MLS Exam 3: GI disorders/UTI/stones
1/452
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
453 Terms
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus and occasionally up to the throat/mouth
what are etiologies/exacerbating factors of GERD?
LES dysfunction/incompetence
Hiatal Hernia
Irritant effects of refluxate
Decreased esophageal clearance of acid
Delayed gastric emptying
what is a common complication of GERD?
reflux esophagitis
what are the typical symptoms of GERD?
Pyrosis
Regurgitation
Dyspeptic symptoms
what is the PE like in a patient with ONLY GERD?
normal
the severity of symptoms of GERD correlates with the severity of disease t/f
false
1 multiple choice option
name some "extraesophageal" symptoms of GERD
Chronic cough
Vocal hoarseness/laryngitis
Sore throat
Globus sensation
Exacerbations of asthma/COPD
Atypical/non-cardiac chest pain
Sinusitis
Dental decay
what are red flag symptoms of GERD?
Dysphagia
Odynophagia
Weight loss
Frequent N & V
Epigastric or non-cardiac chest pain
Early satiety
Iron deficiency anemia
GI bleeding
what do red flag symptoms indicate the need for?
additional testing & work-up in conjunction with empiric medication management
most patients DONT need testing for GERD. you can start treatment without it. what is this called?
empiric therapy
what are diagnostic study options for GERD?
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy(EGD) +/- bx
Barium Upper GI series
24-hour esophageal pH monitor +/- manometry
when would you a barium upper GI series?
For patients with dysphagia
what is a 24-hour esophageal pH monitor +/- manometry indicated for?
patients with persistent symptoms despite BID PPI therapy or pre-surgery
when could you NOT initiated therapy based on history for GERD?
if there are red flag symptoms
what are lifestyle modifications that can help with GERD?
Small frequent meals
Weight loss
Avoid lying down, bending, heavy lifting & tight clothes after meals
Elevate the head of the bed (HOB)
Avoid drugs that decrease LES tone
what are antacids used for?
rapid relief of occasional heartburn
what do H2 blockers do and which is the most potent?
Block stimulation of acid secretion by binding to histamine receptors in the stomach
famotidine (Pepcid®)
what do proton pump inhibitors do?
Covalently bonds to the H+/K+-ATPase enzyme & inactivates it permanently
which inhibits acid secretion better? H2 blockers or PPIs
PPIs
1 multiple choice option
what are DDIs with PPIs?
Interferes with absorption of drugs that require acidic environments - Increase absorption of digoxin (Lanoxin®)
Omeprazole (Prilosec®) also has specific DDIs due to CYP450 interference
what DDIs does Omeprazole (Prilosec®) have?
prolongs metabolism & elimination of of diazepam (Valium®), warfarin (Coumadin®), and phenytoin (Dilantin®)
Speeds up metabolism & elimination of clopidogrel (Plavix®)
what are long term issues associated with using PPIs?
Decrease Ca2+, Fe, Mg2+ & B12 absorption
Increased risk of infectious gastroenteritis
Elevated serum gastrin levels
Gastric atrophy/polyp formation
what is a serious complication of GERD?
Barrett's esophagus (adenocarcinoma)
a complication of GERD is esophageal stricture. what are symptoms of this?
Gradual progression of solid-food dysphagia over months to years
May see DECREASED heartburn as stricture worsens & other symptoms progress
how do you diagnosis esophageal stricture? what is used initially and what is confirmatory?
Barium UGI (initially)
EGD with biopsy (confirmatory)
Barrett Esophagus/Esophagitis
Squamous epithelium replaced by metaplastic columnar epithelium
what confirms diagnosis of barrett esophagus/esophagitis?
EGD with biopsy
what is the worst complication of barrett esophagus?
adenocarcinoma (esophageal cancer)
how do you screen for esophageal cancer?
EGD w/biopsy every 3-5 yrs
what are the treatment options for barrett esophagus?
Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy QD/BID
Ablative therapy
what are indications in which you would do ablative therapy?
Pts with Barrett’s + dysplasia
what is the procedure called for antireflex surgery?
