module 2 - foundations in biology
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
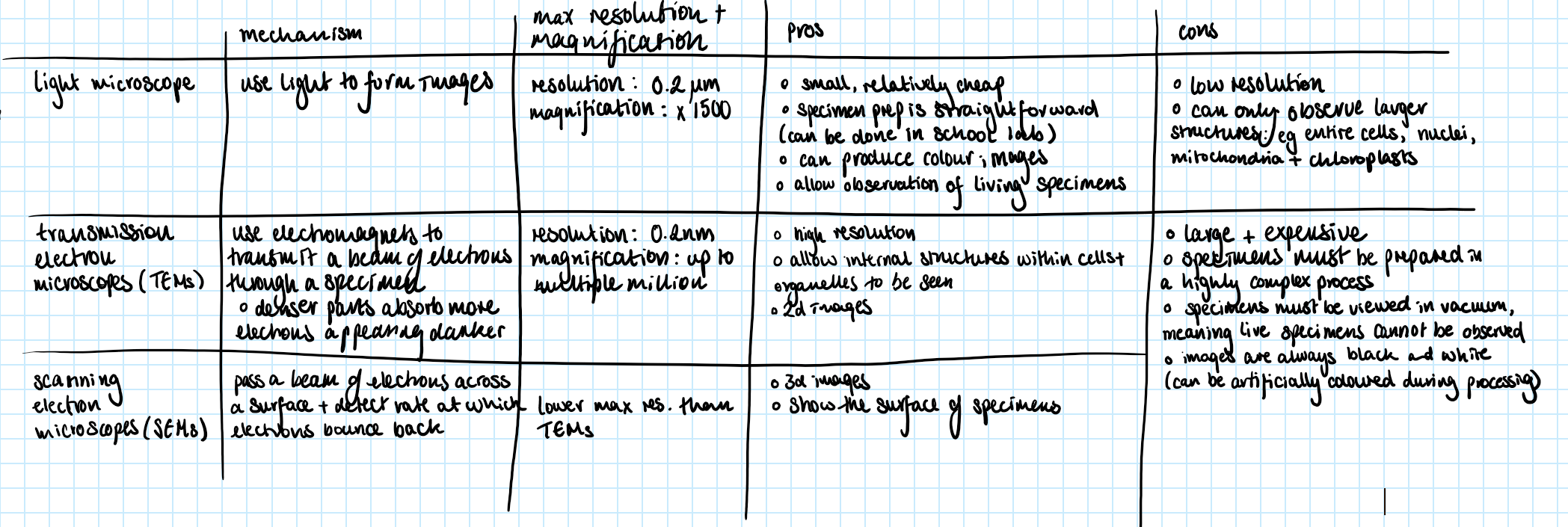
2.1.1 a) the use of microscopy to observe and investigate the different types of cell and cell structure in a range of eukaryotic organisms
2.1.1 b) the preparation and examination of microscope slides for use in light microscopy
graticule: small disc with an engraved ruler, can be placed on eyepiece and act as a ruler in the field of view
has no fixed units so must be calibrated for the objective lens in use
can be used alongside a stage micrometer to work out how much each graticule unit is worth
stage micrometer scale: a scale engraved on a microscope slide
2.1.1 c) the use of staining in light microscopy
many tissues are naturally transparent, allowing both light and electrons to pass through
the dyes used absorb specific colours of light while reflecting others - this makes the structures within the specimen that have absorbed the dye visible
certain tissues absorb certain dyes, depending on their chemical nature
specimens or sections are sometimes stained with multiple dyes to ensure the different tissues in the specimen show up - known as differential staining
most colours in photomicrographs are not natural - apart from chloroplasts
toluidine blue turns cells blue
phloroglucinol turns cells red/pink
2.1.1 f) the difference between magnification and resolution
magnification: the number of times larger an image is than the object
resolution: the ability to distinguish two separate points on an image as separate objects

2.1.1 g) the ultrastructure of eukaryotic cells and the functions of the different cellular components
nucleus: contains chromatin (material that chromosomes are made of) - chromosomes are made of sections of linear DNA tightly wound around proteins called histones, separated from the rest of the cell by a double membrane (nuclear envelope) with many pores
nucleolus: sites of ribosome production within the nucleus that can be observed as darkly stained regions
nuclear envelope: separates nucleus from cytoplasm - has many pores, allowing mRNA and ribosomes to travel out of the nucleus and enzymes and signalling molecules to travel in
rough endoplasmic reticulum: formed from continuous folds of membrane continuous with the nuclear envelope - surface covered in ribosomes, processing the proteins made there
