Chapter 8: Groups 2 + 7, Qualitative Analysis
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
what are Group 2 sometimes called?
alkaline earth metals
Group 2 elements often act as …. agents
reducing → they become oxidised by losing the 2 outer electrons in the outer s subshell
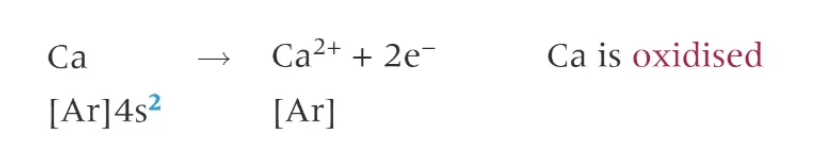
Group 2 metal + oxygen →
MO → a metal oxide
magnesium + oxygen appearance:
brilliant white flame
group 2 metal + water →
M(OH)2 + H2

the reactivity of group 2 … going down the group
increases
in the reaction between a group 2 metal and water, are all hydrogen atoms reduced?
no

metal + acid →
salt + hydrogen
ionisation energies … down Group 2
decrease
attraction between nucleus+ outer electrons decreases
as a result of the increasing atomic radius + increasing shielding
Group 2 oxide + water →
metal hydroxide + water
alkaline solution
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca2+ (aq) + 2OH-(aq)
group 2 hydroxides are only slightly soluble in water. when the solution is saturated, further metal + hydroxidei ons
2OH-(aq) + 2OH-(aq) → Ca(OH)2(s)
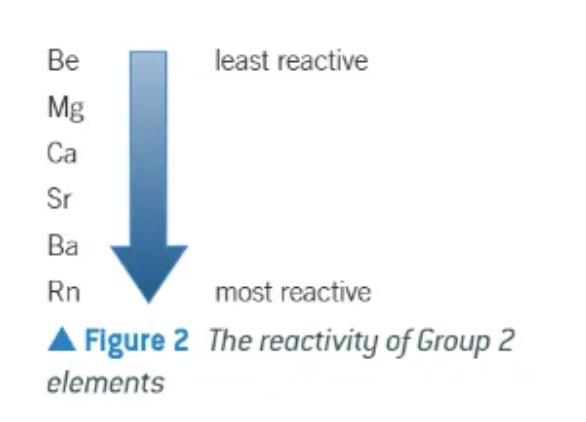
the solubility of hydroxides in water [does what] going down the group
increases → resulting solutions are more alkaline
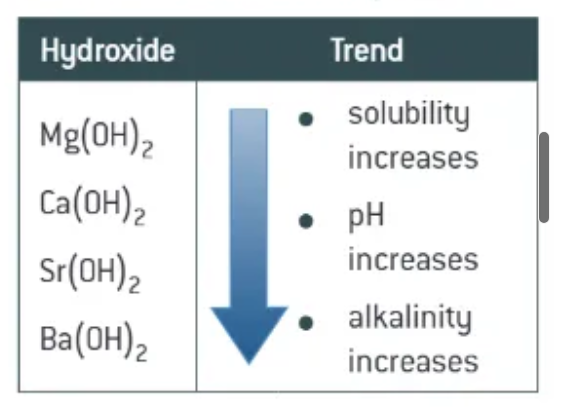
going down the group, the [what] of metal does [what]:
reactivity
ionisation energies
solubility of hydroxides
reactivity increases
i.e. decreases
solubility of hydroxides increases
what do farmers add to fields to increase the pH of soil?
Ca(OH)2
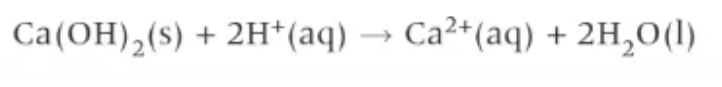
which group 2 compound is used as an antacid?
Mg(OH)2 → ‘milk of magnesia’ → suspension of white magnesium hydroxide in water
or
CaCO3 (but causes gas)

