Week 6 - 9 PNC121
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:12 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
1
New cards
Research
It is a systematic process in which questions that generate knowledge are asked and answered.
2
New cards
Nursing Research
is a systematic examination of phenomena important to the nursing discipline, as well as to nurses, their patients, and families. Its purpose is to expand the knowledge base for practice by answering nurses' questions. addresses a range of issues related to actual and potential patient populations and to individual and family responses to health problems.
3
New cards
quantitative nursing research
is the investigation of nursing phenomena that can be precisely measured and quantified. Examples are pain severity, rates of wound healing, and body temperature changes.
4
New cards
Qualitative nursing research
Poses questions about nursing phenomena that cannot be quantified and measured. Examples that may be used in nursing research include ethnography, phenomenology, grounded theory, participatory action research, interpretive descriptive research, and narrative inquiry.
5
New cards
Nursing Theory
is to organize knowledge about nursing to enable nurses to use it in a professional and accountable manner
6
New cards
Research Literacy
An essential competency for evidence-informed practice; It is the ability to locate, understand and critically evaluate empirical literature for application in practice
7
New cards
Evidence-Based Nursing
The evidence-based nurse knows what needs to be done, how it should be done, and the evidence that supports his or her practice.
8
New cards
Evidence-Informed Practice (EIP)
Continuous, interactive process involving the explicit, conscious, and judicious consideration of the best research evidence available to make collaborative decisions between the health care team and the patient and family when providing patient care
9
New cards
Steps of the Evidence-Informed Practice Process
1. Ask a question that clearly presents the clinical problem, using the PICOT format.
2. Identify and gather the most relevant and best evidence.
3. Critically appraise the evidence.
4. Integrate all evidence with clinical expertise, patients' preferences, and patients' values to make a practice decision or change.
5. Evaluate the outcome of the practice decision or change.
2. Identify and gather the most relevant and best evidence.
3. Critically appraise the evidence.
4. Integrate all evidence with clinical expertise, patients' preferences, and patients' values to make a practice decision or change.
5. Evaluate the outcome of the practice decision or change.
10
New cards
medical diagnosis
the identification of a disease condition on the basis of a specific evaluation of physical signs and symptoms, the client's medical history, and the results of diagnostic tests and procedures
11
New cards
Clinical Manifestations
· Signs evident upon examination
· Symptoms identified through client history and interview
· Symptoms identified through client history and interview
12
New cards
Medical or Surgical Interventions
Interventions ordered based on medical diagnosis, e.g. medications, catheterization, wound care, g-tube insertion
13
New cards
Nursing Assessments
focus on the patient's response to health problems
14
New cards
Common Nursing Diagnoses/Nursing Problem Statements
· Nursing diagnoses or problems can include an actual problem or an at-risk problem that affects the patient
· Includes a diagnostic label of the problem e.g., impaired physical mobility
· Includes a diagnostic label of the problem e.g., impaired physical mobility
15
New cards
Nursing Interventions
Activities that the nurse plans and implements to help the patient achieve identified outcomes
16
New cards
Independent Nursing Interventions
actions that a nurse initiates without supervision or direction from others. Such as bathing, ongoing assessments, making referrals to other health care professionals, initiating wound care, raising an edematous leg
17
New cards
Dependent Nursing Interventions
actions that require an order from a physician or another health care professional. · E.g. medication administration, specific diet, test and treatments
18
New cards
Critical Thinking
is a complex phenomenon defined as a process acquired through learning and experience.
· Requires purposeful and reflective reasoning.
· Requires purposeful and reflective reasoning.
19
New cards
Importance of critical thinking in nursing
· allows you to test and refine nursing approached, learn from successes and failures, apply nursing research findings, and ensure holistic patient-centred care.
