History GCSE revision
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Reasons for distrust between USSR and USA
1945: Post-WW2 disagreements on future began
USSR claimed Finland, Lithuania, Estonia, Latvia + land from Czechoslovakia and Romania
Stalin helps to make Bulgaria, Hungary, Poland communist
Churchill makes statement of an ‘iron curtain’ dividing Europe’s capitalist west and communist east
March 1947: US willing to pay huge amounts of money to Europe’s devastated countries through Marshall Plan
Truman makes speech, US would help any country threatened by communism to ‘contain’ communism
September 1947: Stalin confirms communist leaders are coordinated in work + policies
1949: USSR conducts first successful nuclear bomb test to make them the 2nd nation to detonate nuclear weapon
USA, Britain, France, Belgium, Canada + other European countries form NATO
Communists form Warsaw Pact as a response with Albania, Bulgaria, Romania, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Poland
Cold War starts with proxy wars and words, bluffs, threats and propaganda and carries on this way
Background to Korea
Occupied by Japan in early 1900s
In 1945 when Japan defeated in WW2, it had to give up Korea
Soldiers in north surrendered to USSR forces, north surrendered to US forces. Divided into 2 separate zones, intended to be temporary with plans for elections for a united, independent country
1948: pre-elections, Soviets allowed Kim-il-Sung to take power so there were no elections
In the southern Us part, Syngman Rhee elected who had strong ties to the USA
North’s capital Pyongyang and Soviet-backed leader, South’s capital Seoul and US-backed leader.
Both leaders wanted unified Korea but they had contrasting plans and ideas
Start of the war + things that triggered it
Stalin gave permission to invade in April, but invasion started on June 25 1950
They took control of everything except Pusan in less than 2 months
Triggered international response
US vetoed decision to let communist china back in to UN
US sent troops to defend SK
US antagonism like Marshall plan and Truman doctrine angered USSR
USSR forced KIS into power and they were father country of NK
Provided military support in weapons, equipment and training
USSR boycotted UN due to China being rejected, so it meant they couldn’t prevent counter-attack
China’s communist revolution led by Mao Tse-tung creates fear in US
China sent troops to help NK which escalated the war
The division of Korea meant SK reliant on US support and the growth of nationalism
UN sent 16 states’ troops to fight which expanded a localised invasion to an international war
Truman, General MacArthur + stages of the war
Truman came from a poor farming family and became vice president in 1944 and president from 1945-53
Supported Marshall plan and hated communism
MacArthur was son of a US army general and was strong-willed, arrogant and stubborn, even described as a bully
Appointed chief of UN forces in Korea
He decided to stop collapse of SK forces and land at Pusan and Inchon to push back NK forces
By early October 1950, all NK troops had been driven out from the south
There were 590,911 SK troops, 302,483 US troops and 14,198 UK troops in Korea
Un decided to cross border into NK and hoped to unify Korea
MacArthur believed China would not get involved
China warned on 19 October 1950 if UN forces continued to move north towards china, China would support and join NK in the war
UN ignored the warning and 200,000 Chinese troops fought back
Chinese pushed and re-took Seoul
Un then took back Seoul and two sides were roughly back where they started by March 1951
Truman wanted to stop the conflict as he feared it might end in nuclear war
MacArthur wanted to unify Korea and was prepared to use nuclear weapons
MacArthur sacked as he refused to follow orders
US public hated this as he was a ‘war hero’
Gains and losses of Korean war
NK:600,000 civilians killed, ~406,000 military killed, 1.5m military wounded
SK: 1m civilians killed, 217,000 military killed, 429,000 military wounded
US: $60bn cost, 36,568 military killed, 103,284 military wounded, failed to achieve a unified Korea but ‘saved’ SK from communism, containment policy worked
USSR: closer relationship with china but increased tensions with US and also cost them a lot economically
UN: stopped aggression and gained respect but Norwegian Secretary General resigned, 3,063 military killed, 11,817 military wounded
