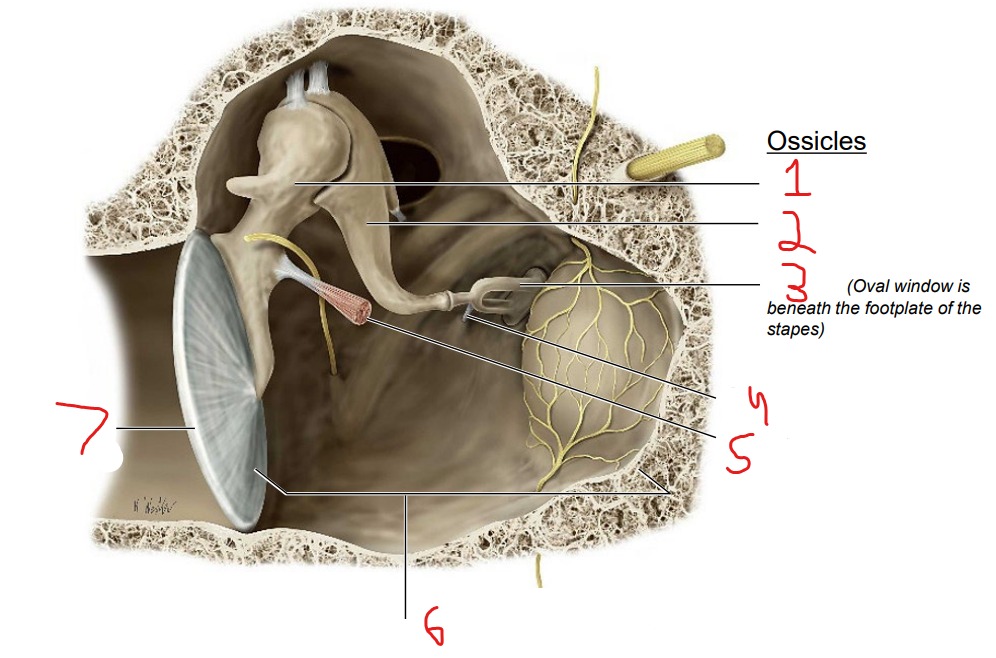
What is #4?
Stapedius muscle
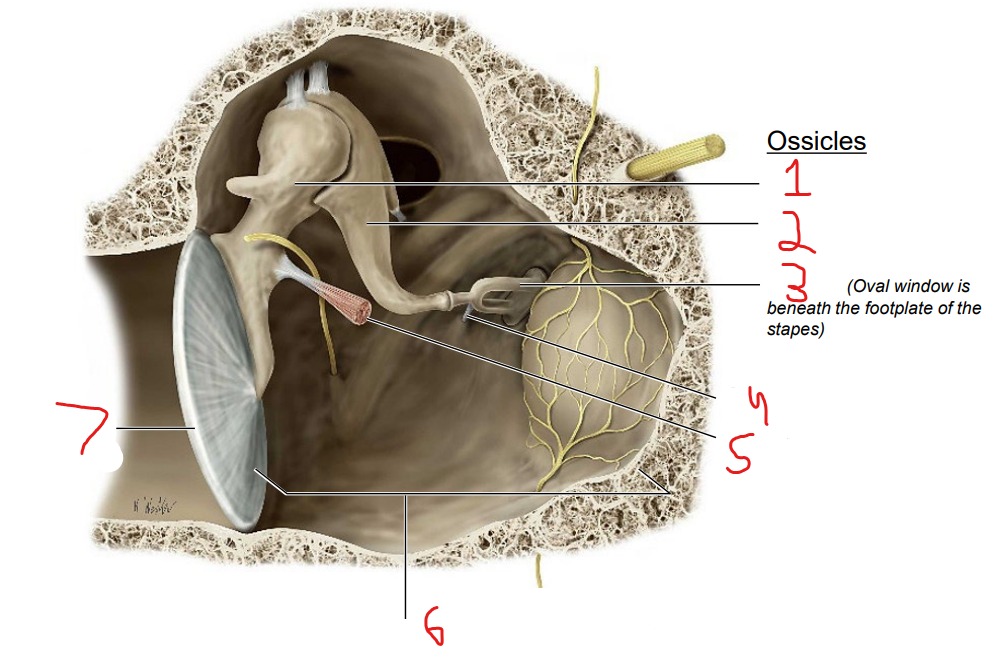
What is #5?
