Experimental Methods Exam 2
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
describe a research design where one way ANOVA would be the appropriate statistical technique for analysis
when we have an IV and three or more groups
describe the basic logic of ANOVA
1) based on the ratio of 2 variances [within group and between group]
2)create an F ratio
3)individual treatment will tend to divide out; therefore, f=treatment
within group variance
sensitive to individual differences
between group variance
sensitive to the treatment and individual differences
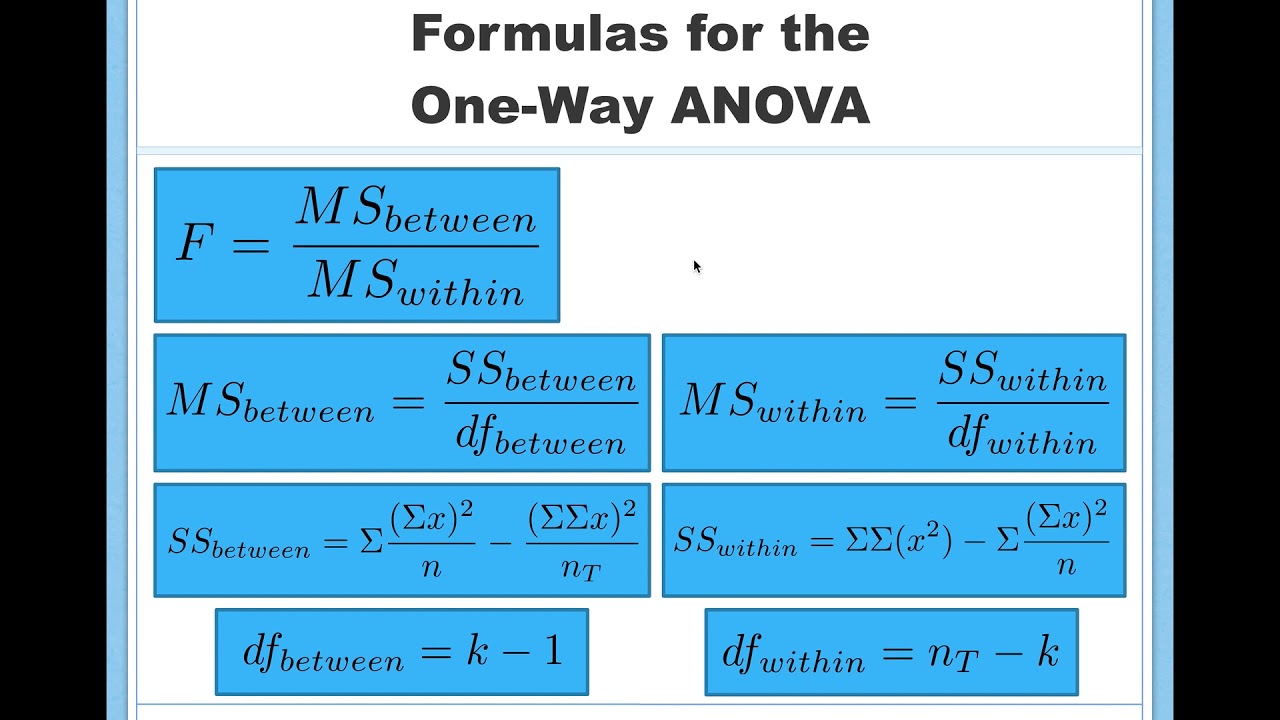
F ratio
between group variance/within group variance (aka treatment + individual differences/individual differences)
what value for F would we expect if the null hypothesis were true?
numbers around 1
why do we expect an f value around 1?
this means that there is no treatment effect. it is just individual differences/individual differences which equals 1
what is the purpose of post hoc tests?
the purpose is to determine which groups are significantly different from one another
what is actually measured by sum of squares between?
take each group mean minus the grand mean
what is actually measured by sum of squares within?
take each score and subtract out the group mean; measure of individual differences
you will need to report F tests using APA style formatting
F(2, 27)= 18.971, p= 0.000
F(df) = (f value), p= (sig value)
what are factorial designs?
a design that has two or more independent variables
what is a factor?
is either an independent variable or a subject variable
what is a level?
the groups in a factor
what is a main effect?
the effect of one factor averaging over the levels of the second factor
what is an interaction?
when the effect of one factor depends on the level of the second factor
what is a marginal?
the average across the levels of a factor
What is a subject factor in experimental design?
A subject factor, also known as a between-subjects factor, is an independent variable where different participants are assigned to different conditions, allowing comparison between distinct groups.
What is a within-subject factor in experimental design?
A within-subject factor, or repeated measures factor, is an independent variable where the same participants are exposed to all conditions, allowing for control of participant-related variability.
what is a mixed factorial design?
has one between subject factor and one within subject factor
how many subjects would be needed if you wanted to conduct a 2x3 completely between factorial design with 10 subjects per group?
60
what is a synergistic interaction?
lines become close at one point
what is a cross-over interaction?
there is a clear cross; best kind of interaction
what is the problem associated with conducting factorial designs with more than 3 factors?
it becomes complicated very quickly
in factorial notation, which factor is listed 1st and which is listed 2nd?
between factors are listed 1st
within factors are listed 2nd
what is the basic problem associated with the one group pretest-posttest design?
doesn't allow researchers to eliminate alternative explanations for results (doesn't rule out potential confounds)
how can you modify the pretest-posttest design to make it better detect the influence of confounds?
you could add an additional pretest or change it to a mixed factorial design
one way repeated measures experimental design
has two pretests and one post test
what advantage does the mixed factorial design have over the one way repeated measures design as a means of detecting the influence of temporal confounds in an experiment?
you have a treatment and a control group
what are the two types of error that need to be controlled in experiments?
systematic error: (bias that occurs in a study; confounds)
random error: (individual differences)
temporal confound: history
anything external to the experiment that could cause bias over time
temporal confound: maturation
anything internal to an individual that might change across time
temporal confound: sequencing
bias due to the sequence that you give the different experimental conditions
temporal confound: statistical regression
extreme scores on a first measure tend to regress toward the mean on a second measure
temporal confound: mortality
when subjects drop out of the experiment
non-temporal confound: selection
biases in the way subjects are assigned to groups
non-temporal confound: differential reactivity
when people react differently to the experimental condition they were placed in