China: 600,000 military killed, 716,000 military wounded, was a poor country and war was costly, US cut ties with them for 25 years, but gained a closer relationship with USSR
Overall impacts on Korea: Civilian and military casualties, 80% industrial and government buildings destroyed, ~50% housing and most of transportation services, no gains as it is technically still in a state of war
Background on Vietnam
1945: Ho Chi Minh declares Vietnam independent after Japanese withdrawal
1946-54: First Indochina War as France tries to reclaim and keep control of Vietnam
1947: Truman promises to fight communism
1954: France withdraws from Vietnam and it is partitioned into 2
1957: Civil war breaks out in Vietnam
1964: USA begin fighting directly in Vietnam
1969: Peace talks begin
1973: Paris Peace Agreement signed and USA withdraw from Vietnam
1975: Communist North Vietnam invades south and unifies the country
French defeat in Vietnam
Vietminh
Wanted Vietnam to be independent and comunist\
Wanted French to stop ruling them
Guerrilla warfare, surprise attacks + interfering with communication, strategic approach
12,000 wounded, 8,000 killed
French
Wanted to reclaim Vietnam as part of its empire
Controlled towns, cities and ports
Counter attacking with brute force, not much tactics
190,000 severely injured, 80,000 killed
Ngo Dinh Diem
Was a Catholic who worked for the French for a while
In 1945, captured by Ho Chi Minh but refused to join their government
Went to US and JFK saw him as a good president for Vietnam
In 1954, he became president of SV, used violence and nepotism to keep control
Americans had issues with him like him acting independently and refusing to take their guidance, Americans didn’t like his decisions, he held early elections, ignored their advice to announce a more believable 70% majority rather than his claim of 98.2%, where he supposedly beat former emperor Bo Dai
Americans put Diem’s name in red for the election, a sign of good luck in Vietnam. Diem ordered supporters to intimidate people who looked like they weren't voting for him
Killed in a coup on 2 November 1963
Buddhists opposed him as he gave preferential treatment to Catholics and put in anti-Buddhist policies
His downfall started when his brutal regime reached the US press and due to the backlash, US stopped supporting him
The people revolted against him on 1 November 1963 and him and his brother were surrounded by troops and they surrendered the next day- while they were being taken away, they were shot dead on 2 November 1963
Opposition to Diem
The NLF (national liberation front) were a group of nationalists who wanted land to be given back to peasants, and to unite Vietnam. They wanted to overthrow Diem and get rid of him regime of Catholic dominance, and create a government that supported all social classes and religions. Targeted officials in Diem’s government and many hundreds of government workers were murdered.
Buddhists were organised and used hunger strikes, mass rallies and invited foreign press to cover events
Most famous protest was self-immolation of a monk, Thich Quang Duc, while people handed out leaflets calling for Diem to show compassion to other religious groups
Civil war
Many of Diem’s opponents believed only armed rebellion could stop him and lot joined NLF. US supported Diem and sent around $1.6 in the 1950s and military advisors. Civil war broke out in 1957
Vietcong (NLF) tactics against Diem
Travelled very light with an accurate and reliable AK-47, ration of rice and punji sticks to make traps with
Reliant on peasants and workers help
Key aims:
1.Replacement of Diem with a government representative of all social classes and religions
2.Unification of Vietnam free from foreign influence
3.Promotion of peasants’ rights and to stop poverty
Eisenhower’s Involvement in Vietnam
Propaganda against Ho Chi Minh and NV
Supplied Diem with money, weapons and military equipment and advisors to help fight Vietcong (NLF)
Invited SV to join SEATO (Southeast Asia Treaty Organisation) including Australia, Britain, Pakistan, New Zealand and France who aimed to work together to stop communism in SE Asia
Sent military advisors to SV
Sent CIA intelligence to SV’s largest city, Saigon, to gather info for US government
Key facts: Served in US army, 1920s-30s
Became supreme commander of NATO forces in Europe, Dec 1950
Agreed to ceasefire in Korea, July 1953
President from 1953-61, lived from 1890-1969
Kennedy’s Involvement in Vietnam
Born into wealthy and political Irish-American family
Assassinated in 1963 in Dallas, Texas
