Parasites
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
(Platy)Helminths
Flatworms
Nematodes
Roundworms
Worms associated with foods
Animal parasites: need animal host to develop - therefore worms are only found in meat products
Life cycle: egg, intermediate stage(s), mature worm
Classified according to shape adult worm:
Flatworms: Trematodes and Cestodes
Roundworms: Nematodes
Do not grow in foods
The four most important worms, their hosts and the food vehicles.
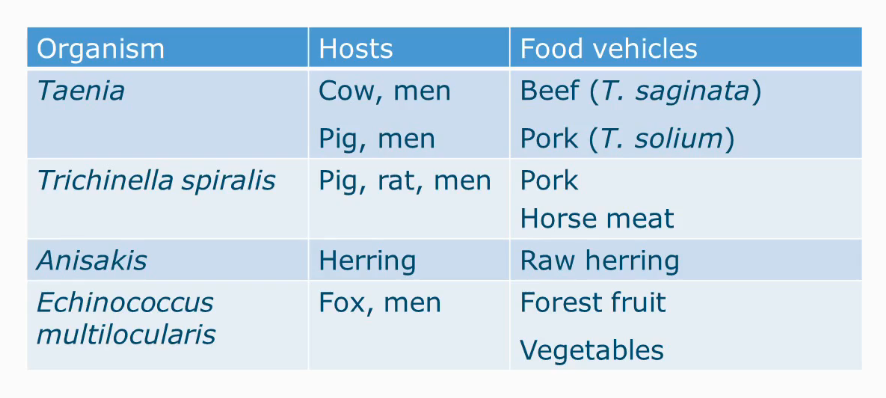
Transmission cycle Taenia solium
Pig tapeworm
Only in humans the larvae will mature, not in the food.
Similar cycle for T. safinata but instead it grows in beef.
Human health effect Taenia
Mature tapeworm only develops in human hosts
4-12 m long (1000-2000 segments, proglottids)
Symptoms: asymptomatic, nausea, abdominal pain, weight loss, anemia
Effects more severe in young and immuno-compromised
Efficient drugs are available.
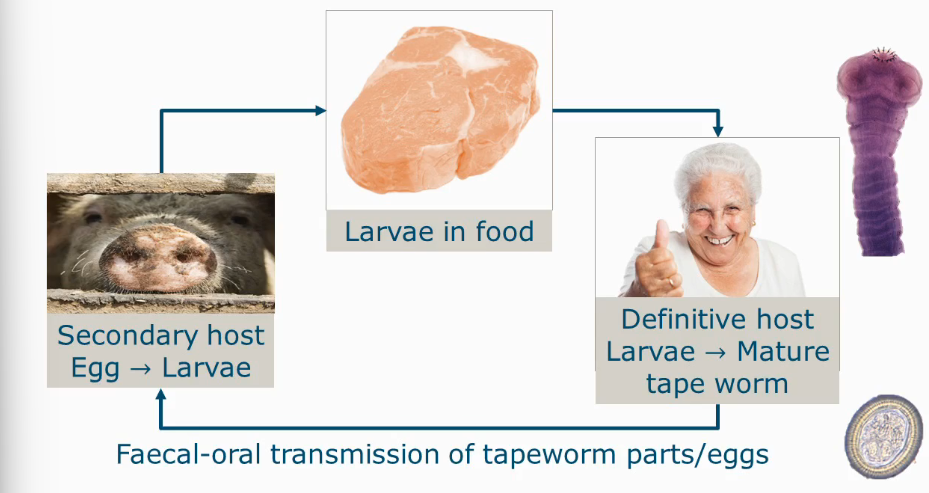
Transmission cycle Trichinella spiralis
primary vs secondary source host parasites
A primary host, or definitive host, is where a parasite reaches sexual maturity and reproduces. A secondary host, or intermediate host, harbors the parasite during its development but not to sexual maturity, serving as a transition to complete its life cycle. The distinction is about the parasite's development and reproductive stage within the host.
Trichinellosis
Roundworm
caused by consumption of Trichinella spiralis
Encysted larvae released in stomach
Larvae mature to adult worm (3-4 mm) in intestine
Female worm releases larvae
Larvae invading intestinal mucosa, causing symptoms
Incubation time: few days - month
Symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhoea
Larvae invade and encyst in muscle tissue
Symptoms: muscle pain, fever
Efficacy of drugs uncertain
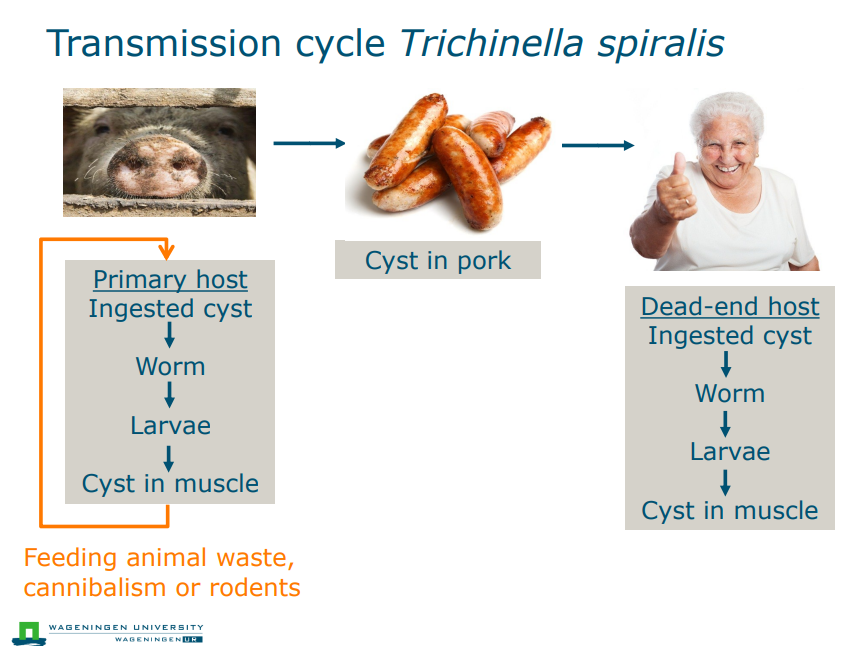
Contamination cycle of Echinococcus multilocularis
Echinococcossis
Disease caused by consumption of Echinococcus multilocularis
Which is a parasite found in foxes
Alveolar cysts (lungs, liver), treatment may not be effective.
Fish parasites
Anisakis: herring worm
Symtpoms: abdominal pain
Therefore all freshly caught fish, has to be frozen for 24h at -18C which kills the worms
This makes it safe to eat the fish raw.
Preventative measures against worms
Examination of slaughter animals before and after slaughter
Multiple spots of parasites → rejection
Local contamination → approval after treatment
Severe cold treatment of contaminated fish or meat, e.g. Taenia saginata, -18C, 10 days in calf meat
Educate consumers: adequate heating of food before consumption, wash (wild) berries