Mechanics of Breathing
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
breathing
bodily function that leads to ventilation of the lungs
also known as external respiration
ventilation
process of moving gases in (inspiration) and out (expiration) of lungs
mechanics of breathing
describes structural and physiological bases of ventilation
diseases affecting ventilation
obstructive conditions:
asthma
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
lung cancer
restrictive conditions:
intrinsic e.g. pulmonary fibrosis
extrinsic e.g. pneumothorax
Boyle’s law
pV=constant
Ohm’s Law
Q=ΔpR
Q= flow
p=pressure
R=resistance
relevance of pressure in breathing
gas will flow through patent airways according to pressure gradient between atmosphere (barometric pressure) and alveoli
inspiration: atmospheric pressure>alveolar pressure
expiration: alveolar pressure> atmospheric pressure
generation of ΔP
atmospheric pressure is constant
ΔP generation is dependant on a cycle of pressure changes in the chest
respiratory muscles- inspiration
quiet breathing:
diaphragm
external intercostals stabilise rib cage
increasing effort:
diaphragm
external intercostals lift and expand rib cage
accessory muscles
neck muscles
shoulder girdle muscles
respiratory muscles- expiration
quiet breathing:
elastic recoil of tissues
increasing effort:
internal intercostals
abdominal wall muscles
thoracic cage expansion
pleura are important in trasmitting thoracic cage expansion into lung volume expansion
thoracic cage expansion exerts increasing negagtive pressure on intrapleural space
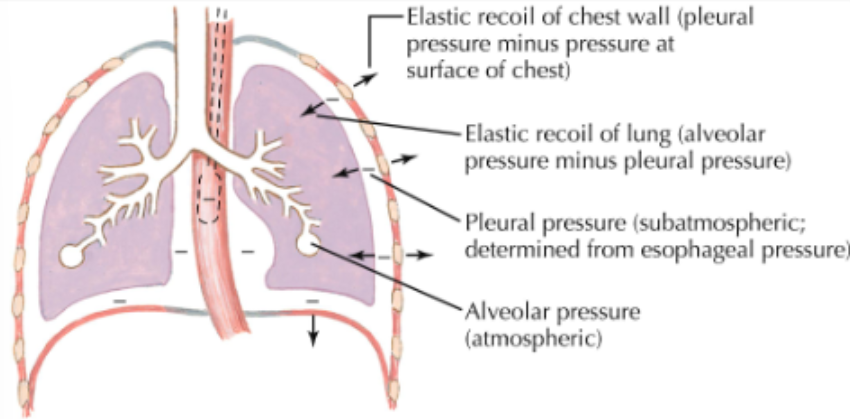
lungs at rest
respiratory muscles at rest
recoil of lung and chest wall are equal but opposite
pressure along tracheobronchial tree is atmospheric
no airflow
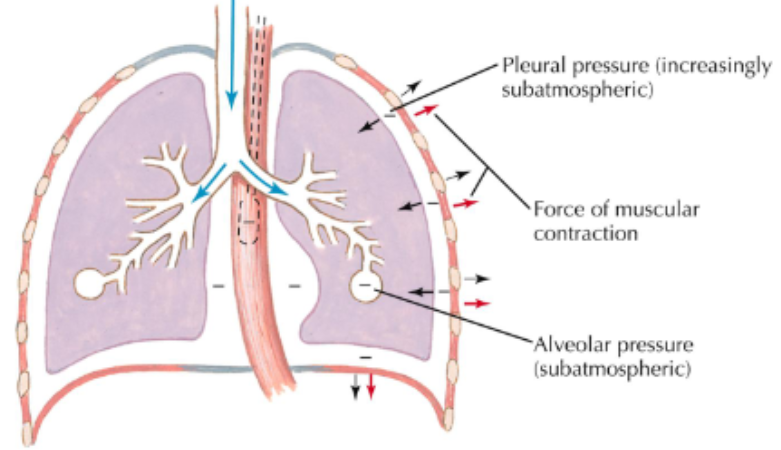
during inspiration
inspiratory muscles contract and chest expands
pleural and alveolar pressure becomes subatmospheric
air flows into lungs
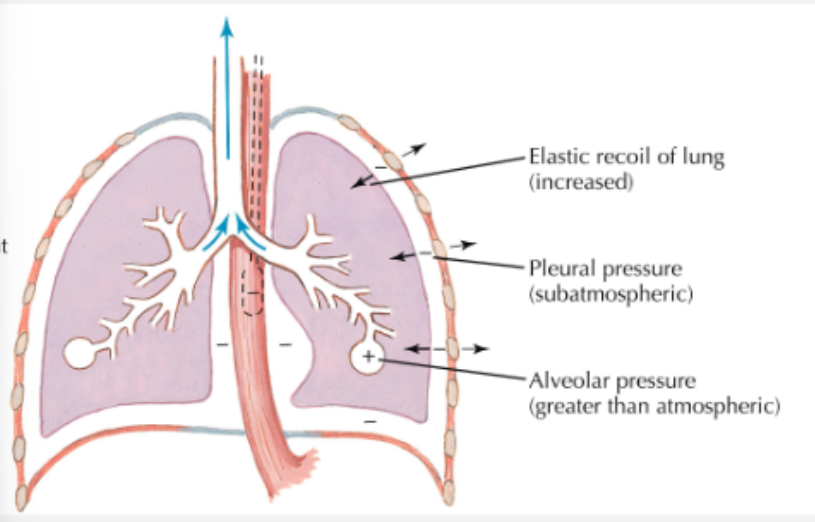
during expiration
inspiratory muscles relax
recoil of lung causes alveolar pressure to exceed pressure at airway opening
air flows out of lung
