lecture 18, the male reproductive system
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
the male and female reproductive system consist of
gonads
testes in males and ovaries in females
produce gametes
egg or sperm
ducts
function in the transportation and storage of gametes
allows for transport
accessory glands
produce secretions that lubricate gamete passageways and support gametes
nutrients and buffer
need to be able to support the gamete
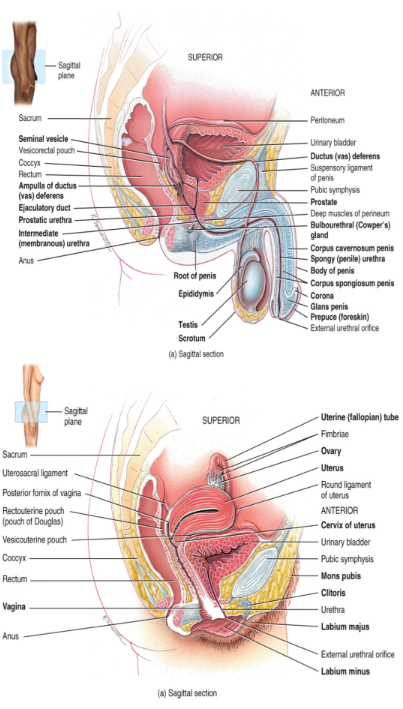
the male reproductive system
the testes are the male gonads
located within a sac-like structured called the scrotum (low temperature)
the scrotum consists of
skin and connective tissue
comprised of two layers
the tunica vaginalis
the outer covering of the scrotum
a serous membrane (peritoneum)
the tunica albuginea
comprises the inner capsule of the scrotum
extends toward the inside of the testicles dividing into 250-300 lobules (segregates compartments)
each lobule contains
seminiferous tubules (sperm reproduced, mitotic division)
Leydig cells (also called interstitial cells) floating between
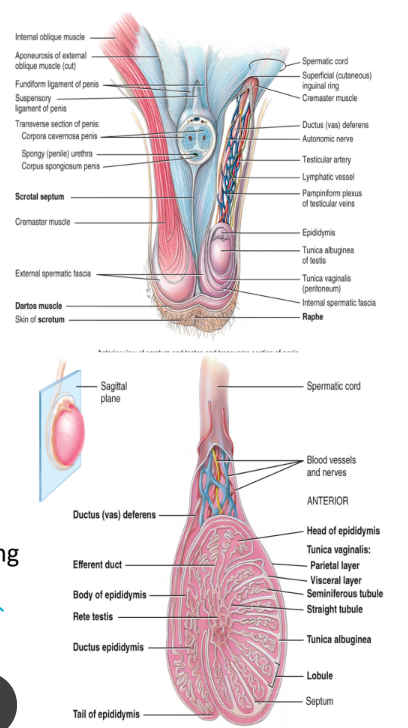
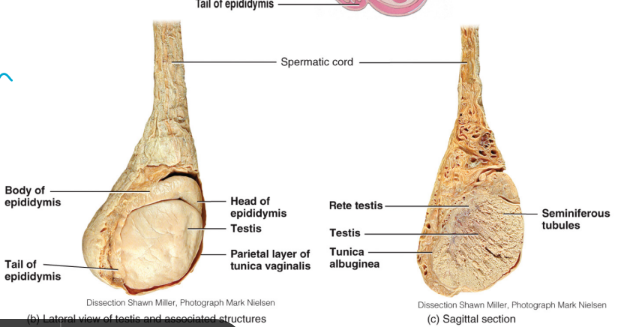
the seminiferous tubules
the seminiferous tubules are the site of sperm production
sperm are produced by a process called spermatogenesis (just mitosis but with different cell structures)
seminiferous tubules from each lobule unite to form the rete testis
a net of seminiferous tubules that the sperm must pass through when they exit the testes (all lobules to his one location)
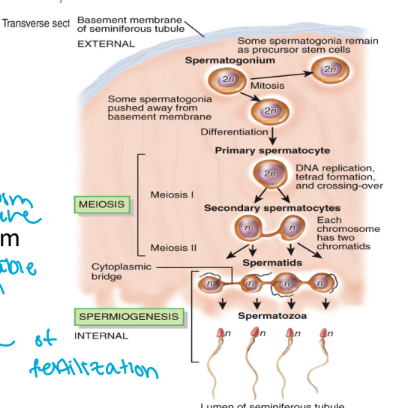
spermatogenesis
spermatogonia (2n cells)
mitosis
photocopying
create population of diploid
too many chromosome to be sperm
1x primary spermatocyte (2n cell)
meiosis I