· Nurses recognize that an issue exists, analyzes information about the issue, evaluates information and draws conclusions
· Nurses recognize that an issue exists, analyzes information about the issue, evaluates information and draws conclusions
20
New cards
3 levels of critical thinking in nursing
Basic, Complex, Commitment
21
New cards
5 components of critical thinking
· specific knowledge base, experience, critical thinking competencies, attitudes and standards
22
New cards
General Critical Thinking Competencies
scientific method, problem solving, decision making
23
New cards
The Scientific Method
1. Identification of the problem
2. Collection of data
3. Formulation of a research question or hypothesis
4. Testing of the question or hypothesis
5. Evaluation of the results of the test or study
2. Collection of data
3. Formulation of a research question or hypothesis
4. Testing of the question or hypothesis
5. Evaluation of the results of the test or study
24
New cards
Problem Solving Process
· Involves working through a process of recognizing, clearly defining and then solving a problem
· The nurse obtains information that clarifies the nature of the problem and evaluates possible solutions, then possibly in collaboration with other health care professionals, chooses the best one to implement, and continues to monitor outcomes to determine the effectiveness of the solution
· The nurse obtains information that clarifies the nature of the problem and evaluates possible solutions, then possibly in collaboration with other health care professionals, chooses the best one to implement, and continues to monitor outcomes to determine the effectiveness of the solution
25
New cards
Decision Making
· The product of critical thinking that focuses on problem resolution
26
New cards
Decision making process
identifying the problem, assessing all options, weighing each option against a set of criteria, considering the consequences and then making a final decision
27
New cards
Specific Critical Thinking Competencies
diagnostic reasoning, clinical inference, and clinical decision making
28
New cards
Diagnostic reasoning
the process of determining a patient's health status after making behavioural and physical observations and after assigning meaning to the behaviours, signs and symptoms exhibited by the patient
29
New cards
Clinical Inference
part of diagnostic reasoning and refers to the process of drawing conclusions from related pieces of evidence.
30
New cards
Clinical Reasoning
· nurses collect cues, process the information, come to an understanding of a problem or situation, plan and implement interventions, evaluate outcomes, and reflect on and learn from the process.
31
New cards
Clinical Decision Making
recognizing the most important aspects of a clinical situation, interpreting their meanings, and responding appropriately
32
New cards
How does critical thinking influence clinical judgement and clinical decision making?
· Critical thinking is central to both these processes.
· It helps to help choose the best action to meet a desired goal
· It helps to help choose the best action to meet a desired goal
33
New cards
How do nurses apply critical thinking to nursing?
· Nurses apply the nursing process as a critical thinking competency by assessing , diagnosing, planning, implementing and evaluating patient care
34
New cards
Reflective Practice
a tool for developing critical thought that uses the process of reflection to purposefully recall a situation in order to discover its purpose or meaning.
35
New cards
Reflective writing
gives you the opportunity to describe a clinical experience in your own words, explore your perceptions and understanding of the experience, and become more aware of how you use clinical decision-making skills.Helps you monitor your competency in nursing practice.
36
New cards
Concept Mapping
· Technique that uses a graphic depiction of linear and nonlinear relationships to represent critical thinking
· Allows one to organize (and reorganize) and connect information, making meaning of the concepts
· Allows one to organize (and reorganize) and connect information, making meaning of the concepts
37
New cards
3 steps of concept mapping
38
New cards
5 steps of the nursing process
1. Assessment
2. Diagnosis
3. Planning
4. Implementation
5. Evaluation
2. Diagnosis
3. Planning
4. Implementation
5. Evaluation
39
New cards
Assessment Phase
· Systematic collection of data to determine the client's current and past health and functional status
40
New cards
Diagnosis Phase
Analyze data
Identify health problems, risks, and strengths
Formulate diagnostic statements
the nurse's perspective on the appropriate focus for the patient
Identify health problems, risks, and strengths
Formulate diagnostic statements
the nurse's perspective on the appropriate focus for the patient
41
New cards
Planning Phase
Creations of a formal plan, prescribes strategies and alternatives to attain the expected outcome.
42
New cards
Intervention Phase
A phase when The plan of care would be carried out.
43
New cards
Evaluation Phase
compares the patient's current health status with the desired outcome,
44
New cards
Types of Data
subjective and objective
45
New cards
Subjective Data
are obtained through the health history and the nurse's questions. Patient's verbal descriptions of their health concerns
46
New cards
Objective Data
are observations or measurements of a client's health status, based on an accepted standard (Celsius, kilograms, known characteristics of behaviour such as anxiety or paranoia).
47
New cards
primary source of data
‐Information obtained from the patient (only)
48
New cards
secondary source of data
data acquired from another individual (such as a family member, health care team, or medical records)
49
New cards
tertiary source of data
literature, nurse's experience
50
New cards
Methods of Data Collection
Nursing Health History, Family history, physical exam including observation of client behavior, diagnostic and laboratory data
51
New cards
Body system method
· data is clustered under body systems such as cardiovascular, respiratory, integumentary, etc.