Kept US involvement secret as he worried about public opinion, approved a coup in SV to remove Diem
Increased financial aid to Vietnam
Strategic hamlets forced peasants to leave Vietcong-controlled areas and move to small villages loyal to Diem
Increased military experts to 16,000 who trained SV army
Sent 300 US helicopter pilots to SV to transport ARVN soldiers, strictly told not to fight
Gulf of Tonkin
3rd August: American USS Maddox followed by torpedo boats, they both retaliated and US shot down all 3 boats, US were in enemy waters
7th August 1964: G.o.T resolution led to escalation in US involvement and direct US soldiers, had no limit to amount of spending in Vietnam
Operation Rolling Thunder, 13th Feb 1965: US aircraft bomb oil storage and 2 other areas along with government building, lasted 3 years
US sent in 200,000 soldiers to directly fight in Vietnam
US tactics in Vietnam
Lots of young and inexperienced soldiers, soon average age was 19 and most had never been abroad
1966: Racial inequality as 41% were black while only making up 11% of US population
1968: Black people made up 12% of army but 50% were frontline
1970: made up 11% of army but were 22% of casualties#
Lots of soldiers weren’t used to other different environments and cultures
US dropped more bombs in Vietnam than have ever been dropped in whole of human history
Used superior firepower and technology to use search and destroy tactics where they would search villages for Vietcong soldiers, if any were found, they would destroy village as a warning
Used lots of chemical warfare like agent orange used to destroy the jungle and napalm, which would burn through anything, even muscle and bone
Disrupted Ho Chi Minh trail(supply routes for NV)
MI6 rifle unreliable and got jammed, especially when coming into contact with water
Tet Offensive
All out assault on 100 cities in the South by Vietcong
April 1967: commander of US forces in Vietnam (Westmoreland) told US public war was nearing the end
Vietcong carried out some major attacks in early 1968 (Tet Offensive)
Around 84,000 VC troops simultaneously attacks >100 cities, towns and US military bases
US responded by regaining control of all places , some took hours while others took weeks
Devastation seen on Tv severely damaged national confidence in president Johnson’s war policies
Turning points of Tet
Post-Tet, US public increasingly disillusioned with the war and realised it wasn’t over
President Johnson didn’t re-run for election in Nov 1968
Although US regained control, it cost them lots of artillery and airpower - by now war was costing $30bn/year and 300 US soldiers killed every week, number of deaths surpassed Korean war
Lots of Vietnamese civilians killed and ancient monuments and cities destroyed, made US citizens question US involvement
Impacts of Tet on US
A military victory as they regained control of major cities, but war was costing a lot
Number of US and ARVN troops were less than 10,000
A political defeat as American opinion turned against involvement in the war
Credibility gap grew between what government was saying and what public believed and saw on TV
President Johnson chose not to re-run shortly after
Impacts of Tet on Vietcong
A major military defeat as 50,000 NV army and 10,000 VC killed
Political victory
Changed ‘hearts and mind‘ in US against the war
Number of anti-war demonstrations increased
My Lai massacre
Charlie Company suffered a few casualties despite never directly fighting Vietcong which lowered morale and made them feel vengeful
A search and destroy mission was planned to kill expected VC soldiers and destroy food and water sources
Began immediately firing at buildings and throwing grenades into houses
Unsuccessful as no VC soldiers were found
Investigation by Us army and government revealed 347-504 unarmed civilians had been massacred and event was deliberately covered up by Charlie Company
Lt. William Calley only one charged which was controversial as 100s of others took part doing worse things, army recommended 25 others should be prosecuted
Nixon’s plans to stop the war: Bombing campaigns
More bombs dropped under Johnson
Cambodia secretly bombed to avoid public outcry
Bombing on Laos partially worked as an attack but ARVN troops soon beaten back
1969-72, lots of bombing raids concentrated in SV and Cambodia, also in Laos and NV
Vietnamisation
Wanted to build up SV’s army (ARVN) until it could carry on the war independently
US soldiers trained, equipped and expanded the ARVN and they could return home
