KIN 216 - Angular Kinetics
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
quiz 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
what is the center of gravity?
the point around which a systems weight is equally distributed in all directions
what can the center of gravity also be referred to as?
the center of mass
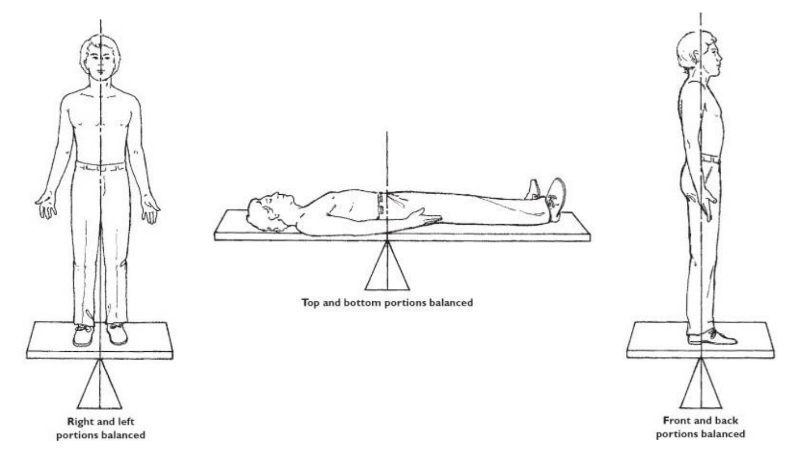
what is the point around which the masses are balanced?
center of gravity; same amount of forces above/below, side/side, front/back
what does the position of the center of gravity determine?
how the body responds to external forces (ie. control)
where is the location of the center of (gravity) mass?
not a fixed position
can be outside of the body
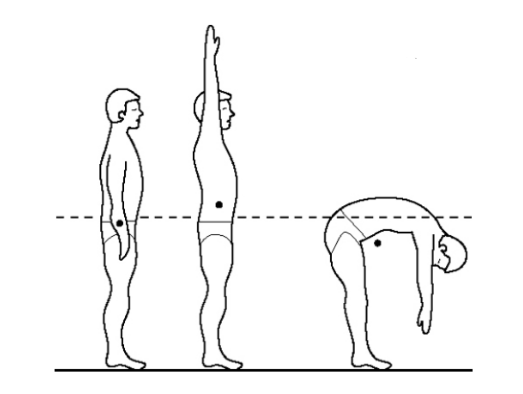
how can we locate the position of the center of gravity?
a simple balance procedure using a wooden board where weight is equally distributed in all directions
what is it called and movement is produced when a force acts directly at the center of gravity?
center force: translation only - rectilinear motion
what is it called and movement is produced when a force acts away from the center of gravity?
off-center force: some translation and rotation - curvilinear motion
what is it called and movement is produced when two forces that are in equal magnitude but opposite in direction, act equidistant from the center of gravity?
a couple: only rotation - pure moment
a couple: two eccentric forces that cause rotation ONLY
eccentric force is a force that is applied to an object but does not pass through its center of gravity
a pure moment: a purely rotational force without any linear translation
any eccentric force will cause rotation, but how does a force (linear) create rotation (angular)?
a force applied away from the anchor point; this offset from the center creates a turning effect called a torque
the system must be anchored at a point: axis of rotation, fulcrum, or pivot point
what is tourque?
a force that MAY produce rotation because it acts at a point away from the axis of rotation, causing rotational movement.
a force that has a tendency to rotate an object about an axis
can be thought of as a twist to an object
the following are all other names for what?: rotational force, moment of force, or moment (moment means dealing with rotation)
torque!
what three things determine if a force has an angular effect (if it actually produces rotation)?
magnitude
the point if application
direction (the angle of force)
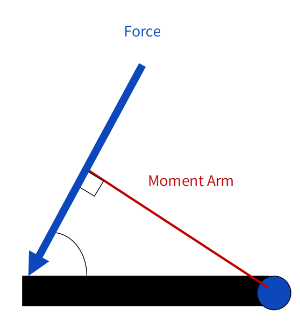
what is the equation for torque?
T = F x moment arm
(Nm)
what is the moment arm?
the perpendicular distance between the line of action of the force and the axis of rotation
if applying a force to a wrench produces rotation, where should you grasp the wrench?
farther away - the longer the moment arm - the more torque - the easier it is to move
if you grasp closer to the head of the wrench then its harder to move
why do squash players frequently slide their hand up and down the racket depending on the shot they want to play?
amplifies the effect of force
sliding hand up decreases power but increases control
sliding hand down increases power but sacrifices control
why do physical therapists use manual resistance (torque) to assess injuries?
to asses strength and pain free range of motion
what is a lever?
a relatively rigid object that may be made to rotate about an axis by the application of a force
what do levers magnify?