Tensor tympani muscle
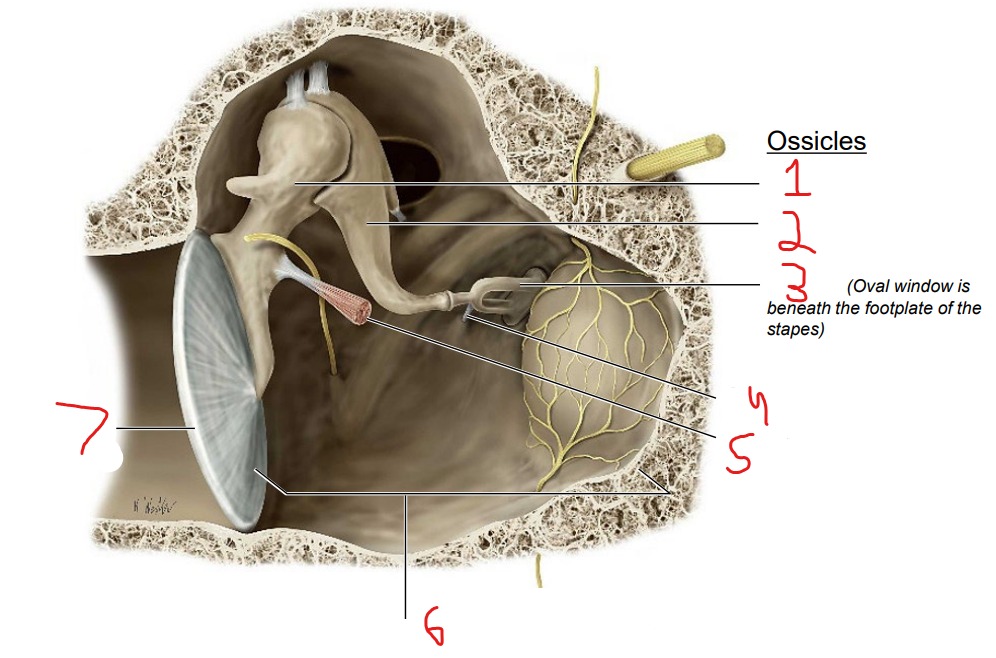
What is #6?
Tympanic cavity (air-filled cavity)
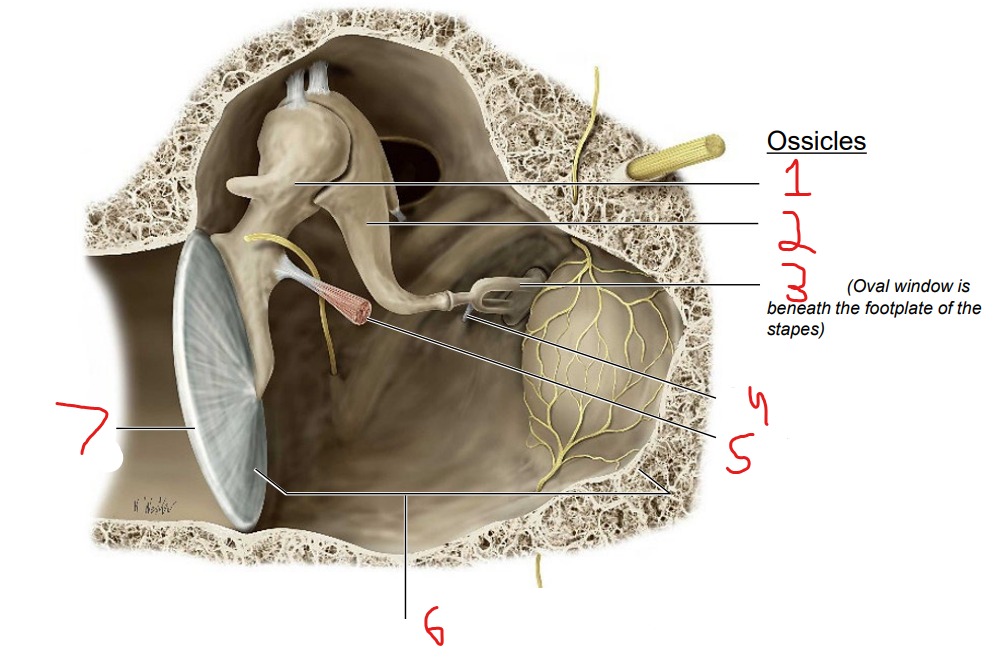
What is #7?
