Meiosis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Genes
Unit of inheritance passed onto offspring
Three parts of Nucleic Acid
N-base, Pentose sugar, phospate group
2 types of Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA
Two families of nitrogen bases w types
Purines(A+G) and pyrimidines(C+U+T).
How do the purines/pyrimidines bind?
A+T is two bonds, C+G is three bonds
Difference between Deoxyribose and ribose?
Deoxyribose is in DNA lacking one oxygen on carbon-2 while Ribose is in RNA with the oxygen on carbon-2.
Heredity
Transmisison of traits from one generation to the next.
Humans contain __ chromosomes in their somatic cells, and __ in their gametes.
46,23
Human genome
The complete set of genetic information for a human being, consisting of all the DNA stored in the 2323 pairs of chromosomes in the nucleus plus mitochondrial DNA. Approx 20,000 genes total, one chromosome as 100s to 1,000s of genes on it.
Locus
A gene’s specific location on the chromosome.
Why and how is DNA’s message transcribed?
DNA is too big to exit the nucleus, so it relies on mRNA to transcribe or carry DNA’s message out of the nucleus.
How is DNA’s message translated?
mRNA arrives at a ribosome where the message gets translated into the making of a protein.
Reproduction that brings about genetically identical clones
Asexual reproduction
Number of chromosomes from each parent
23
Karyotype
When chromosomes are arranged in pairs starting with the longest
Homologs/Homologous pairs/chromosomes/tetrads
Chromosomes that carry the same traits
Alleles
one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same loci on a chromosome.
Autosomes
22 pairs of non-sex chromosomes in humans
Number of inherited chromomes
23
Haploid
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes.(1n)
Diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.(2n)
Zygote
single-celled organism formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg
If you want to take a 2n down to a 1n, the process that halves chromosome numbers is _____.
Meiosis
Meiosis results in how many divisions and how many daughter cells?
2,4
Synapsis
Pairing of homologous chromosomes during prophase I so that crossing over can occur
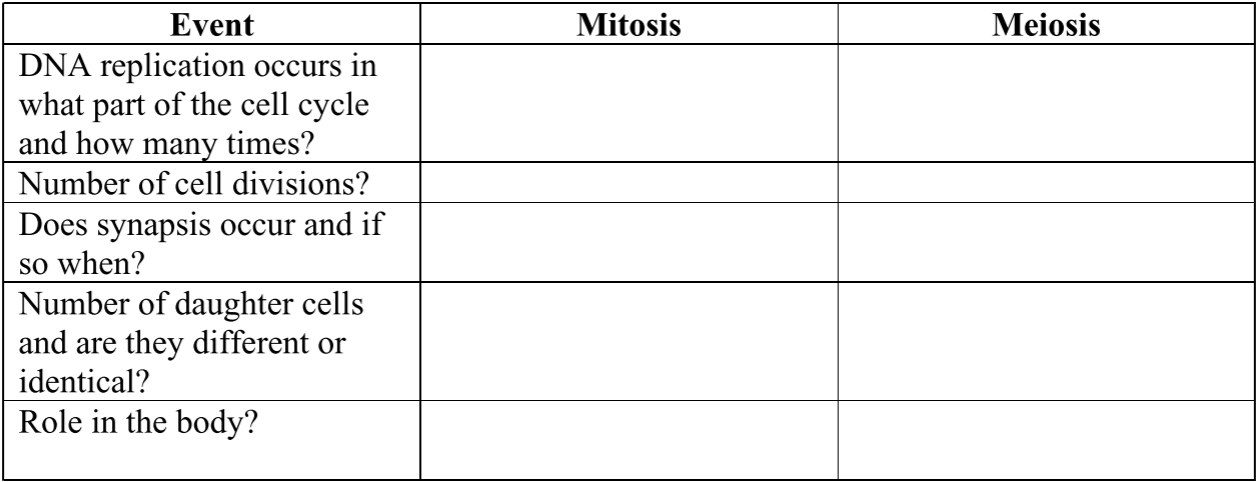
Mitosis
S-phase
1
No
2, identical
growth + tissue repair
Meiosis
S-phase
2
yes, prophase I
4, different
produce gametes
Independent Assortment
This means that when homologues line up at the equator of the cell in metaphase I, it is an “independent”/ random event for each homologous pair.
Crossing Over
Occurs during prophase I of meiosis when homologues come together during synapsis to form homologs. Then, non sister chromatids trade places.
Chiasmata
The regions created from crossing over
Random Fertilization
Refers to the fact that each parent has 8 million possible ovules/sperm cells.
What creates the greatest number of new genetic combinations?
mutations