the effect of a muscle
what are the three kinds of levers? what are they classified by
first class, second class, and third class
classified by the relative positions of forces to the axis of rotation
what does EACH lever consist of?
the rigid body
the fulcrum
the effort
the resistance
in levers, what is the rigid body?
the system being moved
in a lever, what is the fulcrum?
the axis of rotation or pivot point
in a lever, what is the effort?
the input force or the applied force
in a lever, what is the resistance?
the output force
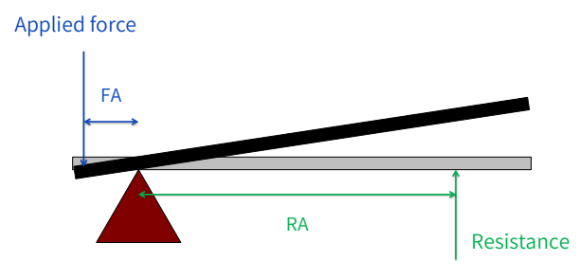
the effectiveness of the lever is determined by what… ?
the mechanical advantage
what is the mechanical advantage?
the ratio of the output force to the input force
MA = effort/load
measured by the distances between the forces to the axis of rotation
a force can balance a larger resistance when the force arm is ______ than the resistance arm?
larger

what is the relationship between the length of the force arm and the mechanical advantage?
the bigger the force arm the greater mechanical advantage
the smaller the force arm the less mechanical advantage
as mechanical advantage increases the lever amplifies _____ but sacrifices _____?
strength, speed
a force can move a resistance through a large range of motion when the force arm is ______ than the resistance arm
shorter
as mechanical advantage decreases the lever amplifies _____ and _____, but sacrifices _____?
speed and range of motion, strength
what are the characteristics of a first class lever?
fulcrum is in the middle (pivot point)
mechanical advantage may be greater or less than 1
ex. scissors, see-saw, head
what is unique about the first class lever?
the only lever that could either magnify strength or movement kinematics
mechanical advantage may be greater or less than 1
what are the characteristics of a second class lever?
the resistance is in the middle
mechanical advantage is always greater than 1; amplifies strength
ex. wheelbarrow: allows you to use less effort to move a heavy load a longer distance
what are the characteristics of a third class lever?
the effort is in the middle
mechanical advantage is always less than 1: amplifies movement kinematics
ex. stapler, ligaments, an arms flexor muscles attach 2-3 cm below the elbow joint leaving the a long resistance arm for speed and range of motion
where do we see third class levers in the day to day life (real-world application)?
muscles generate forces which act over a distance to move the body
the majority of musculoskeletal systems are third class levers — even the ones that arent third class have a mechanical advantage close to 1
the arrangements of the musculoskeletal tissues amplify the _____ and _____ generated by the muscular effort.
speed and range of motion
the turning effect created by a force is a moment of force, also known as ______
torque
is torque vector or scalar?
vector; its direction is defined by the angular movement created (clockwise or counterclockwise)
what is newtons first law?
the law of inertia
what is the law of inertia?
every object has the desire to maintain in a static state.
what does the law of inertia look like for linear motion?
every object persists in its state of being at rest or in uniform motion straight forward, unless it is acted upon by an external force
what does the law of inertia look like for angular motion?
every object persists in its state of rest or rotating uniformly, unless acted upon by an external torque
what is a moment of inertia?
the name given to rotational inertia; the resistance of any physical object to any change in its angular state of motion
moment of inertia (I) = mass x (radius of gyration)²
I = mk²
what is the radius of gyration?
the linear distance (meters) between the axis of rotation to a point where the body mass is concentrated
the moment of inertia is specific to what?
a chosen axis of rotation
what examines how the amount of resistance to change relative to one of the principal axes of the body
the principal moment of inertia; how difficult it is to move the body in a particular direction
in order to move, what must we overcome?
inertia
the rotational inertia is dependant upon what?
the distribution of body masses… while mass is a fixed concept, we can manipulate the radius of gyration to alter the moment of inertia
what is angular momentum?
the quantity of motion for a rotating object
angular momentum (H) = moment of inertia x angular velocity
why is it that the angular momentum in one instance be the same and the angular momentum in another instance? what is this called?
conservation of angular momentum
(H1 = H2) because according to newtons first law, every object should remain at a constant rotational state unless acted upon by an external torque
what is the tradofff in conservation of angular momentum?
tradeoff between moment of inertia and angular velocity
H is constant and m is constant so:
if k² increases than angular velocity must decrease
if k² decreases than angular velocity increases
why can a diver be an example of the conservation of momentum
mass remains the same
in the absense of torque the system remains in a constant rotational state
moving the arms can shift the axis of rotation, can make them speed up or down depending and the direction of the spin depends on which arm movesw
what is a compensatory movement?
