8.3 (done)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what can muscles do
be stimulated by a nerve impulse
shorten in length
be stretched
return to their original length
sliding filament theory
as the thin actin and thick myosin filaments slide over one another, the Z-lines are drawn closer together and the sarcomere is shortened
this results in shortening of the muscle fibres and shortening of the whole muscle
ATP is required for the shortening of muscle fibres
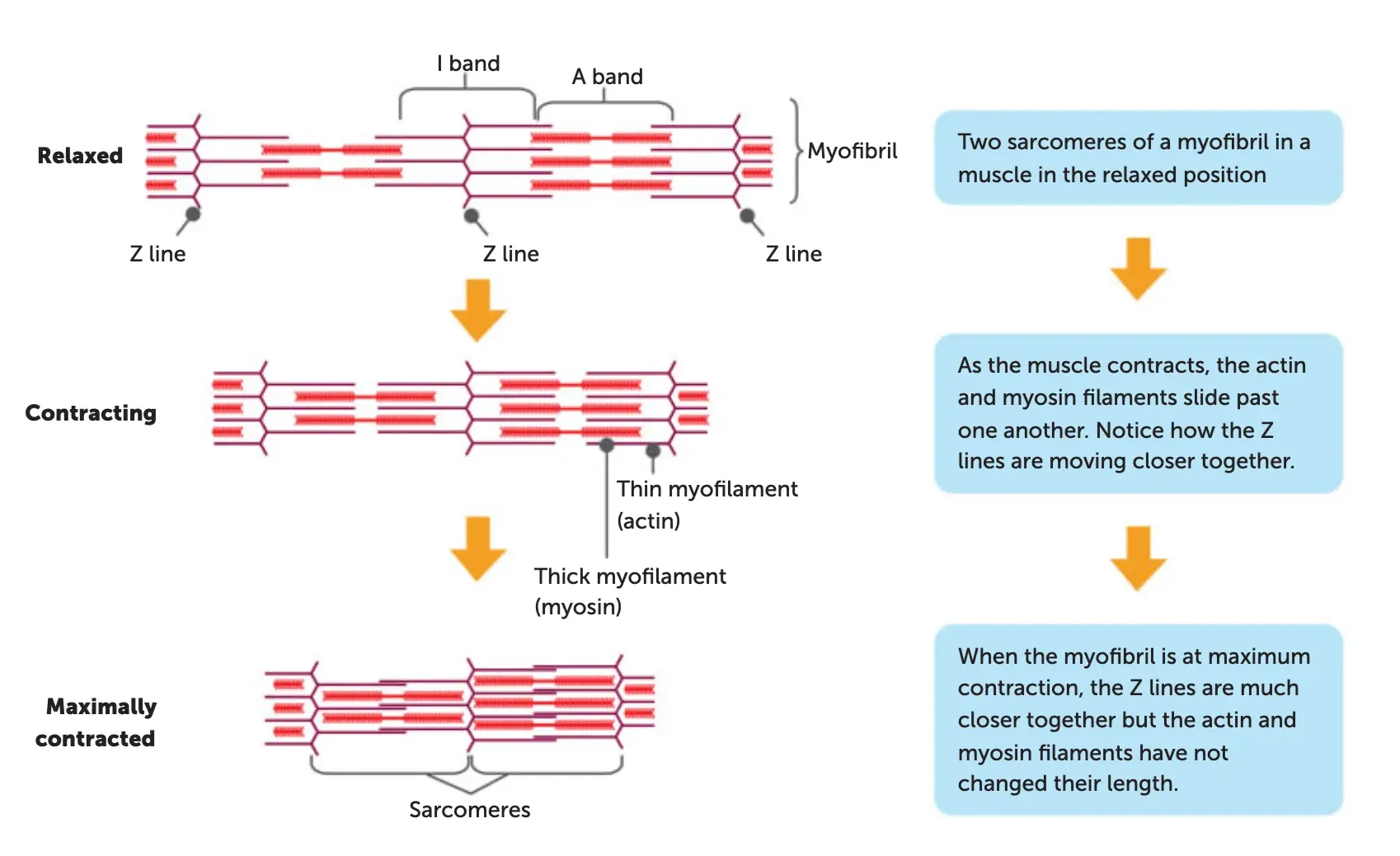
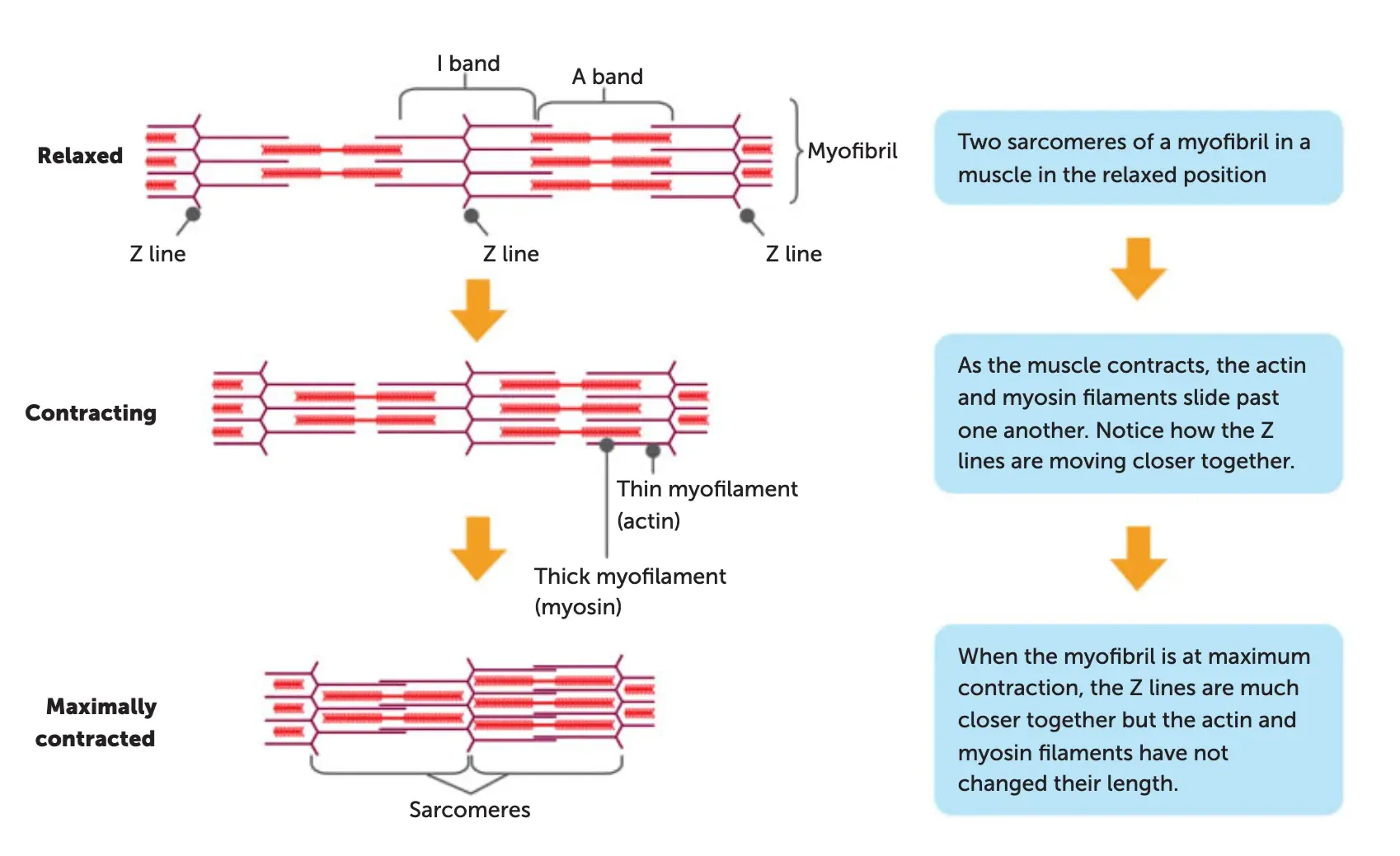
steps of the sliding filament theory
Nerve impulse reaches the muscle fibre, triggering release of Ca²⁺ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
The calcium binds to the actin myofilaments and this causes the myosin binding sites to be exposed to the myosin.
The myosin myofilament joins to the myosin binding sites on the actin and forms crossbridges.
The formation of crossbridges requires energy (ATP).
