ITP: Chapter 1
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Science or study
Logos
Mind of soul
Psyche
Study of the mind and the scientific study of behavior
Psychology
any response or reaction to a stimulus.
Behavior
Natural/Instincts
Innate
Learned
Acquired
Examples of these are tick disorders, beating of the heart, and breathing
Involuntary
Examples of these are coping mechanisms, decisions, and choices
Voluntary
A person is aware that they are doing certain things.
Conscious
A person is unaware of their actions and they’re completely oblivious that they’re transforming as another person
Unconscious
Basic structures or elements components of consciousness. This is also the first school of psychology and the major tool for this is Introspection.
Structuralism
He is the father of psychology
Wilhem Wundt
How the mind allows people to adapt, live, work, and play.
Functionalism
It is holism. This also means “good figure” and it focuses on sensation and perception
Gestalt psychology
This focuses on the unconscious and this theory was based on the work of Sigmund Freud
Psychoanalysis
This focuses on observable behavior only. It is the basic data of scientific psychology.
Behaviorism
It focuses on the development of a sense of self and the discovery of other motivations behind a person’s behavior than sexual motivations
Psychodynamic Perspective
Enumerate the psychologists who shared theories about the psychodynamic perspective
Sigmund Freud
Carl Jung
Alfred Adler
Erik Erikson
Karen Horney
Examines how we understand and think about the world
Cognitive Perspective
It looks at man as a rational being endowed with intellect and will.
Phenomenological Perspective
An extensive network of specialized cells that carry information to and from all parts of the body.
Nervous System
The nervous system is made up of two types of cells. Enumerate these two.
Neurons and Glial cells
Information processors that connect and transmit messages in the nervous system. Basic cells and building blocks of the nervous system.
Neurons
Provides scaffolding on which the nervous system is built and they support the neurons. This also support the neurons.
Glial Cells
A neuron outer surface is made up of?
Semipermeable membrane
These are branch-like structures that receive messages from other neurons
Dendrites
This is the cell body of the neuron. Responsible for maintaining the life of the cell
Soma
This is a long, tube-like structure that carries the neural message to other calls
Axon
A white fatty coating on axon; coats and insulates axon and makes messages flow down axon quicker and more efficiently
Myelin/Myelin Sheath
These are positive or negative charged particles in the fluids that bathe the neuron inside and out. This also generates an electrical charge which sends messages down the axon
Ions
This is the name for the electrical charge generated by the ions which sends messages down the axon
Action Potential
The electrical charge that travels down the axon
Depolarization
The state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse
Resting Potential
These are sack-like structures found at the terminal buttons which are at the end of the axon and they contain chemicals
Synaptic-vesicles
Chemical found in the synaptic vesicles which, when released, has an effect on the next cell
Neurotransmitter
(NEUROTRANSMITTER) Involved in every move because it transmits messages relating to our skeletal muscles. Involved in memory and may lead to Alzheimer’s
ACETYLCHOLINE (Ach)
(NEUROTRANSMITTER) Plays a role in memory
GLUTAMATE
(NEUROTRANSMITTER) Found in brain & spinal cord. Moderates behaviors (eating to aggression)
GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID (GABA)
(NEUROTRANSMITTER)Movement, attention, and learning. Drugs with significant dopamine release are found effective in physical and mental ailments like Parkinsons’s
DOPAMINE
(NEUROTRANSMITTER) Associated with the regulation of sleep, eating, mood, and pain. Has a movement with alcoholism, depression suicide, impulsivity, aggression, and coping with stress
SEROTONIN
(NEUROTRANSMITTER) Similar in structures to painkilling drugs such as morphine. Release of the reflects the brain’s effort to deal with pain and elevate mood. Might also explain the phenomenon of placebos.
ENDORPHINS
The action potential causes synaptic vesicles to release the neurotransmitters into the synapse
Neuron Communication
Sites on the dendrites which receive neurotransmitter. The neurotransmitter fits into the receptor sites like a key into a lock
Receptors
Neurons are also called?
