World War 1
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
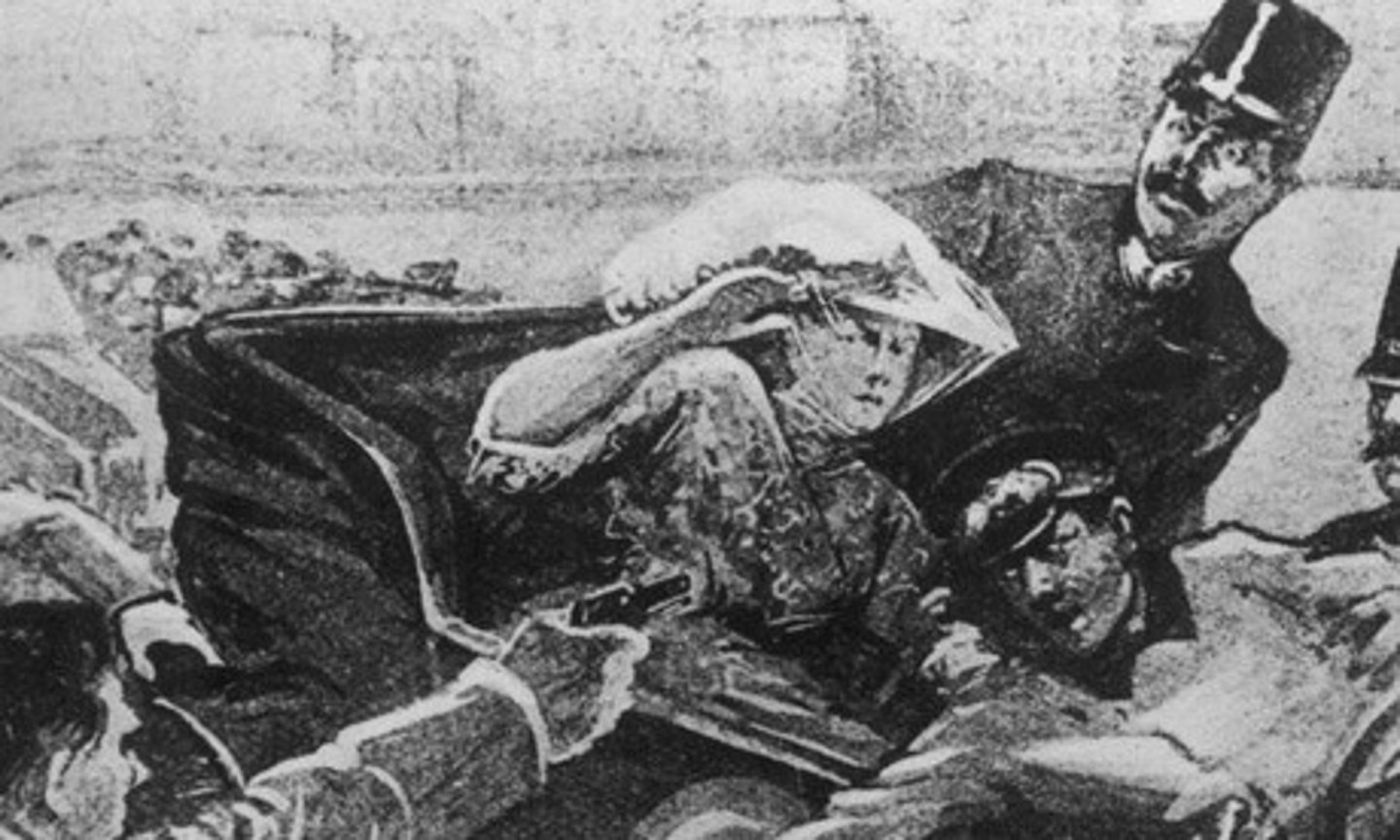
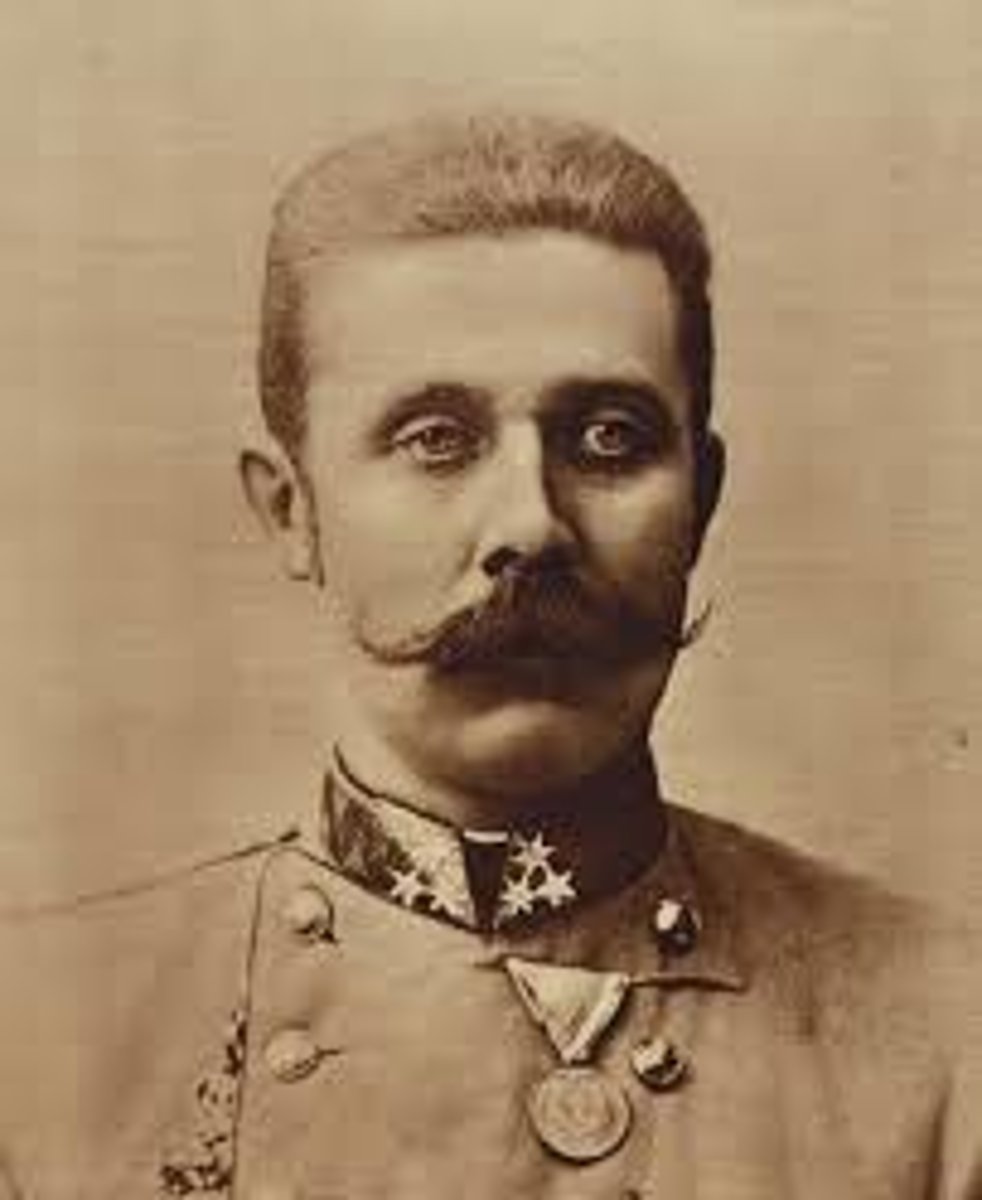
Archduke Franz Ferdinand
(crown prince) heir to Austrian throne from 1896: assassinated on June 28, 1914 during good-will mission in Sarajevo, Bosnia (Aus-Hung) by