Skin, Hair and Nails
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
What is subjective assessment?
What the patient tells you
What are the main areas of focus in a subjective assessment? (7)
Issues
Changes
Past medical history
Family history
Medications
Allergies
Lifestyle
What acronym helps us remember all the areas to cover when discussing the issues of a patient?
OLDCARTS
What does OLDCARTS stand for in a subjective assessment?
Onset
Location
Duration
Characteristics
Aggravating/Alleviating Factors
Related Symptoms
Treatments by patient
Severity
In OLDCARTS, what does onset mean?
What came on (when it started)
In OLDCARTS, what does location mean?
Where the issue is located
In OLDCARTS, what does duration mean?
How long the issue has been present
In OLDCARTS, what does Characteristics mean?
Qualities of the issue
In OLDCARTS, what does Aggravating/Alleviating mean?
What makes it better or worse and when is it better or worse
In OLDCARTS, what does related symptoms mean?
What else is happening with this issue
In OLDCARTS, what does treatment by patient mean?
What the patient has tried at home (ointments/medications/etc)
In OLDCARTS, what does severity mean?
Pain level and if it has been better or worse
What is an objective assessment?
What the nurse examines
What should always be done first in an objective assessment?
General survey before systematic approach
What order is used to inspect the skin?
Head to toe approach
Which areas should be especially focused on during a skin exam?
Areas prone to skin breakdown, eyes, lips, and inside the mouth
What does the ABCDE format stand for when inspecting lesions to see if they are malignant?
Asymmetry
Border irregularity
Color variety
Diameter greater than 6 cm
Evolution over time
What do you check for when palpating the skin? (3)
Temperature
Turgor
Edema
What is a normal skin turgor result?
Less than 4 seconds
Where is turgor assessed in adults vs older adults?
Adults should be on top of the hand, older adults should be on the medial thigh
What do you note for when assessing hair?
Texture
Hygiene
Lesions
Nits
Which hidden areas should not be forgotten during a hair inspection?
Behind the ears and at the base of the scalp
Why are hair styles relevant in a hair assessment?
They can hide or contribute to scalp/skin issues
What is the order of assessment for nails?
Inspect
Palpate fingernails
Palpate toenails
What is a normal capillary refill time?
Less than 2 seconds
What is the normal nail angle?
Less than 160 degrees
What does a nail angle of greater than 160 indicate?
Clubbing which happens due to poor perfusion (usually due to chronic respiratory conditions like COPD)
What are the 5 main types of data collection tests?
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP)
Cultures
Allergy Testing
Biopsy
What does a CBC tell you about?
RBC count
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
RBC morphology
Platelet count
Platelet size
WBC count
What does hemoglobin measure?
How well oxygen is being carried by proteins through the blood
Is hemoglobin higher in men or women?
Men
What does hematocrit measure?
The percentage of RBCs in the blood (Volume of RBCs/Volume of blood)
Is hematocrit higher in men or women?
Men
What does RBC morphology tell you?
The shape of RBCs
What does WBC count tell you?
Infection or inflammation status (higher WBCs means more infection)
What is a CBC with differential?
A CBC that breaks down the different types of WBCs specifically (helps know what stage of infection the patient is in)
What does a BMP tell you about?
Sodium levels
Chloride levels
Potassium levels
BUN
Creatinine levels
GFR
Calcium levels
Glucose levels
What do BUN, creatinine and GFR tell you?
How good the patients kidney function is
What does glucose level indicate?
Blood sugar status
What is a wound culture?
A swab of a wound sent to the lab to grow and identify organisms
What is allergy skin testing used for?
To detect allergies by observing skin reaction to certain substances
What is a biopsy?
A sample of tissue sent to the lab to understand more about a lesion or condition
What are examples of biopsy types?
Bone marrow biopsy
Excisional biopsy
What are the three phases of wound healing?
Inflammatory
Proliferative
Remodeling
When does the inflammatory phase begin and how long does it last?
Within 30 minutes of injury and lasts 2-3 days
What occurs in the inflammatory phase?
Vasoconstriction
Platelet aggregation
Inflammatory reactions
Swelling
Erythema
When does the proliferative phase begin and how long does it last?