Realised process would be gradual so he spent vast sums of money on this plan
Within months, around half of the adult SV population had signed up
Peace talks
USA + USSR had very bad relations by late 1960s
To fix this in 1970 talks began on limiting the amount of nuclear weapons they both had and Nixon asked USSR to pressure NV to end the war
In 1972, Nixon went to China and became first US president to do so after it became communist
Also asked China to encourage NV to end the war
Withdrawal of US troops
Realised that he couldn’t immediately withdraw the troops, decided to destroy as many Vietcong bases as possible before the US army left
However, the Vietcong had bases bordering Cambodia and were supplied by Ho Chi Minh trail, where a lot of their bases were too
Invasion of Laos and Cambodia
Nixon tried to bomb the Ho Chi Minh trail and Vietcong bases in Cambodia but failed
Ordered the invasion of Cambodia and 150,000 more Vietnam troops
Communist Khmer Rouge gained a lot of support quickly by the peasants and membership rapidly grew
In Laos, there was an attack on Vietnamese troops, however, ARVN were beaten back and NV troops launched major attack on SV in spring 1972
Increased support for communists called Pathet Lao and by 1973, controlled most of the country
USA financial cost
Cost $170bn (close to $1tn today)
Additional costs in terms of benefits and pensions to US vet.’s and families (estimated to double war cost)
USA human cost
58,000 Americans with an average age of 23 were killed
Over 300,000 injured
Many returning soldiers faced stigma from anti-war protesters as well as war supporters (as they lost the war)
Many survivors were affected psychologically and suffered from what we now recognise as PTSD
Other war vets were affected by drug addictions as a result of their experiences
Investment in services such as education and medical care suffered as a result of money being diverted into the war eg. Johnsons plans for social reforms known as the Great Society and War on Poverty couldnt be completed
USA political cost
Politicians failed to deliver on their promises due to conflict, damaged rep’s
Anti-war movement caused a split within American society
Cover up of My Lai massacre and other events damaged credibility of US government, led people to suspect and distrust it
USA’s int’l rep as big superpower damaged
Rep as leader of peace and freedom destroyed due to Kent state shooting
War proved US couldn’t contain communism
Domino theory disproved as India and Thailand never became communist
Vietnam financial cost
Financial cost a lot lower than US but country left more economically damaged
Many people faced starvation due to the war
Vietnam human cost
~1m soldiers (N+S) and 2m wounded
~2m Vietnamese civilians killed and 5m injured, with a lot having lifelong effects
11m became refugees as homes were destroyed by the war, lots of these had lives ruined because of the war
Around 100,000 children born as result of US soldiers and Vietnamese women
In 1975, ~3000 infants flown out of Vietnamese orphanages and adopted by people around the world called ‘Operation Babylift‘
1000s others remained and ridiculed, some sold or given away to relatives
Vietnam political cost
Vietnam faced hostility from US post war
Was communist but many citizens in south resented communist rule
>1m Vietnamese citizens rejected communist government completely and left in search of a better life elsewhere (Malaysia and Hong Kong but many later settled in US/ Europe)
Vietnamese environmental cost
Huge areas of farmland and jungle that fed the Vietcong and hid their troops were deliberately destroyed in by US
In 1969, >1m hectares of forest was destroyed using Agent Orange
Between 1962 and 1969, nearly 300,000 ha of farmland was sprayed with chemicals to make it barren
Lots of soldiers and civilians developed cancer or other illnesses due to the chemicals
Children born with disabilities because of the chemicals
Vietnam became most heavily bombed country in history
Between 1964 and 1973, >7m tonnes of bombs dropped (WW2=2m tonnes)
Bombs destroyed roads, bridges, cultural landmarks and crucial irrigation systems
Even today, UXBs continue to cause death and injury
1272 England - Power of the king
Main source of wealth and power was land
Marcher Lords = strong landowners on border regions with Wales and Scotland
Tried to extend power at the cost of their neighbours
Kings kept land to hunt or recreation