still have double genetic material
haploid
2x secondary spermatocyte (n cells)
meiosis II
segregate sister chromatids
4x spermatid (n cells )
spermiogenesis
sperm develop and acrosome and a flagellum
not mature yet
has to be able to swim and break egg membrane
4x spermatozoa (n cells)
still haploid
mature now and capable of fertilization
spermatogenesis produces 4 haploid spermatozoa from 1 diploid primary spermatocyte
histology of the testes: Leydig cells
also called the interstitial cells
in between everything to help provide support
located in the connective tissue that surrounds the seminiferous tubules
predominately secrete testosterone
endocrine tissue
primarily functioning for reproduction
testosterone is needed for the development of male sex characteristic and spermatogenesis
facial hairs
deep voice
females don’t have this production of testosterone
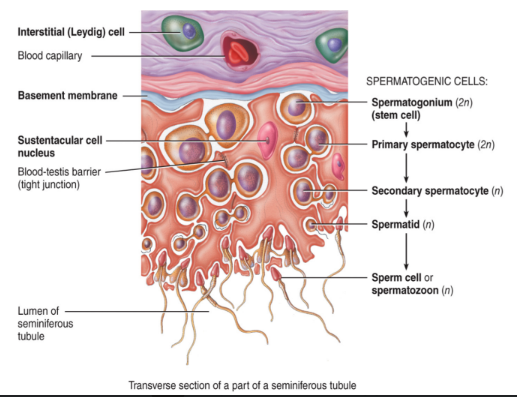
histology of the testes: seminiferous tubules
the walls of the seminiferous tubules contain
germ cells
gametes in various stages of development (on the wall)
seratoli cells (sustentacular cell)
located between the germ cells
extend from the basement membrane to the lumen of the tubule
cells contain tight junctions which form the blood-testos barrier
protect the sperm from blood components such as alcohol, drugs, etc.
support and nourish developing sperm cells
“want glucose?” allows them to be well fed
regulate sperm production
need protein channels to take in what we need
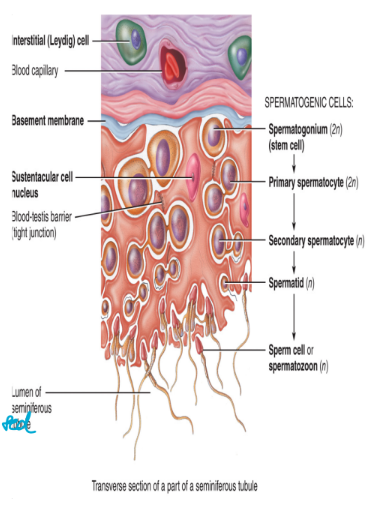
sperm structure
head
contains the haploid sperm cell nucleus
23 chromosomes
also contains the acrosome (like toolkit)
contains enzymes that assist in penetration of the egg during fertilization
helps to digest membrane
body
