UE Conditions & Interventions
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
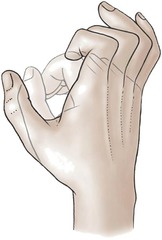
Ulnar Nerve Deformity
Claw Hand
Radial Nerve Deformity
Wrist drop and impaired wrist extension.
Median Nerve Deformity
Ape hand
Where are extrinsic muscles located?
extrinsic muscles are in the forearm with tendons leading into the hand
Where are intrinsic muscles located?
Intrinsic muscles are completely within the hand
What is the keyline for orthotics?
“Immobilize early to protect, mobilize later to correct”
What are the stages of healing?
Inflammation: avoiding infection (few days), stabilizing
Reduce edema
Cryotherapy instead of heat
Proliferation: forming scar tissues (few weeks), stabilizing & cautiously grading movement/activity
Begin ROM
Continue to protect
Maturation: remodeling (few months to years), getting back to more typical function
Push for full function
Contracture management
What is the purpose of a static splint?
to immobilize, protect, and position (preventative and functional)
What is the purpose of a serial static splint?
to mobilize and improve ROM. splint that you keep remolding over time.
based on the therapist
What is the purpose of a static progressive splint?
to mobilize, improve ROM, effective on stiff joints, follow wear with active use, adjustable
based on the client
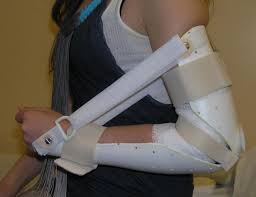
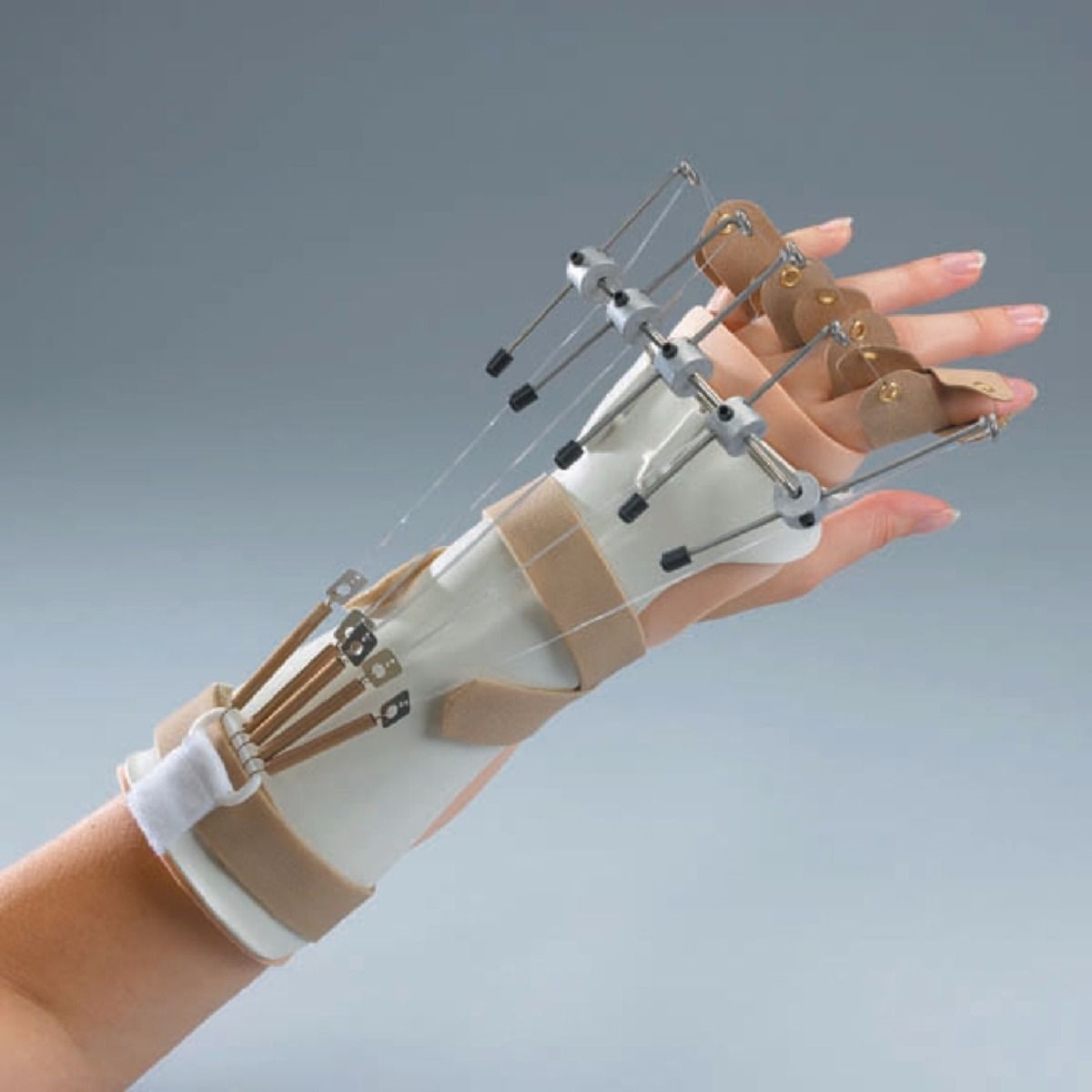
What is the purpose of a dynamic splint?
to mobilize, improve ROM, resistance exercise, and assist with movement (radial nerve palsy)
Orthoses Immobilization Purpose
pain relief
protection
positioning (functional, preventative)
prevent/manage contractures
manage muscle force
Orthoses Mobilization Purpose
remodel scar tissue
address contractures
increase ROM
facilitate movement
resistance exercise
joint fracture reduction
Orthoses General Guidelines (Wear)
tend to increase TERT (total end range time) before increasing force
watch for red spots, blanching, sensation changes etc. especially if they persist for longer than 10-20 minutes after removing the splint
Resting Hand Splint Use
general comfort
Antideformity Splint Use
positioning after trauma/edema
Short Thumb Spica Splint (Short Opponens) Use
Arthritis of CMC and MP of thumb
Long Thumb Spica Splint (Long Opponens) Usage
De Quervain’s Syndrome
Dorsal Blocking Splint Use
Post flexor tendon repair to limit tension on flexor tendons of digits to minimize risk of rupture
Wrist Cock-up Splint Use
radial nerve injury (holds wrist in extension)
radial tunnel syndrome
carpal tunnel syndrome (positions wrist in neutral)
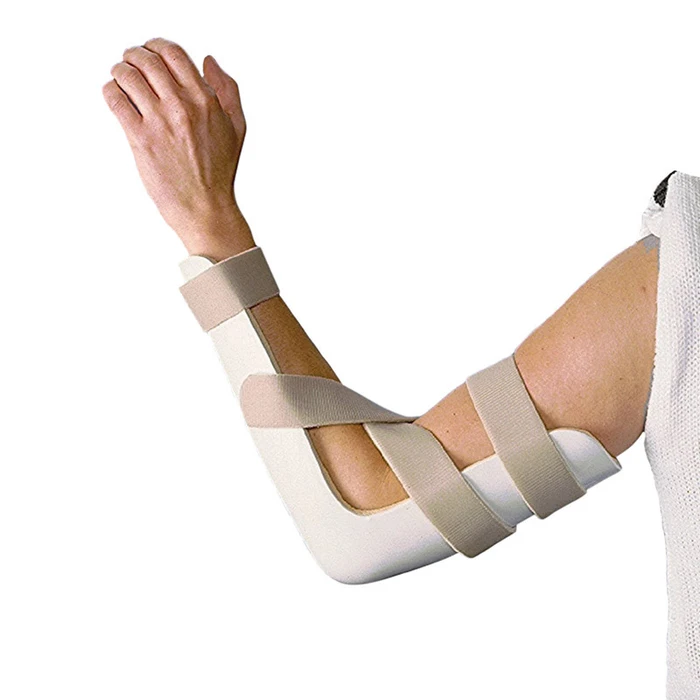
Posterior Elbow Splint Use
positions the elbow into more flexion
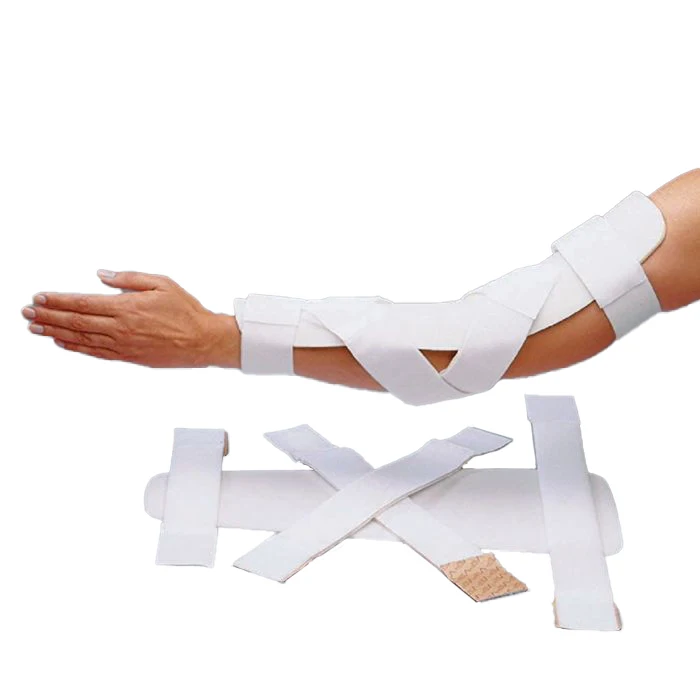
Anterior Elbow Splint Use
postions the elbow into more extension
burns on the dorsal aspect of the arm
Purpose of PAMS
address pain, inflammation, muscle tone and encourage healing and muscle function
Heat (PAMS)
Very common
Relaxes tissues - vasodilation, tendons, muscles
Results in improved healing, stretch, pain relief
Superficial heat penetrates 1-2cm, Deep heat penetrates 2-5cm
What comes first after heat, PROM or AROM?