Landowners wanted grazing land as sheep were more profitable
The Church
Church courts wanted more power than royal courts and vice versa so this caused issues
Monasteries provided healthcare
Clerics (churchmen) employed by the King as they were literate
Agriculture
Population in 1272 was around 4.75m
Wool was the most important trading commodity
Towns
Population of London was around 10,000
Winchester, Lincoln and Norwich had >5,000 population
Villeins could be free if they survived a year without being caught so it was worth the risk
Greater risk of illness in towns rather than villages
Guilds were powerful as there was a lot of craftsmen with high wages and were similar to a worker’s union
Food
Pottage was common and a stew that contained beans, peas and oats, with herbs, meat or fish depending on availability
Wealthy thought vegetables were only for poor people so often refused to eat them
Many animals were slaughtered in autumn as there was a lack of animal food in winter
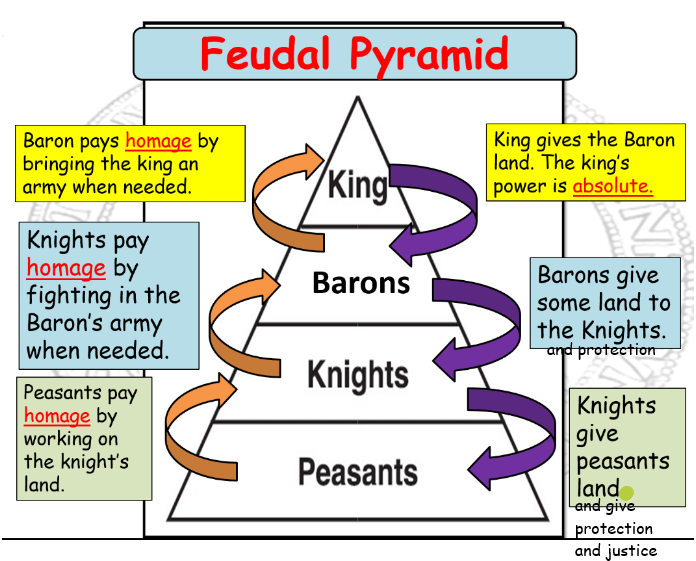
Feudal system
Villein - a peasant who was trapped at the bottom of the feudal system
Freeman - an ex-villein who managed to escape the feudal system and weren’t tied to a manor, and could own land
Homage - A ceremonial act that formalised the relationship between knights and barons
Overlord - a lord who had authority over one or more vassals
Edward 1 background pt 1
Plantagenets was a royal house of England, which reigned from 1154-1485 and provided 14 kings
Magna Carta (1215)
Included access to a fair and free trial, no new taxes without barons’ agreement and a council of barons to ensure the king followed the laws
King John, Edward’s grandfather, refused to follow the MC
Led to First Barons’ war (1215-1217)
Civil war in England
Barons rebelled after King John refused to follow MC
When John died, his son Henry III was forced to reissue MC 3 times and in 1297 Edward I renewed it again
Some of its principles can be seen in modern democracies today
Edward 1 background pt 2
Provisions of Oxford (1258)
Council of 15 barons to advise the king, who cannot make decisions without them
Taxes decided locally, not by the King
No foreigners can hold senior positions
Provisions of Westminster (1259)
Replaced PoO
Introduced more restrictions on the king, especially on tax collection
Led to Second Barons’ War
Struggle between Henry III and Simon de Montfort from 1264-1267
In 1264, de Montfort took Henry and Edward captive after defeating them at Battle of Lewes
De Montfort’s rule of England came to an end in 1265 when he was killed at the Battle of Evesham
Key events in early life (b.1239)
1246 - serious illness but nursed by his mother, shows he was resilient, religious, believed he was divine
Late 1240s - Edward develops a keen interest in the legend of King Arthur and the Knights of the Round Table, shows he was curious and interested
1254 - Edward is married off to Eleanor of Castille, 2nd cousin, in a political marriage to reaffirm English control of Gascony, shows he was respectful of his parents
1254 - Edward is given land in Wales, Ireland and Channel Islands, shows he was powerful
Key battle events (age 19-33)
1258 - Barons revolt in the 2nd Barons’ War and force the King to accept the PoO, which reduced his authority and reintroduced a baronial governing council, Edward goes against his father and supports barons, shows he was rebellious, independent, fair ruler
1261 - Barons’ power increases, Edward supports his father now, shows he was indecisive, unsure, adaptable
1264 - De Montfort captures Edward + dad at Battle of Lewes, takes over kingdom, De Montfort calls Europe’s 1st elected parliament with 2 representatives from towns + counties
1265 - Edward escapes prison and defeats DM at battle of Evesham, shows he was strong and good in battle
1265-1272 - Edward effectively rules England for his father, shows he was independent
1270 - Edward leaves for 8th crusade, with 250 knights + 1000 men, defeated by Muslims + wounded by poisoned dagger, he survives, shows he was resilient, believes he was chosen to be a leader, devout
1272 - Edward’s dad dies while E is on crusade, returns to England in 1274 and coronation takes place
Issues Edward faced when becoming King - Barons
Father pushed them too far + DM made his father look weak
Edward was determined to never look weak or overpowered
Knew the nobles were a huge threat and couldn’t rule without them
Wasn’t willing to follow PoO but was aware he couldn’t do as he liked
Finances
