Business unit 1
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
challenges for starting a business
lack of finance
unestablished customer base
cash flow problems
marketing problems
people management problems
production problems
legalities
high production costs
poor location
not able to handle external influences
opportunities for starting a business
growth— increase in value
earnings—profit
transference and inheritance— something you can pass onto your children
personal challenge
autonomy
security— you’re your own boss
hobbies
public sector
owned by the government
private sector
controlled and owned by private individuals rather than by the government
aims of private sector companies
earn profit
aim of public sector companies
provide essential goods and services that would be underprovided or inefficiently provided by private sector.
reasons for public sector business activity
ensure everyone has access to basic services such as education, health care, etc.
avoid wasteful competition as gov. is able to achieve huge economies of scale.
protect citizems and businesses through institutions such as the police
create employment opportunities
sole trader
an individual who owns their personal business. Unincorporated(no difference between person and their business)
sole trader advantages
few legal formalities
profit taking
being your own boss
personalised service to customers
privacy(dont have to make financials public)
quicker decision-making
sole trader disadvantages
unlimited liability
limited sources of finance
high risks
workload and stress
limited economies of scale
lack of continuity
partnership
for-profit private sector business owned by 2-20 persons
silent/sleeping partners
raise money from owners who do not actively take part in the running of the partnership but have a financial stake in it
advantages of partnerships
financial strength
specialisation and divison of labour
financial privacy
cost-effectiveness
disadvantages of partnerships
unlimited liability
lack of continuity
prolonged decision-making
lack of harmony
privately held companies
businesses owned by their shareholders
limited liability that cannot raise share capital from the general public via stock exchange
shares only sold to friends and family
shareholders
individuals who have invested money to provide share capital for a company or corporation
owners of a limited liability company. shares in a company can be held by individuals or other organisations
Annual general meeting
shareholders vote on resolutions
re election of BOD
ask questions to CEO
approve financial accounts
limited liability
shareholders do not stand to lose personal belongings if the company goes into bankrupcy or liquidation.
advantages of limited liability companies
raising finance— can raise lots by selling shares
limited liability— easy to attract investors
continuity— business is a separate legal entity
benefit from economies of scale
productivity— can hire directors + specialists to run firm— no need for owner’s direct involvement
tax benefits
disadvantages of limited liability companies
communication problems— as it becomes larger, more impersonal
added complexities
compliance costs
disclosure of information— more bureaucracy
loss of control
publicly held companies
shares many similarities with privately held companies
able to advertise and sell shares to general public via stock exchange
flotation
when a publicly held company first sells all or part of its business to external investors(shareholders) (IPO)
Initial public offering
makes the publicly held company listed on a public stock exchange
social enterprise
revenue-generating businesses with social objectives at the core of their operations.
main goals:
achieve social objectives
earn revenues in excess of their costs
benefits of social enterprises
use financial surplus to benefit others in society, beyond personal rewards for shareholders and owners
create employment opportunities, thereby improving the economic and social landscape of local communities
run in a transparent way, providing tangible benefits
can be private sector, public sector or a cooperative
private sector for-profit social enterprise
reinvest or donate any surplus to create positive social change
ethical business practises
public sector for-profit social enterprises
state-owned social enterprises run in a commercial way
help raise gov. revenue and provide essential services that may be inefficient or undesirable if left to private sector
cooperatives
for-profit social enterprise owned and run by their members, such as employees or customers, with the common goal of creating value for their members by operating in a socially responsible way.
advantages of cooperatives
incentives to work bc have a stake in cooperative— enhances self-motivation and productivity
decision-making power— employees have a say in how business is run
social benefits— run on socially responsible principles
public support— people want to help them succeed
disadvantages of cooperatives
disincentive effects— inefficient management bc cooperatives do not pay high
limited sources of finance
slower decision-making bc democratic
limited promotional opportunities
non-governmental organisations (NGOs)
private organisations that pursue activities to relieve suffering, promote basic social services or undertake community development.
private sector or not for profit social enterprises
vision statement
outlines an organisations aspirations in the distant future
mission statement
simple declaration of the underlying purpose of an organisation’s existence and its core values. clearly defined and realistically achievable
differences between mission and vision statements
vision addresses ‘what do we want to become’ while mission addresses ‘what is our business’
mision statements updated more frequently than vision statements
objectives
The goals or targets an organisation strives to achieve.