Serbians, sparking WWI: caused Germany and other Austro Allies to declare war on Serbia and its allies
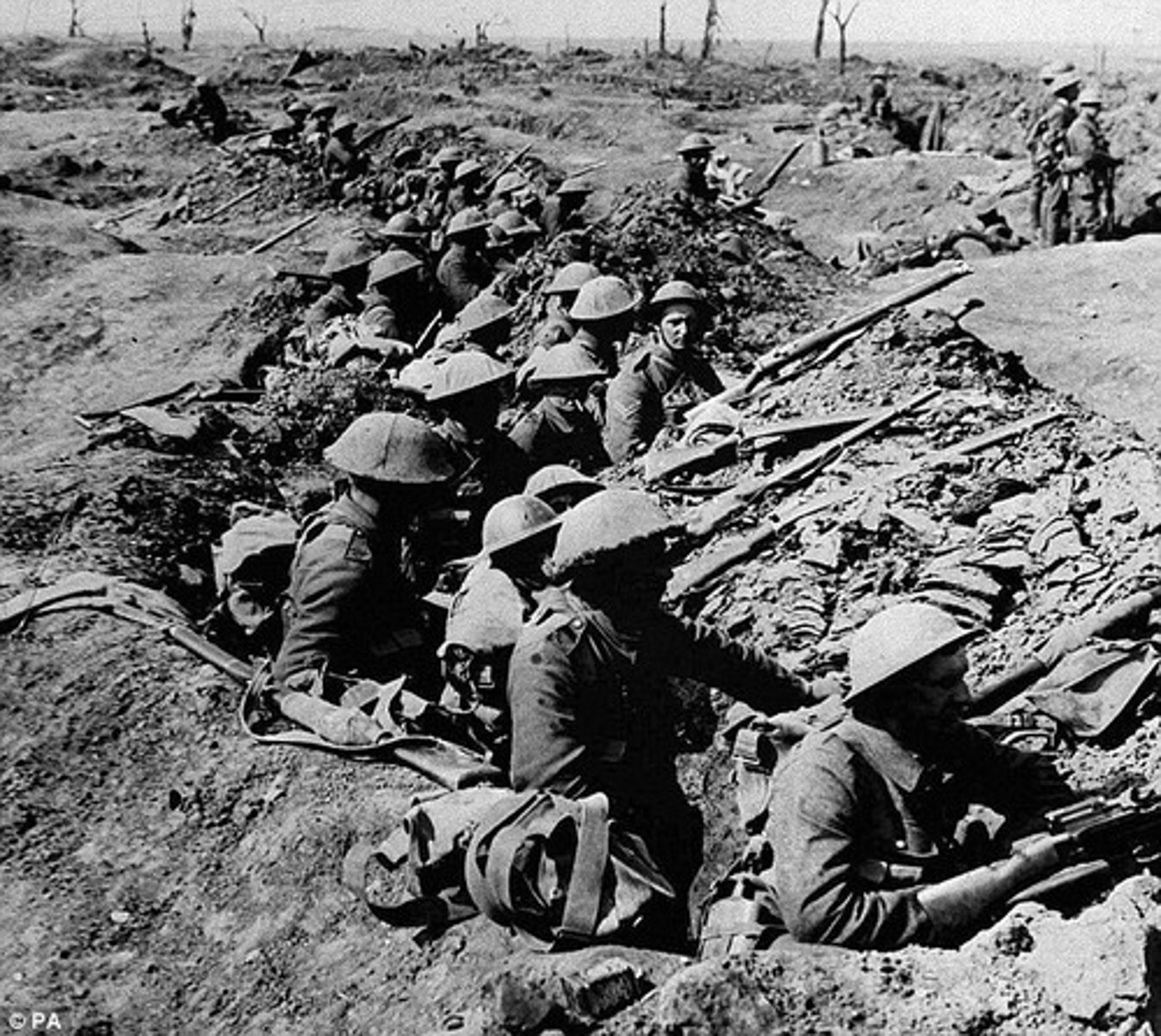
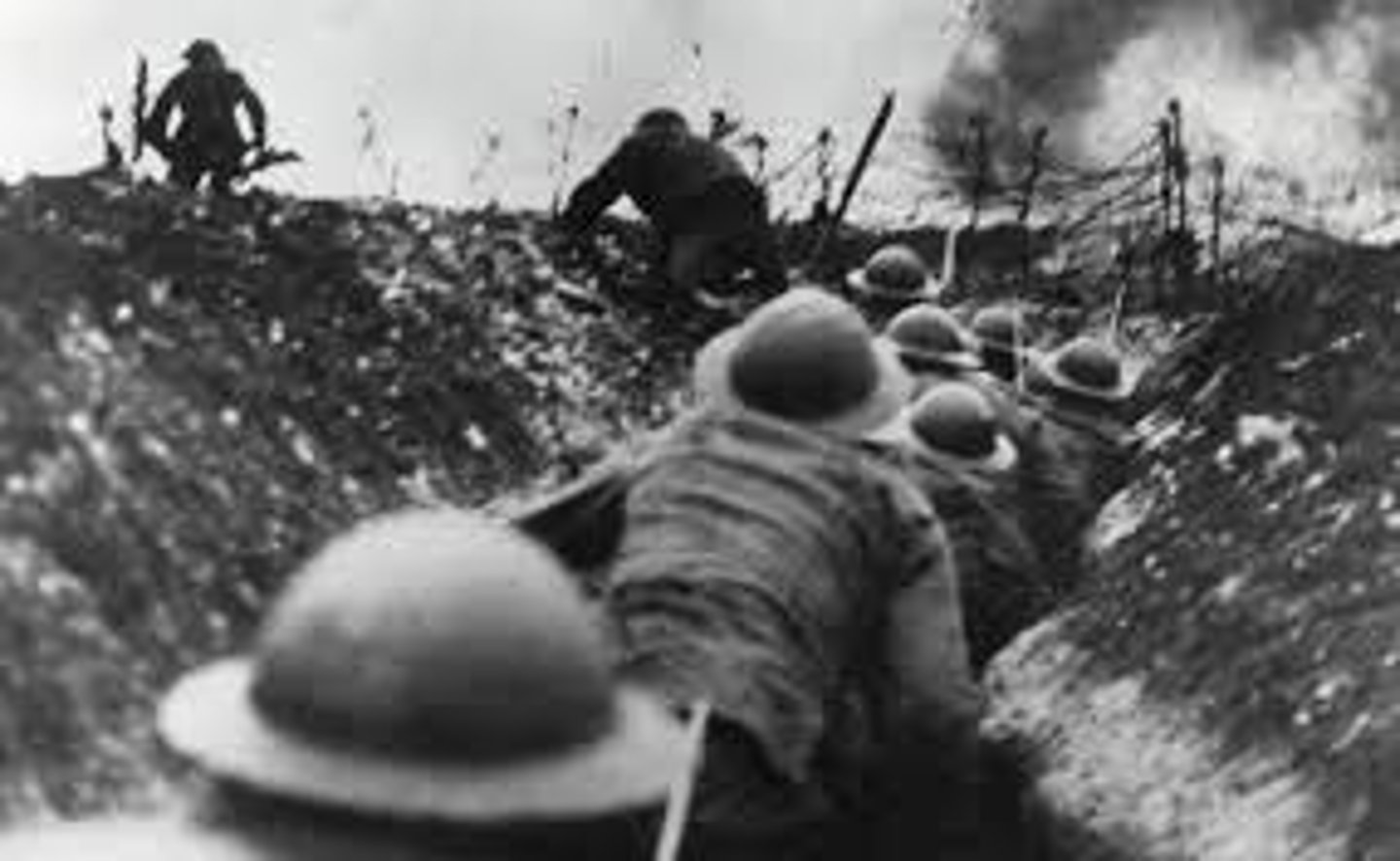
Trench Warfare
Fighting with trenches, mines, and barbed wire. Horrible living conditions, great slaughter, no gains, stalemate, used in WWI.

