Physics Flashcards - Relationship between Force, Mass and Acceleration
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nat's Year 10 Science - Physics Unit Flashcards 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Scalar
Quantities that are fully described by a magnitude alone, without a direction.
Example of Scalar Quantity
Distance = 10km
Vector
Quantities that are fully described by both a magnitude and a direction.
Example of Vector Quantity
Displacement = 1440m north-east
Properties of Scalar Quantities
Magnitude = Yes, Direction = No, Representation = Number and Unit, Mathematical Rules = Ordinary Algebra, Examples = Temp, Speed and Mass
Properties of Vector Quantities
Magnitude = Yes, Direction = Yes, Representation = Number, Unit and Direction (Arrow), Mathematical Rules = Vector Algebra, Examples = Velocity, Force and Acceleration
Speed
Defined in terms of distance and time - both scalar quantities, so speed is also a scalar quantity. Speed is the same, whether traveling north or south.
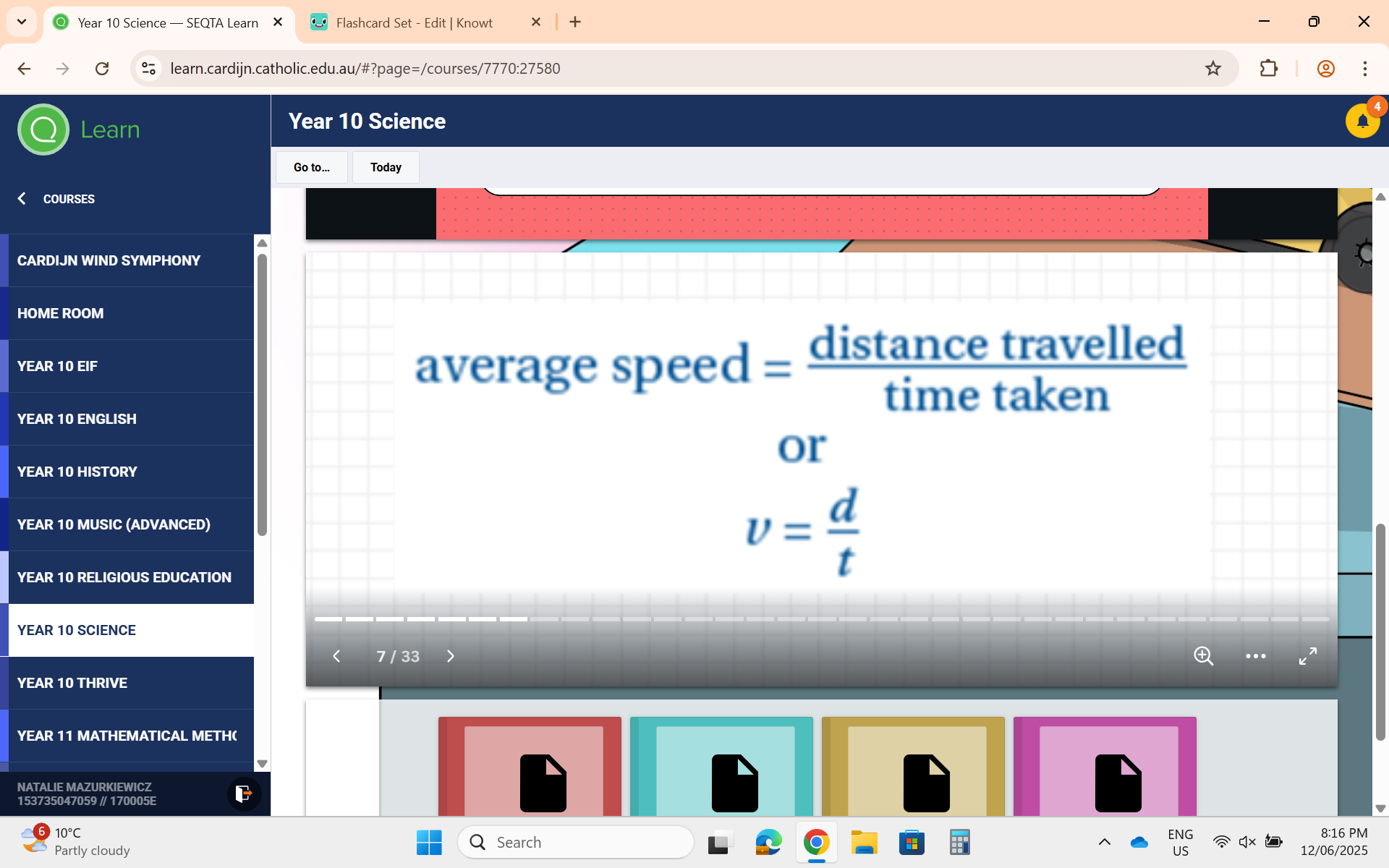
Average Speed Formula
Speed = v, Distance = d, Time Taken = t.