Begins at the end of the inflammatory phase and may last up to 4 weeks
What occurs in the proliferative phase?
Fibroblasts deposit collagen and growth factors and the wound beds show granulation (formation of new, soft, red tissue)
When does the remodeling phase begin and how long can it last?
Begins right after proliferative phase and may last as long as 2 years
What occurs in the remodeling phase?
Rapid collagen replaced by mature collagen, increasing tensile strength of the wound
What are 9 common types of primary skin findings?
Macule
Papule
Patch
Vesicle
Bulla
Plaque
Wheal
Cyst
Pustule
What is a macule?
A flat, circumscribed, discoloration on the skin the is LESS than 1 cm
What is a patch?
Flat, circumscribed, discoloration that is GREATER than 1 cm
What is a papule?
A raised, defined, solid bump under the skin
What is a vesicle?
A small, fluid filled sac or blister that is LESS than 1 cm
What is a bulla?
A fluid filled sac that is GREATER than 1 cm
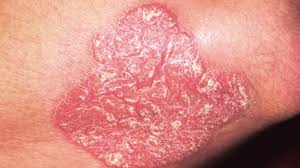
What is a plaque?
A raised, flat topped lesion that is greater than 1 cm
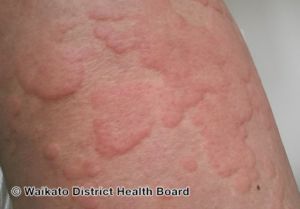
What is a wheal?
A raised, irregular, transient lesion due to edema
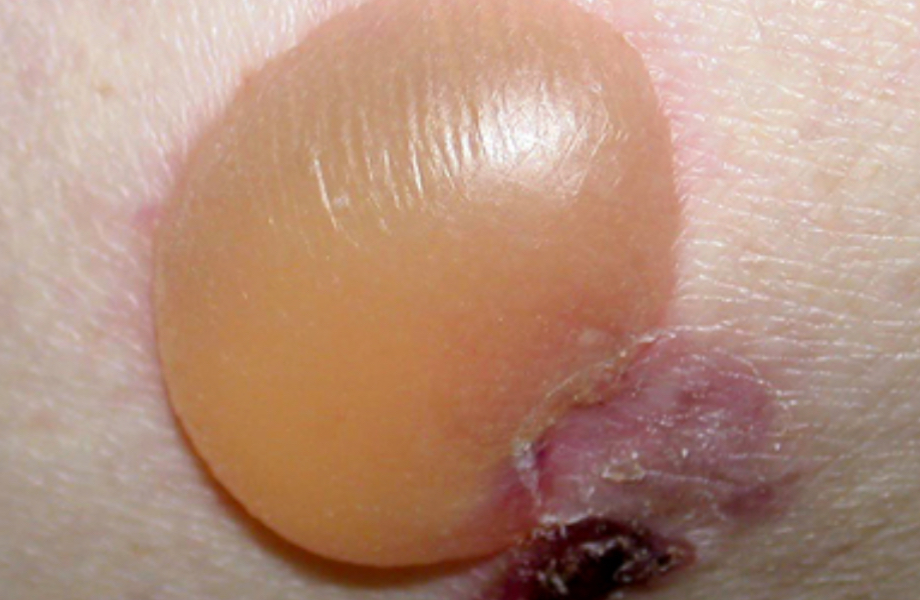
What is a cyst?
A sac filled with fluid or semi solid material
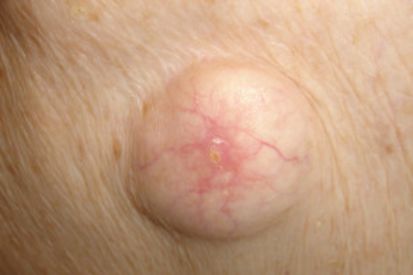
What is cystic acne?
Inflamed, deep, pus filled cysts on the skin caused by blacked pored and infection
What is a pustule?