Father’s reckless rule left Edward with insufficient funds and father’s attempt to raise taxes fuelled conflict with barons, so Edward had to be careful
He wanted to go to war but knew it would hurt the country, so looked to trade as a fix, especially customs payments
Started wool trade in 1275 and was effective in making money. This was a good solution
Wales
E found Wales annoying as there were rebellions often
He saw this as a threat to England’s security
Prince of Wales had become more powerful during Henry’s reign and in 1275 refused to pay homage to E
From H’s experiences with DM, he refused to allow this disrespect
War and Foreign Policy
E wanted to win back land in France lost by his father to prove superiority
E was Duke of Aquitaine in SW France, a title he got from his father, made him answerable to French king
Could never accept French king was superior and hoped to lead another crusade to unite Europe in bringing Christianity to the Holy Land
How did Edward deal with nobility
Established he was willing to work with them and include them in his government✅
He used parliament to listen to advice and enact his ideas into law, but they were his laws ✅
In 1278, Parliament passed Statute of Gloucester to reclaim lands and powers of the king✅
He wouldn’t tolerate any disrespect or challenges to his authority❌
He removed many of his father’s ministers and officials and appointed his close associate, Robert Burnell, as Chancellor, effectively his Chief Minister who would step in if the king was unavailable ❌
Any baron who couldn’t produce proof that the land he claimed or the power he held was legal would have to return it to the king. This established all rights and power belonged to the king. The men known as General Eyres would travel the country on behalf of the king to visit and investigate landowning nobles, called Quo Warranto, they had to prove they had a royal license and they had owned it since ‘time immemorial‘ (1189), and the General Eyres followed the law closely so the king couldn’t be accused of seizing land or being unfair ❌
Subinfeudation vs Substitution
Subinfeudation: land transferred down the feudal hierarchy but should be traced back to the king. However, as more and more land was divided (the buyer), more mesne lords were created who owed homage to another lord (the seller), rather than the king
Substitution: The 3rd statute of Westminster banned subinfeudation in 1290 and replaced it with substitution. once land was sold, the previous owner had no further claim to it. Buyer was not expected to pay homage to the seller, this transformed the transfer of land from a feudal transaction to a commercial one
Statute
A law
Subinfeudation
Splitting estates into smaller estates within the feudal system, previous holder becomes the mesne lord of the new tenant
Mesne lord
A middle lord who owes homage to another lord rather than directly to the king
Substitution
Transferring land from one person to another without becoming their feudal lord
Frankalmoign
Transfer of lands to the Church as a gift
First statute of Westminster
1275
Re-established that all power and authority came from the king
To establish all authority and land came from the king and to get his land back
Statute of Gloucester
1278
Also known as “Quo Warranto“
Men known as General Eyres investigated landowners for validity of their landownership and checking for their royal license
If they didn’t have the land/ property since ‘Time Immemorial‘, 1189, King Richard’s coronation
To reclaim the land and power of the king
First + Second Statute of Mortmain
1279
Stopped loophole of transferring land to the church as frankalmoign, and not paying rent to their lord or providing military service
To gain support from barons
Second Statute of Westminster
1285
Known as ‘De donis conditionalibus‘
Land was passing between mesne lords and even peasants through sale or wedding gifts
Some people gave land to the Church against the heir’s wishes, who had no say. This law stopped this problem
Established the wishes of the landowner must be followed
Third Statute of Westminster
Banned subinfeudation, replaced with substitution
To stop too many mesne lords being created
Hundred Rolls
A census to uncover issues and loopholes, and to reclaim royal rights
Targeted specific counties
Document to
Establish royal authority
stop creation of mesne lords through subinfeudation
stop land disputes
ensure he had a clear overview of the state of the country and what problems needed addressing
Why did Edward invade Wales?