the mid-piece of the sperm
contains a large number of mitochondira
produce large quantities of ATP needed for sperm to swim to the egg
swim far so need lots of mitochondria
tail
flagellum formed from microtubules (whips to move)
propels the sperm forward
eukaryotic organism
one cell
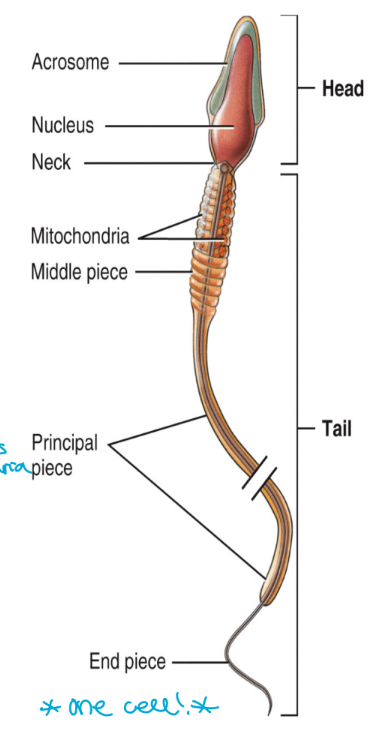
ducts for sperm transport
once the sperm have formed they move from seminiferous tubules into the rete testis
from the rete testis they move into the
epididymis
vas deferens (ductus deferens)
ejaculatory duct
urethra
penis
epididymis
located at the posterior, superior and lateral border of the testis
sperm mature here
during ejaculation the sperm move into the vas deferens
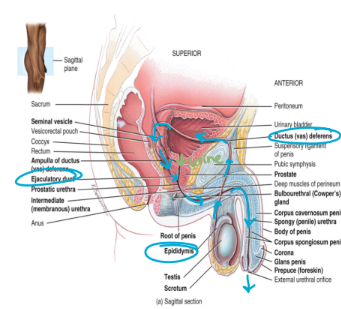
vas deferens (ductus deferens)
enters into the pelvic cavity (come back in, transit through)
loops over the posterior surface of the bladder (up and over)
a vasectomy severs and ties the vas deferens in order to prohibit sperm transport
sperm continue to be produced but are broken down by macrophages in the epididymis
sperm move from the vas deferens into the ejaculatory duct
want to make sure defense against urine
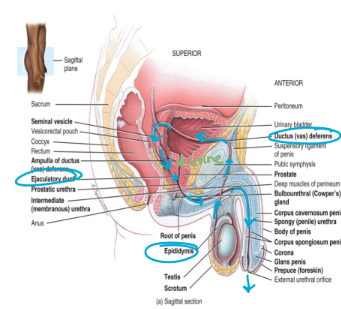
ejaculatory duct
formed from the union of the vas deferens and the duct from the seminal vesicle (produces a component of semen)
urethra
functions to transport both sperm and urine
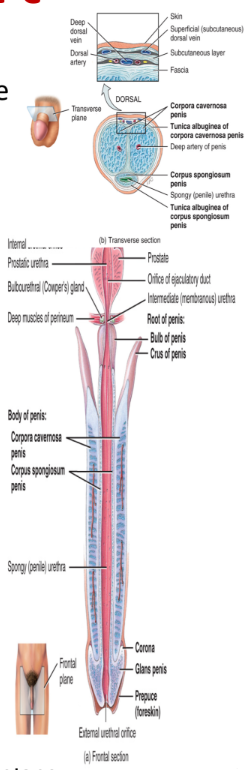
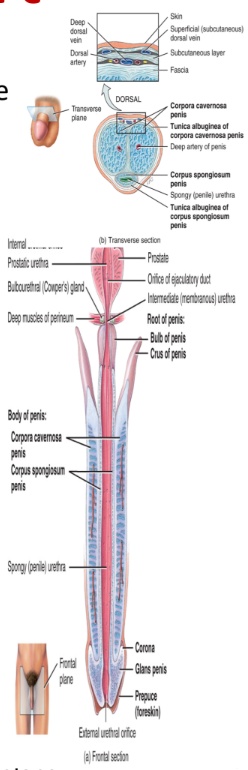
contains three segments
the prostatic portion → passes through the prostate gland
the membranous portion → passes through the urogenital diaphragm
the penile portion → passes through the penis
opens into the glans penis
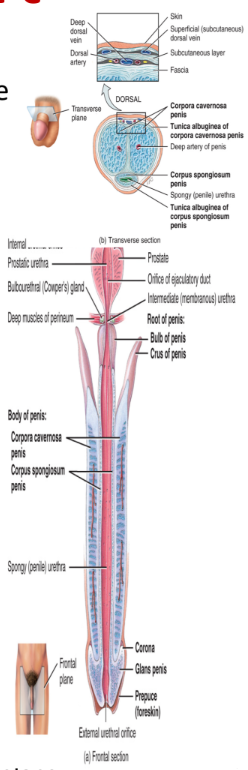
penis
contains a root, a shaft, and an enlarged tip called glans penis
