Introduction to Environmental Assessment
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/88
Earn XP
Last updated 4:05 PM on 2/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
1
New cards
Environmental Impact Assessment
A process used to predict the environmental consequences of a plan, policy, program or project prior to the decision to move forward with the proposed action.
2
New cards
Environmental Change
The difference in the condition of a particular element over a period of time.
3
New cards
Environmental Effect
The difference in the condition of a particular element under project-induced change versus what that condition might be in the absence of the project.
4
New cards
Steps in the EIA process
1. Pre-Project Planning
2. Project description
3. Screening
4. Scoping and baseline assessment
5. Impact assessment
6. Identifying strategies for managing impacts
7. Significance determination
8. Submission and reviews of the EIS
9. Recomendations and decision statement
10. Implementation and follow up programs
5
New cards
Impact Prediction
The identification of potential changes in the environment which requires a knowledge of the baseline conditions
6
New cards
Screening
The narrowing of the application of EA to projects that require assessment because of the potential for adverse effects or because EA is required by way of certain regulations
7
New cards
Three approaches to screening
1. Case-by-Case approach
2. List-based approach
3. Hybrid approach
8
New cards
List-based approach
Relies on a project list delineating which projects require an EIA based on thresholds or project type
9
New cards
Precautionary Principle
States that a lack of information on the project's impact should not be an excuse to approve the activity and avoid an EIA.
10
New cards
Scoping
Determining the issues and parameters that should be addressed in EA, establishing the spatial and temporal boundaries of the assessment, and focusing the assessment on the relevant issues and concerns
11
New cards
Valued Components (VCs)
Aspects of the environment, physical and human, that people value and that are considered important from scientists and public perspectives, thus warranting detailed consideration in the EIA.
12
New cards
How do we measure variation in VEC?
* Identification of indicators
* Establishing VEC objectives using benchmarks, points of reference, or threshold, limit to change accepted;
* Establishing VEC objectives using benchmarks, points of reference, or threshold, limit to change accepted;
13
New cards
Impact management
The phase that follows the identification of environmental effects. Translates those findings into recommendations to enhance positive outcomes.
14
New cards
Impact Management Hierarchy
The adequacy of impact management strategies in EA depends on their success in reducing the significant, risk or severity of adverse effects
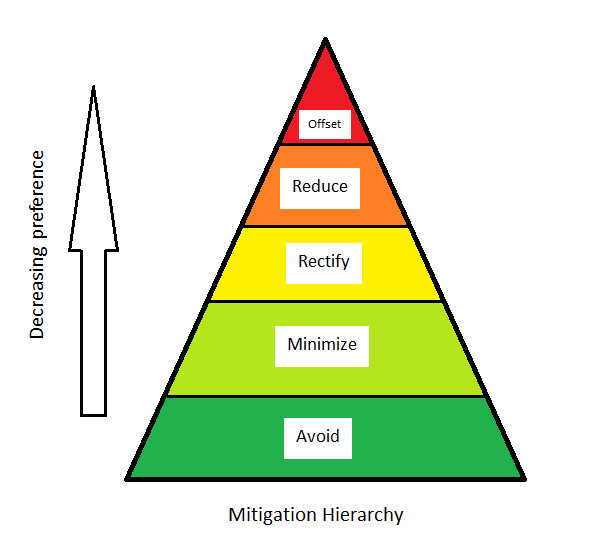
15
New cards
Accuracy
The closeness of a predicted value to its true value.
16
New cards
Precision
The level of exactness assocated with an impact prediction
17
New cards
Determine impact significance
The importance or value if the affected component is usually based on societal, ecological, economic, and political values or level of public concerns.
18
New cards
Duty to consult
The formal, legal obligation for the government to consult with any Indigenous peoples. Cannot be wholly delegated to other parties, such as a project proponent
19
New cards
Public participation
The involvement of individuals and groups that are positively and negatively affected by a project that is subject to a decision-making process.
