Ch.11: Emotion, Reward, Aggression, and Stress
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
emotions
positive or negative experience associated with a certain pattern of physiological activity
two components: physical/physiological reaction & conscious experience or feeling
James-Lange Theory of Emotion
bottom-up: emotion happens b/c of physiological response
external stimulus → perception → physiological response → emotional reaction
Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion
top-down: emotion and physiological response happens at the same time
external stimulus → perception → physiological response & emotional reaction
Schachter-Singer Theory of Emotion
two factor theory: cognitive processing of physiological response (categorize to emotion: happy, sad based on response)
physiological arousal contributes to emotion's intensity, while identity of emotion is based on cognitive appraisal

Voluntary Facial Expression
Cranial Nerve VII originates in facial nuclei in pons
motor cortex
contralateral: right up control left bottom
bilateral: left up control left down
involuntary/spontaneous facial expression
subcortical regions (cortex NOT involved)
basil ganglia → red nucleus → facial nucleus VII → facial nerve VII → contraction of face
Brain regions involving emotional regulation
cingulate cortex: amygdala → cingulate cortex → motor cortex → behavioral response
hypothalamus: physiological response
amygdala: emotion and fear
prefrontal lobe: top-down control over amygdala
judging a situation and respond accordingly
regions associated with reward
MFB
lateral hypothalamus (orexin)
mesolimbic pathway (dopamine)
medial forebrain bundle (MFB)
connects VTA to lateral hypothalamus (orexin) and nucleus accumbens
mesolimbic pathway
dopamine in VTA → nucleus accumbens → activate receptor → feel pleasure
lateral hypothalamus
orexin (increase motivation) → VTA and nucleus accumbens
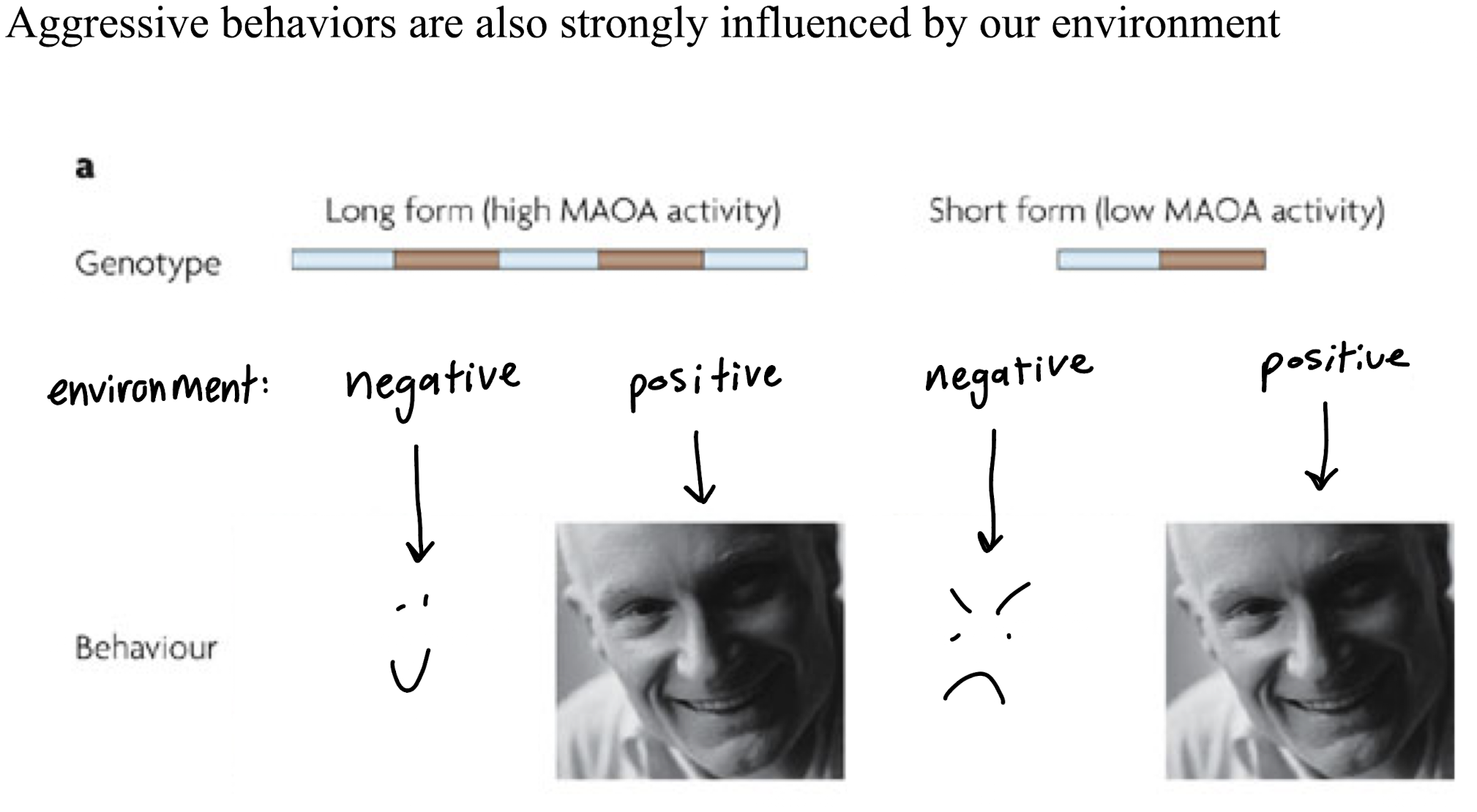
genetic of aggression
MAO-A protein = destroys monoamine
low MAO-A = not efficient in destroying → more monoamine = more aggressive