Nerve Cells
Complex neural network carrying information throughout the body
Nervous System
This consist of the brain and spinal cord
Central Nervous System
The primary means of transmitting messages between brain & body. This also has the memory for pain.
Spinal Cord
This consists of the neurons with long axons and dendrites
Peripheral Nervous System
Records the electrical activity of the brain
ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM (EEG)
Biochemical activity within the brain
POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY (PET) SCAN
Detailed, 3D image of the brain. Functioning of the brain
FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (fMRI)
Causes momentary interruption of neural activity
TRANSERANIAL MAGNETIC STIMULATION (TMS)
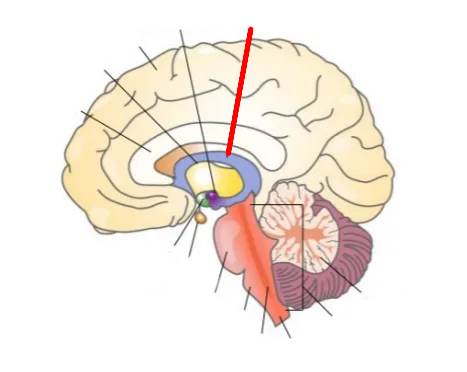
What part of the brain is this?
Hippocampus
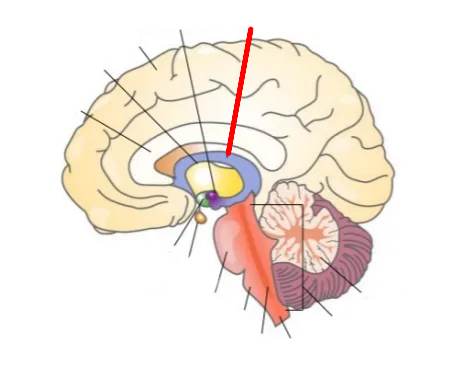
What part of the brain is this?
Hypothalamus
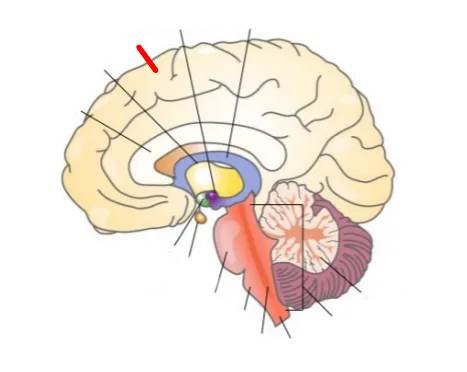
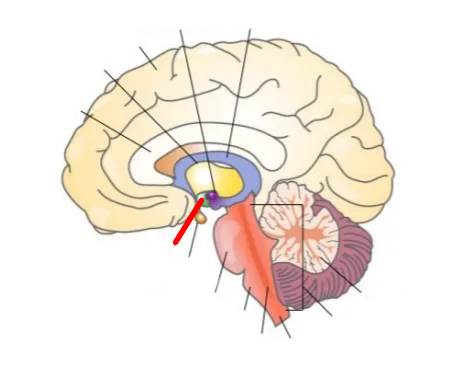
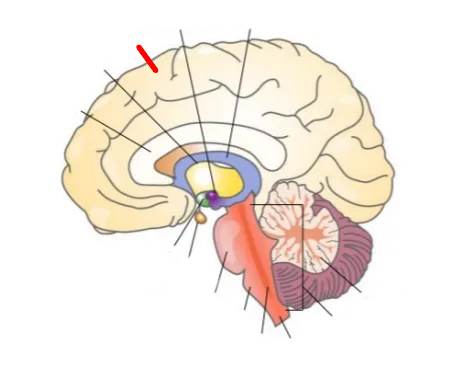
What part of the brain is this?