52
New cards
Interpreting Assessment Data:
nurses think about the assessment information, they determine the presence of abnormal findings, validation of assessment data is necessary to avoid making incorrect inferences.
53
New cards
Components of Nursing Diagnosis
diagnostic label, related factors, "as evidenced by" portion
54
New cards
Diagnostic Label
describes the essence of the client's response to health condition in as few words as possible
55
New cards
related factor
A condition or etiology identified from the client's assessment data. Associated with the clients actual or potential response to the health problem and can be altered though the use of nursing interventions
56
New cards
"As evidenced by" portion
connects the diagnoses to the signs and symptoms
57
New cards
Establishing Goals and Expected Outcomes
- Statements of client behavior or physiological responses that a nurse sets to achieve problem resolution
- Provide a clear focus for the type of interventions necessary
- Aim, intent or end
- When the goals and outcomes are met, the client's health problems are resolved
- Provide a clear focus for the type of interventions necessary
- Aim, intent or end
- When the goals and outcomes are met, the client's health problems are resolved
58
New cards
client-centered goal
specific and measurable behavior or response that reflects a client's highest possible level of wellness and independence in function
59
New cards
short-term goal
objective behavior or response that the client is expected to achieve in a short time, usually less than 1 week or in acute care may be in just a few hours
60
New cards
long-term goal
expected to achieve over a longer period, several days, weeks, or months.
61
New cards
Client safety
The aim of the Canadian health care system is to provide quality care and access for all.
This includes the following:
· Cultural Competence, Safety and Humility
· Evidence-Informed Practice (EIP)
· Quality and Patient Safety
· Quality Workplaces
· Improved Patient Outcome Metrics
This includes the following:
· Cultural Competence, Safety and Humility
· Evidence-Informed Practice (EIP)
· Quality and Patient Safety
· Quality Workplaces
· Improved Patient Outcome Metrics
62
New cards
Quality Improvement
Use data to monitor the outcomes of care processes and use improvement methods to design and test changes to continuously improve the quality and safety of health care systems.
63
New cards
Risk Management
· a system of ensuring appropriate care by identifying potential hazards and preventing harm from occurring.
64
New cards
Patient Safety Incidents
An event or circumstance that could have resulted, or did result in unnecessary harm to a patient
· Harmful incident - resulted in patient harm
· Near miss- did not reach the patient
· No-harm incident - reached the patient but did no harm
· Harmful incident - resulted in patient harm
· Near miss- did not reach the patient
· No-harm incident - reached the patient but did no harm
65
New cards
Factors Affecting Patient Safety:
· Patient and Provider Factors
· Task Factors
· Technology Factors
· Environmental Factors
· Organizational Factors
· Task Factors
· Technology Factors
· Environmental Factors
· Organizational Factors
66
New cards
Risk Factors at Developmental Stages
· Infant/toddlers - poisoning
· Toddlers/preschoolers - not restrained properly in vehicles, drowning
· Adolescents - risk taking behavior, substance use
· Adults - accidents due to alcohol or drugs
· Older people - age related changes
· Toddlers/preschoolers - not restrained properly in vehicles, drowning
· Adolescents - risk taking behavior, substance use
· Adults - accidents due to alcohol or drugs
· Older people - age related changes
67
New cards
Prevention of falls
room environment safe - call light within reach at all times, bed in low position, wheels locked, side rails, visual cues to alert staff (label doors, wristbands)
68
New cards
Medication Errors
any event that could lead to a patient either receiving inappropriate medication therapy or failing to receive appropriate medication therapy.
· Causes of medication errors include nurse fatigue, burn out, distractions and interruptions.
· Causes of medication errors include nurse fatigue, burn out, distractions and interruptions.