disruption of expansion
pneumothorax→ air leaks into thoracic cavity, so lung will collapse
pleural effusion→ excess fluid build up in pleural space
spirometry
most lung volumes can be measure via spirometry
can be used to measure volume or flow
lung capacity→ sum of two or more lung volumes- derived value
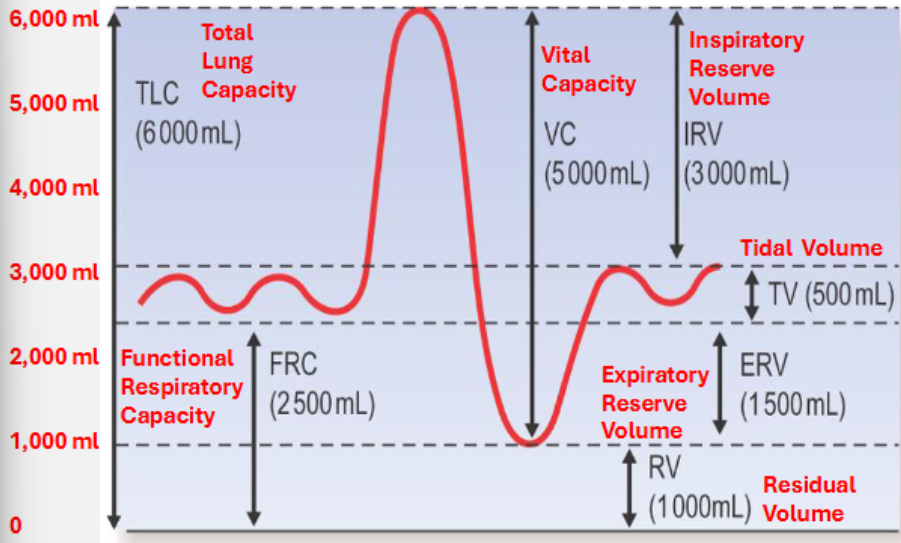
tidal volume
volume of air moved in/out of lungs during normal breathing
at rest→ 6-7ml/Kg
during exercise→ 15ml/Kg

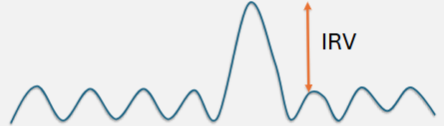
inspiratory reserve volume
after normal expiration, take as deep a breath in as possible
typical value (70kg male)→ 3000ml
expiratory reserve volume
after normal inspiration, breathe out as deeply as possible
typical value (70kg male)→ 1500ml
residual volume
air remains in the lungs even after maximal expiration
due to rigid nature of thorax and pleural attachments of lungs to chest wall→ prevents complete emptying of lungs
cannot be measured by spirometry
typical value (70kg male)→ 1000ml
lung capacities
combinations of lung volumes
total lung capacity→ TV+IRV+ERV+RV
vital capacity→ TV+IRV+ERV
functional residual capacity→ ERV+ RV
vital capacity
after maximal inspiration make a maximal expiration
typical value (70kg male)→ 5000ml
chest diseases affecting lung volumes/capacities
restrictive lung diseases (pulmonary fibrosis):
reduced RV, FRC, VC, TLC
obstructive lung disease e.g. asthma, COPD, emphysema
increased RV
TLC may be reduced (COPD) or increased (emphysema)
FRC increases in emphysema
diagram of lung volumes and capacities
what determines lung volumes
balance between lung’s elastic recoil properties and properties of the muscles of the chest wall
without external forces, elastic recoil of lung= lungs almost airless (10% TLC)
without lung parenchyma, resting volume of chest wall increases (60% TLC)
FRC
relaxation point of respiratory system when chest wall and lung recoil pressure are equal but opposite
alveolar and transpulmonary pressure
alveolar pressure→ sum of pleural pressure and elastic recoil pressure
transpulmonary pressure→ difference between alveolar pressure and pleural pressure