Cerebrum
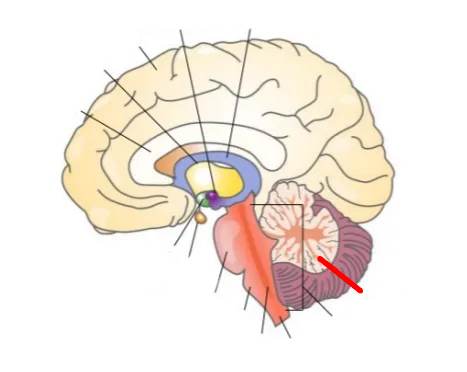
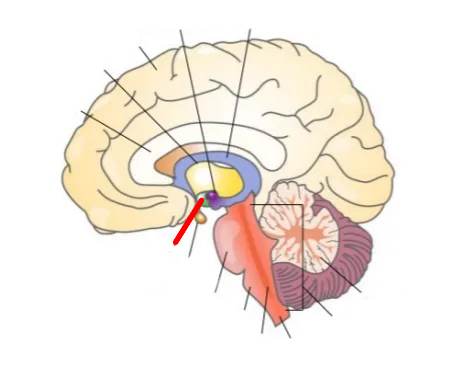
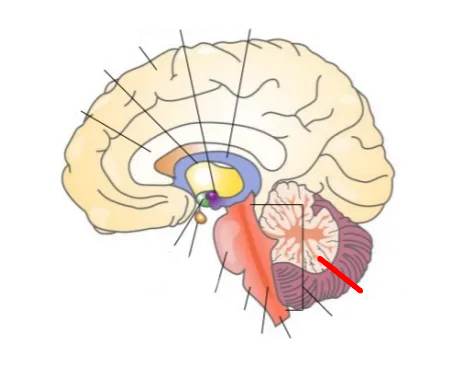
What part of the brain is this?
Cerebellum
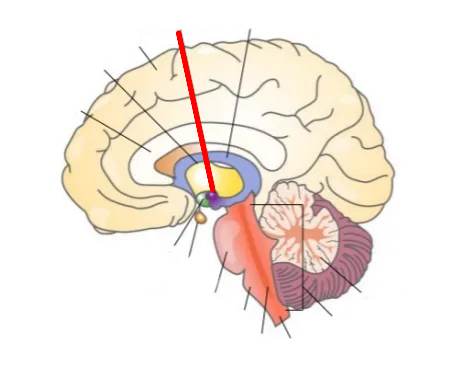
What part of the brain is this?
Amygdala
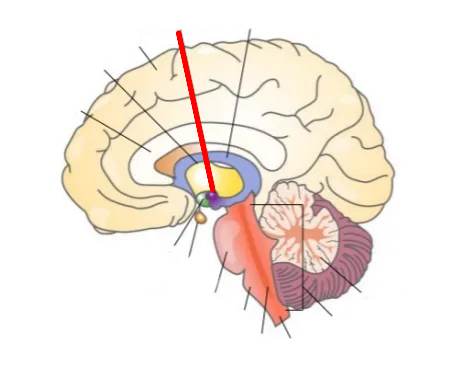
What part of the brain is this?
Medulla
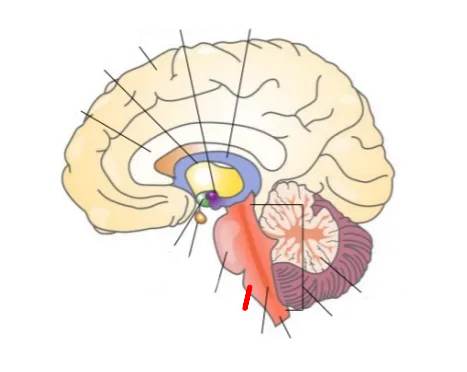
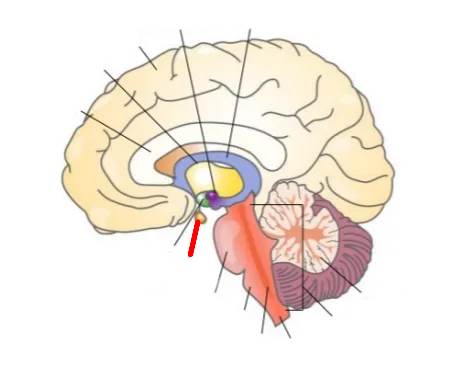
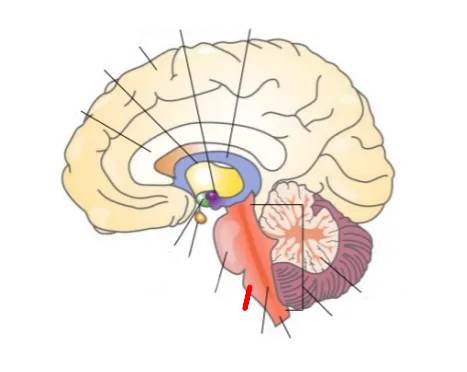
What part of the brain is this?