Rate
Rate is a scalar quantity per unit time.
Examples of Rate
m/s (minutes per second) and km/h (kilometers per hour).
Distance
How far something travelled. It is a scalar quantity.
Displacement
The straight-line distance between finishing and starting points. Specifies not only distance from starting point but also the direction from the starting point. Displacement is a vector quantity.
Formula for Displacement
a² + b² = c². Remember to include direction in final answer.
Velocity
A vector quantity that refers to the rate at which an object changes its position.
Example of Velocity
A car travelling 80 km/h north.
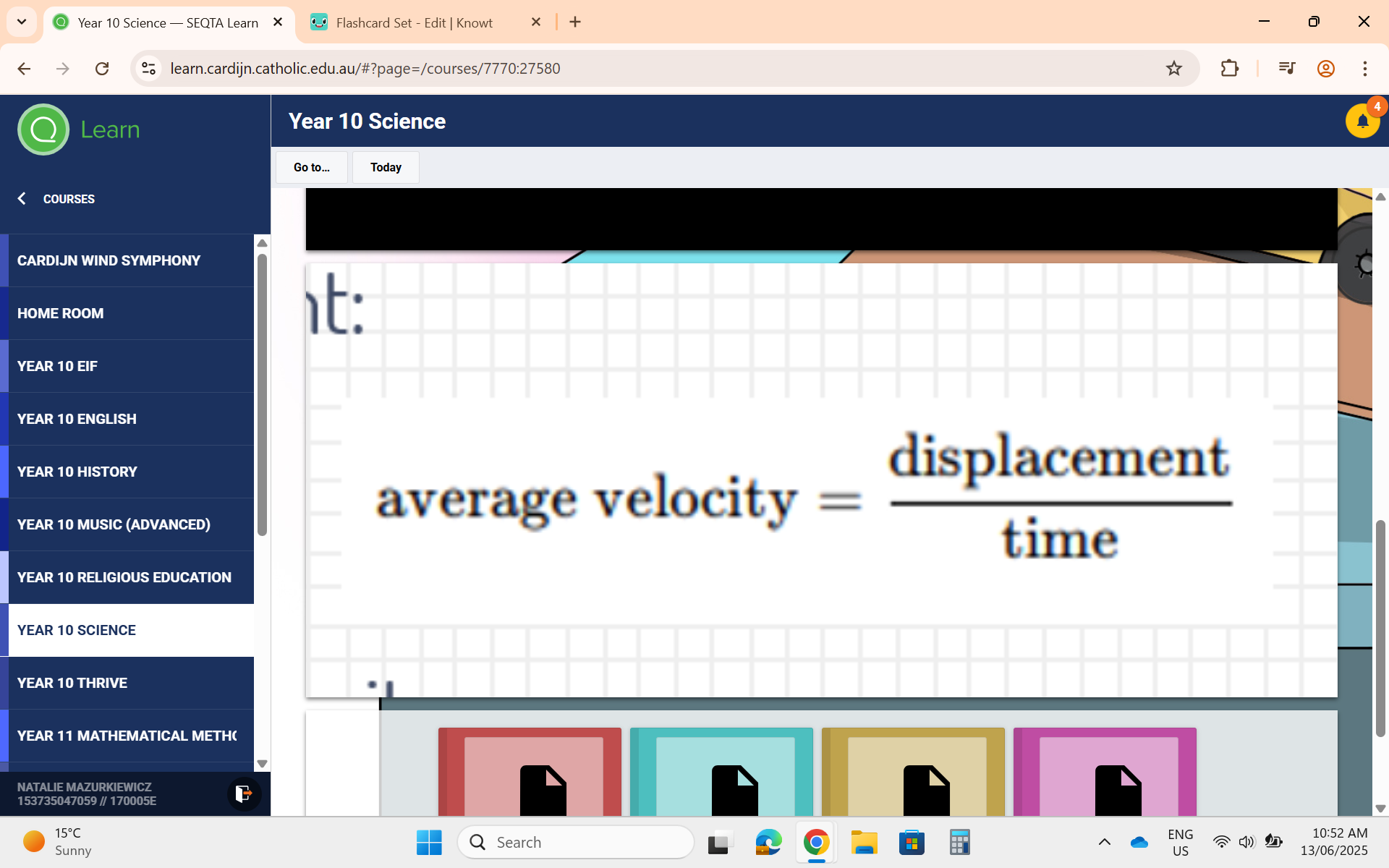
Average Velocity Formula
Average Velocity = v, Displacement = s, Time = t
Symbol and unit for distance/displacement
Symbol = s, Unit = m (meters)
Symbol and unit for speed/velocity
Symbol = v, Unit = m/s, ms^-1 (meters per second)
Symbol and unit for time
Symbol = t, Unit = s (seconds)
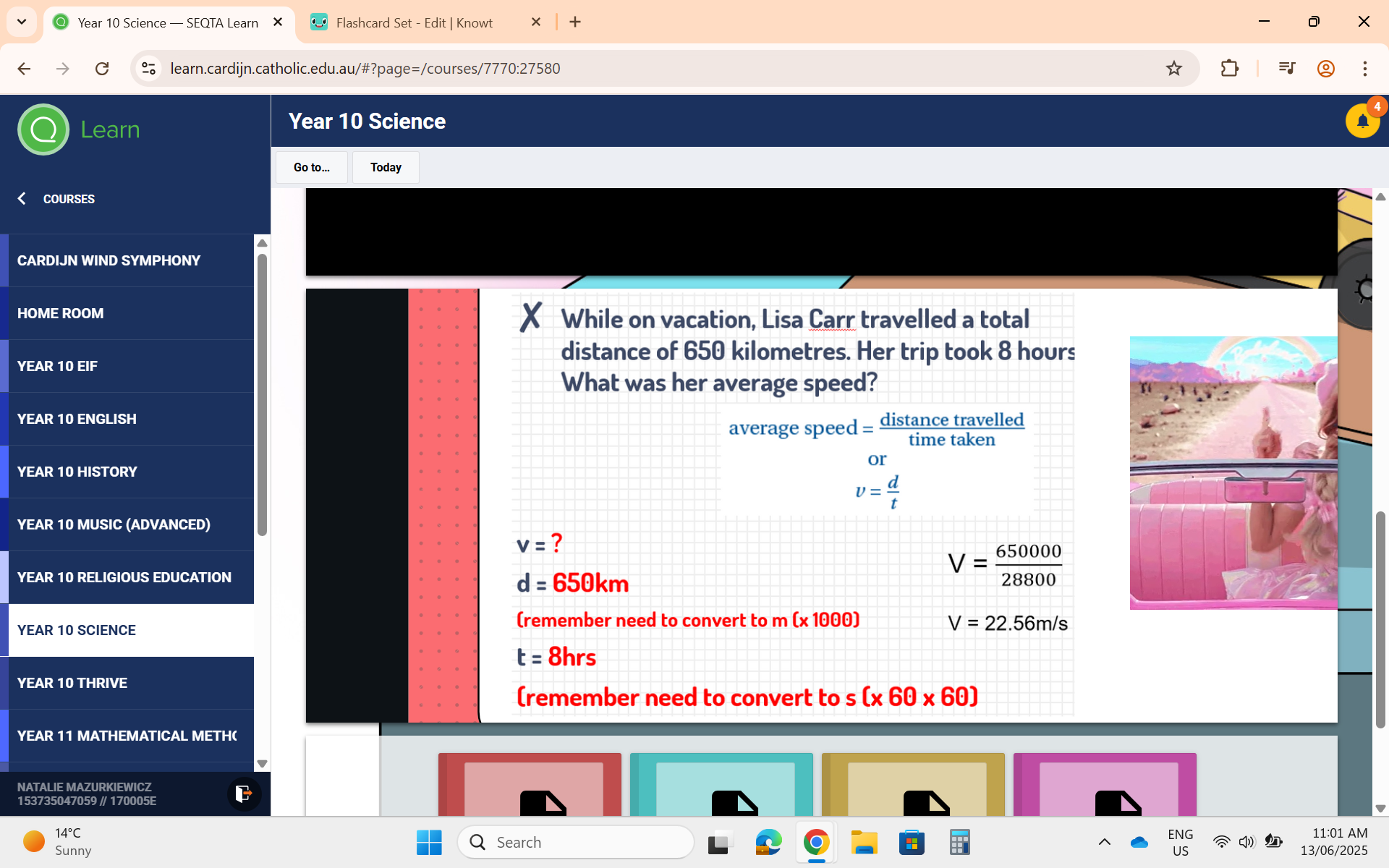
Conversions for Average Speed
km to m = (x1000), hrs to s = (x60 ×60)
Acceleration
The rate at which velocity changes. Change in acceleration can be caused by increase/decrease in speed or the change in direction.