smooth endoplasmic reticulum: does not have ribosomes on the surface, involved in the production, processing and storage of lipids, carbohydrates and steroids
Golgi apparatus: flattened sacs of membrane similar to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum - modifies proteins and lipids before packaging them into Golgi vesicles - vesicles transport proteins and lipids to required destination - proteins are usually exported, put into lysozymes or delivered to membrane-bound organelles
lysozymes: specialised vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes - break down waster material such as worn-out organelles and used extensively by cells of the immune system and in apoptosis
centrioles: hollow fibres made of microtubules - two perpendicular centrioles form a centrosome, which organises the spindle fibres during cell division
2.1.1 i) the interrelationship between the organelles involved in the production and secretion of proteins
the nucleolus manufactures ribosomes for protein synthesis in the the rough endoplasmic reticulum
the nucleus manufactures mRNA which is needed by the ribosomes to make proteins
the ribosomes in the rough endoplasmic reticulum makes proteins
the rough endoplasmic processes the proteins which are then sent in vesicles to the Golgi body
the Golgi body further processes the proteins and sends them in vesicles to the plasma membrane
the vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane to secrete the finished protein product
2.1.1 j) the importance of the cytoskeleton
extensive network of protein fibres - made up of microfibres and microtubules
microfilaments: solid strands mostly made from protein actin
microtubules: tubular strands mostly made from protein tubulin
strength + support: forms scaffolding that helps to maintain shape of cell + keeps organelles in position
intracellular movement: forms tracks along which organelles can move
cellular movement: enables movement via cilia + flagella
protrude from cell surface + contain microtubules that are responsible for moving them
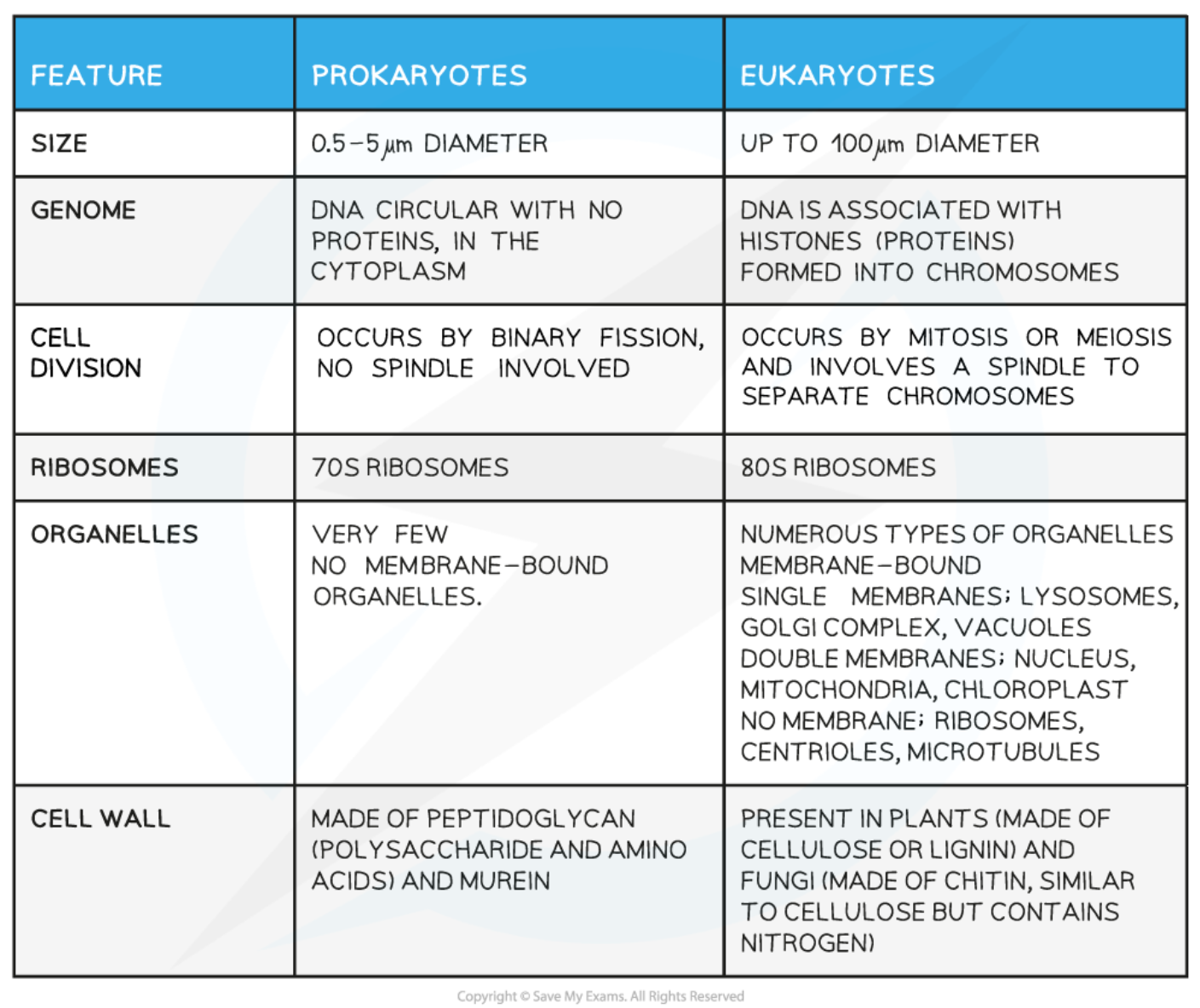
2.1.1 k) the similarities and differences in the structure and ultrastructure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells