Central Nervous System & Neurophysiology
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Last updated 1:10 AM on 2/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
the central nervous system’s main parts are
the brain and the spinal cord
2
New cards
what are the two anatomic sections of the nervous system?
the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system
3
New cards
the two types of nerves in the peripheral nervous system are..
afferent and efferent
4
New cards
the peripheral nervous system has _ cranial nerves
12
5
New cards
the peripheral nervous system has _ spinal nerves
31
6
New cards
afferent neurons are..
sensory neurons that transmit impulses from external/internal to the central nervous system
7
New cards
efferent neurons are..
motor neurons carry impulses from the central nervous system to muscle cells
8
New cards
examples of efferent neurons are..
smooth, cardiac, and some skeletal muscles
9
New cards
interneurons neurons are…
association, relay/local circuit neurons that are found in neural pathways in the central nervous system
10
New cards
interneurons neurons are what kind of neuron? .
connect sensory and motor neurons
11
New cards
the two subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system are...
somatic division and the autonomic division
12
New cards
the somatic division is the…
voluntary movement of skeletal muscles
13
New cards
the autonomic division is the…
involuntary movement of smooth muscles (organs) and glands (endocrine)
14
New cards
the three subdivisions within the autonomic divisions are…
the sympathetic system, parasympathetic system, and the enteric system
15
New cards
the sympathetic nervous system is..
the system that stimulates the body’s response to stress, fight or flight
16
New cards
the parasympathetic nervous system is…
the system that controls the homeostasis of the system, rest and digest, feed, reproduction
17
New cards
neuroglia cells are..
cells classified as support cells for neurons, they hold neurons together and sustain regeneration post-birth.
18
New cards
neurons are..
cells also known as nerve cells and are specialized cells with the ability of transmitting messages
19
New cards
regeneration happens where?
within the PNS
20
New cards
can regeneration take place in the CNS?
no
21
New cards
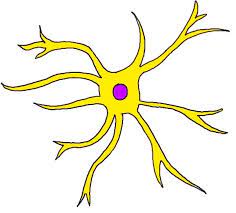
Astrocytes are..
star-shaped cells that brace neurons that form a barrier between capillaries and neurons, and control the chemical environment of the CNS
22
New cards
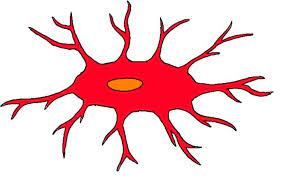
microglia are…
spider-like phagocytes that dispose of waste and debris
23
New cards
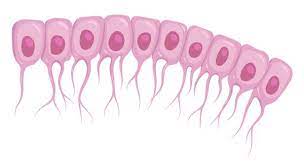
ependymal are…
tissue that line cavities of the brain and spinal cord and circulate cerebrospinal fluid
24
New cards
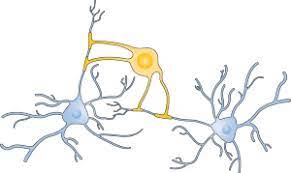
oligodendrocytes are..
cells that produce myelin sheath around the nerve fibers in the central nervous system. only in the CNS
25
New cards
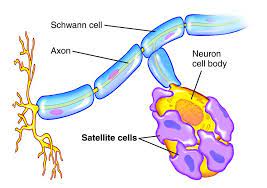
satellite cells are..
cells that sit outside or on top of the cell line are rather calm and do not move much. they are capable of differentiation to repair neurons and involve efferent nerves within the PNS
26
New cards
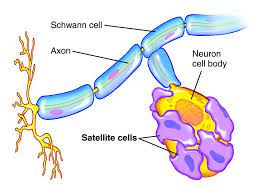
Schwann cells
form the myelin sheath in the PNS
27
New cards
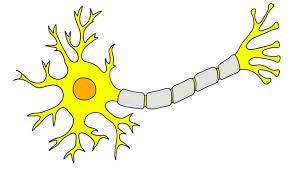
what are the four primary segments of neurons?
soma, axon, dendrites, and the axon terminal
28
New cards
the soma is…
a cell body that contains a single, large nucleus and all the organelles of a typical cell
29
New cards
the axon is…
a long slender extension of the neurons that conduct electrical across the neuron
30
New cards
what are the three aspects of the axon?
the axon hillock, myelin sheath, and the nodes of Ranvier
31
New cards
the axon hillock is..
a conical mound of cytoplasm that gives rise to an axon
32
New cards
the myelin sheath is the..
sheath of fatty acids ( plasma membrane) that serves as an electrical insulator
33
New cards
the nodes of ranvier are..
gaps on the axon that allows the exchange of ions for regeneration of the action potential
34
New cards
dendrites are..
nerve processes that transmit action potential toward the neuron cell body that receives chemical signals from adjacent neurons
35
New cards
the axon terminal is..
the nerve processes that transmit the action potential away from the neuron cell body, they signal to adjacent neurons and to the target tissue and terminates at the synapsis
36
New cards
pre-synapses is..
synapses at the neuron transmitting electrical impulses
37
New cards
post-synapses is..
synapses at the neuron/effector tissue receiving the electrical impulse, through the dendrite of adjacent neuron and the target tissue
38
New cards
synaptic vesicles are..
vesicles containing neurotransmitters, and releases when it reaches the membrane
39
New cards
the synaptic cleft is..
the gap between pre and post-synapse/ effector tissue
40
New cards
the three general morphologies of neurons are
unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar neurons
41
New cards
unipolar neurons are..