Nissen fundoplication
Helicobacter pylori
Gram-negative rod that resides in antrum of stomach
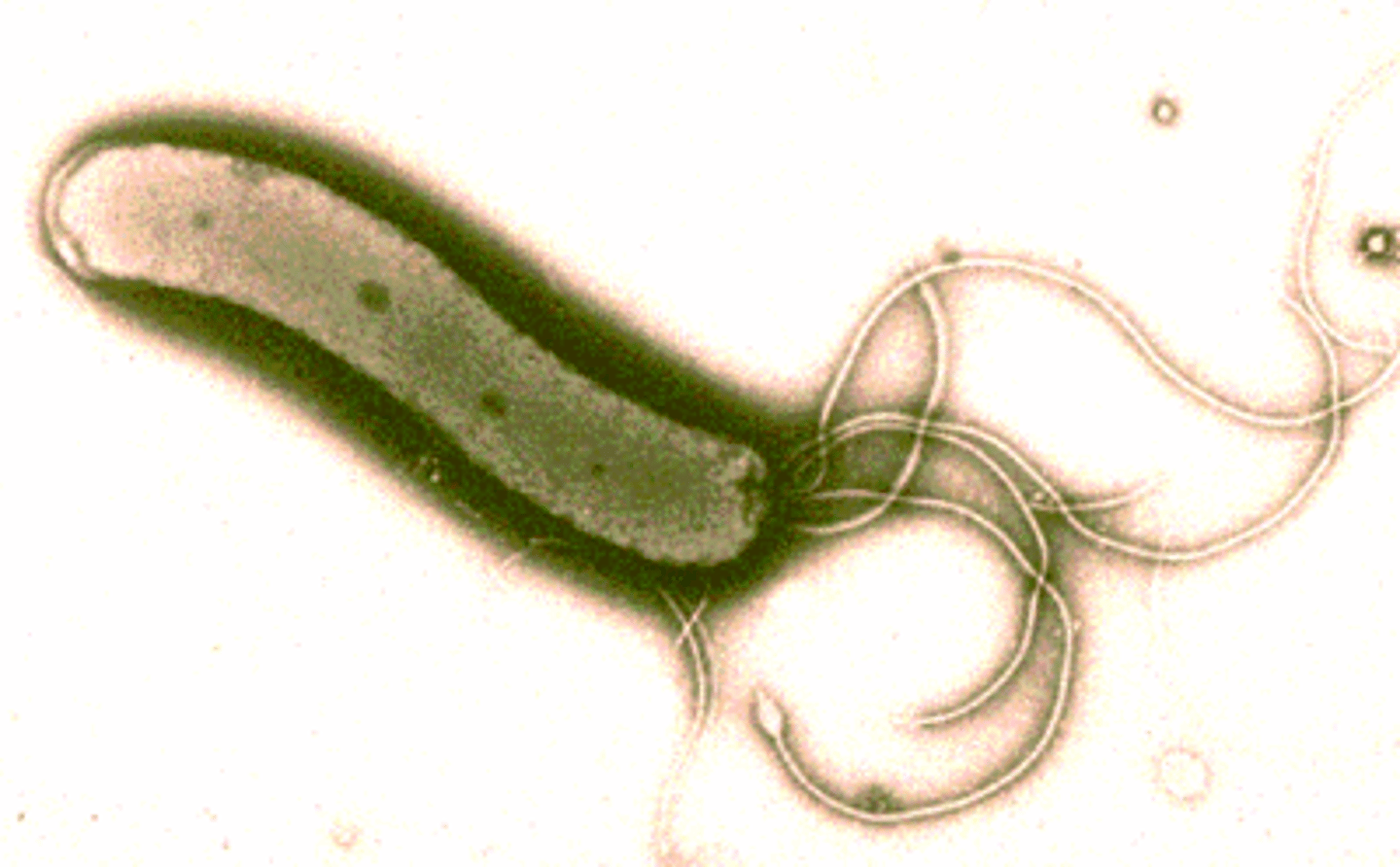
H. pylori secretes many factors that compromise integrity of gastric/duodenal mucosa. name 1 example.
urease
Human host mounts an additional inflammatory response to H. pylori, further damaging epithelium causing what?
