GES 121 - Clouds
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
About Clouds
made up of water droplets and/or ice crystals, in between this is generally 100% relative humidity - saturation within a cloud
equilibrium between water vapour/liquid
forms when air is nearly saturated AND contains particles (condensation nuclei needed to induce condensation)
cloud nights are warmer than clear nights because clouds continue to radiate depending on temperature
10 types of clouds
Supercooled
Water can remain in liquid state much below freezing in a clean atmosphere
water vapour needs particles to condense upon
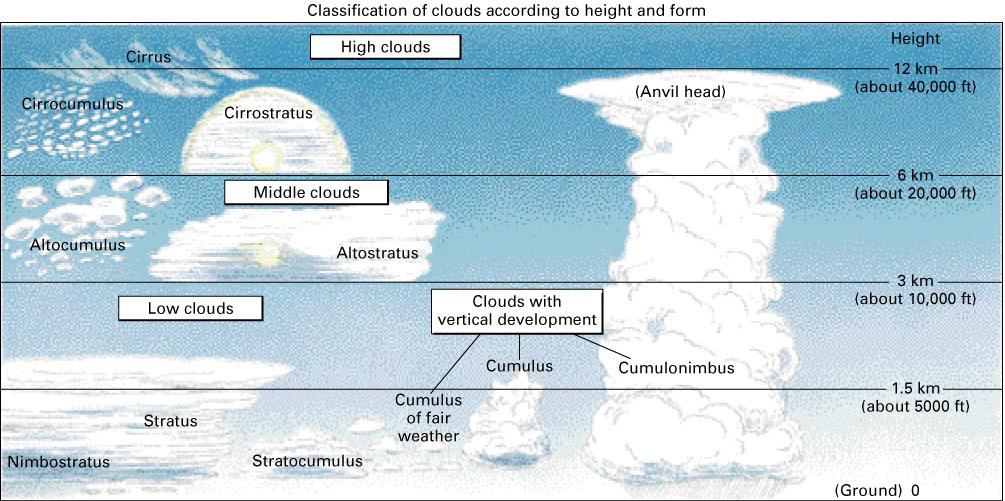
Cloud Classification
10 (11-ish) types generally classed by:
altitude:
low (stratus, cumulus)
composed of water droplets
middle (alto-)
composed of both ice crystals and water droplets
high (cirro-, cirrus)
all ice crystals, often wispy
clouds can transcend levels
cumulonimbus has vertical development - anvils out because can’t extend into stratosphere
and shape:
heaped up (-cumulus)
piled up clouds, lumpy appearence
layered (-stratum)
whether they’re producing rain (nimbus)
usually at least 2k of thickness before precipitation, dark
Types of Clouds
low:
stratus
statocumulus
mid:
altocumulus
altostratus
high:
cirrostratus
cirrus
cirrocumulus (extra!)
cumuliform:
cumulus
cumulinimbus
mamatus
funnel clouds
Low Level Clouds
Stratus:
uniform grey tone
Stratocumulus
alternating dark/light, not a lot of vertical development, unlikely for precipitation
Mid Level Clouds
Altocumulus:
heaped up, rows across sky, appear larger because they’re closer to the ground, may/may not have dark base (can get reflection off of the surface or lower clouds)
3-5 fingers in size
Altostratus:
like the sun is dimly visible through the cloud, because of likely water vapour, will not form halo, fairly uniform gray
High Level Clouds
Cirrostratus:
forms veil, light tone, made up of ice crystals
sun shining through will form a halo around the sun, maybe moon
sundogs are a similar phenomenon, internal reflection of ice crystals; crystals close to the surface form false suns
Cirrus:
“hooked”, fibrous, happens when precipitating, snow carried by high altitude winds to create “fall streaks”
Cirrocumulus:
ice crystals, heaped up in atmosphere, some precipitation but never reaches ground, appear small because high up
a finger held at arm’s length = 1° of angle (if same size, probbaly cirrus)
never cover the whole sky
Cumuliform Clouds
Cumulus:
fluffy, flat bases
towering cumulus can give showers, but not severe precipitation
Cumulonimbus:
often but not always “animal top”, considerable vertical development, big!
Mammatus:
often on the base/side of a cumulonimbus, look kinda creepy, most thunderstorms have them, signify unstable conditions in the atmosphere
often can’t see them without specific lighting from the side-ish, like oblique sun angle, or lightning
Funnel Clouds:
cold core, fairly high up in the atmosphere, very rarely touches ground unless large and lots of circulation around it
if you see spinning and it reaches the surface, then tornado or small land spout
Fog
Cloud layer close/at the surface, essentially a stratus cloud close to the ground
Two types:
Radiation/ground fog
forms overnight when temperature is close to the dew point, high humidity (clouds have high relative humidity)
no wind! must be clear and calm because wind is turbulent and mixes the air
sun warms the ground through fog, warming and circulating the air, so fog then disperses or lifts to become a stratus cloud
Advection fog
wind! warm moist air blowing over cold surface
contact causes temperature to fall to dew point