Propaganda
Information, especially of a biased or misleading nature, used to promote or publicize a particular political cause or point of view.
Militarism
A political orientation of a people or a government to maintain a strong military force and to be prepared to use it aggresively to defend or promote national interests
Nationalism
Pride for your country
Imperialism
A stronger nation taking over a weaker nation
trench warfare
A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield.

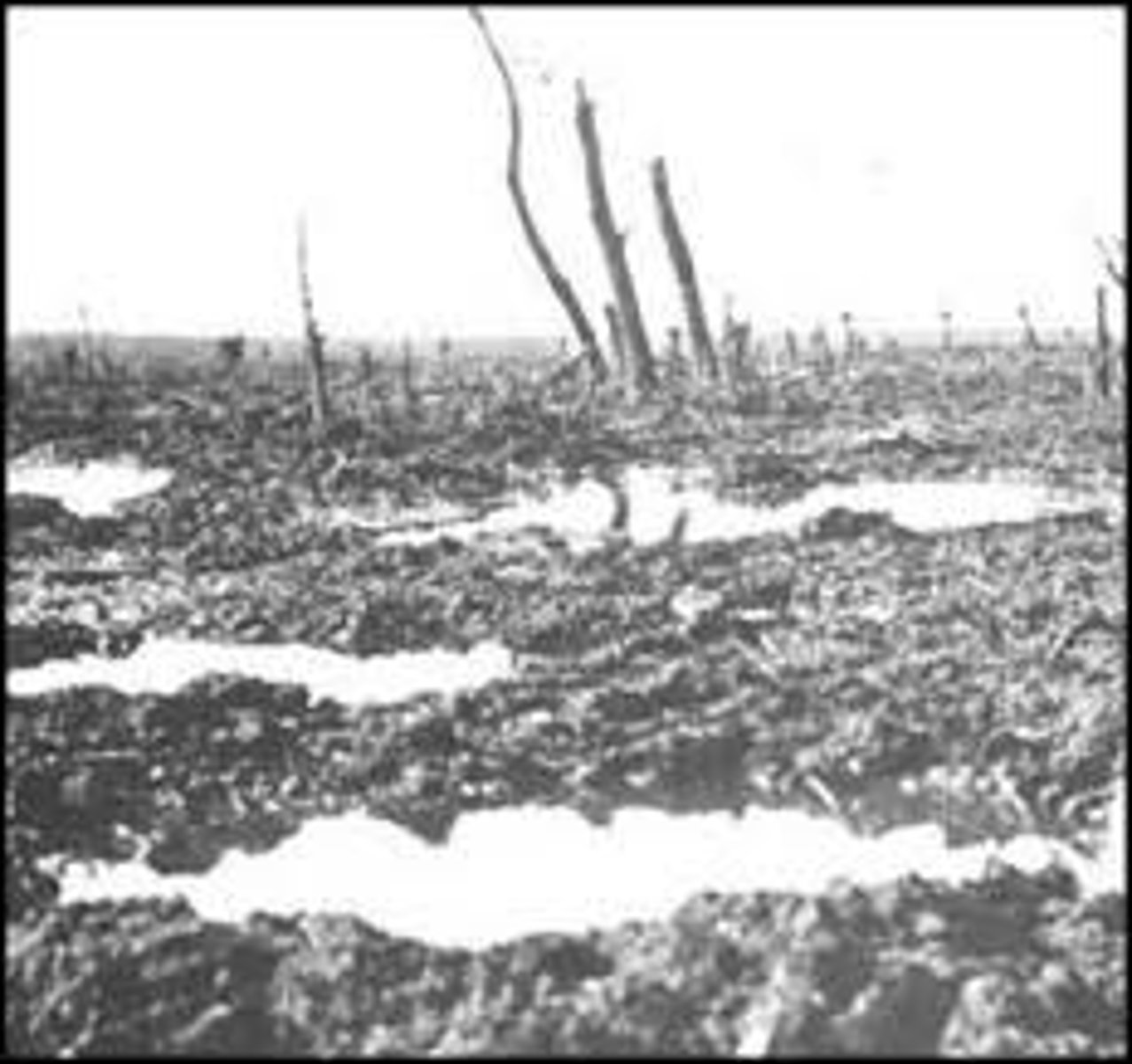
no man's land
A strip of land between the trenches of opposing armies along the Western Front during WW1

total war
A conflict in which the participating countries devote all their resources to the war effort
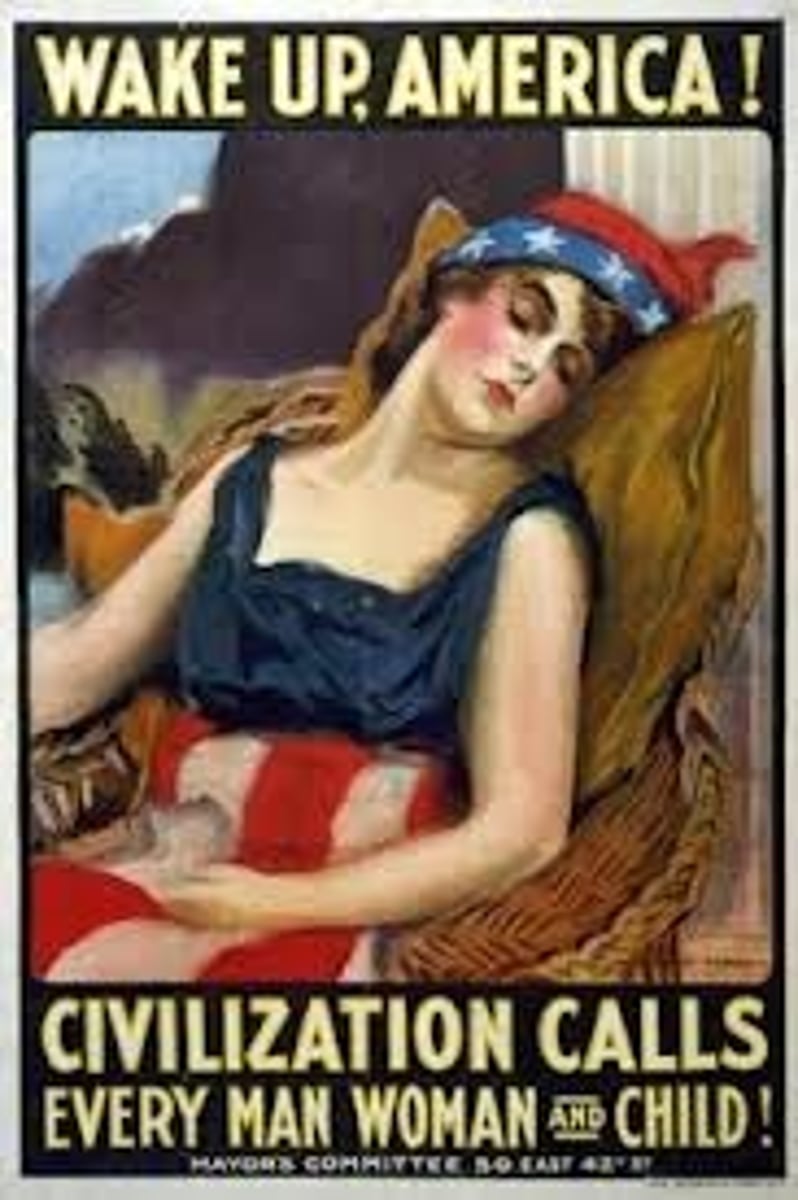

propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion

armistice
A temporary peace agreement to end fighting.

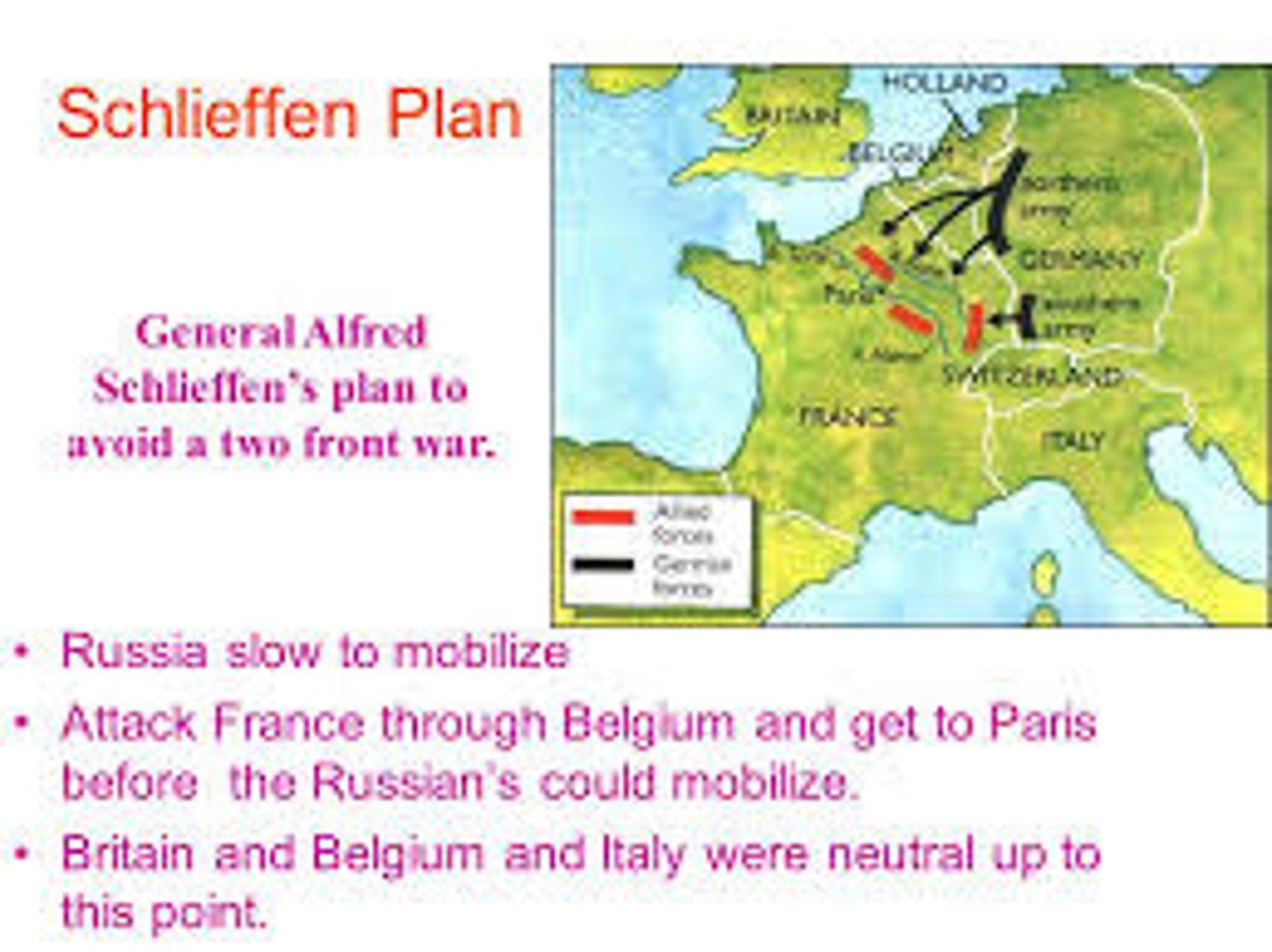
Schlieffen Plan
A strategy drawn up by Germany to avoid fighting a war on two fronts
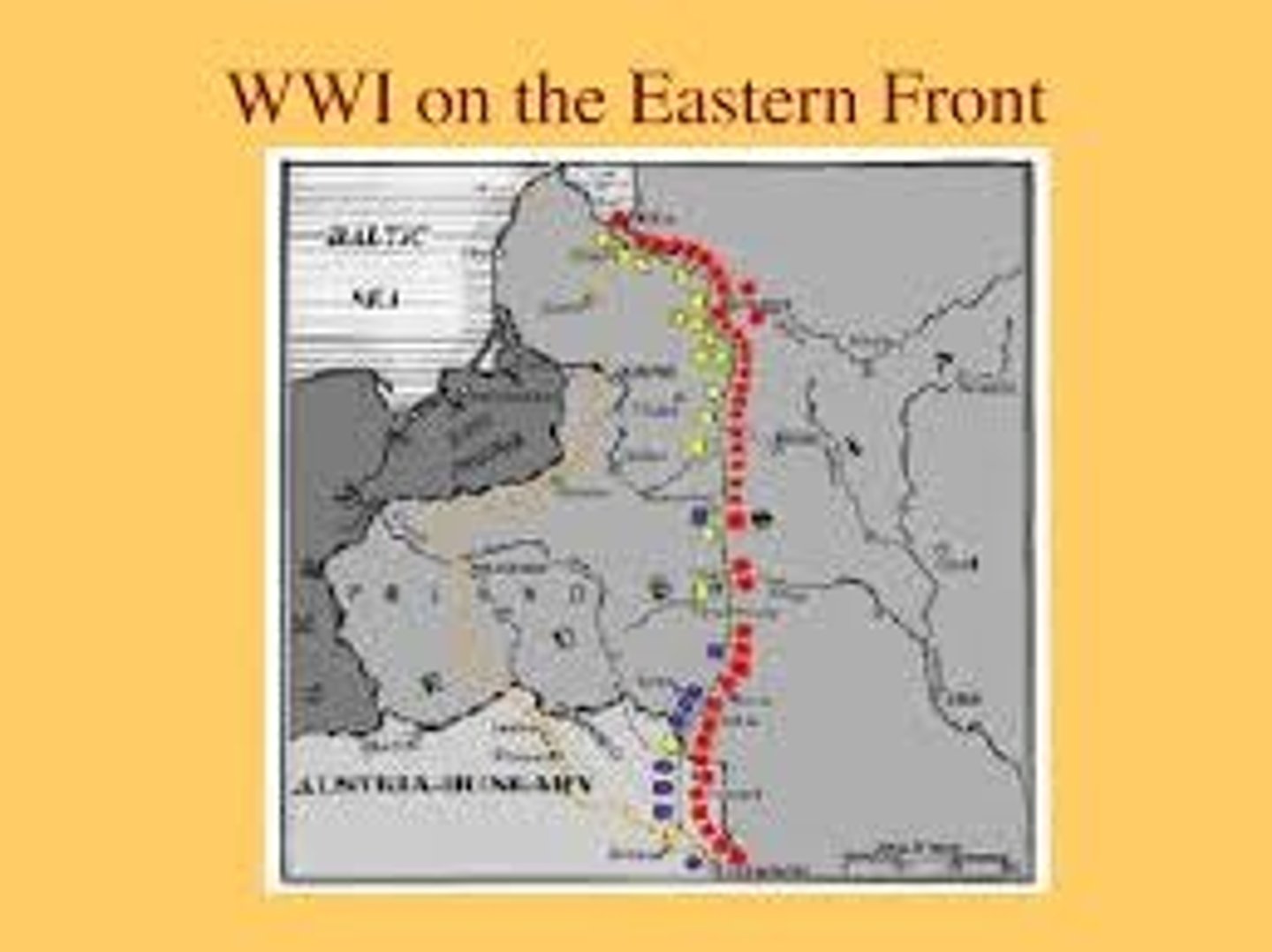
Eastern Front
In WWI, the region along the German-Russian Border where Russians and Serbs battled Germans, Austrians, and Turks.
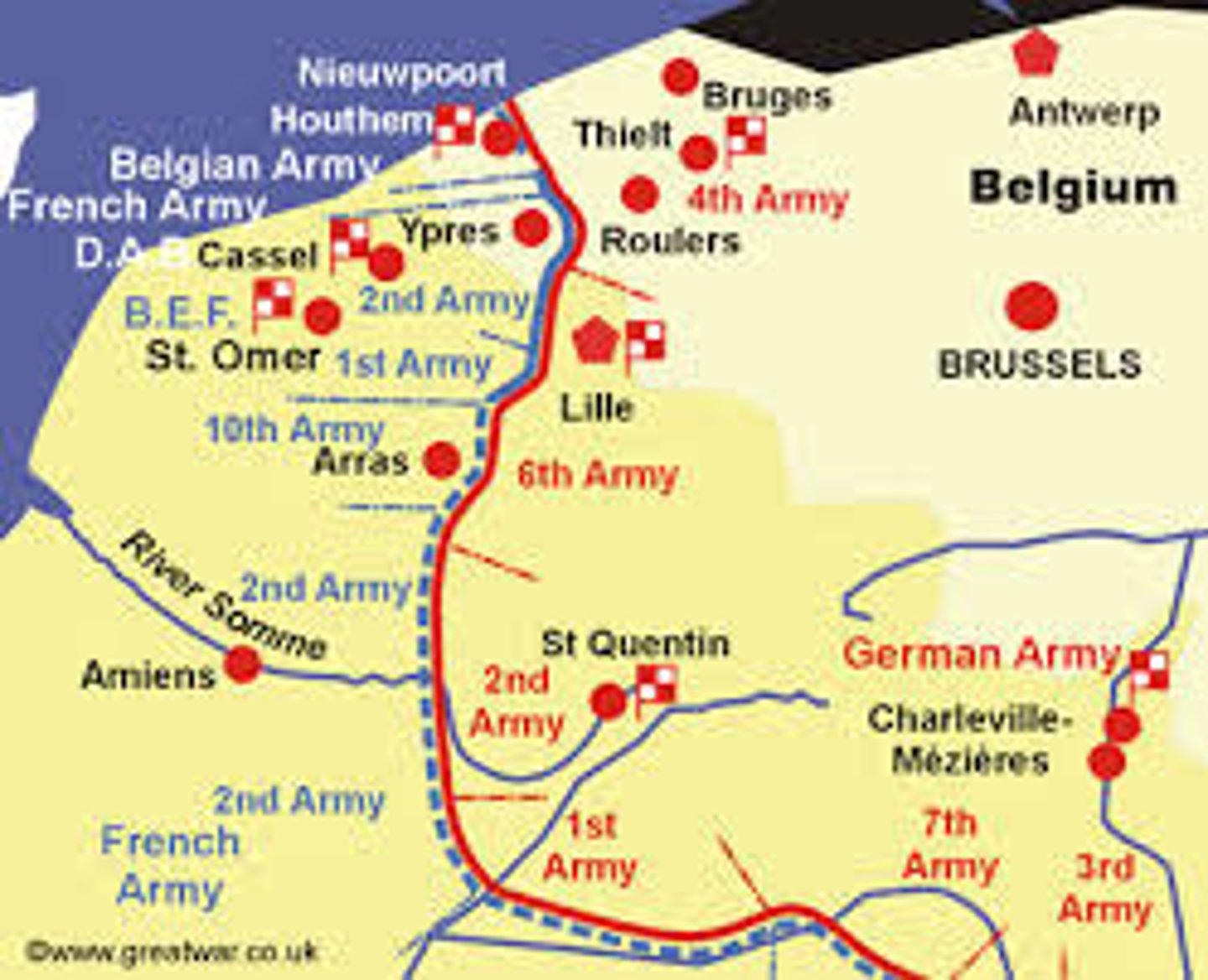
Western Front
in WWI, the region of northern France where the forces of the Allies and the Central Powers battled each other
unrestricted submarine warfare
A policy that the Germans announced on January 1917 which stated that their submarines would sink any ship in the British waters

Treaty of Versailles
Treaty that ended WW I. It blamed Germany for WW I and handed down harsh punishment.

Fourteen Points
A series of proposals in which U.S. president Woodrow Wilson outlined a plan for achieving a lasting peace after World War I.

League of Nations
an international organization formed in 1920 to promote cooperation and peace among nations

reparations
As part of the Treaty of Versailles, Germany was ordered to pay fines to the Allies to repay the costs of the war. Opposed by the U.S., it quickly lead to a severe depression in Germany.

Powder Keg of Europe
nicknamed this for the festering quarrels over the Balkans that eventually pushed Europe into war.
Franz Ferdinand

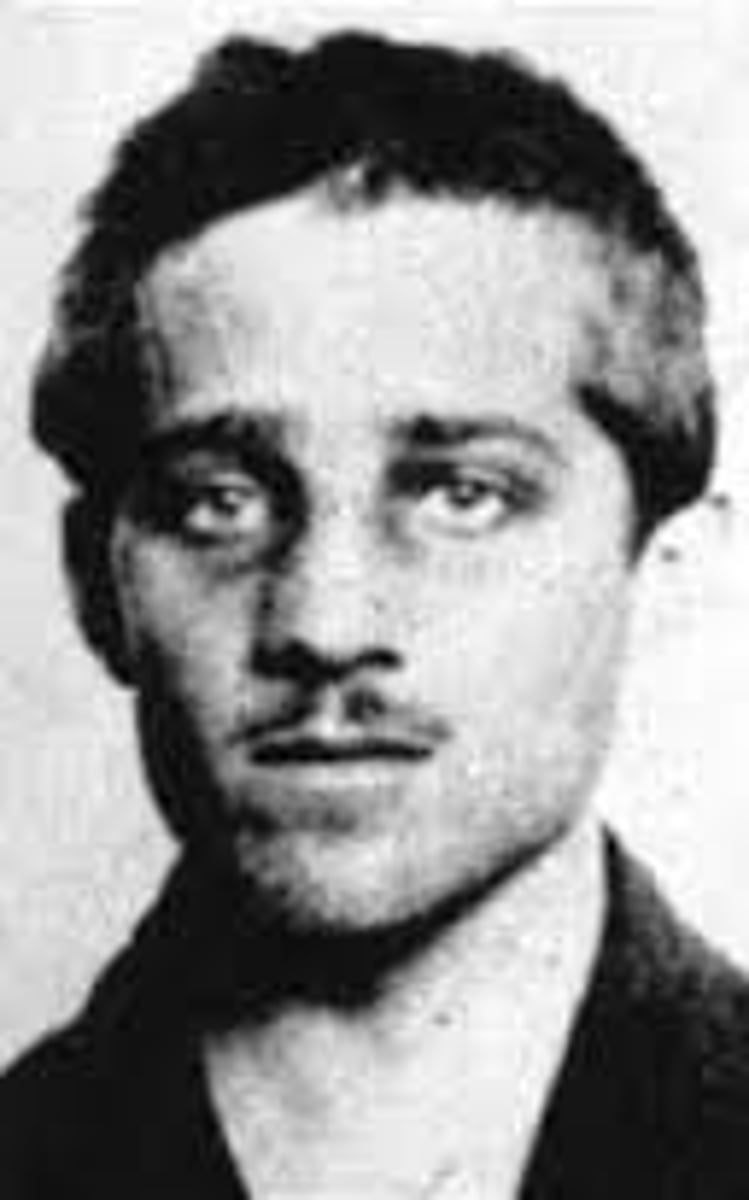
Gavrilo Princip
The assassin of Archduke Francis Ferdinand of Austria, a member of the Black Hand