Tympanic membrane
The auditory tube connects the air-filled middle ear to the…..
nasopharynx
Otitis media:
infection of the middle ear
Middle Ear Structures are usually _______ but open up to equilibrate pressure in middle ear
closed
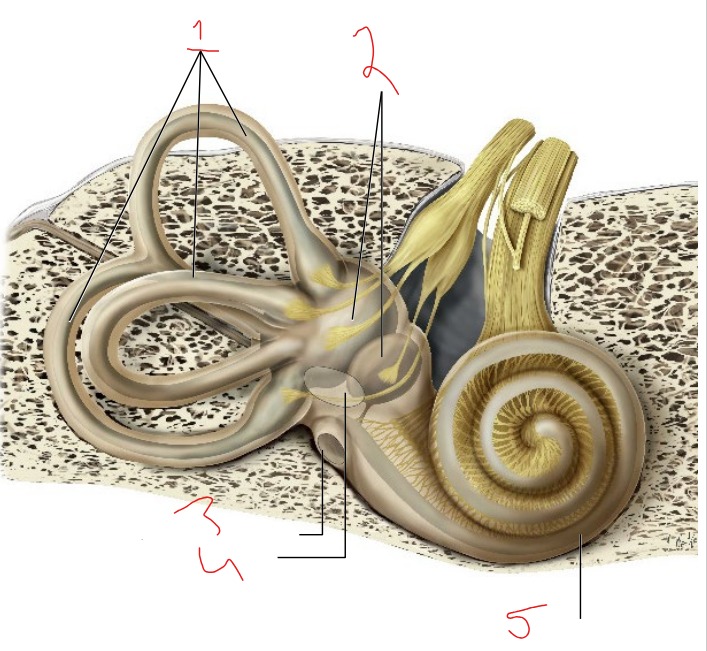
What is #1?
Semicircular canals
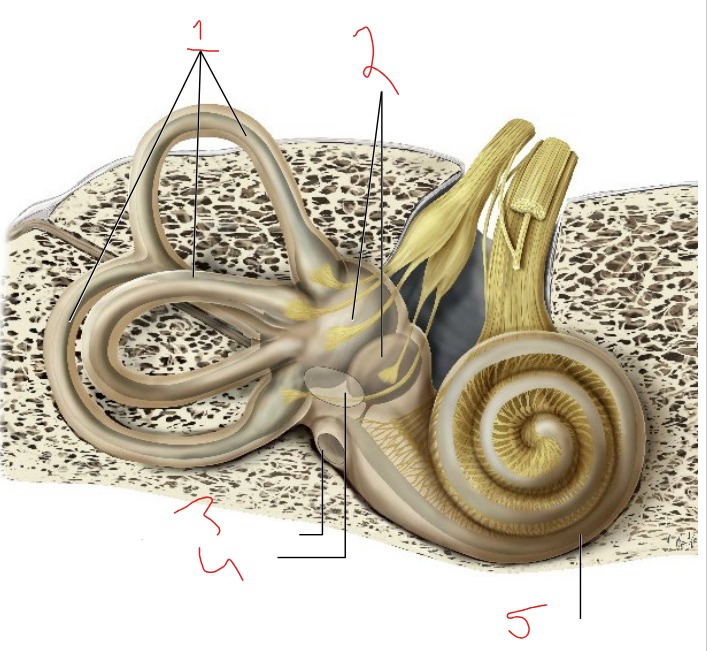
What is #2?
