Chapter 23 - Types of Reactions in Organic Chemistry
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
substitution reaction
a chemical reaction in which an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms
mechanism of a reaction
detailed step-by-step description of how overall reaction occurs
show movement of electrons represented with arrows
one electron → half arrow head
electron pair → full arrow head

example of substitution reaction
alkanes with halogens in presence of UV light
free radicals
any atom or group of atoms with an unpaired electron
homolytic fission
process in which a bond breaks in such a way that each atom joined retains one of the two electrons
chain reaction
a reaction that continues on and on because a product from one step of the reaction is a reactant for another step of the reaction
4 steps of the mechanism of a substitution reaction
initiation
propagation 1
propagation 2
termination
evidence for mechanism of substitution reaction
use of ultraviolet light even for very short period of time causes chain reaction
for every light photon absorbed, thousands of chloromethane atoms formed
evidence for the combining free radicals comes from fact small amounts of ethane found among products
adding tetramethyl to reaction increases speed of reaction as it promotes chain reaction by providing free radicals as it decomposes
use of halogenated alkanes
flame retardants
→ halogenated alkanes don’t support combustion and added to fabrics to reduce tendency to catch fire
what are the types of substitution reactions?
monochlorination
esterification
saponification (base-catalysed hydrolysis of esters)
what types of reactions is esterification?
condensation reaction (water formed)
substitution reaction (H attached to -OH replaced by alkyl group)
saponification
esters are hydrolysed in presence of a base
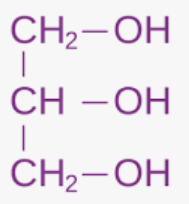
molecular formula of glycerol (propane- 1,2,3-triol)
C3H5(OH)3
addition reaction
a reaction in which two or more molecules react together to form a singular molecule
hydrogenation
addition of hydrogen to a molecule
halogenation reaction
addition of halogens to a molecule
steps for addition reaction between bromine and ethene
polarisation
heterolytic fission
carbonium ion formation
ionic addition
uses of 1,2-dibromoethane
fumigant for treating timber against termites
control moths in beehives
uses of 1,2-dichloroethane
used to manufacture chloroethane and make PVC
uses of chloroethane
used in dentistry to diagnose a ‘dead tooth’
what differs about reaction between ethene - hydrogen to ethene - bromine
already polarised hydrogen chloride further polarised by repulsion of double bond’s electrons
how is margarine made?
hydrogenation of vegetable oils
polymers
long chain molecules made by joining small molecules, they consist of a repeating pattern
common polymers
polythene
polypropene (plastic beakers)
PVC (poly(chloroethene))
what are polymers commonly referred to as?
plastics
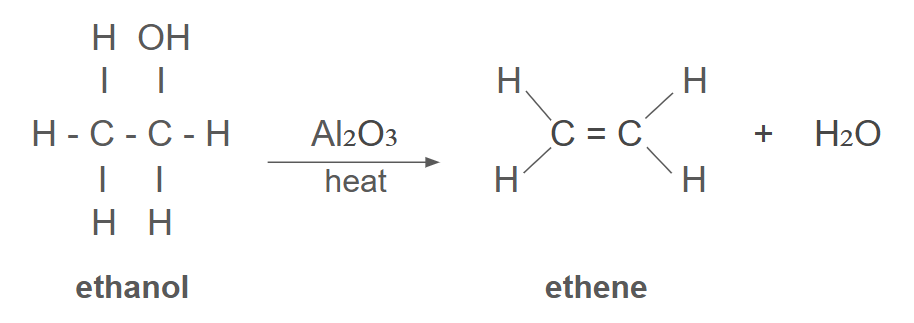
elimination reaction
reaction in which small molecule removed from a larger molecule to leave a double bond in larger molecule
dehydration reaction
water is removed during a reaction
(type of elimination reaction)
oxidation
the loss of electrons from a substance
reduction
the gain of electron to a substance
mnemonic for redox reactions
Oxidation
Is
Loss
Reduction
Is
Gain
oxidising agent
substance that is responsible for oxidation of another substance
reducing agent
substance that is responsible for reduction of another substance