20
New cards
3 elements of follow-up programs
1. Monitoring
2. Auditing
3. Ex-post evaluation
21
New cards
Environmental Impact Statement
Describes the proposed undertaking, the affected environment, likely impacts, and actions to manage and monitor those impacts
22
New cards
Berger Inquiry of 1974
Shaped expectations about how EIA should engage with communities and Indigenous peoples, began the conversation on how to incorporate Indigenous knowledge systems into EIA
23
New cards
Alternatives to a project
Functionally different ways of meeting the need and purpose of the described project, including the option of no project
24
New cards
Alternative means
Different options for carrying out a project when it has been accepted that the proposed project is the most suitable alternative to meet the need or opportunity at hand
25
New cards
Peterson Matrix
One of the several methods for comparing/evaluating alternatives
26
New cards
Screening
Ensures that no unnecessary assessments are carried out but that developments warranting assessment are not overlooked
27
New cards
Physical Activities Regulations
Defines those projects for which an EA is required under the IAA (Designated activities)
28
New cards
Terms of Reference
Provide a roadmap for project proponents , outlining the minimum requirements that must be met when preparing the EIS
29
New cards
Precautionary Principle
Suggests that when scientific information is incomplete but there is a threat of adverse impacts, the lack of full certainty should not be used as a reason to preclude or to postpone actions to prevent harm
30
New cards
Environmental baseline
Considers the past, present, and possible future state of the environment without the proposed project or activity
31
New cards
Baseline study
The identification and analysis of conditions over space and time for the purpose of delineating change, trends, patterns, or limits to assist in impact assessment, impact evaluation, and impact monitoring activities
32
New cards
Impact Matrices
Two-dimensional checklists that consist of project activities on one axis and potentially affected VCs on the other
33
New cards
Advantage of the Leopold Matrix
Can be easily expanded or contracted based on the specific project and environmental context
34
New cards
VC indicators
Important to understanding and tracking actual change in VC conditions and to provide early warning to potential adverse effects
35
New cards
Condition-based indicators
Indicators that provide direct, measurable information about the condition or state of the VC
36
New cards
Stress-based indicators
Indicators that focus on measurable stress or disturbances that affect the VC
37
New cards
Cautionary Threshold
Increased monitoring of VC or indicator conditions and implementation of best-management practices to prevent any further adverse change
38
New cards
Target threshold
Typically political or socially defined - a margin of safety and a mandatory tigger for management action
39
New cards
Critical threshold
Defines maximum acceptable change, socially or ecologically, beyond which impacts may be long-term or irreparable
40
New cards
Basic principles for Spatial Bounding
* Boundaries must be large enough to include relationships between the proposed project, other existing projects and activities, and the VCs
* Natural boundaries should be respected
* Different receptors will require assessment at different scales
* Both local and regional boundaries should. be established
* Natural boundaries should be respected
* Different receptors will require assessment at different scales
* Both local and regional boundaries should. be established
41
New cards
Temporal bounding
Involves the consideration of previous and current activities in the project’s region affecting environmental condition and the reasonably foreseeable activities
42
New cards
Cumulative impacts
The total effect of all activities in an area, accumulating over time and across space, combined with larger-scale stress caused by climate change and transboundary effects acting on a single VC
43
New cards
Measures that can address uncertainty in impact prediction
* Probability analysis
* Sensitivity analysis
* Confirmatory analysis
* Uncertainty disclosure
* Sensitivity analysis
* Confirmatory analysis
* Uncertainty disclosure
44
New cards
Uncertainty disclosure
Requires that practitioners disclose their assumptions and uncertainties about impact prediction
45
New cards
Uncertainty Matrix
Can be used by practitioners to help communicate uncertainties and determine whether or when additional information might be required
46
New cards
Environmental Management Plans (EMPs)
Prepared by the proponent and detail the specific impact mitigation strategies and the ways in which they are to be implemented (typically required)
47
New cards
Adaptive Management Strategy
A structured, iterative process of robust decision making in the face of uncertainty, with an aim to reducing uncertainty over time via system monitoring.