Acceleration Formula
a = acceleration, v = final velocity, u = initial velocity, t = time taken
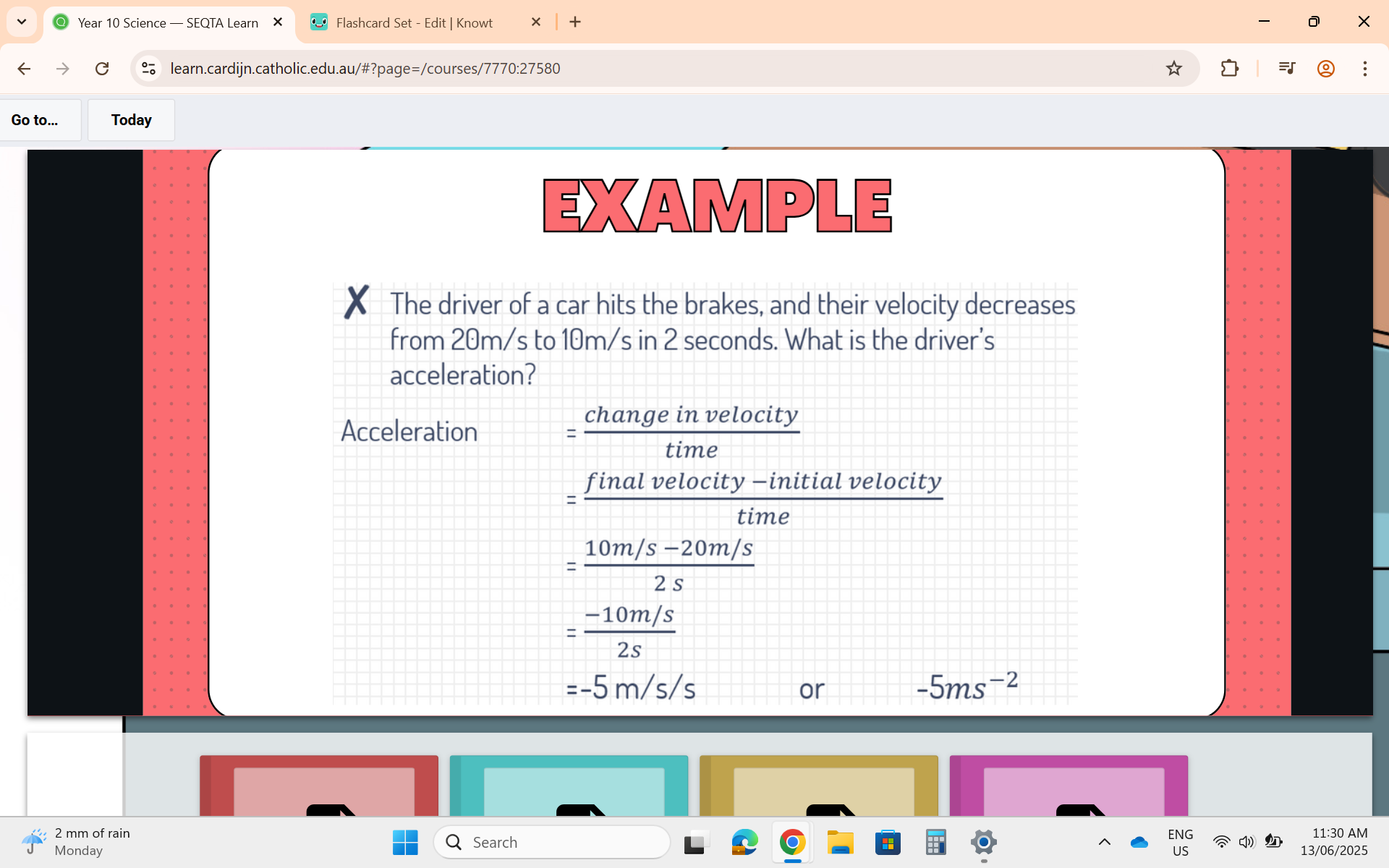
Example for Acceleration Formula
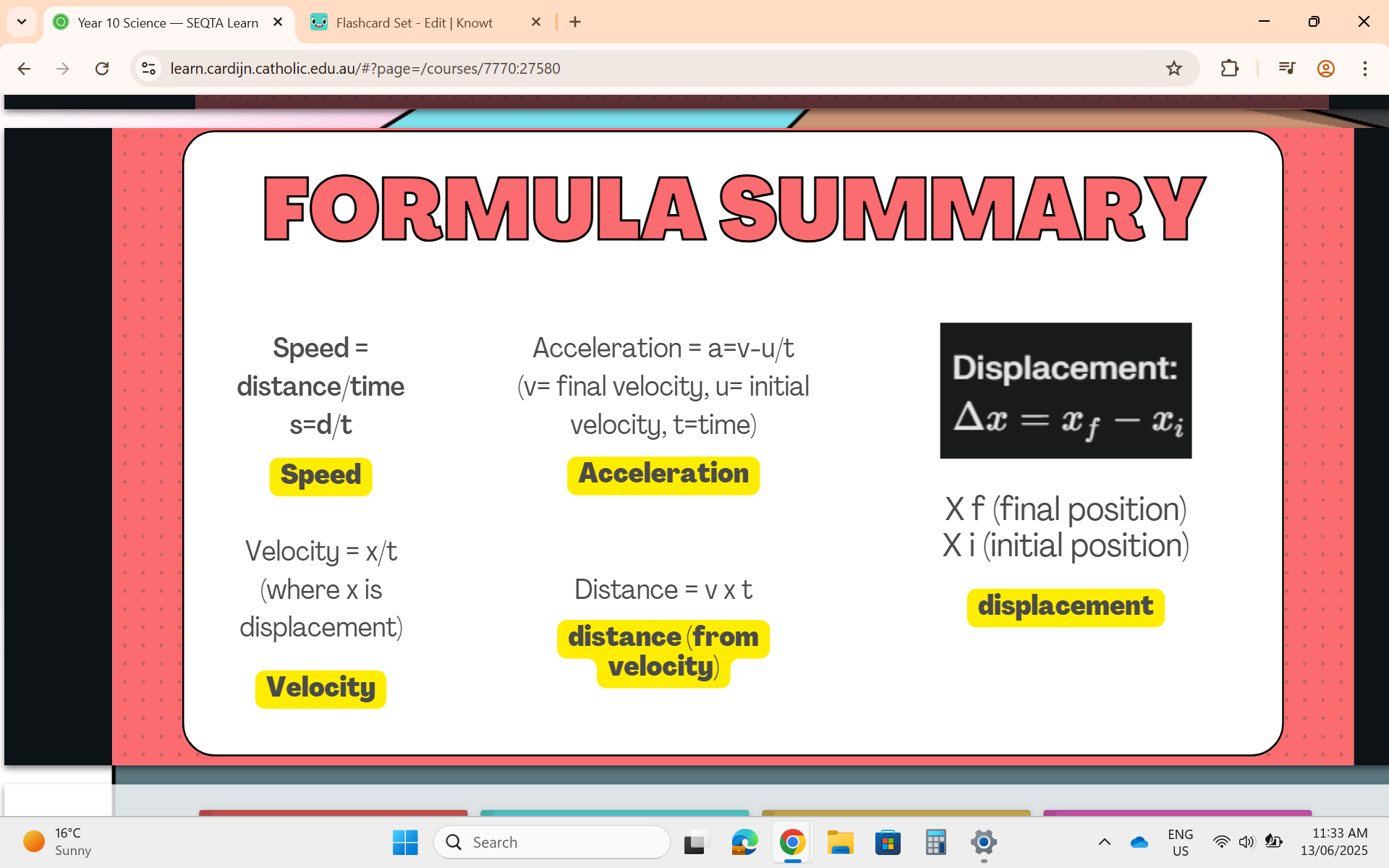
Formula Summary Sheet