Gastritis, ulcer formation
describe the incidence and prevalence of H. pylori disease in the US
Rare in childhood, incidence increases with age
Present in ~100% of patients by age 70
how is H. pylori transmitted?
oral-oral
fecal-oral
H. pylori is almost always associated with what?
chronic active gastritis
H. pylori accounts for majority of?
PUD cases
what can H. pylori infection lead to and what does it also play a role in?
B12 malabsorption & anemia; MALT lymphoma & gastric CA
what are all the ways to test for a H.pylori infection?
Serology – IgM, IgA, IgG*
Urea breath test (UBT, [BreathTek®])*
Fecal H. pylori antigen testing (FAgT)*
Rapid urease testing (RUT, [CLOTest®, PyloriTek®])*
Bacterial culture (again, EGD sample)
what is an important consideration in regards to testing for H.pylori?
Must be off PPI x 7-14 d & ABX 28 d before test
what is gastritis and how is it histologically documented?
Inflammation (-itis) of the gastric mucosa
EGD biposy
what are the 3 categories of gastritis?
1. Erosive/Hemorrhagic*
2. Non-Erosive/Non-Hemorrhagic*
3. Histologically-specific gastritis
Erosive/Hemorrhagic
acute gastropathy
Non-Erosive/Non-Hemorrhagic
chronic gastropathy
Acute Erosive/Hemorrhagic Gastritis is related to local irritants/pathology like?
NSAIDs/ASA, Alcohol, toxins, caustic ingestion, portal hypertension/varices (end result of chronic liver disease), etc.
stress gastritis falls into the acute erosive/hemorrhagic gastritis category due to severe?
medical or surgical illness
EGD findings of acute erosive/hemorrhagic gastritis include?
Hemorrhages, petechiae, erosions
Usually superficial epithelial damage only
Very little true inflammation, if any
what is the cause of chronic gastritis type A?
autoimmune
what is inhibited/the problem in chronic gastritis type A?
Antibodies to parietal cells and
H+/K+-ATPase enzyme pump inhibited
why is having antibodies to parietal cells bad?
Parietal cells make intrinsic factor
Associated with pernicious anemia
what can the inhbition of H+/K+-ATPase enzyme pump lead to?
hypo- or achlorhydria with a subsequent ↑ in gastrin secretion (feedback loop)
patients with chronic gastritis type A are at ↑ risk for what?
gastric malignancy
what parts of the stomach is chronic gastritis type A mainly in?
fundus and body
what is the cause of chronic gastritis type B?
H. pylori
Location of chronic gastritis type B depends on predisposing genetic factors. what are the types of disease and which one do majority of patients have?
diffuse mild gastritis (majoirty)
antral predominant disease
body prominent disease
chronic gastritis type B can also increase the risk/lead to what?
gastric malignancy
how do you diagnosis chronic gastritis?
UPPER ENDOSCOPY (EGD) with tissue biopsy
what is an ulcer?
Break in gastric or duodenal mucosa
Occur when normal mucosal integrity and defensive factors are impaired or overwhelmed
what is the depth typically in a peptic ulcer?
through the muscularis mucosa down to the submucosa
how big usually are peptic ulcers?
>5 mm
what the 2 locations for peptic ulcers?
stomach and duodenum
stomach ulcers are typically located where?
antrum
what are more common stomach or duodenal ulcers?
duodenal
1 multiple choice option
what are more risk for malignancy, stomach or duodenal ulcers?
stomach
1 multiple choice option
what are peptic ulcers caused by and what is the leading cause?
Helicobacter pylori infection (leading cause)
NSAID-induced injury
how does gastric acid play a role in peptic ulcers?