why are organisational objectives important
to measure and control— help to control a firm’s plans
to motivate— can help inspire managers and employees to reach a common goal
to direct— provide a clear focus
advantages of having ethical objectives and practices
improved corporate image
increased customer loyalty
cost cutting
improved staff morale and motivation
disadvantages of having ethical objctices and practices
compliance costs high
lower profits
stakeholder conflict
subjective nature or business ethics
stakeholder
an individual, group, or organisation with a direct interest or involvement in the operations and performance of a business
corporate social responsibility
conscientious consideration of ethical and environmental practise related to business activity
internal stakeholders
members of the business namely employees, managers and directors, and shareholders
external stakeholders
not part of the business but have a direct interest or involvement in the organisation. comprised of customers, suppliers, financiers, pressure groups, competitors, the government
conflict between stakeholders
differences in the varying needs and priorities of the various stakeholder groups of a business
economies of scale
lower average cost of production as a firm operates on a larger scale due to an improvement in its productive efficiency
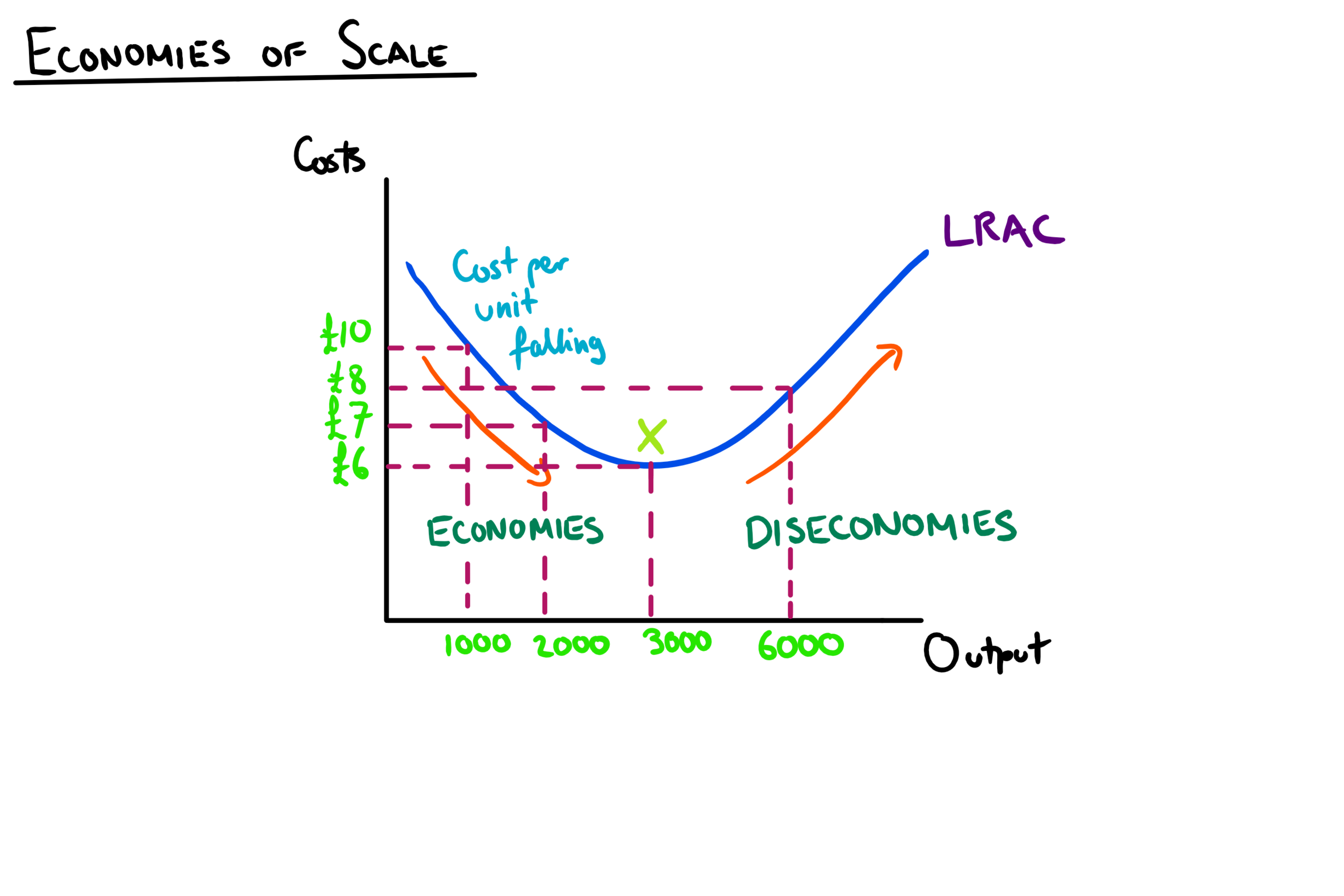
types of economies of scale
technical economies of scale— big companies use sophisticates capital and machinery to mass produce
financial economies— large firms can borrow large sums of money
managerial economies
specialisation economies— division of workforce rather than management
diseconomies of scale
in a larger firm, managers lack control and coordination
likely to be poorer working relationships in an oversiyed business
workers become bored with repeating tasks within larger workforce with high specialisation leads to lower productive efficiency
amount of bureaucracy grows as a business does
internal growth usually generated by
Gaining greater market share
Product diversification
Opening a new store
International expansion
external growth takes place in one of three ways:
Vertical integration (forward or backwards)
Horizontal integration
Conglomerate integration
advantages of internal growth
The pace of growth is manageable
Less risky as growth is financed by profits & there is expertise in the industry
Avoids diseconomies of scale
The management know & understand every part of the business
disadvantages of internal growth
The pace of growth can be slow & frustrating
Not necessarily able to benefit from economies of scale
Access to finance may be limited
advantages of external growth
quicker than organic growth
synergies
reduced competition
economies of scale
spreading of risks
disadvantages of external growth
more expensive than internal growth
greater risks
regulatory barriers
potential diseconomies of scale
conflict
possible loss of control
merger and acquisition
A merger is a mutual agreement between two or more businesses to join together as a single business
An acquisition occurs when one company takes complete control over another by acquiring more than 50 per cent of its share capital
A friendly takeover is where acquisition has the approval and support of the directors of the target company
A hostile takeover occurs against the will of the target company's board of directors
advantages for mergers and acquisitions
increased market share
economies of scale
entering new markets
less competition
disadvantages of mergers and acquisitions
diseconomies of scale
culture clash
inefficiencies
possible lack of expertise in new products/ industries
joint venture
A joint venture occurs when two businesses join together to share their knowledge, resources and skills to form a separate business entity for a specified period of time
Businesses may choose a joint venture to reach a new market as it may be more cost effective than exporting, licensing and franchising
advantages of a joint venture
Economies of scale gained from costs spread over larger output can lead to increased profit margins
Both businesses retain their own identity as the joint venture is set up as a separate business for a limited period of time
