Week 1: Topic 1B - Management Theory
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Breakdown of Viewpoints
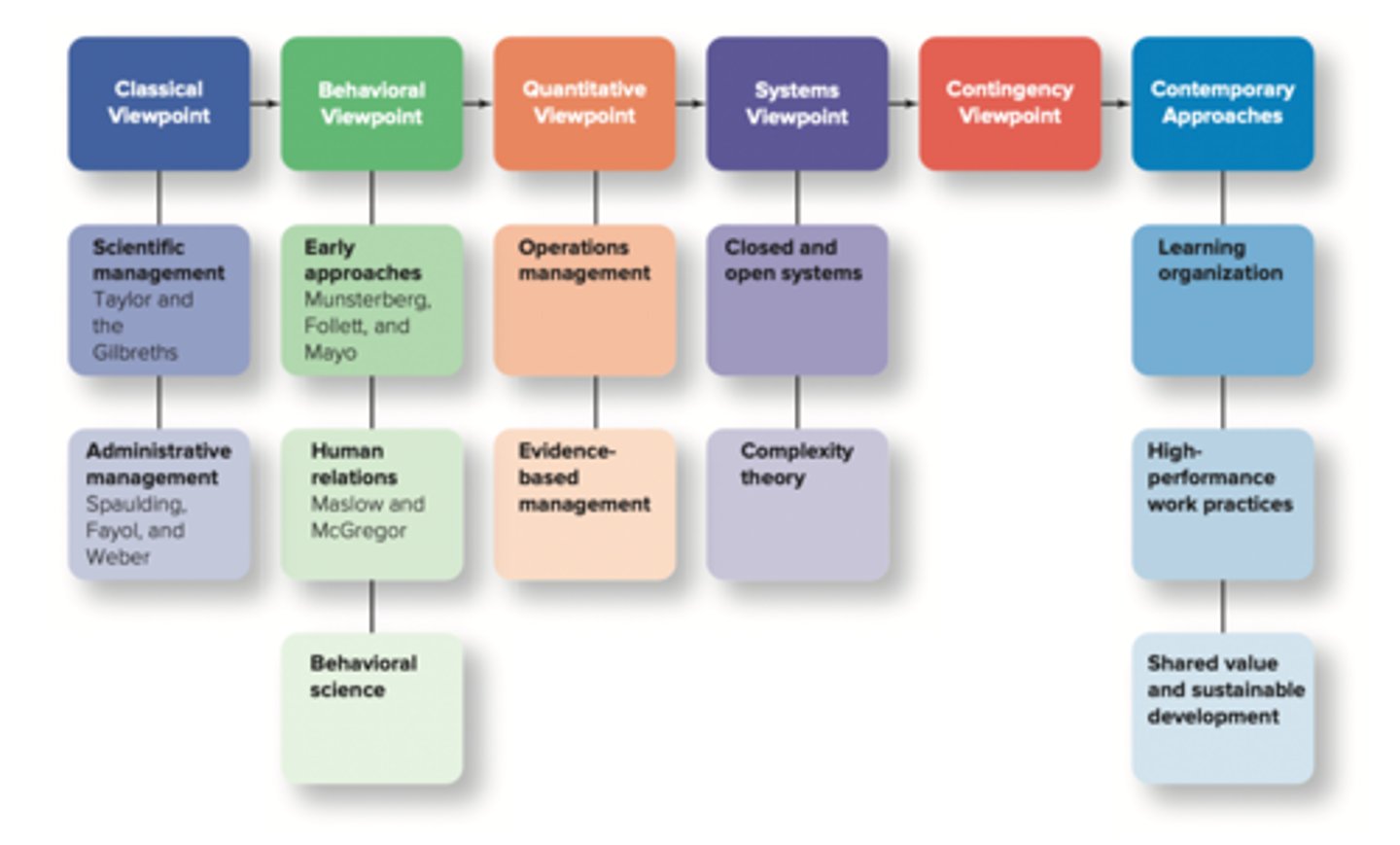
Classical Viewpoint: Scientific Management
- Emphasized the scientific study of work methods to improve the productivity of individual workers
- Key assumption of Scientific Management: people are rational.
Classical Viewpoint: Administrative Management
Concerned with managing the total organization
Behavioral Viewpoint
Emphasized the importance of understanding human behavior and motivating employees toward achievement.
Developed over three phases:
1. Early behaviorism
2. The human relations movement.
3. Behavioral science
Behavioral Viewpoint: Mayo Studies
Mayo led a research group and the conclusion is known as the "Hawthorne effect": Employees worked harder if they received added attention, and thought that managers cared about their welfare and that supervisors paid special attention to them.
Behavioral Viewpoint: Human Relations Movement
Proposed that better human relations could increase worker productivity
Maslow and McGregor
McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y
Theory X: Pessimistic, negative view of workers
Theory Y: Optimistic, positive view of workers
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- Physiological
- Safety
- Love/belonging
- Esteem
- Self-actualization
Quantitative Viewpoint
Application to management of quantitative techniques, such as statistics and computer simulations. Includes operations management and evidence-based management
Quantitative Viewpoint: Operations Management
Focuses on managing the production and delivery of an organization's products or services
Evidence-based Management
Translating principles based on best evidence into practice to make decision making more rational
Systems Viewpoint
Regards the organization as a system of interrelated parts
Systems Viewpoint: The Four Parts of a System
1. Inputs
2. Transformational processes
3. Outputs
4. Feedback
Systems Viewpoint: Open and Closed Systems
Closed: little interaction with their environment
Open: continuous interaction with their environment
Contingency Viewpoint
Emphasizes that a manager's approach should be contingent on the individual and environment situation
Contemporary Approaches
Management theory continues to evolve, three developments of theory:
- Learning organization
- High performance work practices
- Shared value and sustainable development
Contemporary Approaches: Learning Organization
- Creating and acquiring knowledge
- Transferring knowledge
- Modifying behavior
Contemporary Approaches: High-Performance Work Practices
Enhancing an employee's ability and want to contribute, and improves an organization's ability to keep high performers
Contemporary Approaches: Shared Value and Sustainable Development
Literally the definition of sustainable development