DOES NOT play a role in PRIMARY ulcer development
BUT DOES contribute to CONTINUED mucosal injury once the insult has taken place
in NSAID-Induced PUD, severity of symptoms does NOT correlate with pathology t/f
true
1 multiple choice option
what do NSAIDs do?
inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX 1, COX 2 or both) and ↓ prostaglandin (PG) synthesis
what are symptoms of PUD?
Burning epigastric pain with changes related to meals
“Gnawing”
Ill-defined aching sensation
Hunger pain (“pangs”)
Duodenal Ulcer Symptoms
Pain usually occurs 90 min to 3 hours after a meal and is frequently relieved by food or antacids
2/3 will describe pain awakening them from sleep between midnight and 3 A.M.
Gastric Ulcer Symptoms
May be different than duodenal ulcer symptoms
Discomfort may actually be precipitated by food
Nausea & anorexia occur more commonly in gastric ulcer patients
name 3 complications of PUD
bleeding, perforation, gastric outlet obstruction
what is the most common complication of PUD? the least?
most: bleeding
least: gastric outlet obstruction
how does bleeding as a result of PUD present?
hematemesis or melena
penetration
a type of perforation in which the ulcer bed tunnels into an adjacent organ
what is the most common finding on PE in PUD?
Epigastric tenderness
what is the procedure of choice when diagnosing PUD?
endoscopy (EGD)
what are treatment options for gastritis and PUD?
Address underlying cause & heal mucosa
Medication
Surgery
Acid suppression therapy
Mucosal repair therapy
H. pylori eradication
name 3 types of acid suppression therapy
1. Antacids
2. H2 receptor antagonists/blockers (H2RA/H2B)
3. Proton pump (H+ K+ ATPase) inhibitors (PPI)
what are antacids used more for?
symptomatic relief of dyspepsia
how long should a patient be on H2RA/H2B for duodenal and gastric ulcers?
6 weeks for duodenal & 8 weeks for gastric
PPIs
Preferred(?) over H2B for treatment of ulcers
4-6 weeks for duodenal & 8 weeks for gastric
what are 3 things involved in mucosal repair therapy?
1. Cytoprotective Agents - Sucralfate (Carafate®)
2. Bismuth containing preparations
3. Prostaglandin Analogues
what is the most common side effect of cytoprotective agents and how do they work?
constipation; Binds to proteins within the ulcer bed and forms a barrier
Bismuth containing preparations are often used in the treatment of?
H. pylori
what are prostaglandin analogues used to prevent and what are 2 side effects?
used to prevent NSAID-induced ulcers; Diarrhea and
Uterine bleeding & contractions
all PUD patients who are (+) for H. pylori are getting H. Pylori eradication therapy that consists of?
Quadruple therapy and treat x 14 days
gerneral approach to therapy
(1) Document presence of ulcer or gastritis via EGD
(2) Is patient (+) for H. pylori?
No - Acid-suppression therapy
Yes - QT regimen x 14 d + continued acid suppression
(3) Is ulcer likely NSAID-related?
(4) Document Healing - Another scope (EGD)
what are refractory ulcers?
Gastric ulcer that fails to heal by 12 weeks
Duodenal ulcer that fails to heal after 8 weeks
why is document healing with another scope important?
Check for other problem (i.e. Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome [ZES], cancer, etc.)
what are options for surgical therapy for PUD?
Vagotomy
Pyloroplasty
Antrectomy
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES)
Rare condition characterized by gastrinoma (NET) with hypersecretion of HCl & recurrent ulcers
60% of gastrinomas are ______
malignant
diagnosis of ZES
Draw fasting gastrin level If elevated, get imaging to look for tumor:
Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (SRS)
what is the best treatment for ZES?
High dose PPI therapy
etiology/pathophysiology of cholelithiasis
Bile stored in gallbladder becomes supersaturated
Particles precipitate out, form microscopic crystals
Crystals grow, aggregate, & fuse to form stone(s)
etiology/pathophysiology of acute cholecystits
Stone moves & obstructs cystic duct which leads to distention, inflammation, and potential secondary infection of the gallbladder
with acute cholecystitis, you can also have acalculous cholecystitis which is?
Sludge and/or biliary dyskinesia