Pituitary glands
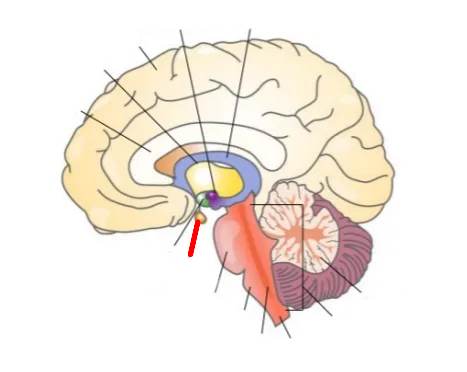
What part of the brain is this?
Spinal Cord
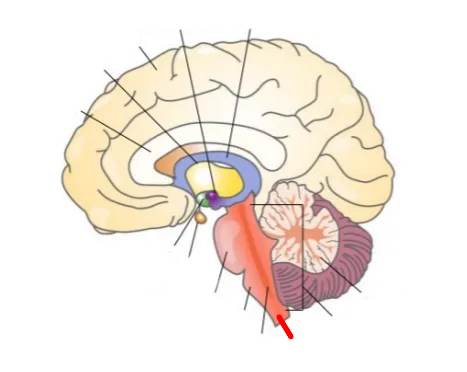
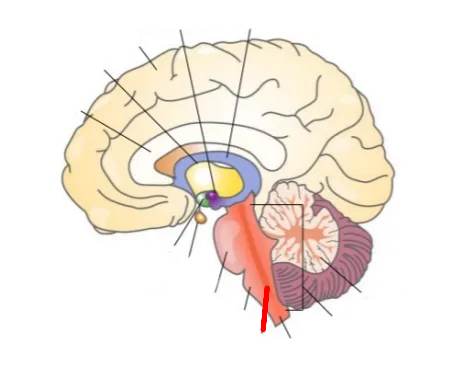
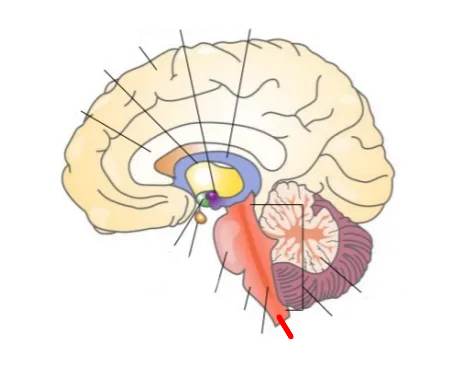
What part of the brain is this?
Reticular formation
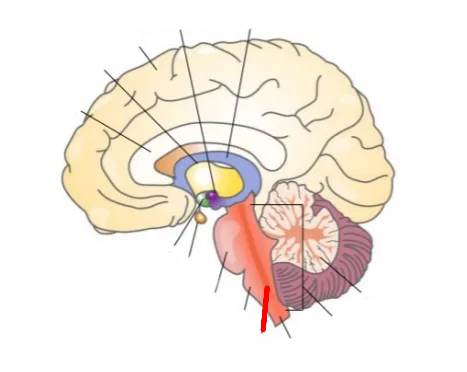
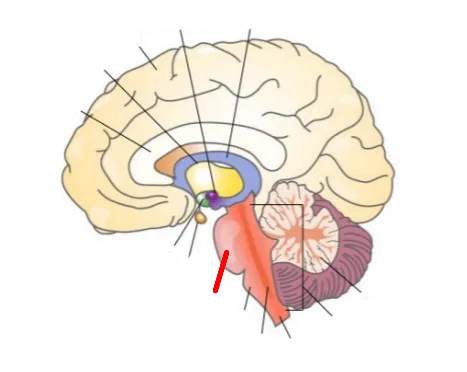
What part of the brain is this?