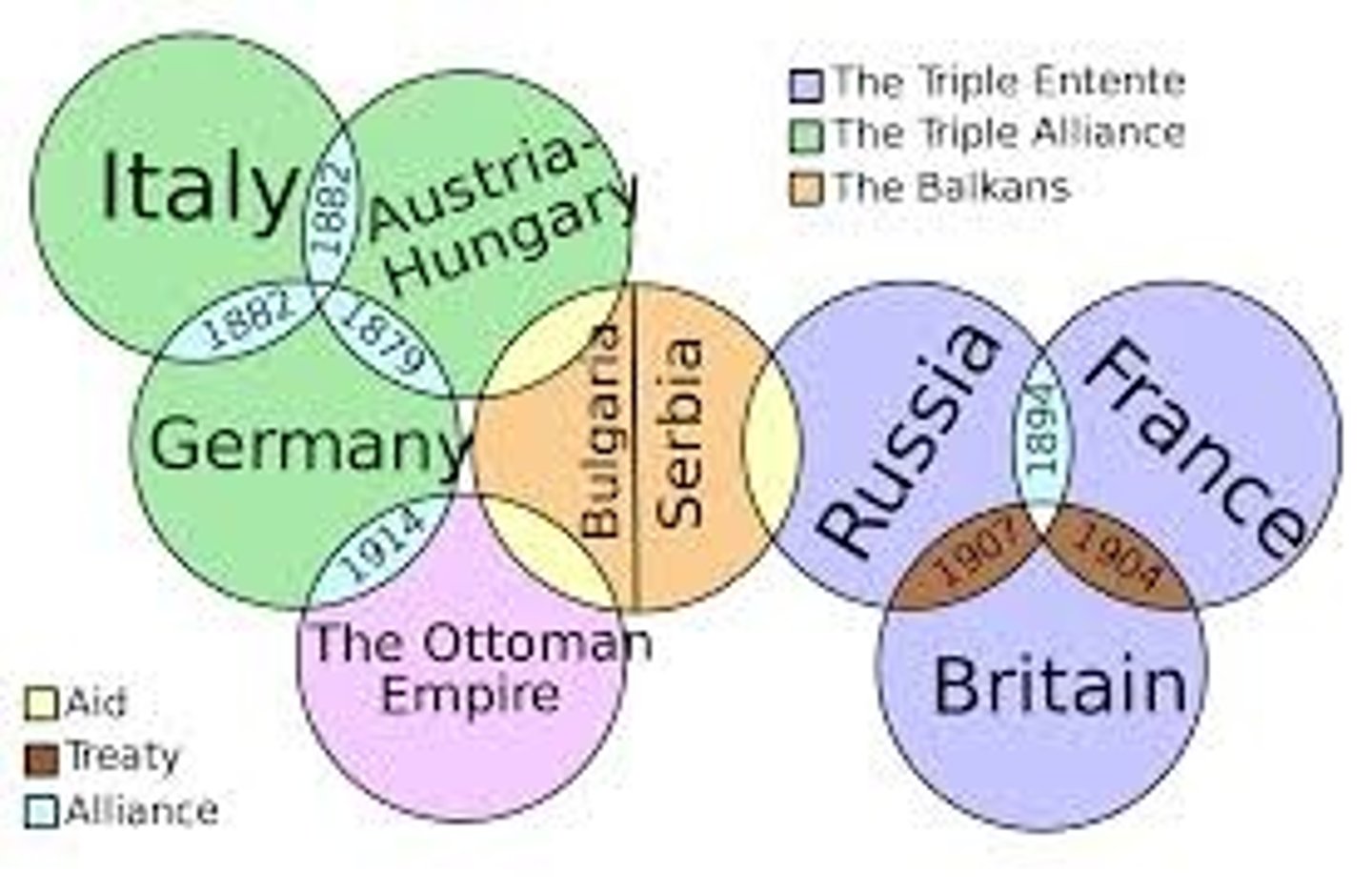
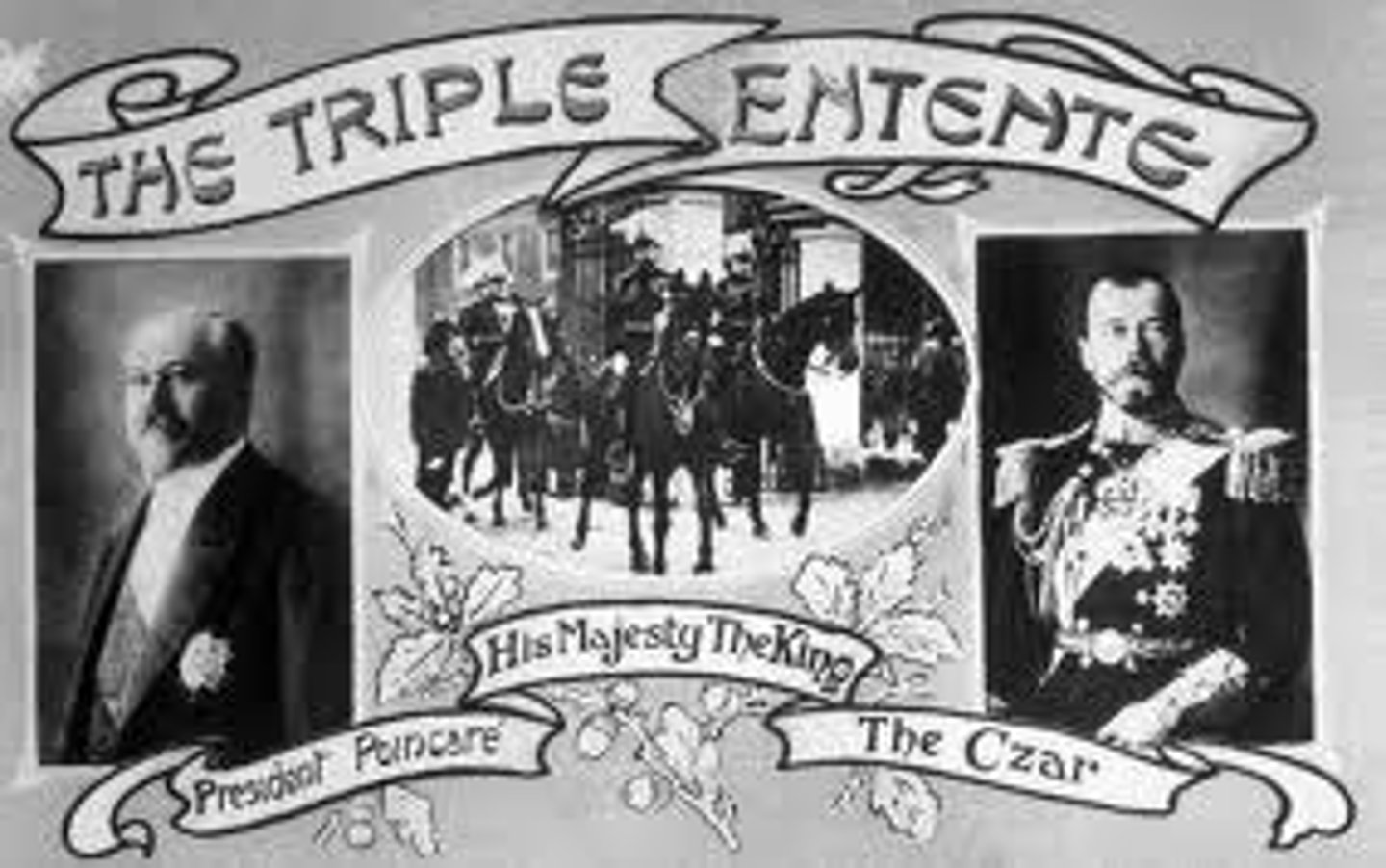
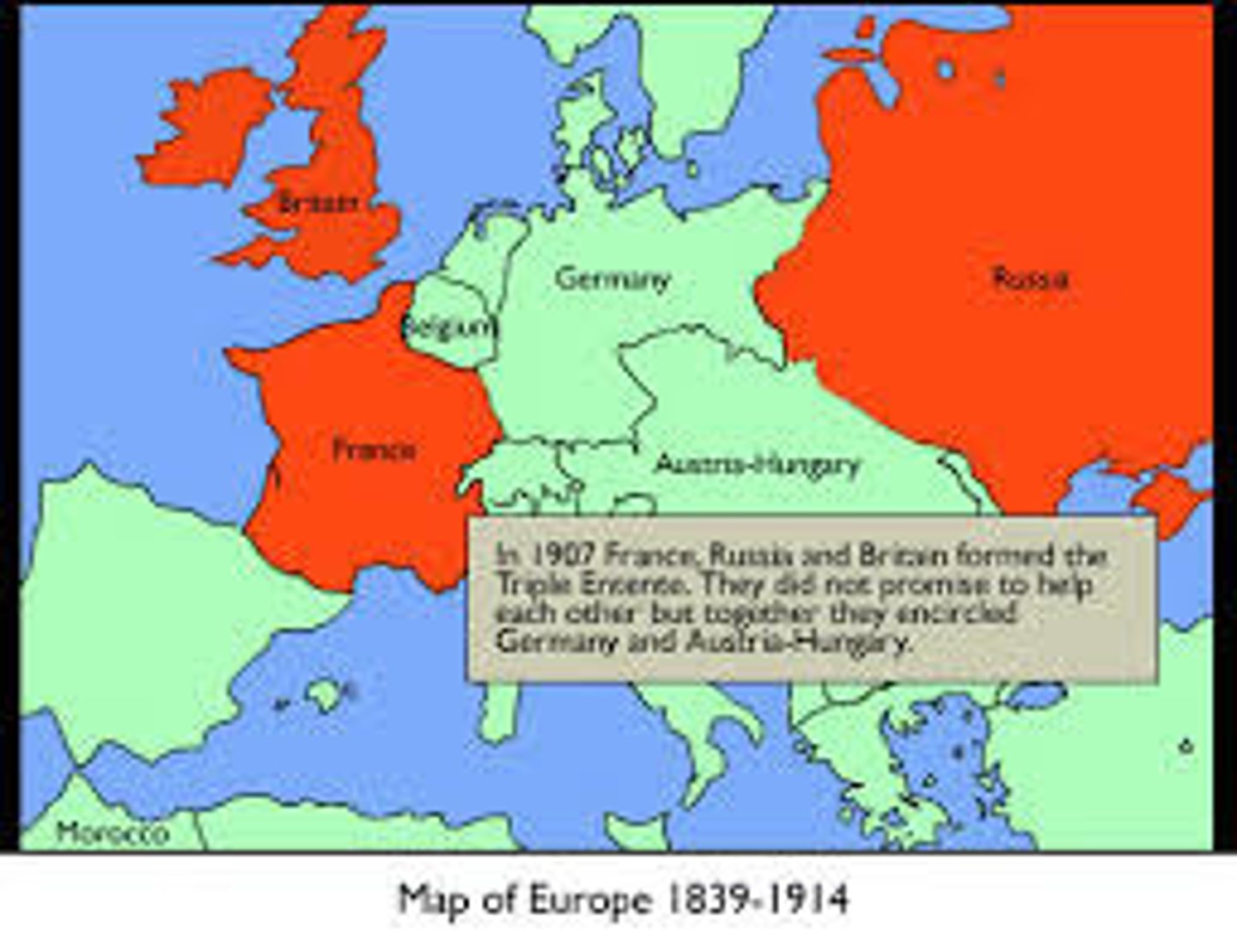
Triple Entente
A military alliance between Great Britain, France, and Russia in the years preceding World War I.
Triple Alliance
A military alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy in the years preceding World War I
Allies of World War I
Composed of France, Britain, and Russia, and later Japan and Italy, the Allies fought the Central Powers in World War I. The United States joined the Allies in 1917.