Vestibule
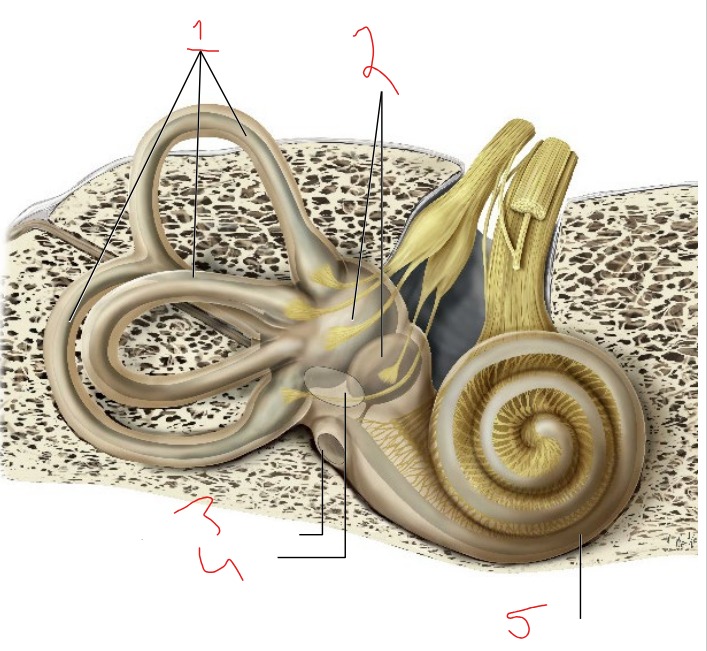
What is #3?
Round window
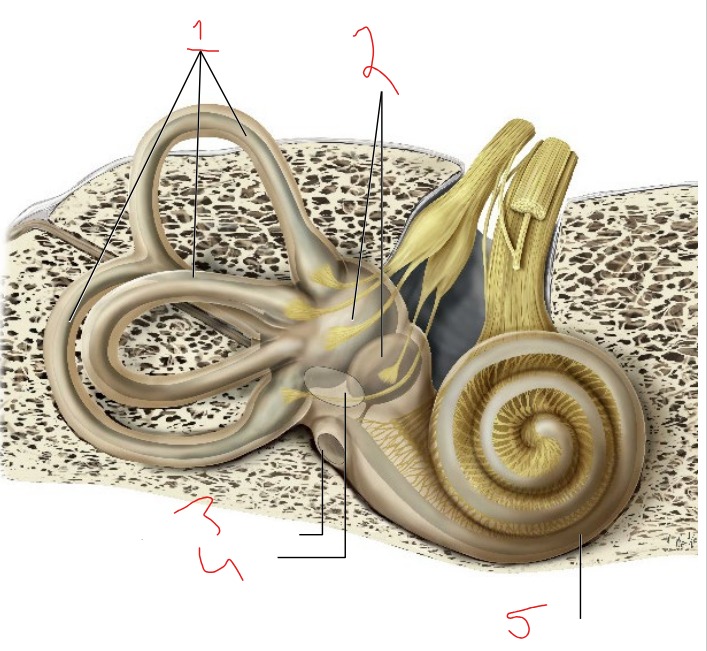
What is #4?
Oval window
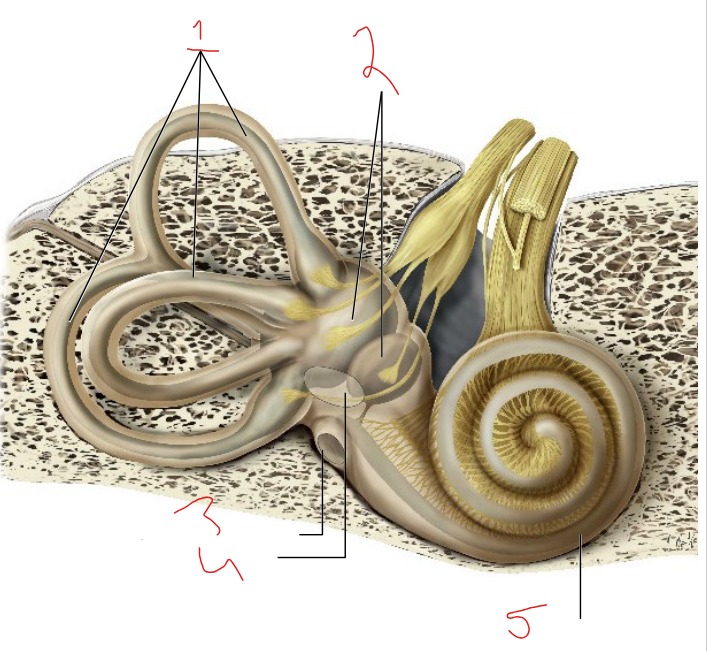
What is #5?
Cochlea
Utricle and saccule
Vestibule
Detects linear acceleration and head position
Vestibule
Helps sense equilibrium
Vestibule
Detect rotational movements
Semicircular canals