Endocrine system Lab exam
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
1
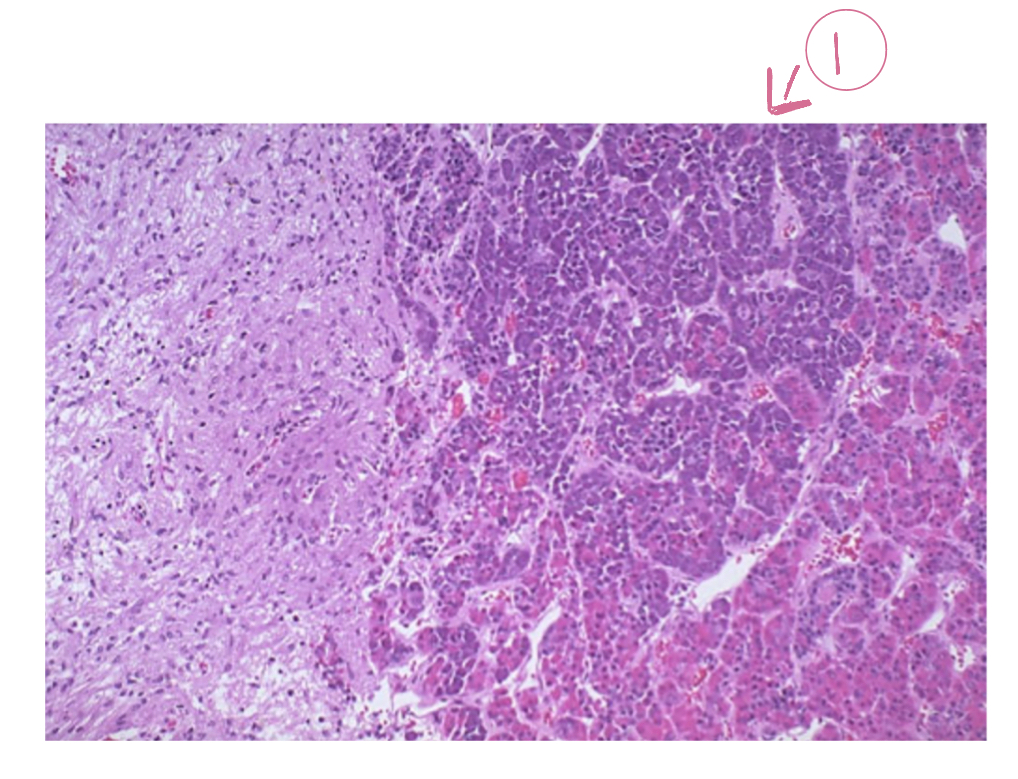
Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary)
What hormones are secreted by adenohypophysis?
TSH(thyrotropin), GH, ACTH (corticotrophin), FSH, LH (gonadotropins), prolactin
Tropic Hormones
Regulate other endocrine glands
TSH
Metabolism
GH
Growth and metabolism
ACTH
Stress hormone (cortisol)
FSH
Egg/sperm production
LH
Ovulation/testosterone
Prolactin
Milk production
2
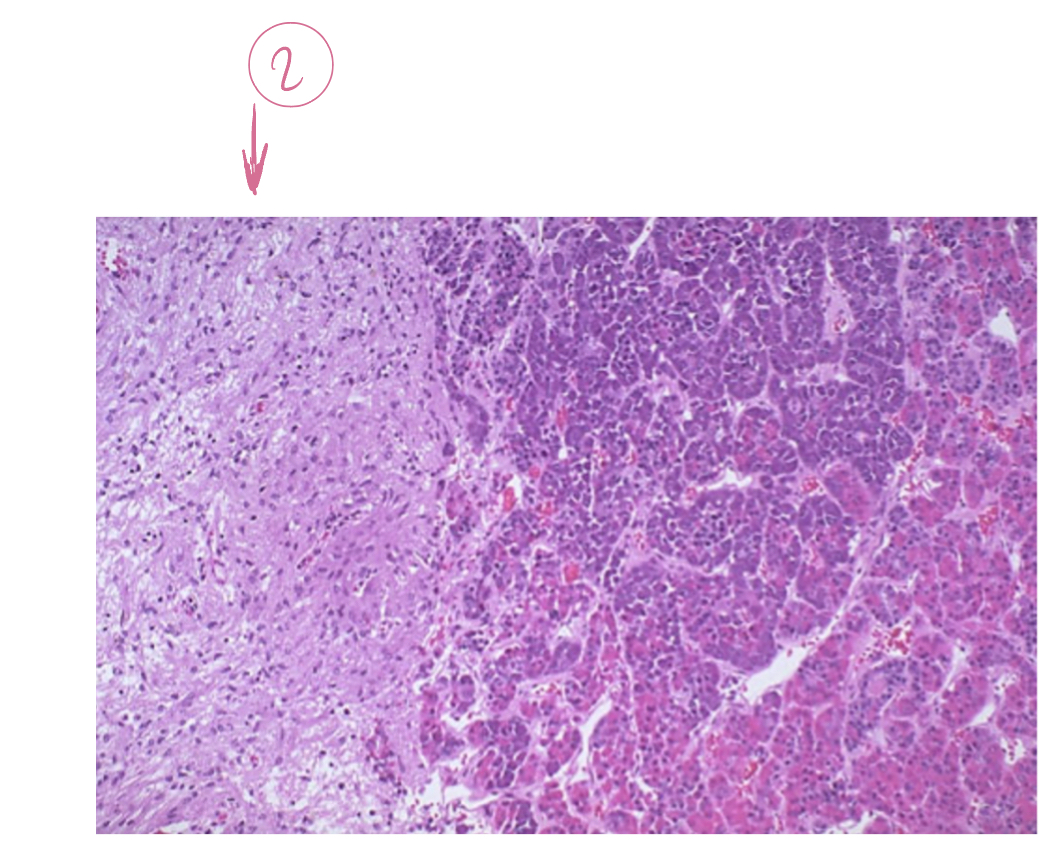
Neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary )
What hormone are stored and released in the neurohypophysis?