Small, raised, pus filled lesion
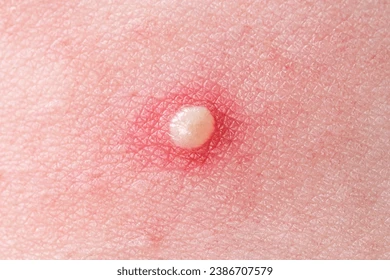
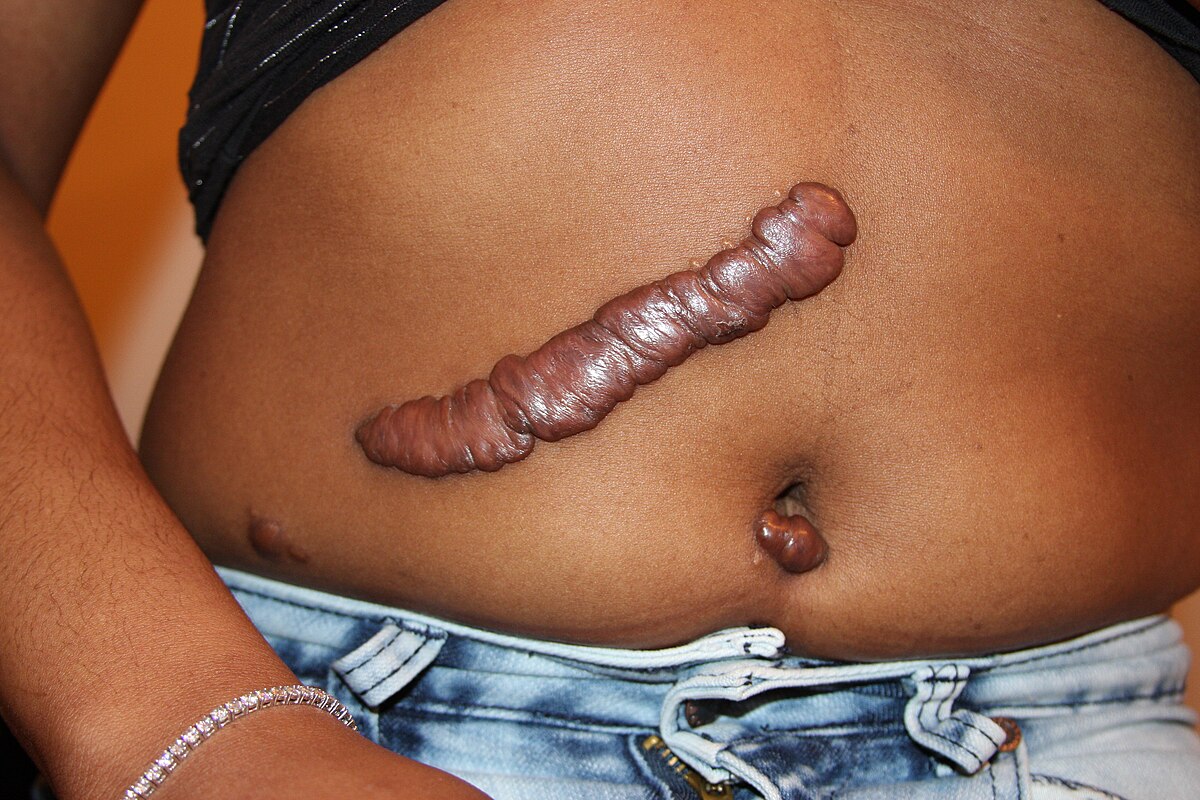
What is a keloid?
Overgrowth of fibrous tissue forming an enlarged scar
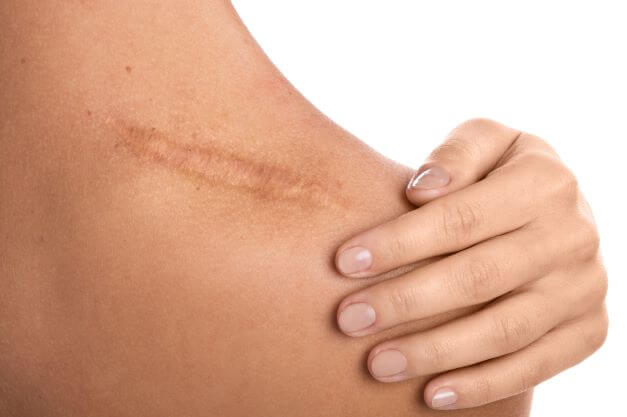
What is a scar?