For economic gain
Political status gain
To achieve personal goals, expand English territory and to settle any scores with rival
1st Welsh campaign
1277
E sent Marcher lords to secure area around Gwynedd
1st July: E marched towards the enemy + Llywelyn finally offered to negotiate, turned down
29 August: E reached Conwy river and sent 2000 to attack the island Anglesey, took control and stole the crops
1 November: Llywelyn surrenders
L loses title as Prince of Wales and become Prince of Gwynedd instead. Brother Dafydd given much of his land
2nd Welsh campaign
English nobles mistreated Welsh princes, led to rebellion
21 March 1282: Dafydd took control of key locations and Llywelyn joined the rebellion
Llywelyn attacked Castle of Builth, valuable link between north and south English forces, also took control of a bridge on River Irfon
August 1282: English force by John Gifford fund another river crossing and ambushed Welsh and destroyed them
December 1282: Llywelyn killed before the battle by a Marcher Lord
June 1283: E destroyed Welsh defences, hung Dafydd
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd
Born c1233, grandson of Llywelyn the great who established Prince of Gwynedd superior to other Welsh princes
Helped to reunite N Wales
In 1258, other Welsh princes began to pay to him as their overlord rather than the King E
Supported S de Montfort in 2nd Barons’ war, 1264
In 1265, de Montfort officially recognised L as Prince of Wales
Henry was weak and agreed to do the same in 1267
Engaged to marry Eleanor de Montfort but married 1278 as she was held hostage by E
Joined younger brother Dafydd in rebellion against E
Causes of Llywelyn’s downfall
Bad relationship with younger brother Dafydd
Refused to pay homage to E although his forces were much worse equipped and fewer
Disliked by E as he supported dM’s rebellion against Henry, as well as marrying dM’s daughter to fuel hatred
Forgiving Dafydd led to his death
Effective castles
Used to intimidate, control, and create a stronghold for loyal followers of the King
Used landscape as an advantage to help for sieges
A curtain wall or moat offered protection
Few entrances and there were barbicans and portcullises to minimise ways enemies could get in through
Round towers harder to climb or undermine than square
Rings of stone walls of different heights allowed defenders to fire over the heads of others
Caernarfon Castle
Made in heartland of anti-English feeling
Made on a naturally advantageous hill
Materials brought by sea to avoid clashes with locals
Had a great northern wall after English regained control
Had a strong King’s Gate
The wool trade
Connected Asia, Africa, and Europe by trade
Connections to France and Italy via European circuits and it intersected with other to link with other continents and the rest of the world
Best wool produced in Wales, SW England, Lincolnshire
Sold across Europe to places like Ghent, Bruges, Flanders
Success of the wool trade was due to the organised system of medieval agriculture
The country life was based around farming year
Before 1066, wool was mainly produced for use rather than a commodity
Trade around Europe and even the world increased relations with other powerful countries
Statute of Acton Burnell passed in 1283 gave mayors the right to force debts to be repaid and to imprison debtors who couldn’t repay
England known for having the highest quality wool in Europe
Economic impacts of wool trade
Gave lots of job opportunities
King financed his wars in France, Wales and Scotland, from wool, so he introduced a wool duty where money was paid paid to the king when wool was sold
Was a commodity and very profitable, number of sheep showed wealth
In 1286-87, exports to foreign traders from Southampton raised £696 (around £350,000 today)
Used as another source of income in case of bad harvest
Why did towns develop under Edward 1?
More trade —> more tax revenue and more money
Could use bastides as military strongholds
Merchants could provide counter-balance to barons and challenge them
Edward’s methods of funding his government - taxes
He risked rebellion if he continued raising them
All his subjects had to give a portion of their wealth to the king
Coinage
Clippings were being taken out of the coins, leading traders to think they were worth less and caused inflation
Coins were also starting to get worn and damaged anyway
When he fixed this with newly minted coins it encouraged trade and led to more duties and money for him
Loans from bankers
Edward got his money quickly and bankers would get a long term return on their loan
He took loans from bankers in exchange for them managing collection of and duties which could’ve allowed them to raise more money
Trade
Wool duties made him the most money
He introduced duties - taxes on sales of certain things where he would get %age of the sale
Edward’s relationship with the Jews
Were brought to the country by William the Conqueror as he thought they would help build a strong country
Lent money to many people
Weren’t trusted though as people thought they were outsiders an people in England were xenophobic at the time
Statute of Jewry passed in 1275 as E felt they had outlived their use
Heavily taxed until he couldn’t tax any more
Banned them from charging interest (usury), deprived them of their business, cancelled debts they were owed
Made them bankrupt and in 1290, Edict of Expulsion called for all Jews to leave England or face execution. By doing this he was clearing the barons’ debt, making them more willing to pay taxes to him