Pons
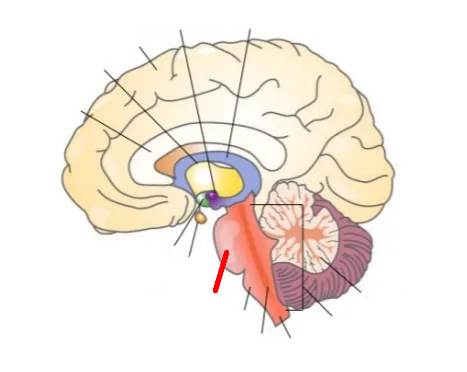
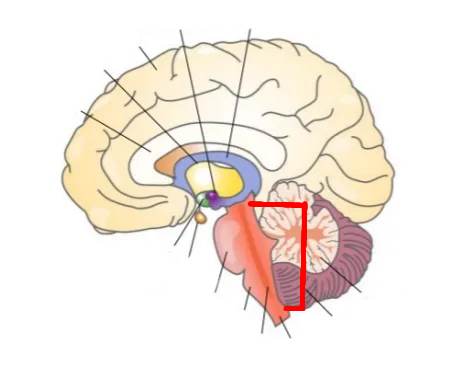
What part of the brain is this?
Brain Stem
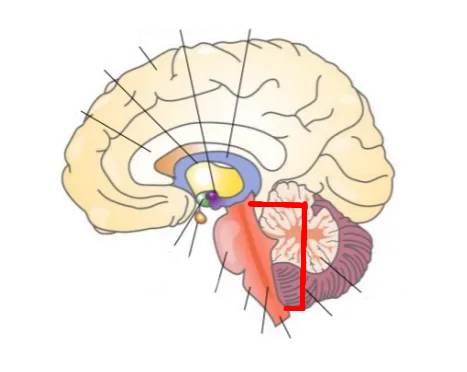
What part of the brain is this?
Corpus callosum
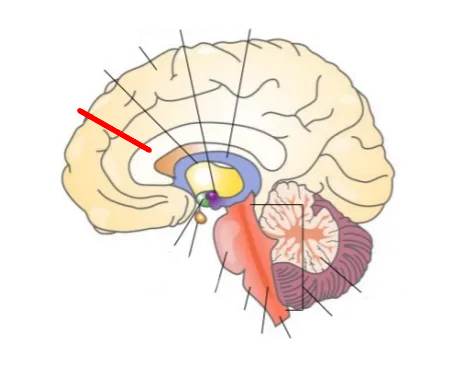
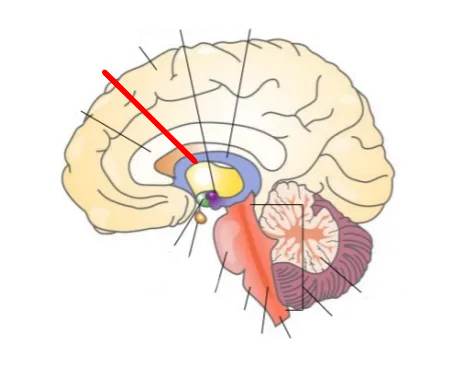
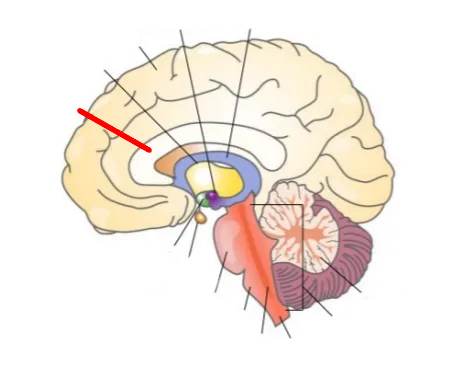
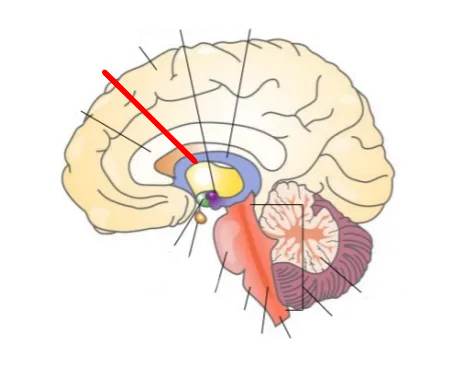
What part of the brain is this?