AROM is preferred, but be gentle when using PROM
Fluidotherapy usage
Allows for motor tasks during heating, sensory component for re-ed
Ultrasound
Deep heat
Continuous: provides benefits of heat to deep tissues (2-5cm)
Pulsed: provides mechanical benefits with minimal heating (on & off)
Cold purpose
AKA: cryotherapy
decreases circulation, inflammation and pain following initial discomfort
extra caution with vascular conditions, Raynaud's Syndrome
Remove cold as soon as numbness sets in to avoid tissue damage
E-stim purpose
Stimulates muscle contractions and sensations
Manual Edema Mobilization
trained technique (not entry level)
light manual mobilization for skin over lymph nodes to promote lymph flow
best for persistent edema from surgery or trauma
Contraindicated for damaged lymph system, infection, blood clots, CHF, kidney problems and cancer
Compression
encourages fluid reabsorption
Contraindicated by DVT, severe cardiovascular concerns, peripheral neuropathy, and active TB
Edema gloves, elastic stockinette, short-stretch bandages, KT tape, Intermittent Pneumatic Compression
Cold
Reduces edema, especially early in the inflammatory phase
decreases blood flow
Isometric movement
holding resistance
Eccentric movement
lengthening of muscles
Concentric movement
shortening of muscles
SPORC
S- Strength
P- Pain
O- Occupations/tasks
R- ROM
C- Coordination
Which level of Spinal Cord Injury would benefit from using a wrist-driven flexor hinge orthosis?
C6
Rheumatoid Arthritis: which type of splint or orthoses is most appropriate for the purpose of resting the joints, decreasing pain, and preventing contractures?
Resting hand orthosis
What is the Shoulder Principle?
Proximal stability leads to distal mobility
What is Scapulohumeral Rhythm?
The humerus comes up 90 degrees; above that, the scapula moves to allow for full ROM
Erb’s Palsy
upper brachial plexus injury, affects the upper arm: shoulder on down
Klumpke’s Palsy
lower brachial plexus injury, affects lower arm: hand on up
Frozen Shoulder Protocols
do not overstretch during the freezing phase
Encourage regular movement through comfortable range
The primary treatment is compensatory strategy training and environmental modification
encourage pain-free AROM and to work around it until it thaws on its own
GH Instability treatment
start with isometrics in neutral position
anterior instability: focus on internal rotators and adductors
global instability: all muscles of the shoulder and scapula
Osteoarthritis
wearing down of cartilage elements of joints
Rheumatoid Arthritis
autoimmune condition that attacks the joints
What is the goal for dealing with arthritis?
to manage and prevent worsening symptoms and maximize function
Common deformities in OA
Boutonniere and mallet finger
Common deformities in RA
Boutonniere, swan neck
Ulnar drift
CMC
Wrist-radial subluxation
Arthritis Treatment - AROM
Pain free AROM of wrist and digits
Strengthening might be a part of treatment but very gentle, pain free
Arthritis Treatment - PAMS
OA: heat (paraffin is common, other heat modalities are effective)
RA: responds to a wider variety including heat, cold, and TENS
What is the standard mobility progression for a wrist fracture?
1- AROM
2- PROM
3- Resistive exercise
What is the standard mobility progression for a hand fracture?
1- AROM
2- PROM (external force)
3- Resistive exercise (external force)
What is the standard ROM progression for the elbow?
AROM to PROM to resistance
What is protective sensation?
sensitivity to touch as well as temperature
What does the monofilament and two-point discrimination test measure?
light touch
Which type of splint is most commonly used for wrist drop?
wrist cock-up splint
What are the functional common issues of the ulnar nerve?
grip strength
key pinch
being able to hold objects in hand
What is a positive froment’s sign
if the thumb slips or bends (compensates), during a key pinch test
What type of splint can be used for an ulnar nerve injury?
Nighttime elbow extension splint to limit elbow flexion
What type of splint is used for a median nerve injury?
Wrist cock-up splint with wrist in neutral, MP, thumb or elbow support might also be necessary
OT Role with peripheral nerve injuries
Manage/prevent complications including pain and further injury
Maintain function - ROM and nerve gliding
Facilitate regaining function
OT interventions with peripheral nerve injuries?