69
New cards
Code Red
Fire Safety in the Clinical Setting
70
New cards
If a fire is suspected call a code RED
R - Remove those in immediate danger
E - Ensure fire is contained, close doors
A - Activate the nearest fire alarm
C - Call fire department
T - Try to extinguish the fire if able to do so safely
E - Ensure fire is contained, close doors
A - Activate the nearest fire alarm
C - Call fire department
T - Try to extinguish the fire if able to do so safely
71
New cards
Class A fire
ordinary combustibles such as paper, wood, cloth
72
New cards
Class B Fire
fires involving flammable or combustible liquids
73
New cards
Class C Fire
fires involving live electricity or power
74
New cards
Class D Fire
combustible metals such as magnesium, uranium spills (not very common)
75
New cards
Class K Fire
fires involving cooking materials such as cooking oils and grease
76
New cards
How to use a fire extinguisher
P - *PULL* the pin;
A - *AIM* at the base of the fire;
S - *SQUEEZE* the levers;
S - *SWEEP* extinguisher from side to side, covering area of the fire
A - *AIM* at the base of the fire;
S - *SQUEEZE* the levers;
S - *SWEEP* extinguisher from side to side, covering area of the fire
77
New cards
Code Green
evacuation
78
New cards
Code White
Violet Patient
79
New cards
Steps to reduce risk of injury
· Prevention - know history, potential for violence, look for signs and symptoms
· De-escalate - use strategies to prevent further escalation and ensure safety of self and others
· De-escalate - use strategies to prevent further escalation and ensure safety of self and others
80
New cards
two types of evacuation
· Horizontal- Evacuation through smoke/fire barrier doors to a safe area on the same floor
· Vertical - Evacuation of all occupants on a floor to another safe floor
· Vertical - Evacuation of all occupants on a floor to another safe floor
81
New cards
Global Harmonized System
· includes criteria for the classification of health, physical and environmental hazards, as well as specifying what information should be included on labels of hazardous chemicals as well as safety data sheets.
82
New cards
WHMIS
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System
83
New cards
3 Main Elements of WHMIS
· worker education programs, cautionary labelling of products and the provision of Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
84
New cards
Compressed Gases
85
New cards
Flammable and Combustible Material

86
New cards
Oxidizing Materials

87
New cards
Materials causing immediate and serious toxic effects
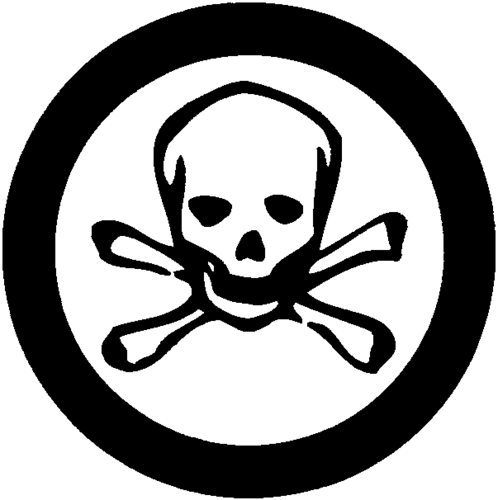

88
New cards
Material causing other toxic effects
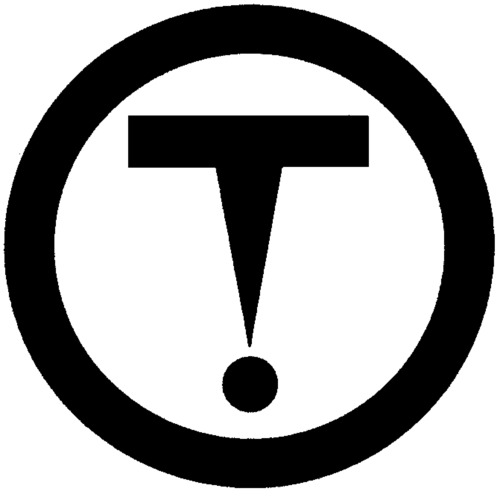

89
New cards
biohazardous infectious material

90
New cards
Corrosive Materials
91
New cards
Dangerously Reactive Material

92
New cards
Infection prevention and control
consists of the implementation of policies and procedures in hospitals and other health care facilities to minimize the spread of health care-associated or community-acquired infections to patients and other staff members
93
New cards
restrain
are physical, chemical or environmental measures used to control the physical or behavioural activity of a person or a portion of his/her body
94
New cards
alternative to restraints
involve family, quiet environment, remove hazards, therapeutic touch, activities (folding towels, crossword puzzles), physical therapy
95
New cards
Code Blue
cardiac arrest
96
New cards
Code Pink
Cardiac Arrest/Medical Emergency - Child (18 and under)
97
New cards
Code Amber
Missing child
98
New cards
Code Yellow
missing person
99
New cards
Code Black
Bomb threat
100
New cards
Code Brown
Hazardous spill