Thalamus
The convoluted part of the brain. It is involved in sensing, thinking, learning, emotion, consciousness, and voluntary movement
Cerebrum
This is responsible for sophisticated, uniquely human information processing
Cerebral cortex
(Lobes of the brain) body sensation
PARIETAL LOBE
(Lobes of the brain) vision
OCCIPITAL LOBE
(Lobes of the brain) hearing and advanced visual processing
TEMPORAL LOBE
(Lobes of the brain) cognition, recent memory, planning of movement, and some aspects of emotions
FRONTAL LOBE
The part of the cortex that is largely responsible for the body’s voluntary movement
MOTOR AREA
The site in the brain of the tissue that corresponds to each of the sense, with the degree of sensitivity related to the amount of tissue allocated to that senses
SENSORY AREA
One of the major regions of the cerebral cortex; the site of the higher mental processes such as thought, language, memory, and speech
ASSOCIATION AREA
Dominance of one hemisphere in specific functions
Lateralization
Bridge of fibers passing information between the two cerebral hemisphere
Corpus Callosum
It controls a variety of basic functions relating to emotion, learning, memory, pleasure, and self-preservation; includes the amygdala and hippocampus
Limbic System
relay center for incoming sensory information
Thalamus
Limbic system structure involved in emotion and aggression; emotional processing
Amygdala
limbic system structure involved in learning and memory; memory processing
Hippocampus
regulates basic biological needs: hunger, thirst, temperature control; master clock.
Hypothalamus
The main role of the hypothalamus is to keep the body in this current state
Homeostasis
Pituitary Gland
“master” gland that regulates other endocrine glands center of human sexuality and reproduction
Connects all parts of the CNS: Cerebral Cortex, Cerebrum, and Spinal Cord. It sends information to and receive order from the brain.
Brain Stem
Integrates information from inner ear (sense of balance); involved in sleep and dreaming; facial sensitivity
Pons
Regulates vital functions like breathing and circulation
Medulla
Group of fibers related to sleep and arousal through the brain stem
Reticular Formation
Coordinates fine muscle movements, balance. It is the Latin word for “little brain”
Cerebellum
Transmits info between brain and rest of the body; handles simple reflexes
Spinal Cord
Carries messages to the central Nervous system. Afferent
Sensory neurons
Carries messages from the central Nervous system. Efferent
Motor neurons
The division for the fight or flight response. It prepares the body for action in stressful situations.
Sympathetic Division
It maintains the normal function and restores the body’s state. It calms the body after the stressful situation ended.
Parasympathetic Division
It is the chemical communication network; sends messages throughout the body via hormones in the bloodstream.
The Endocrine system
regulate the functioning or growth of the body
Hormones
secretes hormones that control growth and other parts of the endocrine system
Pituitary Gland (master gland)
This controls the pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
Regulates growth, water and salt metabolism. Controls thyroid, ovaries, testes, pancreas, and adrenal cortex.
Pituitary gland
Small, pinecone shaped gland. Secretes hormone metabolism, directed by light. Helps your body know when it’s time to sleep/circadian rhythm
Pineal Gland
Located at the neck. Regulates metabolism through secretion of hormones (thyroxin)
Thyroid