Fibrous tissue replacing normal skin after injury or surgery
What is atrophy of the skin?
Thinning or loss of skin, sometimes from aging or sun exposure
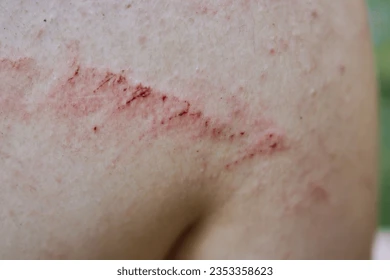
What is excoriation?
A lesion from scratching or excessive rubbing of the skin
What are the 7 main patterns of lesion distribution?
Asymmetrical
Symmetrical
Bilateral
Diffuse
Generalized
Localized
Grouped
What does asymmetrical lesion distribution mean?
Lesions appear only on one side
What does symmetrical lesion distribution mean?
Lesions appear only both sides
What does bilateral lesion distribution mean?
Lesions are EQUALLY distributed on both sides
What does diffuse lesion distribution mean?
Lesions Are widely spread across an area without a clear pattern
What does generalized lesion distribution mean?
Lesions cover one specific large body area
What does localized lesion distribution mean?
Lesions are confined to one distinct area
What does grouped lesion distribution mean?
Multiple lesions or wounds clustered in a pattern
Why are cultural considerations important in skin assessment?
Some findings may appear abnormal but are benign and require no medical intervention
What are common cultural/benign skin findings?
Cafe au lait spots
Congenital dermal melanocytosis
Stork bite
Traction alopecia
Pseudofolliculitis barbae
Cupping
Coining
Skin tone variations
What are cafe au lait spots?
Hyperpigmented lesions that range from light to dark brown, do not go away, but may fade or change shape over time