Sensory Re-education
Pain Management
Desensitization
Modalities (depends on what is effective and safe for the client)
What test is most effective for testing for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Phalen’s sign
What is Wartenburg’s sign?
involuntary finger abduction of the fifth digit
What is the O’Rian wrinkle test and what population benefits from this test?
Keeps the hand submerged and observe lack of wrinkles
Toddlers and infants benefit from this test since they cannot verbally express pain
What is CRPS?
Chronic pain and edema that is marked by hypersensitivity to touch, texture, and temperature
OT Treatment for CRPS
Goal: repair the broken the relationship between the pain centers of the brain and affected.
decrease the perceived threat, and desensitize the area as much as possible
CRPS: Calm, Reflection, Progressive Stimulation
Calm (CRPS)
CBT
Relaxation/Mindfulness
Reflection
Mirror Therapy: touching or moving the unaffected side while looking at its reflection, it is critical that the client attempts to perceive the reflection as their actual body part
Progressive Stimulation
Desensitization: textures, vibration. Start near the painful area and work into it
SHOULD NOT BE PAINFUL
Build tolerance, not enduring pain
What is the primary modality used for CRPS?
Fluidotherapy reduces pain and swelling.
Useful for desensitization
Tendinopathy
Pain in the tendons with movement or tension
collagen breakdown from overuse, not inflammation
What is Lateral Epicondylosis?
Tennis Elbow/Lateral Epicondylitis
Painful extrinsic extensor tendons near the elbow
Painful to the touch
Decreased grip strength
What is Medial Epicondylosis?
Golfer’s Elbow/Medial Epicondylitis
Painful flexor tendons near elbow (involved with pronation)
Painful to touch
Painful to grip/pronation
What is De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis?
tendinopathy of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis of the first dorsal compartment
painful for thumb abduction/extension
Test
Finklesteins test
Tendinopathy Mnemonic
O- Orthotic
A- Activity Modification
S- Stretch
I- Ice
S- Strengthening
What splint can be used for lateral epicondylosis?
Wrist cock-up splint (35 degrees of extension)
What type of splint can be used for lateral epicondylosis?
Wrist cock-up splint (neutral)
How would you splint Trigger Finger?
In MP extension for 6-10 weeks
Extensor tendon tension limiting mobility progression
Standard: Immobilization, gentle AROM, gentle PROM
Tension-limiting: Immobilization, PROM, AROM
Extensor tendon splint for zones 5,6,7 (immobilization)
Pan splint (full hand extension -including MCPs, slight wrist extension) to minimize tension on the extensors
Extensor tendon splint for zones 5,6,7 (early PROM)
Passive extension, active flexion (up to 30 degrees)
Dynamic splint, dorsal outrigger with volar block
Flexor tendon tension limiting mobility progression
Standard: Immobilization, gentle AROM, gentle PROM
Tension-limiting: Immobilization, PROM, AROM
Flexor Tendon (Immobilization) Splint
Dorsal blocking splint (antideformity position)
Flexor Tendon (Early PROM) Splint
Passive flexion, active extension within dorsal block splint
Flexor Tendon (Early AROM) Splint
Use dorsal block for most of the time, and then a separate orthosis with wrist extension for gentle active flexion (place and hold)
Dupuytren’s Contracture
Progressive contracture into MP and sometimes PIP flexion, typically of the 4th and 5th digits
Results from thickening of the palmar fascia
Dupuytren’s Contracture Treatment
Immediate A/PROM, light ADLs
MP Extension splint at night and during the day if necessary
Avoid strenuous activity/sports for 6 weeks
Non-surgical treatment for Dupuytren’s
Soft tissue mobilization
ultrasound
progressive stretching with heat
extension splint at night
NMES & FES
Strengthening: exercise/functional use
TENS Use
Pain management
Best for acute pain: fractures, tendon/ligament repairs, sprains
Different settings can be used to reduce trigger points
What are the best measurements for edema?
Volumetry (dunking the hand in water, measuring change)
best option, but occasionally contraindicated
Figure of Eight & Circumferential Measurement
wrapping flexible measuring tape, problems with consistency
Open Chain
Moving your arm freely
Bicep curl and leg extension machine
Closed Chain
Includes the squat and push-up, where the limb is fixed to the ground, and the body moves against resistance.
The end of the extremity is touching something else
Genu Varus
LCL instability
Elbow deviates inwards
More common compared to Genu Valgus
Genu Valgus
MCL instability
Elbow deviates outwards
Typically seen in throwing athletes (baseball)
Dupuytren’s Contracture Treatment
Immediate A/PROM, light ADLs
MP extension splint at night and during the day if necessary
Monitor for infection
Avoid strenuous activity/sports for 6 weeks
What does the anatomical snuffbox consist of?
abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis of the radial border
Smith’s Fracture
distal radius fracture - volar displacement