2.3 The determinants of the supply of goods and services
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Supply
The quantity of a good or service that a producer is able and willing to supply at a given price during a given period of time.
Supply curves are upward sloping because:
If price increases, it is more profitable for firms to supply the good, so supply increases
high prices encourage new. firms to enter the market, because it seems profitable, so supply increases.
with larger outputs, firms costs increase, so they need to charge a higher price to cover the costs.
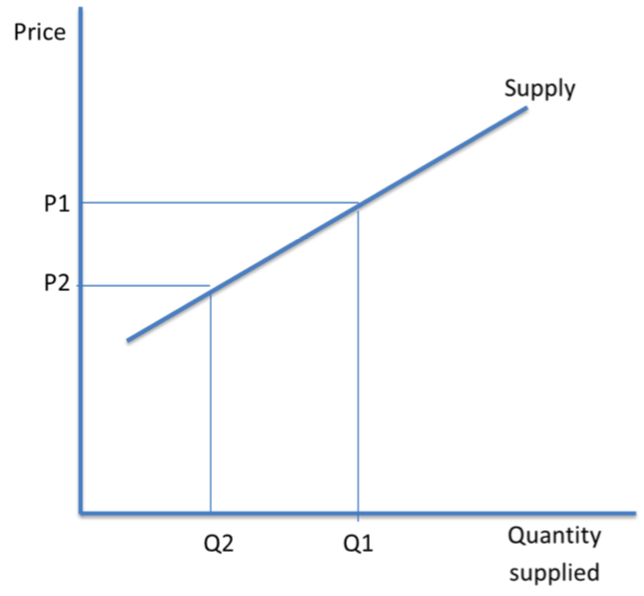
Movements along the supply curve
At price p1, a quantity of Q1 is supplied. At the lower price of P2, Q2 is supplied. This is a contraction of supply. If the price increases from P2 to P1, QS increases from Q2 to Q1. This is an expansion of supply. Only changes in price will cause these movements along the supply curve. This is based on the theory of the profit motive. Firms are driven by the desire to make large profits.
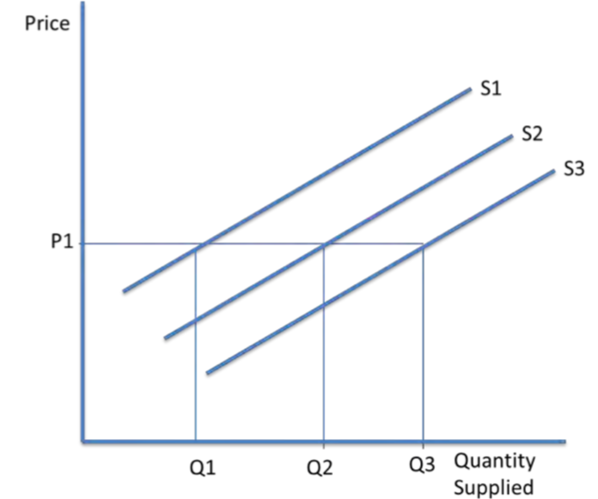
Shifting the supply curve :
Price changes do not shift the supply curve. A shift from S1 to S2 is an outward shift in supply, so a larger quantity of goods is supplied at the market price of P1. A shift from S3 to S1 is an inward shift in supply, More goods are supplied at the market price of P1.
Factors that shift the supply curve
PINTSWC
Pintswc
P - Productivity - Higher productivity causes an outward shift in supply, because average costs for the firm fall.
pIntswc
I-Indirect taxes incward shift in supply
piNtswc
N - Number of firms - The more firms there are the larger the supply
pinTswc
T- Technology - More advanced the technology causes an outward shift in supply
pintSwc
S - Subsidies - Cause an outward shift in supply
pintsWc
w - weather - For agricultural produce. Favourable conditions will increase supply.
pintswC
C - Cost of production - If the cost of production falls the firm can afford to supply more. If the cost of production rises, such as higher wages, there will be an inward shift in supply.
depreciation in exchange rate
will increase the cost of imports, which will cause an inward shift in supply