ADH, Oxytocin
Where are the hormones actually synthesized (neurohypophysis posterior pituitary)
In the hypothalamus, the posterior pituitary only releases and stores
What effect does oxytocin have on the body
Contraction for the uterus and mammary milk glands
What effect does ADH have on the body?
Decreases urine production, constrict arteries to raise blood pressure
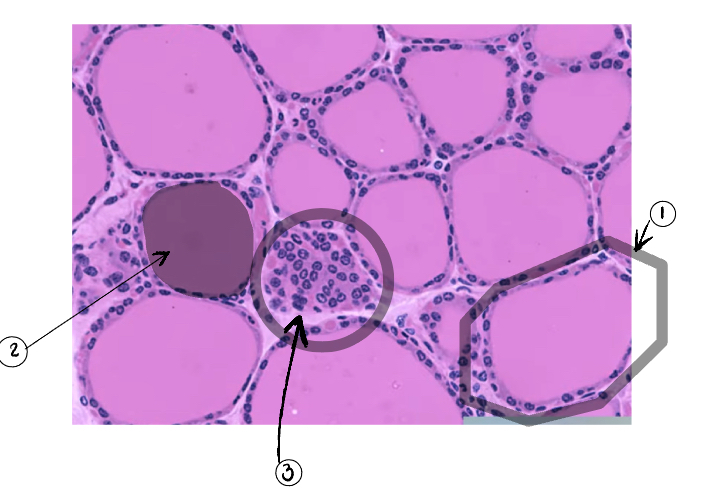
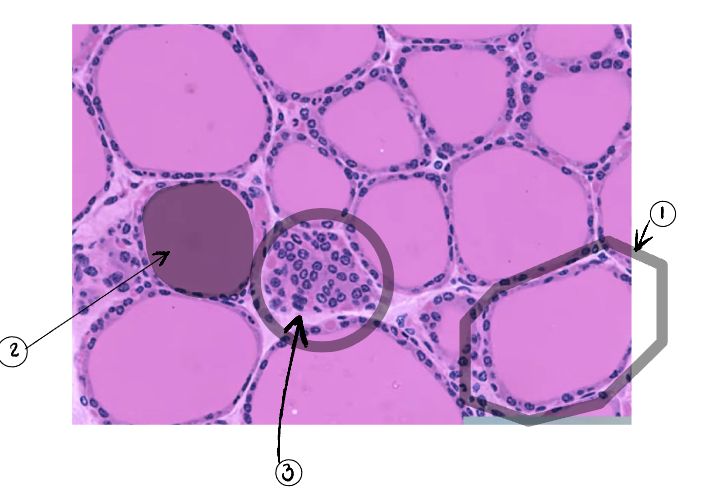
2
Parafollicular cell
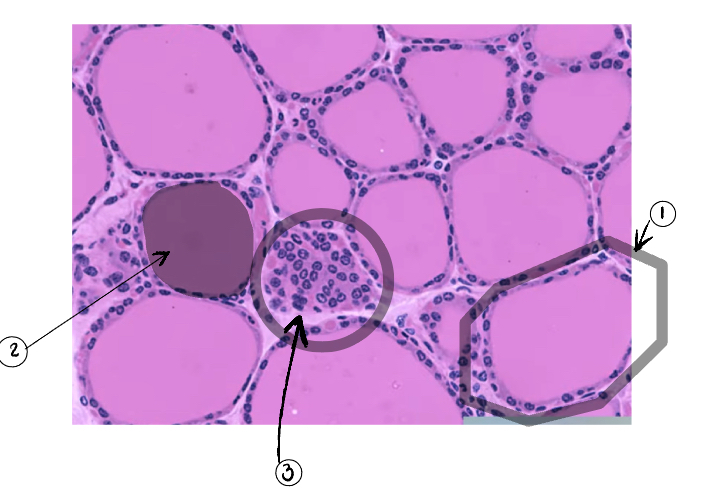
3
Thyroid gland
What do follicular cells secrete
T3 and T4
What is the function of T3 and T4
Metabolism energy levels growth and development and body temp
What is the colloid
substance found in thyroid follicles, storage site until the body needs them, thyroglobin
What do parafollicular cells secrete
Aka C cell but it secretes calcitonin
What is the function of parafollicular cell hormone calcitonin
Regulate calcitonin levels in the blood, inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts and promotes activity of osteoblasts
How is the secretory activity of the thyroid gland regulated
Releases thyroid stimulating hormones (TSH), this stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release t3 and T4
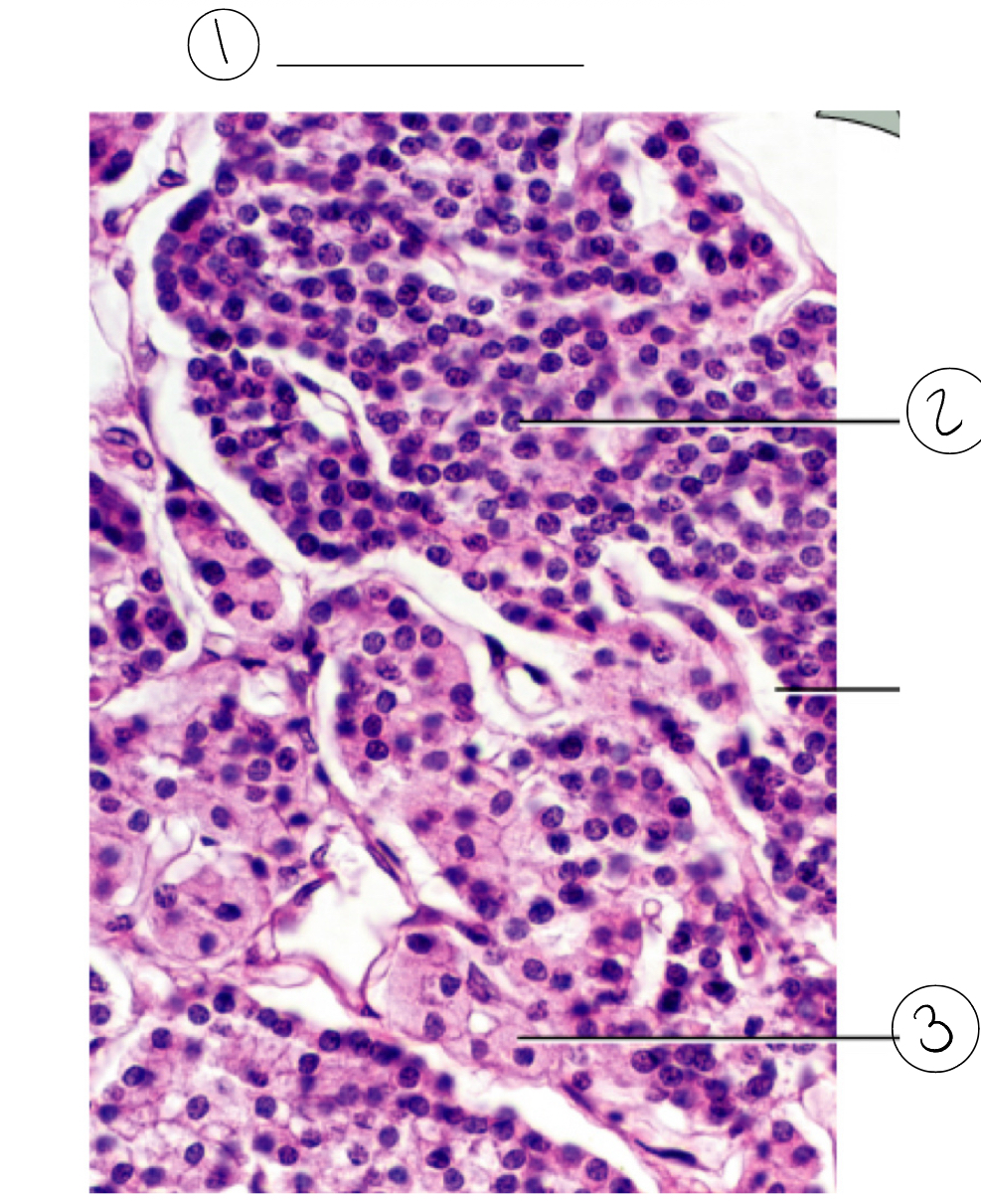
1
Parathyroid
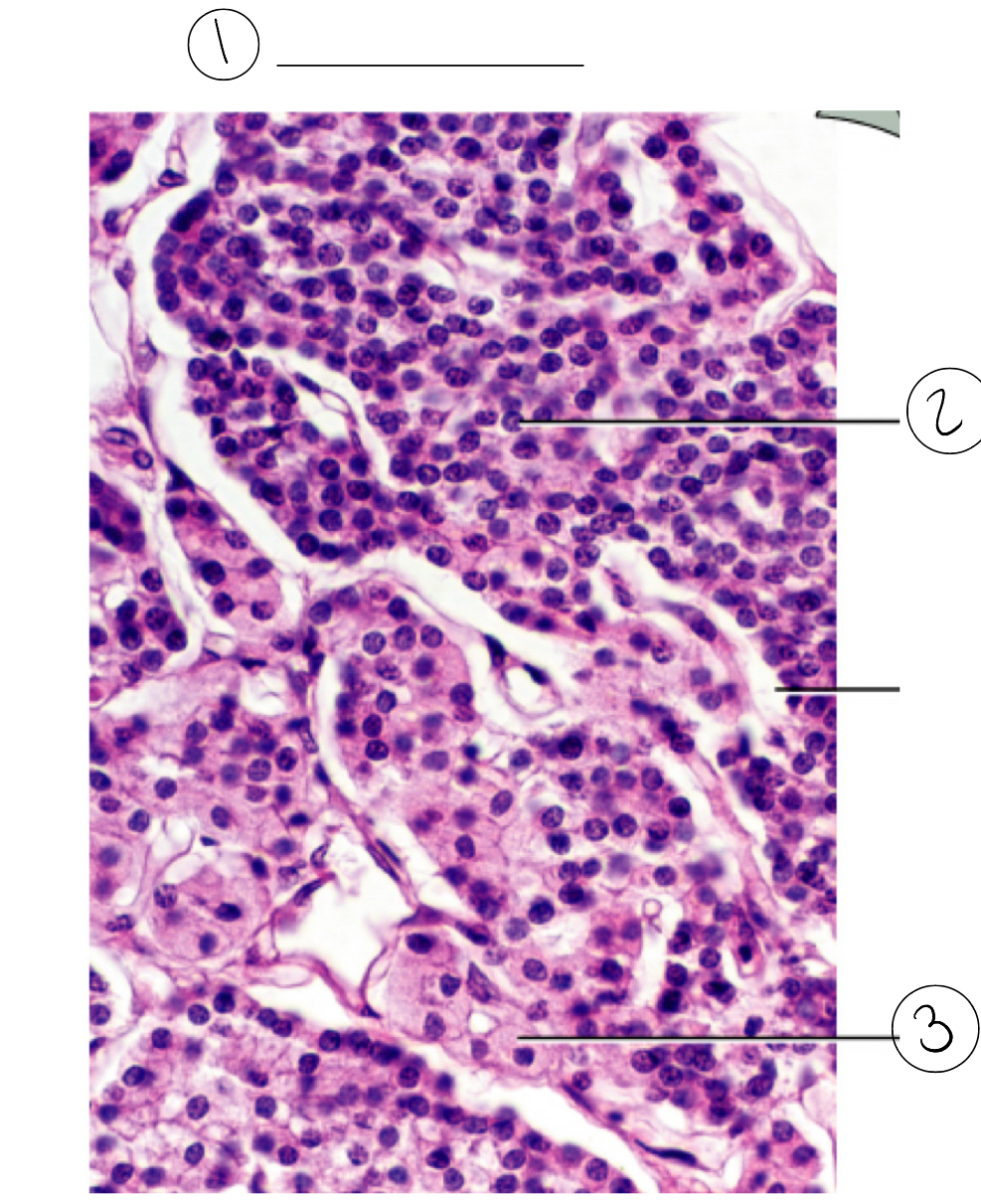
2
Chief cell
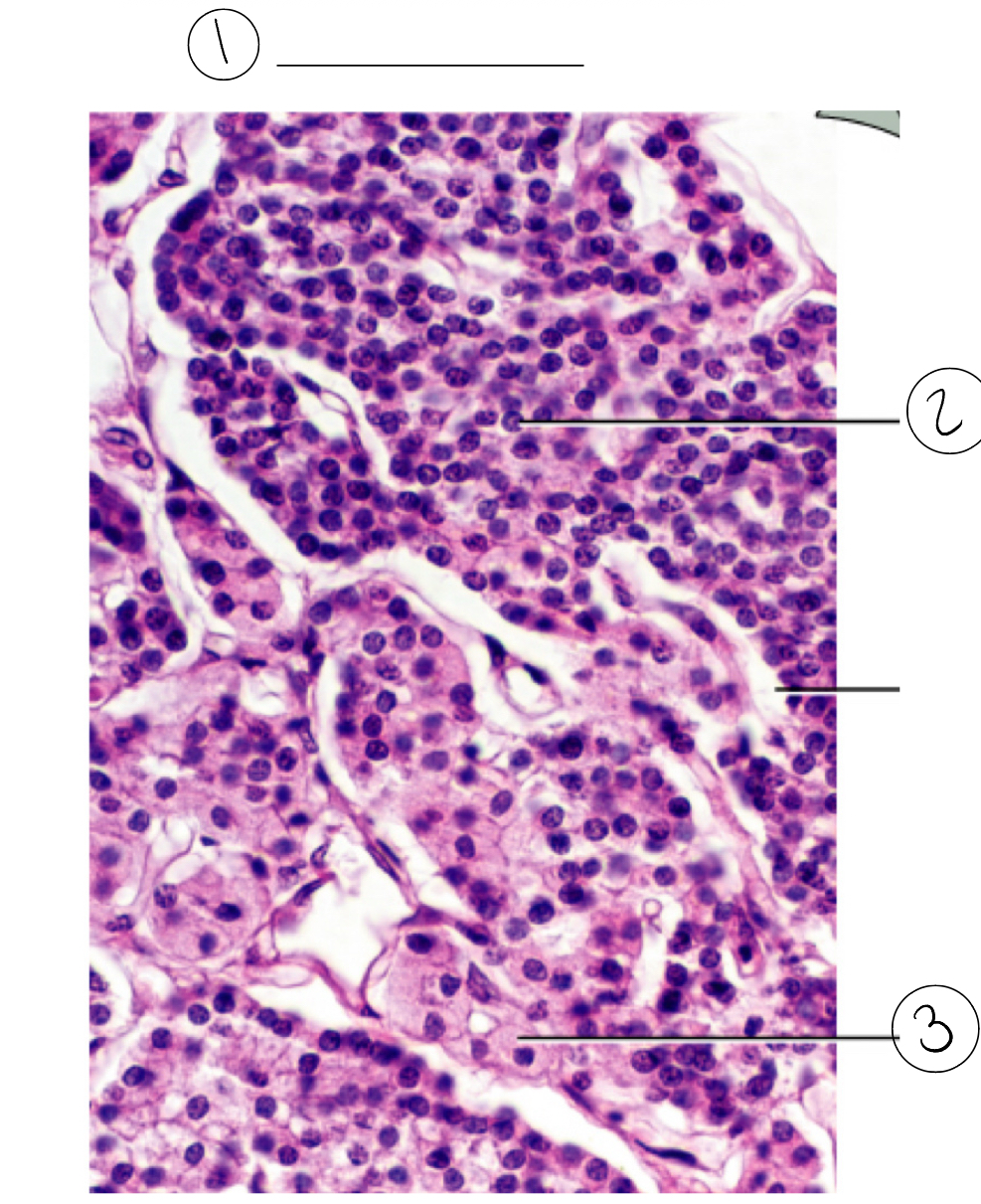
3
Oxyphil cells
What do chief cells secrete
Secrete PTH
What is the function of chief cell hormone: PTH
regulates calcium levels in the blood
How is the parathyroid gland regulated
By calcium levels in the blood, when blood calcium is low it releases more parathyroid hormone into the blood, feedback system
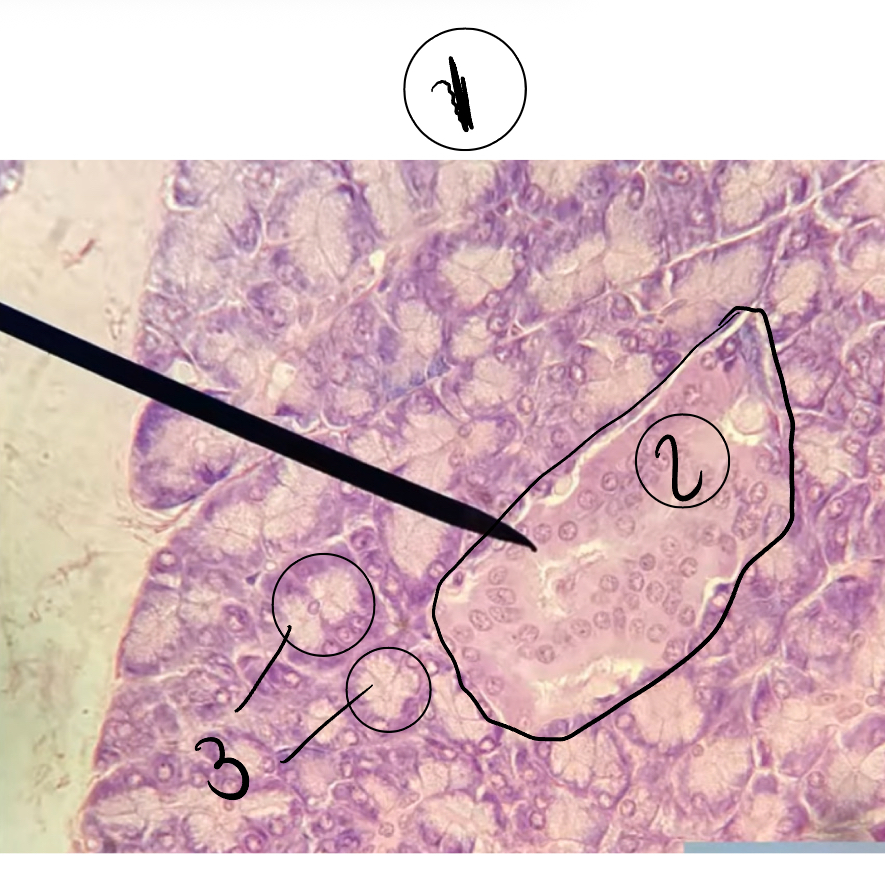
1
Pancreas
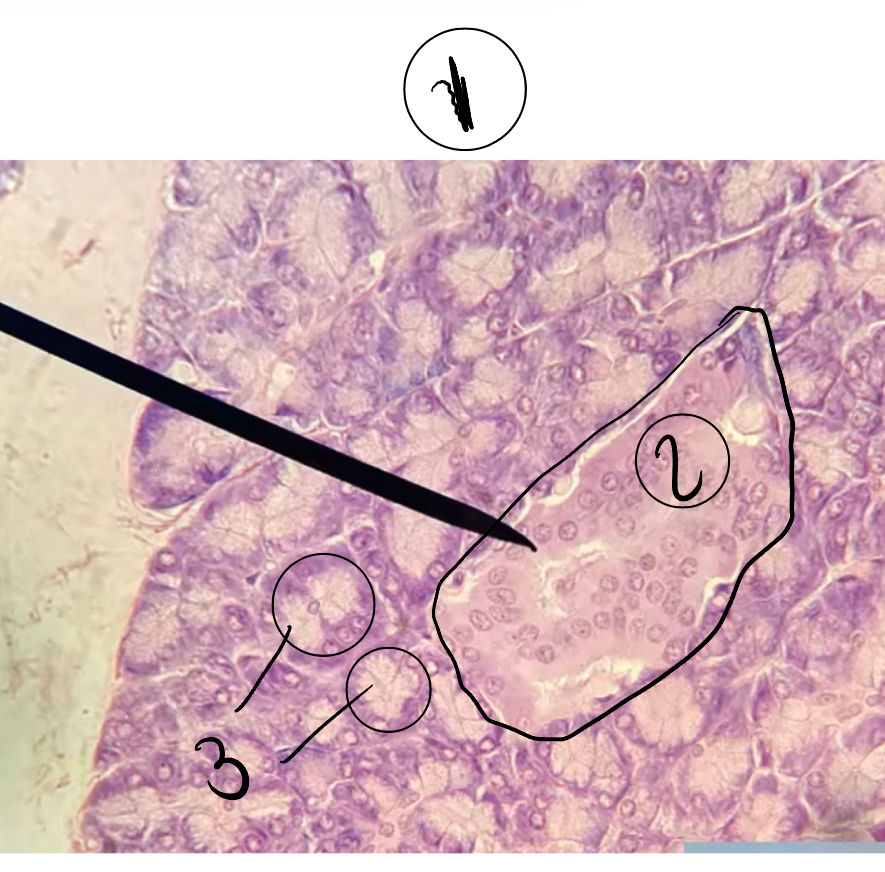
2
Langerhan islets
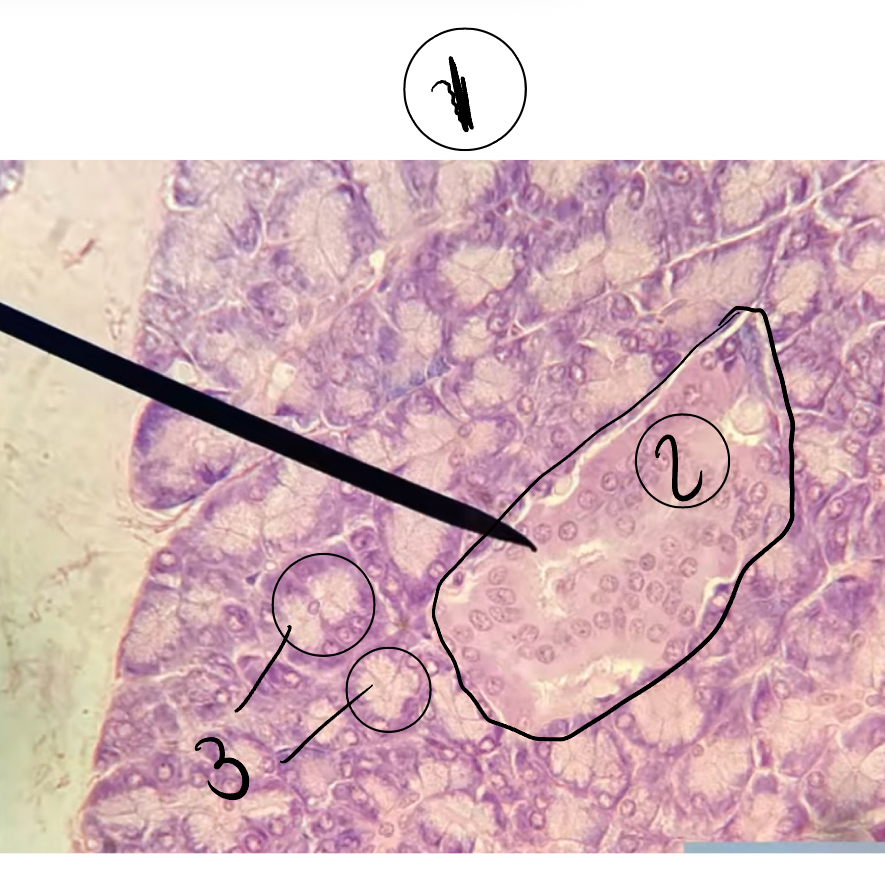
3
Capillaries
What hormones do the islet cells secrete
Insulin (beta cells)
Glucagon (alpha cells)
What are the functions of islet cell hormone:
Glucagon will raise blood sugar and insulin lowers blood sugar
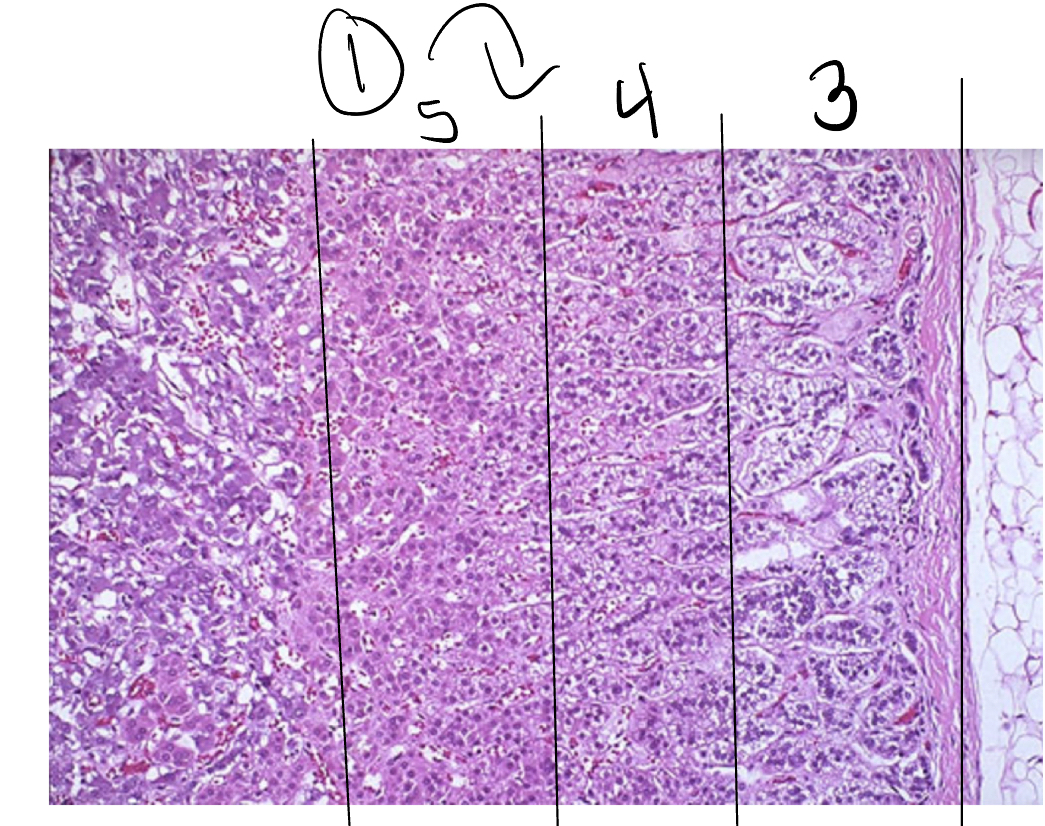