48
New cards
Impact Benefit Agreements (IBAs)
Are external to the regulatory EA process but often occur in conjunction in EA between an industry proponent and (usually) an affected community or Indigenous group
49
New cards
Residual Effects
The effects that remain after proposed mitigation measures are taken into consideration
50
New cards
Monitoring
Determining whether change in a VC or indicator has occurred and to understand the nature, cause, and magnitude of the change by repetitive observation, measurement, and recording over a defined period of time
51
New cards
Auditing
The assessment of the results from monitoring activity against specified standard or expectations and public reporting of results
52
New cards
Ex-post evaluation
The collection and appraisal of information about a project’s impacts and making decisions on remedial actions and communicating the results
53
New cards
Compliance Monitoring
Ensures that a project is operating within the specified guidelines and that mitigations have been implemented as committed by the proponent or as required under the conditions of project approval
54
New cards
Implementation monitoring
Involves checking to ensure that operating procedures are being followed and commitments or conditions are being met
55
New cards
Regulatory permit monitoring
Involved the tracking of conditions that may be required for a proponent’s maintenance or renewal of project permit
56
New cards
Monitoring of agreements
Focused on tracking socio-economic commitments regarding such matters as housing, employment, and infrastructure demands
57
New cards
Ambient environmental quality monitoring
Focuses on the biophysical environment, assessing data about environmental conditions pre and post project implementation ro assess impacts
58
New cards
Effectiveness monitoring
Focuses on the mitigation actions and assesses if those actions are successful in managing impacts at an acceptable level
59
New cards
Types of compliance monitoring
* Implementation monitoring
* Regulatory permit monitoring
* Monitoring of agreements
* Regulatory permit monitoring
* Monitoring of agreements
60
New cards
Types of monitoring for management
* Ambient environmental quality monitoring
* Effectiveness monitoring
* Cumulative effects monitoring
* Effectiveness monitoring
* Cumulative effects monitoring
61
New cards
Effectiveness monitoring
Assessing whether the implemented mitigation actions manage anticipated impacts and hold impacts to acceptable levels
62
New cards
Cumulative effects monitoring
Focuses on monitoring the accumulated state or indicators of stress associated with developments in a region
63
New cards
Types of monitoring for understanding
* Experimental monitoring
* Monitoring for knowledge
* Monitoring for knowledge
64
New cards
Experimental monitoring
Generates information and knowledge about environmental systems and their impacts through research methodologies guided by questions that test specific hypotheses
65
New cards
Monitoring for knowledge
A type of data collection and reporting that takes place after impacts occur
66
New cards
Early warning indicators
Serve to indicate stress of particular VC before the VC becomes adversely affected
67
New cards
Effects-based monitoring
Focuses on the condition or performance of the receiving environment - based on the premise that measuring change in environmental indicators is the most direct means of assessing change
68
New cards
Control-impact design
A monitoring design that compares project-exposed sites to control sites to help differentiate between project impacts and other natural sources of change
69
New cards
Gradient-to-background monitoring
When a well-established control site is not possible, this approach assumes that the effects on a VC should decrease and reach ambient conditions at increasing distances from the project
70
New cards
Indigenous knowledge
A cumulative body of knowledge, practice, and belief,evolving by adaptive process and handed down through generations by cultural transmission, about the relationship of living beings with one another and with their environment
71
New cards
Bridging knowledge systems
Integrating both scientific knowledge and traditional knowledge into EIA
72
New cards
Indigenous-led impact assessment
A process completed prior to approvals or consent for a proposed project which is designed and conducted by Indigenous parties
73
New cards
Project-centered approach
Focuses on the effects of a single project or activity on each of the VC
74
New cards
Valued component-centered approach
Focuses on the VCs and considered the impacts of all sources of distributable or stress - whether caused by individual projects, other types of land use and human activities, or natural drivers
75
New cards
Regional Assessment
Studies conducted in areas of existing projects or anticipated development to inform planning and management of cumulative effects and inform project impact assessments.
76
New cards
Effects-based CEA
Focused on assessing existing environmental conditions relative to a reference condition and is typically retrospective in design
77
New cards
Stressor-based CEA
Focus is on quantifying past and present patterns and trend in the distribution of human disturbance in a region and then projecting disturbances into the future under different scenarios of land use and management
78
New cards
Analysis scale
Used to examine VC and impacts across space, typically represented by ideas such as data resolution, detail, and granularity
79
New cards
Phenomenon scale
Refers to the spacial units within which various processes operate or function
80
New cards
Administrative scale
Reflects the realities imposed by jurisdictions, land-use plans, or regulatory processes
81
New cards
Retrospective analysis
Involves looking at the past to determine key condition changes and drivers of change to understand the present accumulated state
82
New cards
Prospective analysis
Focuses on predicting and evaluating how indicators or conditions might respond to additional stress in the future
83
New cards
Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA)
Identifying and assessing a range of strategic initiatives - typically policies, plans, and programs (PPP) - at an early stage when there is flexibility with respect to future actions and the decisions being taken
84
New cards
Compliance-based SEA
Investigates whether, and to what extent, a proposed PPP complies with specified objectives, policies, or commitments and explores options to ensure compliance
85
New cards
Project-like SEA
Focused on assessing the potential environmental impacts of a PPP, and comparing the PPP’s impacts to viable alternatives
86
New cards
Strategic futures SEA
Identifying and assessing the potential implications of alternative future scenarios or land use, evaluating the relative risks and opportunities, and establishing a preferred strategic direction or PPP approach
87
New cards
Strategic transitions SEA
Used to better understand the governance context of strategic initiatives, including PPPs, and influence institutional transitions towards more sustainable outcomes
88
New cards
Impact measurement
The characteristics of an impact (i.e. magnitude, spatial extent, duration)
89
New cards
Impact meaning
The context by which the characteristics of impact are viewed and interpreted (i.e. regulatory, social, environmental)