Glanzer and Cunitz (1966)
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Evidence supports multi-store model (MSM)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
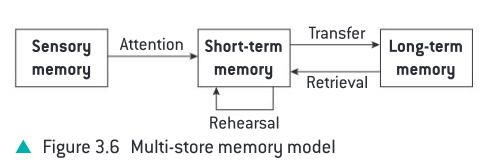
Multi-Store Model (MSM)
Human memory are divided into 3 parts: has different duration and capacity
Sensory memory
Requires attention to transfer the info to STM
Function: detact and transfer (not processing the info)
Sub-components (visual, auditory, …)
Duration: several seconds depends on the component
Capacity: infinite
Short-term memory store
Capacity: 7±2 chunks of information
Duration: 30 seconds
Requires rehearsal to transfer to LTM
Long-term memory store
Capacity: infinite
Duration: infinite
* Most influential memory model
* Able to explain multiple observed phenomenon
* Only one way direction for the information to flow (sensory → LTM) which is not true in many cases
* Oversimplify:
* More way for information to transfer
* STM and LTM can be divided further
* The items in the beginning already go to the longterm memory as it has been repeated too many time
* The items in the end are still in the short-term memory
Participants
46 army enlisted men
* Experiment
Procedure
Participants were read a series of 15-word lists and needed to recall the list of words in any order. They were to do this for 3 conditions (5 lists per condition → total of 15 lists is used) :
Recall immediately after
Recall after a 10 second filler activity
Recall after a 30 second filler activity
A filler activity could include counting backwards from a number; the point was to prevent rehearsal. Each participant went through all the conditions, completing 5 lists per condition (15 total). Conditions were randomized.
* Remembers words at the start → primary effect
* Remembers words at the end → recency effect
Condition 2:
* Still remembers words at the start → primary effect preserved
* No longer remembers words at the end → no recency effect
* However the 30 seconds filler task remove word at the end from their short-term memory → unable to recall in the 2nd condition
\
Since only recency effect disappears → show that short term memory and long term memory are separated → supporting multi-store model
* Large sample (240) → high population validity
* Repeated measures design → low particpant variability → high internal validity
* Free recall → high construct validity
* Multiple lists: some words might be easier or harder to rememeber depends on participant emotional attach
* Practice effect → affect the result
* Participants are all male → no diversity → low population validity
* Boredom, fatigue can impact the result
* Only 30 seconds → duration of STM can be longer → construct validity