how are group 7 elements found on Earth?
stable halide ions in seawater + in compounds like NaCl
at RTP, how do Group 7 elements exist?
diatomic molecules
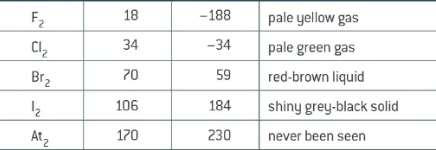
appearance of group 7 elements individually at RTP
group 7 elements act as … agents
oxidising
group 7 displacement reactions:
if a more reactive halogen is added,
a reaction occurs → halogen displaces halide (e.g. Cl2 + 2NaBr → NaCl + Br2)
solution changes colour
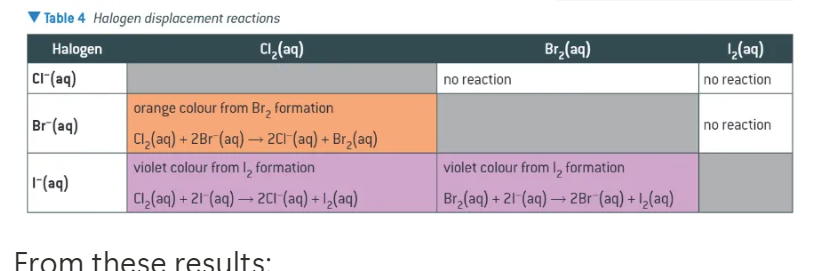
colours of iodine, bromine, and chlorine in (and not in) cyclohexane:
chlorine: pale green → pale green
iodine: brown → deep violet
bromine: brown → brown
fluorine + astatine:
fluorine reacts with almost any substance in comes in contact with
astatine decays rapidly → predicted to be least reactive
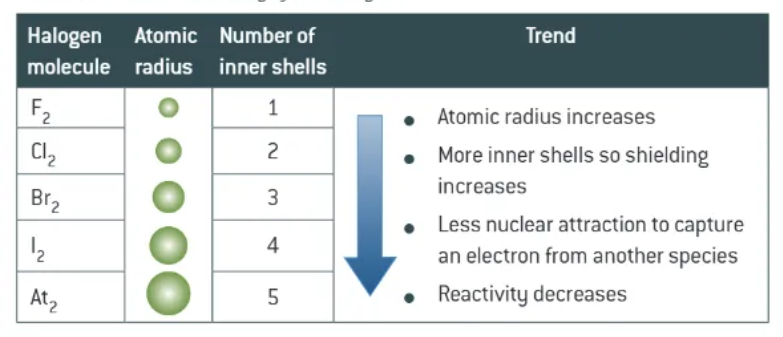
trend in reactivity of halogens
Fluorine = strongest oxidising agent
weaker oxidising agents as you go down
what is a disproportionation reaction?
a reaction in which the same element is both oxidised and reduced
chlorine + water (disproportionation)
c.w.c.h. (can’t want, can’t have!)
chloric acid works as a weak bleach → by adding indicator, the indicator will first turn red (acid) before going white because of the bleaching effect
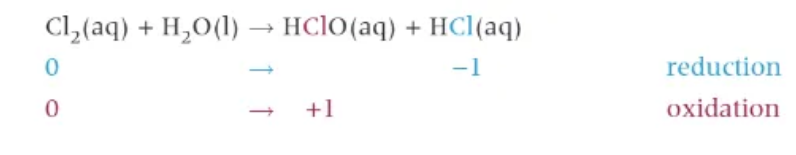
cold, dilute, aqueous sodium hydroxide + chlorine (disproportionation):
C.S.S.S.W
(Charles Second Seriously Sells Water)
NaClO = bleach
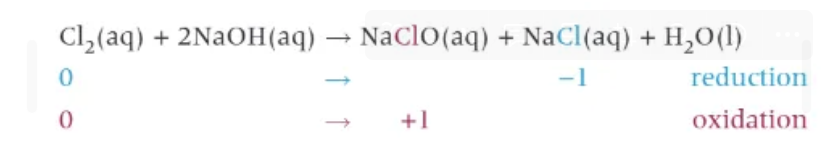
pros + cons of chlorine use:
kills bacteria in water
toxic gas
chlorinated hydrocarbons are carcinogenic
test for carbonates:
add dilute nitric acid to substance being tested
bubbles present prove that the substance could be a carbonate
bubble gas through limewater (saturated aqueous Ca(OH)2)
carbon dioxide reacts to form a white precipitate, CaCO3 → lime water turns milky
reaction for the testing of the gas:
CO2(g) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
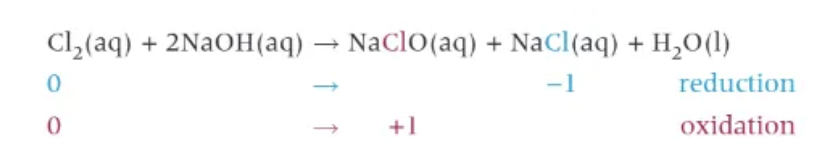
test for sulphates:
add Barium Chloride or Barium Nitrate to solution
more likely Ba(NO3)2 → if we don’t know whether the substance is a chloride!
white precipitate is formed
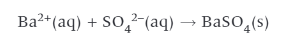
test for halides:
add aqueous silver nitrate, AgNO3 to aq. solution of halide
precipitate will be different colours
THEN
add dilute ammonia + then conc. ammonia → the different compounds have different solubilities in ammonia!!
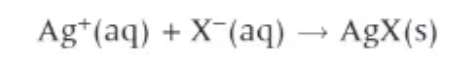
positive test results for halides (when AgNO3 is added)
Chloride = white prec.
Bromide = cream prec.
Iodide = yellow prec.
solubilities of silver halides in ammonia
chloride = soluble in DILUTE NH3
bromide = soluble in CONC. NH3
iodide = insoluble
what order do the anion tests need to be carried out in?
carbonate → definitely/ definitely not a carbonate
sulphate → barium carbonate could be mistaken for barium sulphate
halide → silver carbonate/silver sulphate could be mistaken for silver chloride
test for ammonium ions:
add aqueous sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to ammonium ion solution
heat → ammonia gas is produced
damp indicator paper will turn blue