When the joint venture comes to an end the partners continue to operate their original businesses as before
Opportunity to enter new markets which otherwise may be closed to the business
Joint ventures often involve the exchange of technology, expertise, or specialised knowledge
This can enhance the capabilities of the venture and provide access to new opportunities
disadvantages of a joint venture
In a joint venture both businesses have a say in decision-making
This shared control can lead to conflict especially if the partners have different management styles or strategic goals
Reaching agreement may require extensive negotiations which can slow down the decision-making process
Sharing sensitive information such as trade secrets can be a concern if the partners are competitors
A culture clash between the two businesses can affect the quality of the business, leading to poor sales
Joint venture partners share both profits and costs
If one partner contributes more resources or effort than the other there may be disagreements about the distribution of profits leading to conflicts
strategic alliances
Strategic alliance agreements are similar to joint ventures
Businesses collaborate for a period of time to achieve a specified goal
They agree to work together for their mutual benefit
Resources are often shared
advantages of strategic alliance
limit risk
share resources
access to new markets
less competition
disadvantages of strategic alliance
culture clash
conflicts of interest
share profit
expose trade secrets
franchising
Franchising is a business model where an individual (franchisee) buys the rights to operate a business model, use its branding and software tools and receive support from a larger company (franchisor) in exchange for an initial lump sum plus ongoing fees
Franchising is a popular way to achieve rapid global growth
The franchisee operates the business under the franchisor's established system and receives training, marketing support, access to software and other systems and ongoing assistance
advantages for the franchisor
rapid growth without having to risk large amounts of money
allows company a national or international presence
rapid growth without having to worry about running costs such as recruitment, training and development, staff salaries, etc.
advantages for franchisee
low start up costs
low risk
likely to benefit from large scale advertising by franchisor
disadvantages for franchisor
huge risk in allowing other parties to use franchise’s name
can be difficult to control daily operations of all franchisees
franchising slower than M&A
disadvantages for franchisee
franchisee cant use own initiative to try out new ideas
buying a franchise very expensive
franchisees have to pay significant percentage of their sales revenues to franchisor
multinational company(MNC)
a business that is registered in one country but has manufacturing operations/outlets in different countries
reasons for MNC(multinational company) growth
Factors such as globalisation and deregulation have contributed to the growth of MNC’s
Globalisation has made it easier for firms to do business on a global scale and the number and size of MNCs continues to increase
Deregulation through trade liberalisation and the harmonisation of financial and technical standards has made it easier for businesses to operate in diverse locations
reasons for becoming an MNC
risk management
economies of scale
increased profit
create employment
enter new markets
transportation
avoid trade barriers
tax incentives
impact of MNCs on host countries
Many governments are in favour of MNCs establishing in their country as there are benefits to the wider economy
MNCs offer both advantages and disadvantages for a host country with regard to:
Employment, wages and working conditions
The impact on local businesses
The impact on the local community and environment
The impact on the national economy
advantages of an MNC to host country
boost local economy creating jobs + opportunities for local businesses
MNCs often invest to improve infrastructure
MNCs can bring new technologies and skills to local businesses
disadvantages of MNCs to the host country
MNCs may exploit local workers
may not create jobs for local workers as may just relocate workers from their own country
MNCs can push domestic businesses out of the marker