asymmetrical movements where the initial movement is compensated for by another movement that keeps the bodys position stationary
ex. Initial: swinging the arm at the shoulder joint causes the body to rotate forward in a volleyball hit, thus, the player kicks the legs forward to cause the body to rotate backwards, a compensatory movement of counter-rotation, keeping the body stationary
why must momentum consider the entire system (Htotal = Htrunk + Harms + Hlegs)
because the moment of inertia is effected by both body and segment orientation
what is newtons second law?
the law of momentum and the law of acceleration
what is the law of momentum and the law of acceleration?
creating a change in the state of motion (dynamic motion)
what does the law of momentum look like for linear motion?
the rate of change of momentum of a body is proportional to the force causing it and the change takes place in the direction which the force acts
what does the law of momentum look like for angular motion?
the rate of change of angular momentum of a body is proportional to the tourque cuasing it and the change takes place in the direction in which the torque acts
what is a change in angular momentum produced by?
angular impulse
what is angular impulse
a change in angular momentum (H2-H1)
torque x time
(Nms)
what does the law of acceleration look like for linear motion?
a force applied to a body causes an acceleration of that body of a magnitude proportional to the force, in the direction of the force and inversly proportional to the bodys mass
what does the law of acceleration look like for angular motion
a torque applied to a body causes an angular acceleration of that body of a magnitude proportional to the torque, in the direction of the torque, and inversely proportional to the bodys moment of inertia
why is newtons second law referred to as the law of momentum and the law of acceleration?
if a change in velocity is acceleration than in the law of momentum takes into account the change in velocity over time. A change in velocity over time is the same thing as acceleration therefor equivalent to the law of acceleration
what is newtons third law?
the law of reaction
what is the law of reaction?
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
what does the law of reaction look like for linear motion?
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction of force
what does the law of reaction look like for angular motion?
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction of torque
how can a diver be an example of newtons third law?
the diver pushes down on the spring board - the force acts over a distance creating a rotational force - the reaction torque propels the diver up and into the air creating rotation equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
kinetics is the study of what?
the study of forces; the factors that cuase, change, and prevent motion
what is angular kinetics?
the study of torques
the angular momentum of the hurdlers trail leg must be countered by what?
the angular momentum of the arms and trunk
angular kinetics allows us to move through the air with… ?
control
through what point does the force of gravity act?
through the center of gravity
if the mass is shifted on one side where does the position of the center of gravity shift?
shifts towards the heavier end to balance the mass so that there is the same amount on each side
when an individual is standing upright, where is their center of gravity?
in the middle of the body
if an individual were to lean to one side, where does their position of gravity shift
shifts to the side where the weight is concentrated
what is the vertical position of the center of gravity influenced by? what happpens if weight is added on top of an individual
the distribution of forces - if weight is added on top, the center of gravity will shift upwards towards the added force (heavier end)
why do football players bend down when they play?
with a lower of center of gravity they have more control over their body because the more they are able to withstand external forces
true or false? the position of the center of gravity can be found outside of your body?
true - depends on how your body’s position
what does the amount of movement in the center of gravity depend on?
the weight of the segments moved
the distance moved
what is equilibrium?
a physical state in which opposing forces equal out
the desire to be in control
what is balance?
an even distribution of weight enabling someone or something to remain upright and steady
static concept (motionless)
what is static equilibrium?
in control while not moving, the desire to be as still as possible, the attempt to hold a posture/position
a motionless state; there is no net influence acting on the system
what is stability?
the capacity of an object to return to equilibrium — or to its original position after it has been displaced
dynamic concept
what is dynamic equilibrium?
in control while moving
an attempt to regain control (ex. reflex arc)
a moving state; system is accelerating but in control over any external influence
what is an objects balance point?
the objects center of gravity
where all the external forces acting on it — or the moments of those forces sum to 0
in order for an object to be in balance (or in equilibrium) what must happen?
all the external forces acting on it — or the moments of those forces must sum to 0
how is stability affected by the position of the center of gravity? what is the relationships?
the position of the center of gravity; the base of support
as the base of support increases (area of contact), stability increases
what is a base of support?
the area bound by the outermost regions of contact between a body and a support surface
rank these bases of support in order from most to least stable
one foot
two feet apart
two feet close together
two feet apart
two feet close together
one foot
since stability is affected by position of a the center of gravity, what happens when it moves to the outer edges of the base of support?
stability decreases as it moves to either edge
what happens to stability as the center of mass moves up the system?
decreases
the greater the amount of torque its motion creates
how is stability affected by the mass of a system? what is the relationship?
the mass of a system
the resistance to change (inertia) is proportional to its mass
as mass increases, stability increases, force also increases which increases friction, a form of resistance, making you more stable
what things affect stability?
the object’s:
position of the center of gravity
mass
amount of friction present
base of support
how can humans control stability
by changing their stance and body position
a body in motion is considered to be in a state of ______ equilibrium, with all the acting forces resulting in equal and oppositely directed forces
dynamic
what is an individuals ability to control equilibrium called?
balance!