single short process emanating from the cell body and are rare, being in the vertebrate nervous system
42
New cards
bipolar neurons are..
two processes extending from the cell body and are common in vestibular cochlear, and olfactory pathways. such as the ear, eye, and nose, and are fast so it doesn’t have a myelin sheath
43
New cards
multipolar neurons are..
two or more processes and are the most abundant type of neuron. it is a motor neuron within the ventral horn of the spinal column and contains a large soma with a sizable receptive dendrite tree
44
New cards
projection neurons are..
connection with relatively distance structures
45
New cards
interneurons are..
restricted projection with only local influence on neurons within the same structure
46
New cards
depolarize =
excitatory, mostly motor neurons
47
New cards
hyper-polarize =
inhibitory, GI tract, smooth muscle contractions
48
New cards
What is the function of all neurons?
to transmit info to and from the CNS
49
New cards
The action potential is..
all communication that is a biochemical generate impulse
50
New cards
action potential can originate from the PNS to the CNS from..
afferent neurons to interneurons
51
New cards
action potential can originate from the CNS to the PNS from..
interneurons to efferent neurons
52
New cards
is a neuron a single cell?
yes it is a single cell
53
New cards
is a nerve a bundle of numerous neurons?
yes it is a bundle of numerous neurons
54
New cards
action potential is crated and transmitted through the..
neuron plasma membrane
55
New cards
the transmission of the action potential is regulated by..
ion concentration gradient (CG) between two environments
56
New cards
the concentration gradient is..
the difference in levels between the inside and outside of the cell
57
New cards
the regular state of a neuron CG is..
negative or at rest
58
New cards
negative CG =
resting membrane potential
59
New cards
Extracellular =
> Na+
60
New cards
Intracellular=
>K+
61
New cards
what chemicals are sending positive charges?
K and Na
62
New cards
what chemicals are sending negative charges?
Cl
63
New cards
the ion channel potential..
controls the rate of transportation of specific molecules
64
New cards
the two important ion channel types of the ion channel potential are the..
voltage-gated ion channels and the signal proteins
65
New cards
the voltage-gated ion channels are..
Na+,K+,Cl-
66
New cards
the signal proteins are…
Active transporters, (cellular energy, ATP) and Na+ , K+
They go against the concentration gradient
They go against the concentration gradient
67
New cards
the AP starts..
with the arrival of a signal (neurotransmitters) to the dendrites to the neuron
68
New cards
Biochemical signals are known as..
neurotransmitters
69
New cards
Physical signals are known as
specialized or stretch receptors such as pressure or pain
70
New cards
the signal of AP is transmitted form one neuron or the next with
biochemical or physical signals
71
New cards
the order of the signal transmitted from neurons is…
Afferent→Interneuron, Interneuron→Efferent, or Afferent→Efferent
72
New cards
the signal of the AP is transmitted via the..
synaptic cleft
73
New cards
Signal protein receptors..
restarts the action potential
74
New cards
What is the resting membrane potential?
its how much potential there is for a change
75
New cards
voltage-gated ion channels regulate what?
membrane potential
76
New cards
what is the resting voltage?
\-70 mV
77
New cards
what is the threshold state?
\-55mV
78
New cards
what is the action state?
\-45mV
79
New cards
to create an action potential there must be…
a stimulus transmitted to the dendrites
80
New cards
a weak signal is..
a failed initiation
81
New cards
post-synapsis receives stimulus or a biochemical signal to activate..
signal protein channels
82
New cards
steps of action potential
1. post-synapsis receives signal
2. soma integrates signal
3. the axon transmits action potential
4. AP spreads across the axon terminal
5. AP is transferred to the target tissue or the next neuron
83
New cards
afferent nerves are..
sensory nerves, send nerve impulses form the body to the CNS
84
New cards
efferent nerves are..
motor nerves, send nerve impulses to effector tissue
85
New cards
what are the two divisions of the peripheral nervous system?
somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS)
86
New cards
the somatic nervous system is also known as..
the SNS
87
New cards
the somatic nervous system is..
straight forward, regulates the voluntary contraction of skeletal muscles
88
New cards
the autonomic nervous system is also known as..
the ANS
89
New cards
the autonomic nervous system is..
complex, it regulates the involuntary control of smooth, cardiac muscles and glands Ex: fight or flight, and homeostasis
90
New cards
the two main ideas of the ANS are..
fight or flight and homeostasis
91
New cards
what system does the ANS work with?
the endocrine system
92
New cards
what is the endocrine system fuction?
hormones
93
New cards
the ANS is comprised of central control of the CNS and receives feed back from what?
Sensory receptors, peripheral effectors and reflex conduction pathways
94
New cards
The ANS controls what?
the circulation of blood, activity of the GI tract and regulation of the body temperature.
95
New cards
does the ANS work with voluntary or involuntary muscles?
involuntary muscles (smooth muscles, heart, glands)
96
New cards
what are the two nerve fibers within the ANS?
preganglionic and postganglionic
97
New cards
what is a preganglionic fiber pathway?
its the first fiber pathway that originates within the CNS
98
New cards
what is the postganglionic fiber pathway?
it is the second fiber pathway that originates in the ganglia outside the CNS
99
New cards
what are ganglia?
they are massive nerve tissue
100
New cards
what are the 3 branches of the ANS?
Sympathetic, parasympathetic and enteric