1
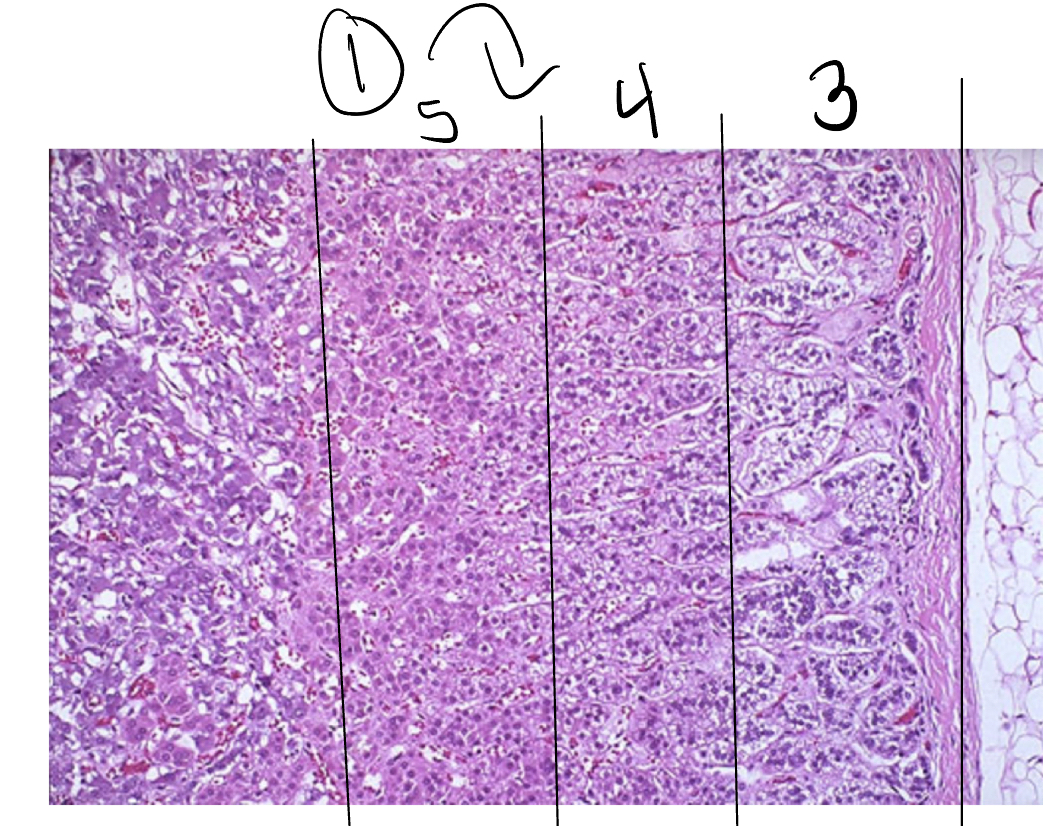
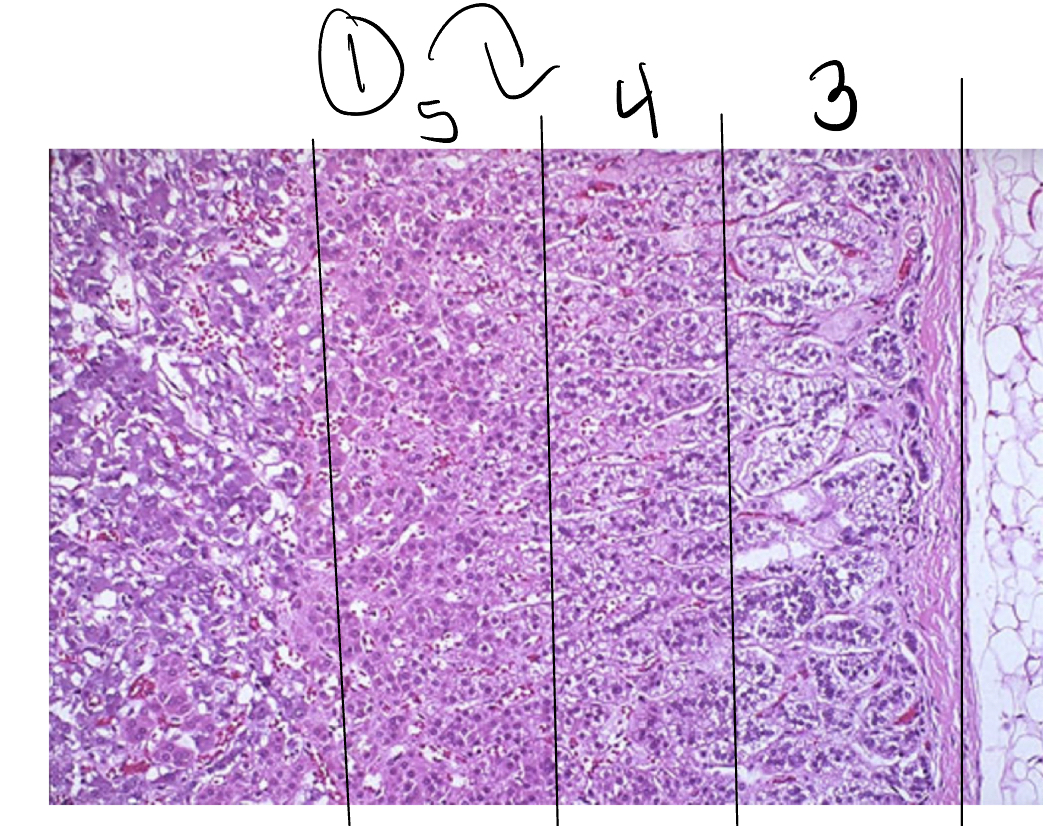
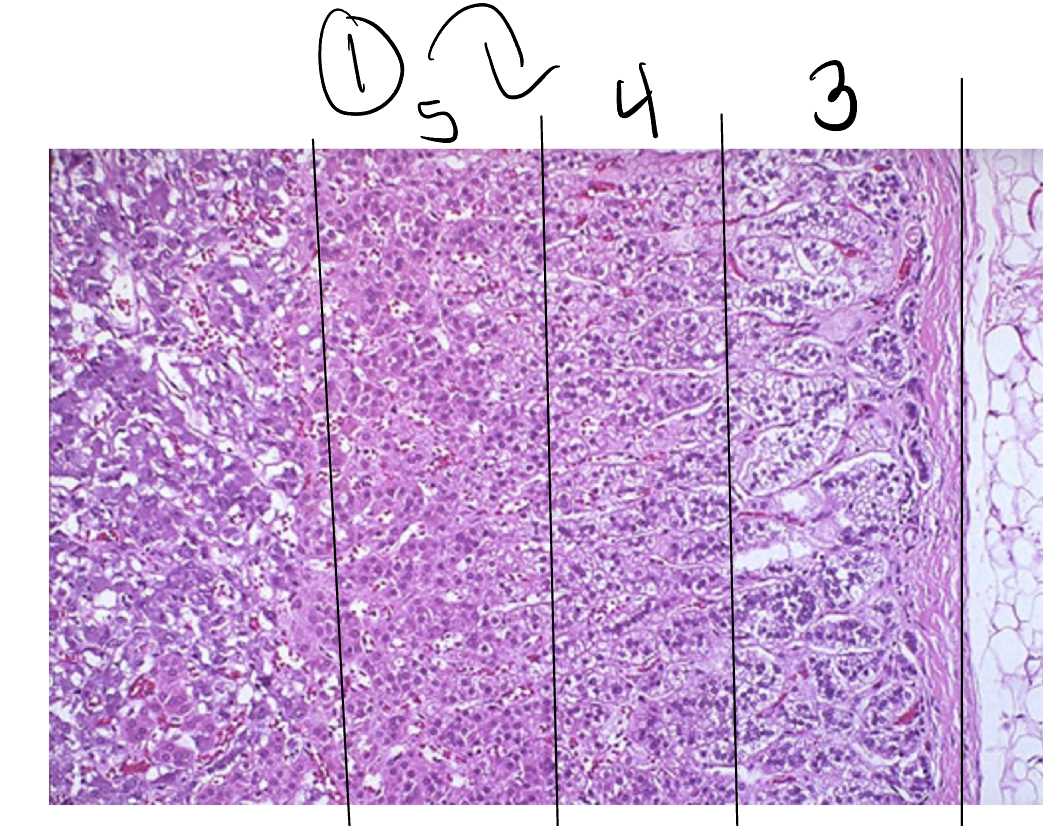
Adrenal cortex
3
Zona glomerulosa
4
Zona fasciculata
5
Zona reticularis
What do Zona glomerulosa cells secrete
Mineralcorticoids
What is the function of Zona glomerulosa hormones: aldosterone
Increases sodium reabsorption in cells
Promotes potassium excretion
regulates BP AND blood volume
How are the glomerulosa cells regulated
Aldosterone helps retain NA and water and excretion of K and raise blood pressure
What do the cells Zona fasciculata secrete
Glucocorticoids, cortisol being the main hormone
What is the function of the hormones of the zona fasciculata: cortisol
Regulate metabolism increasing glucose production, reduce inflammation, help body respond to stress
How are the Zona fasciculata cells regulated
ACTH released by pituitary gland, increase production of cortisol, negative feedback loop
What do the Zona reticularis cells secrete
Androgens, which are male set hormones: DHEA AND ANDROSTENEDIONE.