Central Powers
A military alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire.

alliance system
The alliance system in Europe was a major cause of World War 1.

Woodrow Wilson
28th president of the United States, known for World War I leadership, Treaty of Versailles, sought 14 points post-war plan, League of Nations (but failed to win U.S. ratification), won Nobel Peace Prize

Zimmerman Telegram
A coded message sent by Germany to try to get Mexico to attack the US

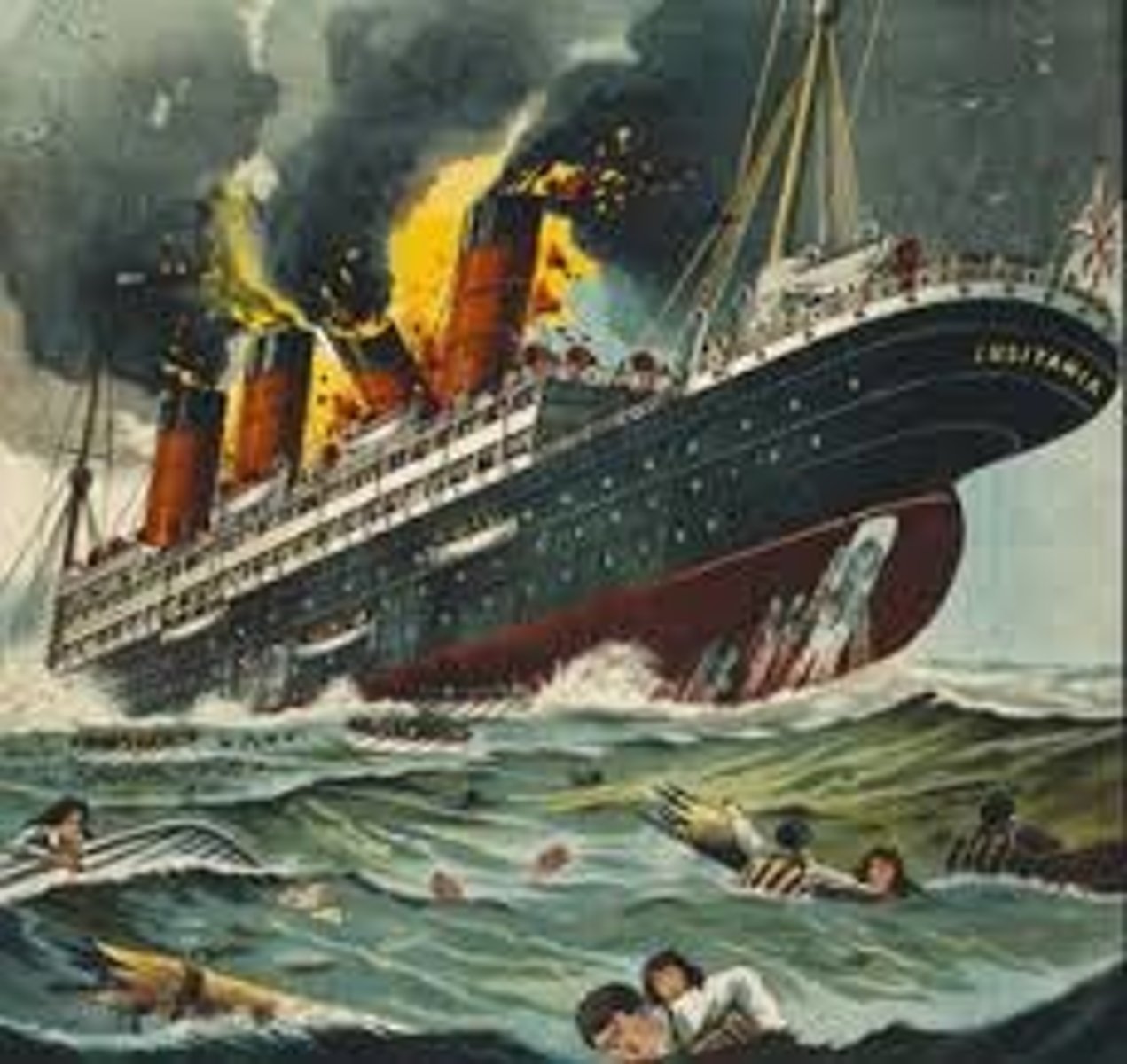
Lusitania
British passenger boat sunk by a German submarine that claimed 1,000 lives. One of main reasons US decided to join the war.

stalemate
A deadlock in which neither side is able to defeat the other.

Versailles Peace Treaty
The Treaty of Versailles (French: Traité de Versailles) was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
U-boat
German submarine - u boat is short of the German word, Unterseeboot (Under Sea Boat)
The Marne
A World War I battle fought from 5-12 September 1914. It resulted in an Allied victory against the German Army.
Stalemate
A situation in which no progress can be made or no advancement is possible
No Man's Land
is land that is unoccupied or is under dispute between parties who leave it unoccupied due to fear or uncertainty. The term was originally used to define a contested territory or a dumping ground for refuse between fiefdoms
Belguim
Germany invaded France through this country, which effectively brought Great Britain into the war.
Self-determination
the right of people to choose their own form of government
War Guilt Clause
A provision in the Treaty of Versailles by which Germany acknowledged that it alone was responsible for WWI
Kaiser Wilhelm II
Emperor of Germany during World War I
Yugoslavia
This country was created after WWI, uniting ethnicities that spoke similar Slavic languages.
Czechoslovakia
created by the Treaty of Versailles from German and Austria territories
Alsace-Lorraine
provinces on the border of Germany and France, lost by France to Germany in 1871; regained by France after WWI
Dulce et Decorum Est Pro Patria Mori
Poem against the War's militarism, nationalism, and destructive nature
Verdun and Somme
the two most deadly wars in WWI fought with battle of attrition
War of Attrition
a war based on wearing down the other side with constant attacks and heavy losses
"Poor Little Belgium"
An expression about Germany's treatment of Belgium and the propaganda that resulted
shell shock
psychological disturbance caused by prolonged exposure to active warfare, especially being under bombardment.
Black Hand
Serbian nationalist/terrorist group responsible for the assassination of Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand which resulted in the start of World War I.
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (1918)
After Lenin in Russia got a hold of the government; he wanted to end the war between Germany. A third of old Russia's population was sliced away by the German meat ax in the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. It was the sacrifice of all of Russia's western territories.