erectile tissue consists of
2 corpora cavernosa and 1 corpus spongiosum which contains the glans penis (enlarged tip)
longest of sections
accessory glands
3 accessory glands produce secretions that combine with sperm to five semen
seminal vesicles
prostate glands
bulbourethral gland
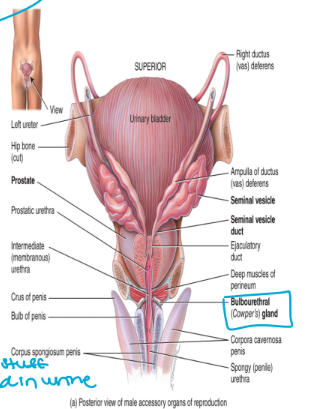
seminal vesicles
paired glands found at the base of the urinary bladder
produces seminal fluid → alkaline fluid that protects sperm from the acidic environment of the vagina
also contains fructose used as energy source for the sperm
accounts for 60% of total semen volume
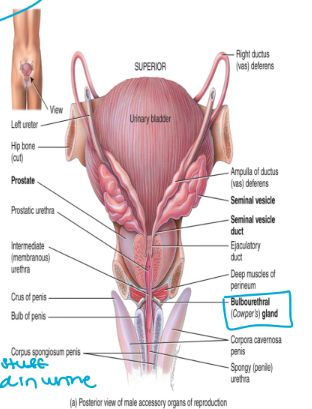
prostate gland
unpaired gland the encircles the urethra (wraps around)
produces a milky, slightly acidic fluid
neutralized by alkaline fluid
also contains enzymes and nutrients needed to feed and activate sperm (aggressive swimming)
accounts for 30% of total semen volume
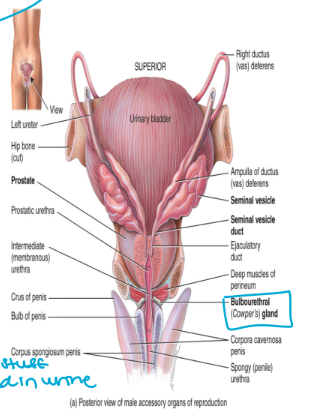
bulbourethral gland
a paired gland located in the urogenital diaphragm
produces a fluid that neutralized urine present in the urethra (bad stuff stored in urine)
accounts for 5% of total semen volume (last part to leave)
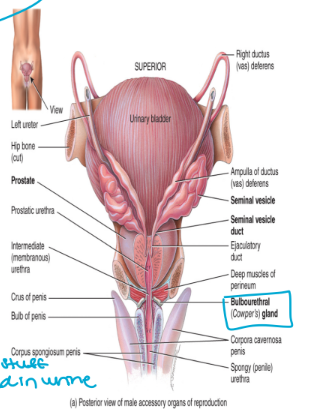
semen
consists of sperm, testicular fluid, and secretions from the prostate gland, the bulbourethral glands, and the seminal vesicles
semen is slightly alkaline → pH 7.3-7.7
modest, close to neutral
acts as a transport medium that also nourishes and protects the sperm present in semen
“ocean water” so they can move
2.5-5.0mL of semen are released upon ejaculation (frequency, last time you cum)
there are 50-150 million sperm per mL of semen
infertility becomes an issue when there are fewer than 20 miion sperm per mL of semen