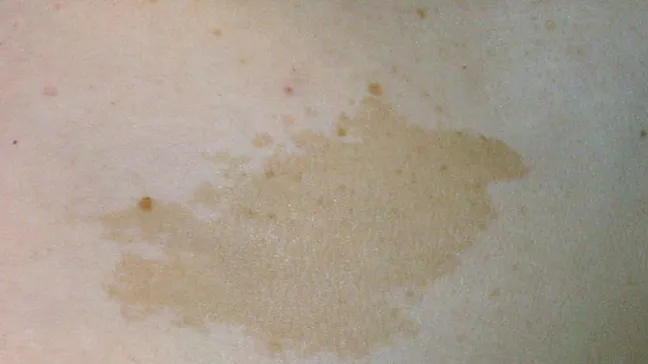
What is congenital dermal melanocytosis? (Mongolian spots)
Flat, gray-blue patches common in darker skinned newborns, often on the lower back, butt, or legs. Caused by melanocytes trapped deep in skin layers. May resemble bruises
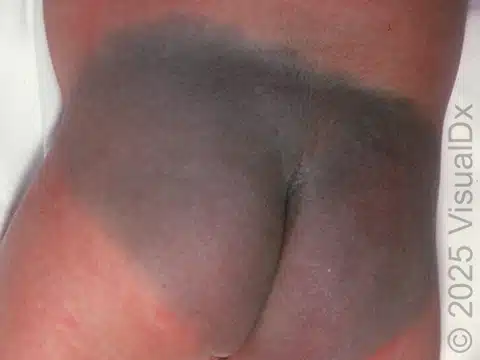
What are stork bites? (Nevus simplex)
Capillary malformations found on eyelids, between eyebrows or nape of neck. Usually fade within 1-2 years of life
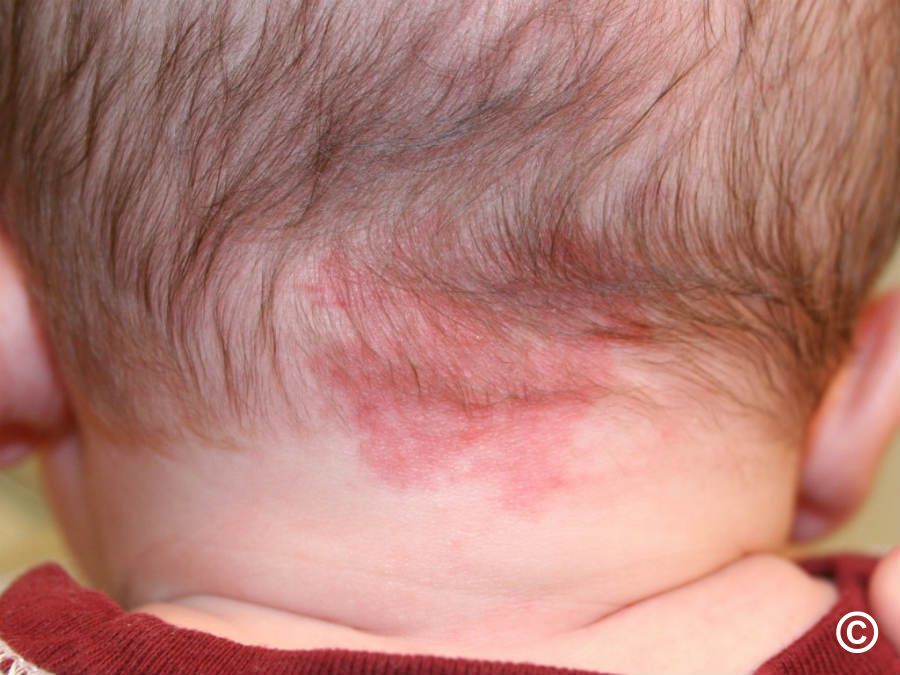
What is pseudofolliculitis barbae?
”Razor bumps” - follicularly based erythematous and hyperpigmented papules/pustules. Usually sterile but can become infected. Can lead to hyperpigmentations, hypertrophic scars, or keloids. Treated with topical steroids, benzoyl peroxide, topical antibiotics, and rest form shaving or tight hairstyles
What is cupping?
A cultural therapy where heated cups are placed on the skin, leaving circular erythematous or bruised marks
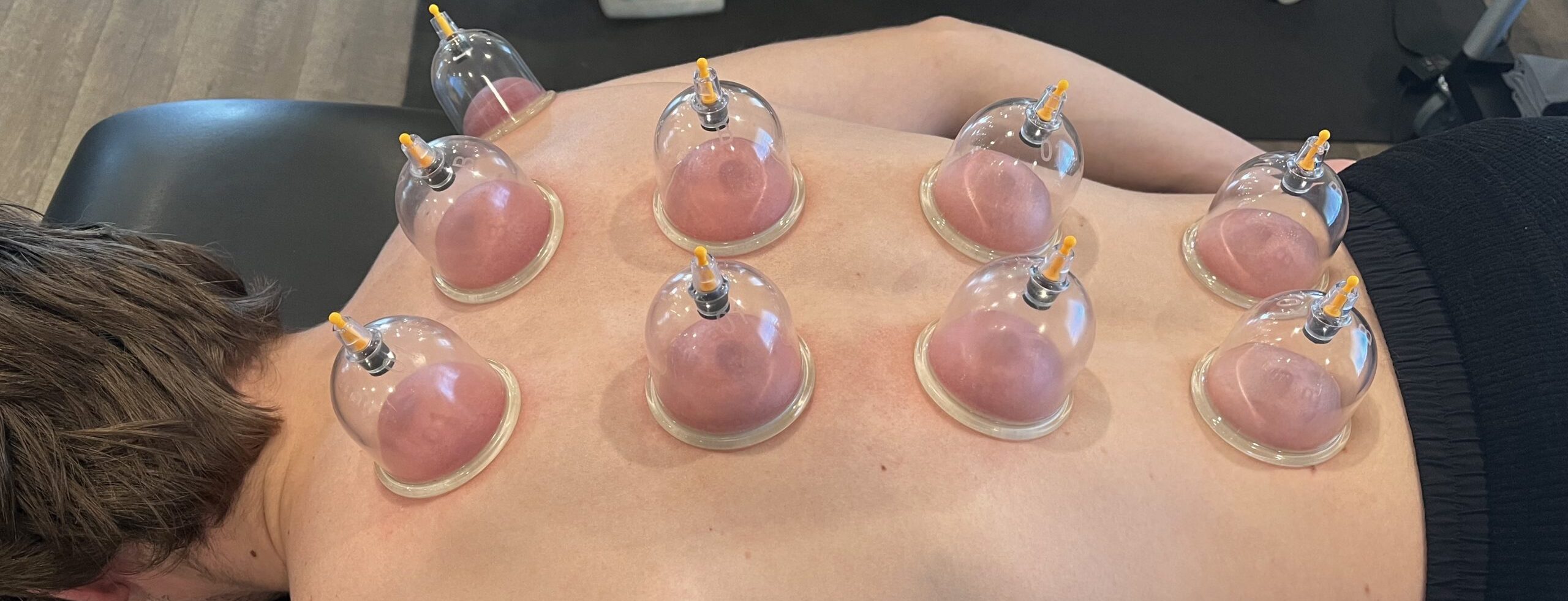
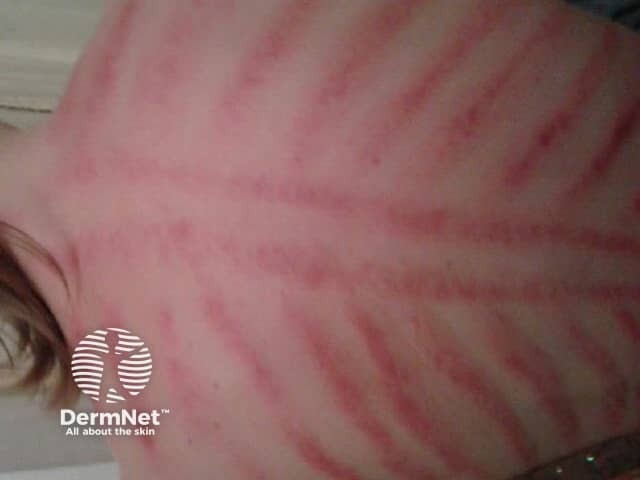
What is coining?
A cultural practice where a coin in rubbed on the skin, leaving linear erythematous marks or petechia

Why should skin tone be considered in assessments?
Certain conditions may appear differently depending on skin pigmentation, and benign findings may mimic pathology in darker or lighter skin tones
What is the Branden Scale used for?
To determine a patients risk of skin breakdown
What are the 6 criteria of the Branden Scale?
Sensory perception