What is the function of the hormones in Zona reticularis: androgens
Contribute to secondary characteristics, libido, muscle mass
How are the cells in Zona reticularis regulated
ACTH, stimulates production of androgens
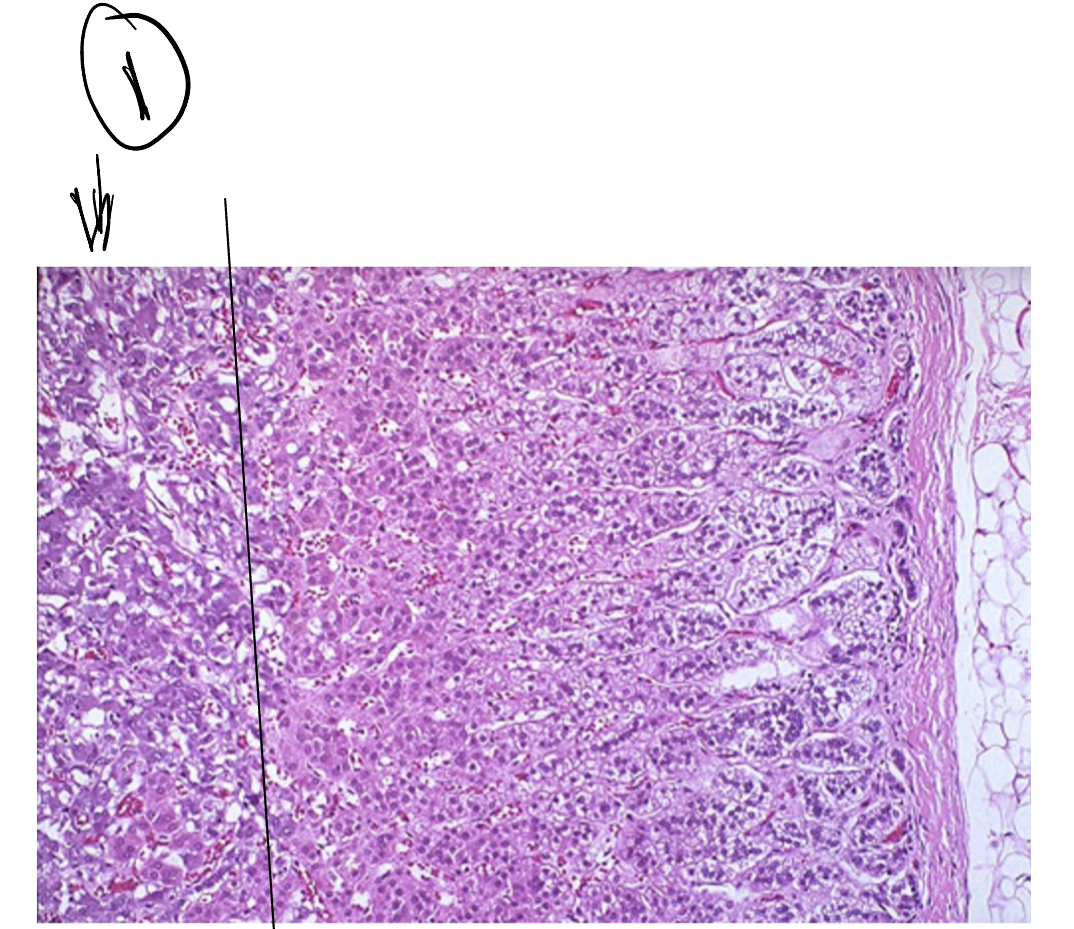
1
Adrenal medulla
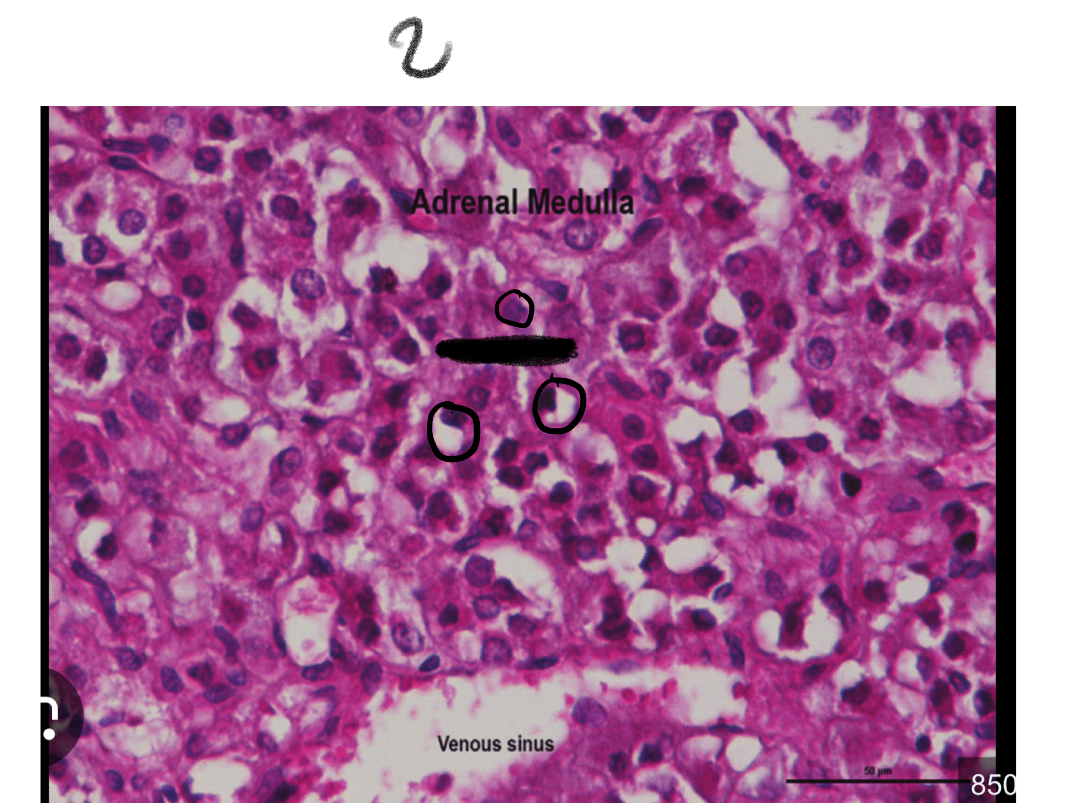
2
Chromaffin cells
What do the cells in the adrenal medulla secrete
Catecholamines: epinephrine,norepinephrine, little dopamine
What are the functions of the hormones in the adrenal medulla: epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine
Epinephrine: increase heart rate, increases blood glucose
Norepinephrine:strong vasoconstrictor, maintain bp
Dopamine: dilate blood vessels in the kidneys
How are the chromaffin cells regulated
By ANS, sympathetic division, flight or fight, preganglionic Sympathetic neurons release ach at synapses for chromaffin cells