Jews werent allowed to return to England for nearly 400 yrs
Edward and the Church
Catholicism the only form of Christianity in Medieval England
Latin was the language of the Church
20% of land owned by the Church in Medieval England
Practice of selling land to the church and leasing it back to avoid tax known as Frankalmoign
Archbishop of Canterbury was the most senior churchman
E tried to nominate Robert Burnell for this role but was denied by the Pope as E would have too much power in the Church
Edward vs Peckham
Peckham insisted Magna Carta should be displayed in all Cathedrals, E disliked this as he thought it reminded people of the power of the barons over a weak king
Considered borrowing money from Jews to be a sin, E and nobles did this regularly
P made repeated used of excommunication which E felt undermined his power
Edward vs Winchelsea
In his oath, he said he only owed E loyalty in secular not spiritual matters
Stopped E from taxing more than 10%, even though he needed it for his wars
In 1296, the Pope announced the Church wouldn’t have to pay tax and W agreed, he refused for a year until he was exiled in 1306
Religious thinker in Edward’s reign: John Duns Scotus
Worked at University of Paris
Scottish priest born in Duns
Nicknamed ‘Subtle Doctor’ due to his careful thought
Challenged Aquinas and Aristotle
In 1303, forced to leave University of Paris
Main theory was ‘Immaculate conception’ which explained Jesus’ crucifixion removed his mother’s sin
Proof God exists - everything that exists came from something before so a higher power had to have started this cycle, God
Appreciated wisdom of Aquinas, Aristotle and Muslim philosophers
Roger Bacon
Supported modern evidence-based science
Worked at university of Oxford and Paris focusing on Aristotle’s ideas
Became a friar in 1256 but studied limited by superiors
1265 - new Pope elected, told him to work in secret
1268 - sent the Pope his work and suggested scientific thinking could be introduced to Christianity but new Pope chosen after Clement died and was ridiculed and put under house arrest
Explored why people make errors or fail to learn things
Argued Bible was start of science and should be studied in original language
Developed modern calendar
Studied experimental science
Studied optics and explained how the eye works relatively accurately
Universities
First appeared in Europe in 11th century and originated from monastic schools which were run by monks in monasteries whereas universities became independent organisations
Clergies attended early versions and law and medicine were taught to young men
Funded by the students’ families or by a wealthy person sponsoring their studies, by the King, or by the Church
Oxford and Cambridge helpful to Edward as they had men who were respected across Europe, and had renowned lawyers to help him win cases
William Wallace
When he was young, fought back 5 English soldiers by killing 3 and scaring the other 2 off
Killed a sheriff
Defeated Edward’s army at Striling Bridge
Strategic
Knighted by Robert de Brus
Used the schiltron
Burnt down schools with children in them and raped women ❌
Very violent ❌
Likely to have fought for Edward as a mercenary in Wales
Came from a lesser noble background
After the defeat at Falkirk, he resigned as Guardian of Scotland and continued to help Scotland but was betrayed by allies and was turned in to the English. Taken to court, found guilty, hung drawn and quartered
1297: A crisis year - Wales
Castle-building programme to create bases from which he could control the Welsh - created a level of order
Iron Ring - these huge castles like Caernarfon, Conwy and Beaumaris cost a lot of money to build which was needed for his wars
Threat of rebellion - Edward couldn’t take his eyes off Wales as some Welsh people remained hostile and he was concerned they could rebel at any time
Scotland
William Wallace humiliated Edward at Stirling Bridge which made Edward vengeful and hungry for full-scale war
Battle of Dunbar (1296) - The Scottish barons attacked Carlisle and Edward responded by crushing the Scottish at Dunbar stealing Stone of Scone an humiliating Balliol
Gascony
E paid homage in 1286 but refused in 1294 and lost Gascony
E was Duke of Aquitaine so he was a vassal to the French king and had to pay homage to him
It did not end until 1299 when E married the French King’s sister Margaret
A group of French ships were captured by the English who also attacked the ort of La Rochelle the relationship between the two kings was in crisis, Phillip ordered for E to pay homage but he refused in 1294 and lost Gascony
y August 1297, E was ready for war but his allies had already been defeated while he was sailing to Flanders
England
E ordered farmers to give me crops to feed the army and seized wool and animal hides for clothing and increased wool tax so he made 200,000 pounds in 3 years from tax
E told the Church they must pay 50% of its earnings to tax, Pope said he shouldn’t pay but eventually backed down in 1296 and gave some money but it wasn’t enough to fund his wars
Aware if their strong position, Bigod and Earl of Hereford gave demands to E, to stop high taxes, when E left for France Bigod went to Exchequer and stopped tax collection an actions that could’ve caused civil war
Bigod was an Earl and baron who was powerful and refused to send soldiers to Gascony where E wasn’t directly fighting
Church was unhappy with 50% tax and taxes cased much dispute with Bigod and Earl of Hereford