high MAO-A = destroys more → less monoamine = more anxiety and affiliative behavior

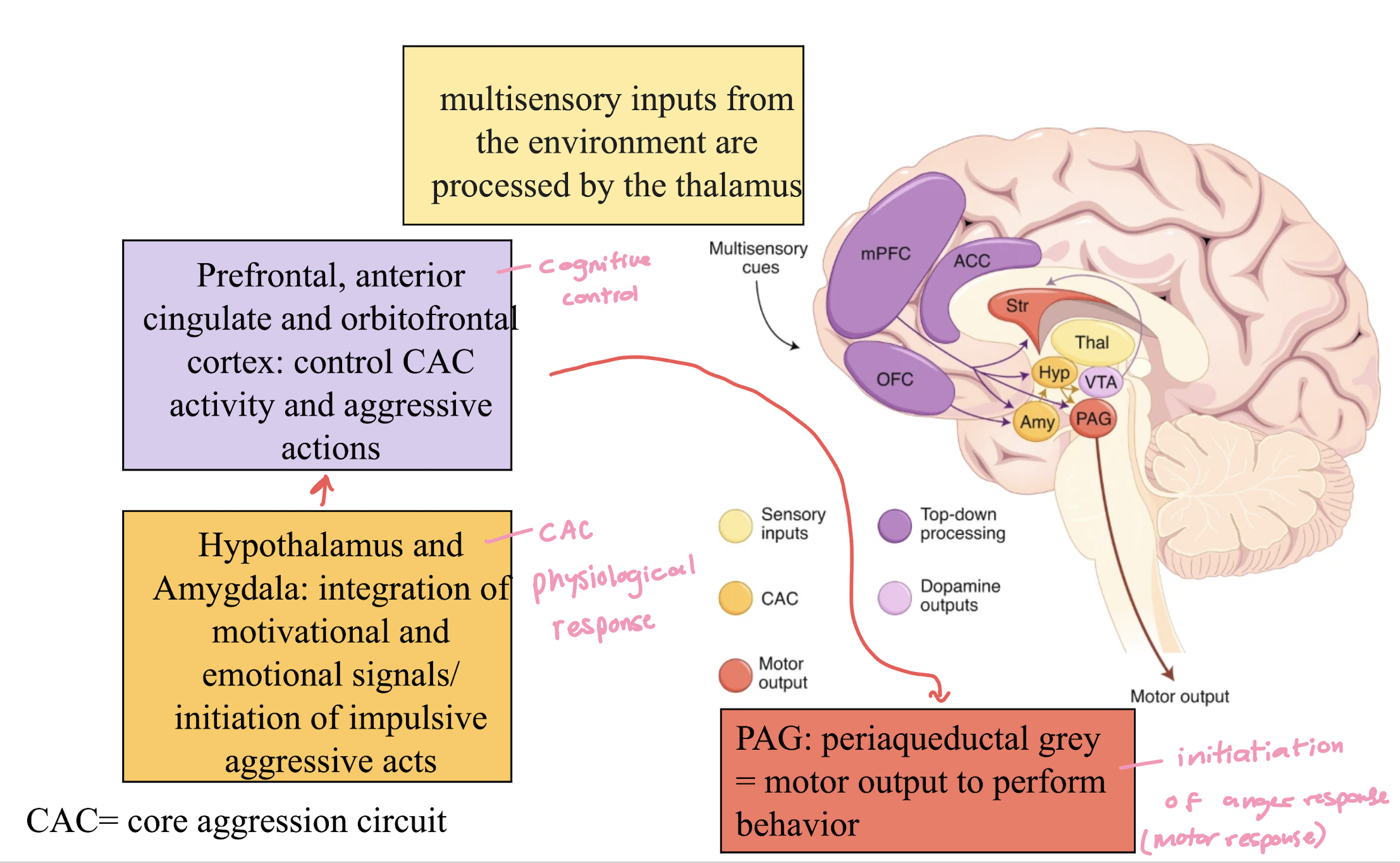
brain regions associated with aggression
hypothalamus & amygdala: motivational + emotional signals/initiations of impulsive aggressive acts (physiological response)
prefrontal, anterior cingulate cortex: control CAC activity and aggressive actions (cognitive control)
PAG: initiation of anger (motor) response
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
SNS stimulates adrenal medulla for norepinephrine/epinephrine/adrenaline = increase output from heart and gives energy for fight/flight response
very fast - first response to stressful stimulus
Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal (HPA) Axis
cortisol = gives even more energy when stress lasts long (a few mins)
slow response and long-lasting (activated after adrenal gland activated)
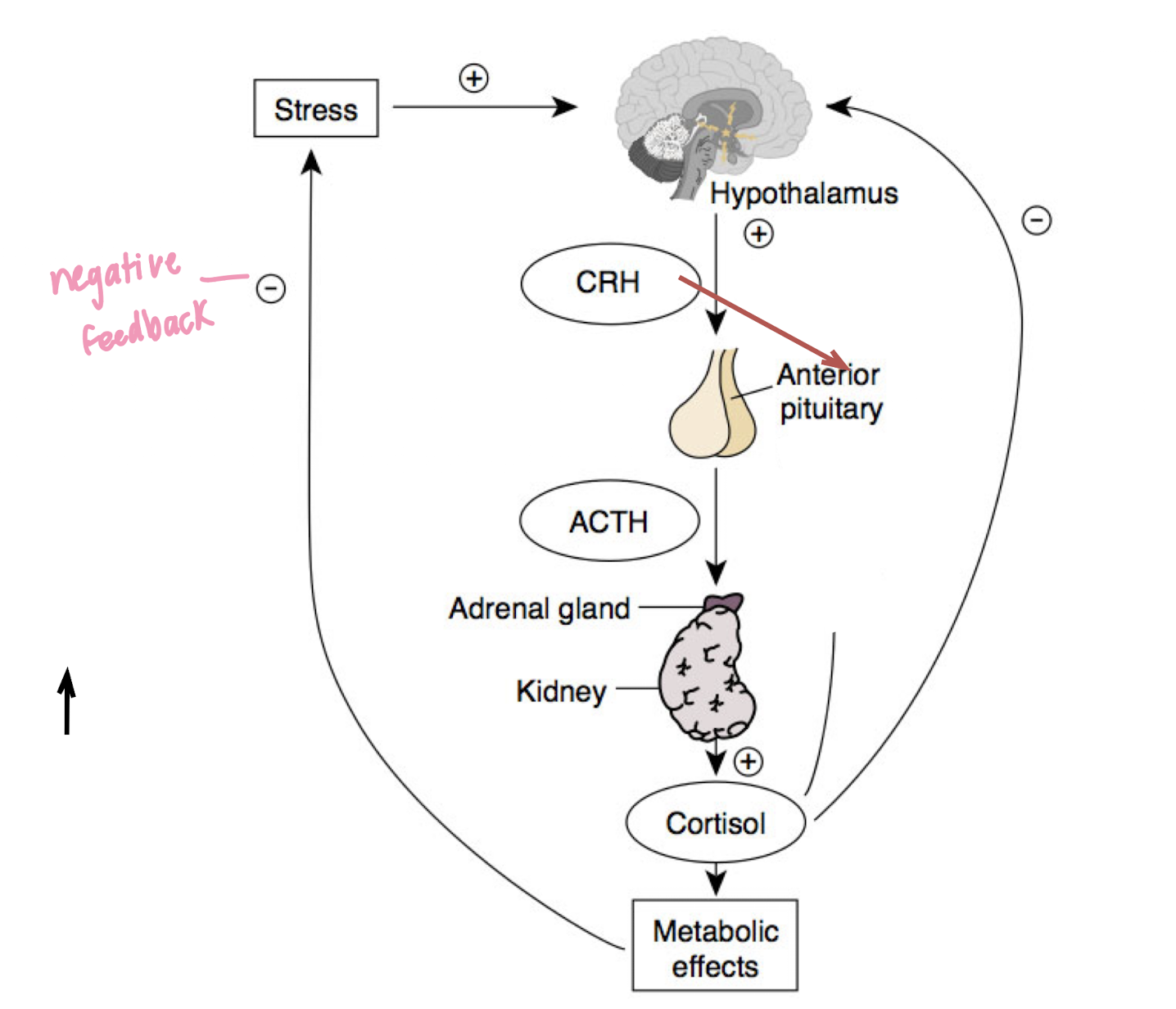
negative and positive effects of stress
positive: can make you more motivated to respond; increase immune system
negative: too much stress = compromise immune system