Moisture
Activity
Mobility
Nutrition
Friction and shear
How is the Branden Scale scored?
Each category is 1-4 (except friction and shear which is 1-3), max score is 23 (higher is better)
What range of score on the Branden Scale indicates no risk?
19-23
What range of score on the Brandon Scale indicates low/mild risk?
15-18
What range of score on the Brandon Scale indicates moderate risk?
13-14
What range on the Brandon Scale indicates high risk?
10-12
What range on the Brandon Scale indicates Severe risk?
9 or below
What is oxygenation?
The process of providing oxygen to cells through adequate gas exchange
What is hypoxemia?
Abnormally low oxygen in the blood (measured through a blood gas)
What is hypoxia?
Insufficient oxygen reaching the tissues (assessed with pulse ox or appearance)
What is clubbing of the nails a sign of?
Chronic hypoxemia due to poor perfusion
Is clubbing reversible and does it require immediate contact to the doctor?
It is irreversible and occurs over a long period of time so it is not something that needs immediate attention, just something to note
Why is cyanosis?
Late sign of hypoxia presented through a color change in the skin
How does cyanosis present in different skin tones?
Lighter skin looks blue and darker skin looks gray or green
What actions can help hypoxia?
Elevate the head of the bed
Give oxygen
Breathing treatments
Treat underlying cause
What is perfusion?
Process of the heart transporting blood throughout the body
What is ischemia?
Decreased blood supply