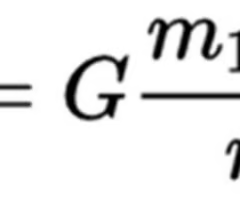astrology unit 1 test
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
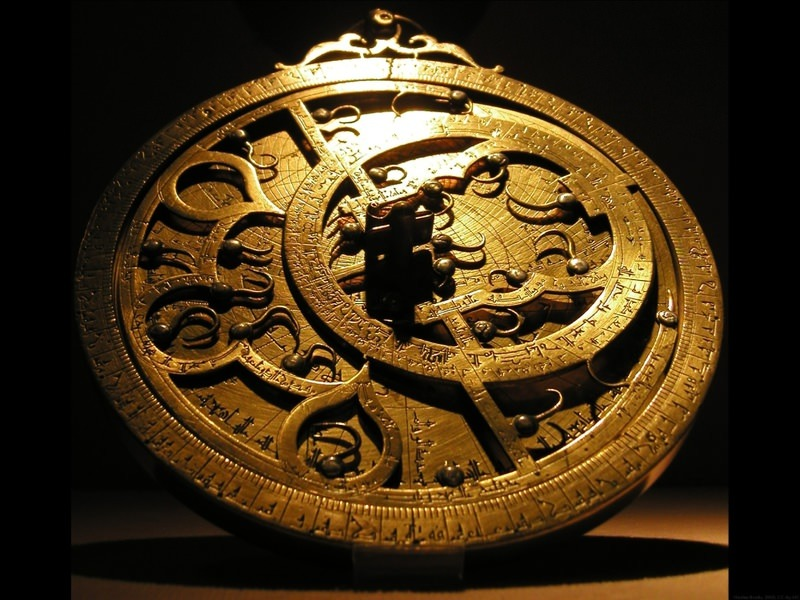
Astrolabe
instrument used to determine latitude by measuring the position of the stars
gnomon
an ancient sundial created by the Chinese to measure days and create a calendar
Cosmology
study of the universe as a totality; theory of the origin and structure of the universe
star chart
The stars and constellations were placed within a grid which helped improve naviagation
planets
The ancient civilizations thought that these were bright stars that moved independently of the heavens
celestial sphere model
a cosmology model which has the earth spinning and the rest of the heavens and stars in a fixed position
geocentric model
a cosmology model which has the earth as the center of the universe. The moon, planets, sun and stars were in independent orbits revolving around the earth.
heliocentric model
a cosmology model which has the sun as the center of our solar system. each planet revolves independently around the sun.
Pythagoras
Theorized that the earth must be shaped like a sphere
Eratosthenes
Calculated the circumference of the moon using the gnomon
Ptolemy
Put forth the theory that the Earth was the center of the universe. Widely believed for 1500 years.
Mayans
Although isolated from the rest of the world, this culture had the most accurate pre-telescope in the world.
Copernicus
Proposed that the sun was the center of our solar system and that each planet revolved around the sun in a circle.
Kepler
Add to Copernicus' theory that the sun was the center of the solar system, except that he proved that the planets move in an elliptical shape vs a circle.
Brahe
Invented number instruments to study the stars. Most importantly, determined that you must collect a large amount of date to prove that your results are accurate
Venus
A planet observed by Galileo using the telescope. he noticed that this planet often appears in various phases, similar to our moon, when observed
Jupiter
Planet observed by Galileo using a telescope. He noticed several moons moving in an orbit around this planet.
moon
Observed to be a huge solid rock by Galileo when he was using a telescope
Newton
Scientist who was studying the movement of the moon when he formulated his theories of gravity and motion.
Retrograde Motion
The movement of planets that create an illusion that the planets are moving backwards at times
Telescope
an instrument which uses lens to view objects which are far away; no known inventor; first used by Galileo to document specific information about some planets
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
Three laws that describe the motion of the planets around the Sun.
Kepler's First Law of Planetary Motion
The orbit of each planet around the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
Kepler's second law of planetary motion
A line segment connecting a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time
Kepler's third law of planetary motion
The square of the orbital period of any satellite is proportional to the cube of its average distance from its central mass.
formula for keplers 3rd law
P² = a³
Egyptians
Culture which considered the stars and heavens an important factor in moving into their afterlife.
Formula for determining the circumference of the Earth
Using a gnomon, determine the degrees which create a shadow when the sun is directly above a tall point. then determine the distance where there is no shadow when the sun it directly above. divide 360 degrees by degree found at first location. Now divide that number by the miles between the cities.
Astronomy
study of the universe
Astrolabe

Formula for Gravitational Attraction