The myosin crossbridges pull on the actin and the actin slides over the myosin (note: myosin doesn’t change in length). This also requires ATP and is the muscle-shortening phase of muscular contraction. This is called downstroke.
Z-lines move close together / sarcomere shortens.
It requires ATP to cause the myosin to “unhook” off the binding sites. Once the crossbridges move off the binding sites, the actin slides back to the “resting” position. Z-lines move further apart / sarcomere lengthens.
tendons
attaches muscle to the bones of the skeleton by fibrous, inelastic connective tissue
can muscles push bones apart
no
muscles can only contract
meaning that they pull bones together but cannot push them apart
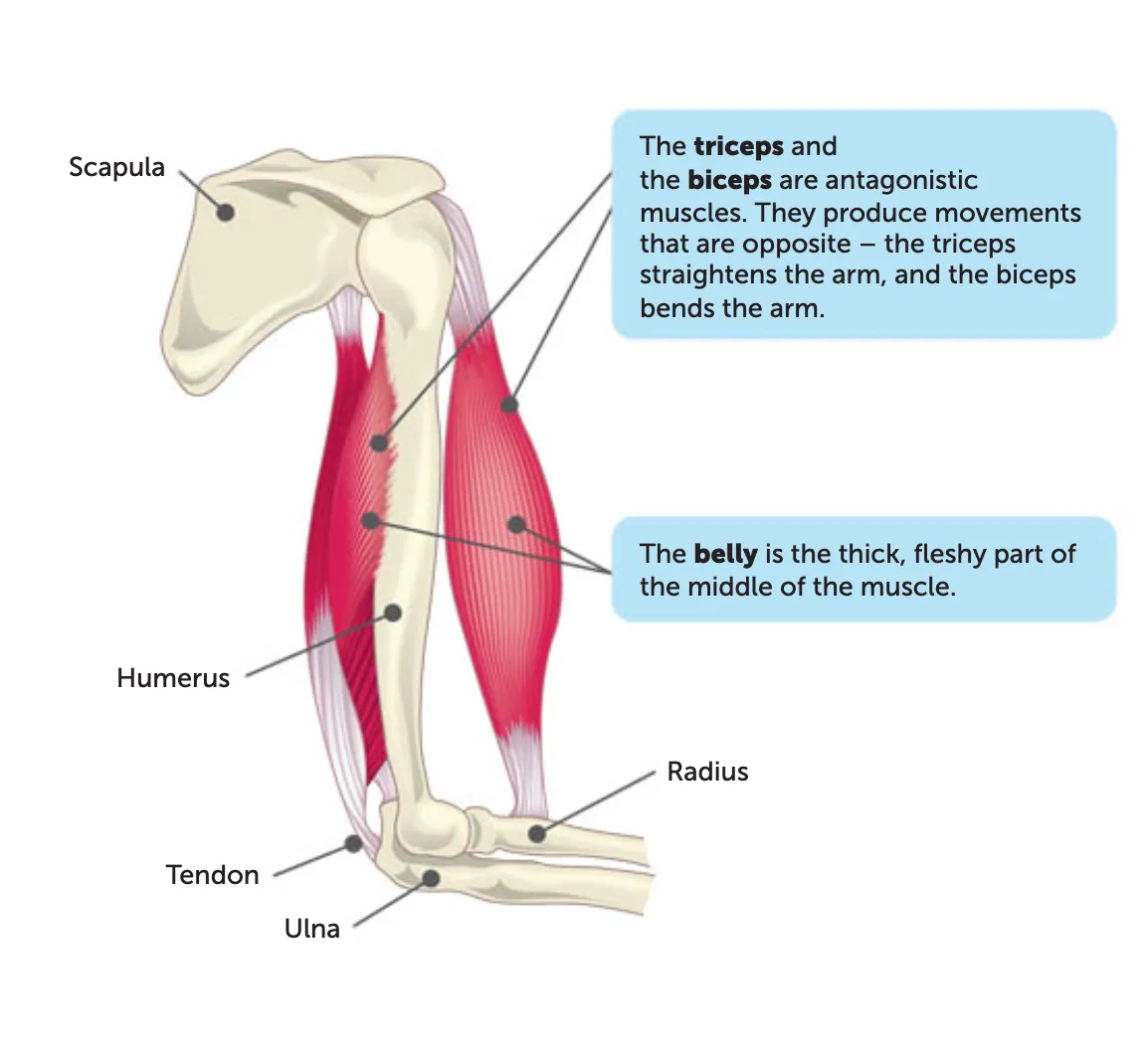
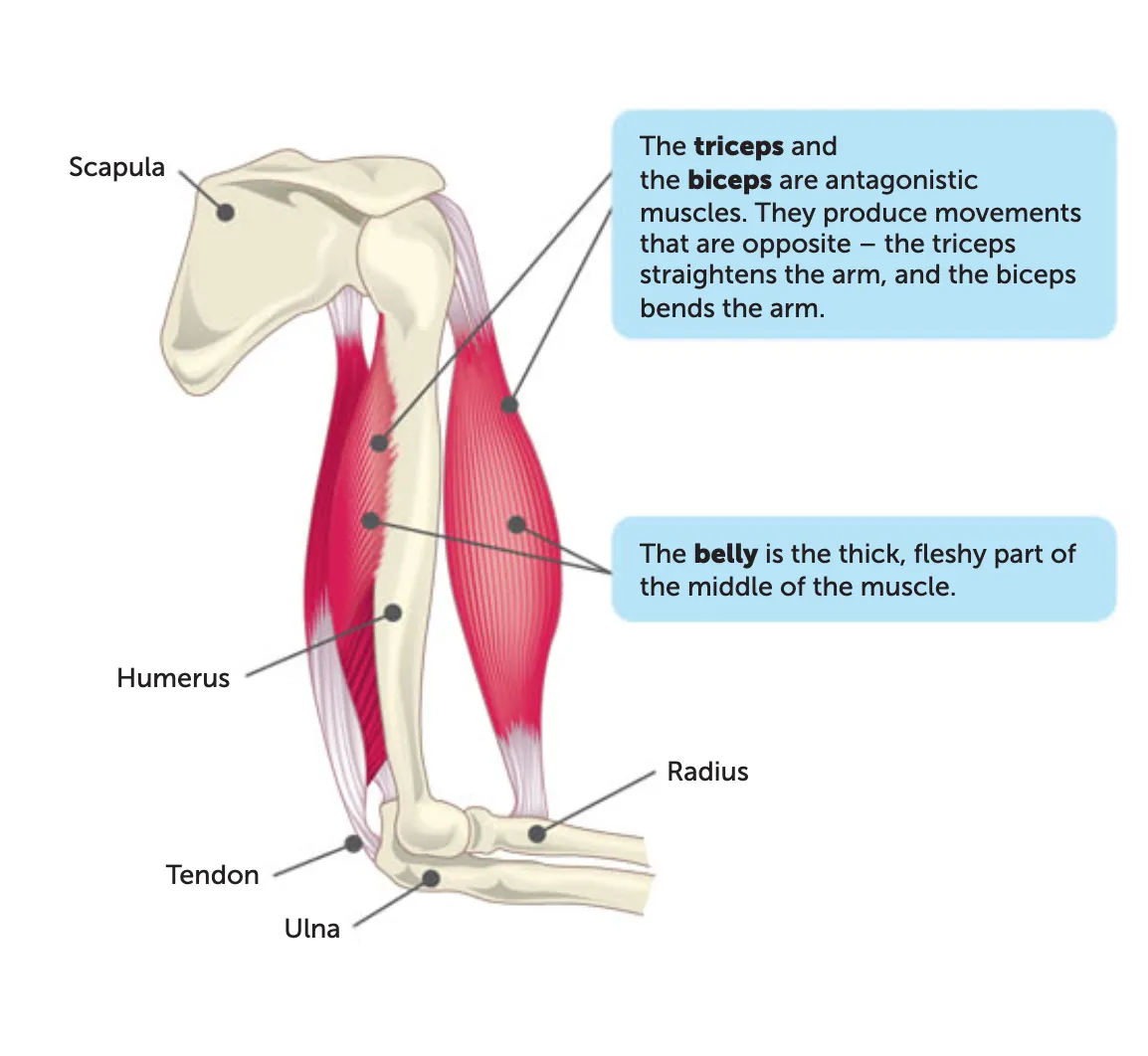
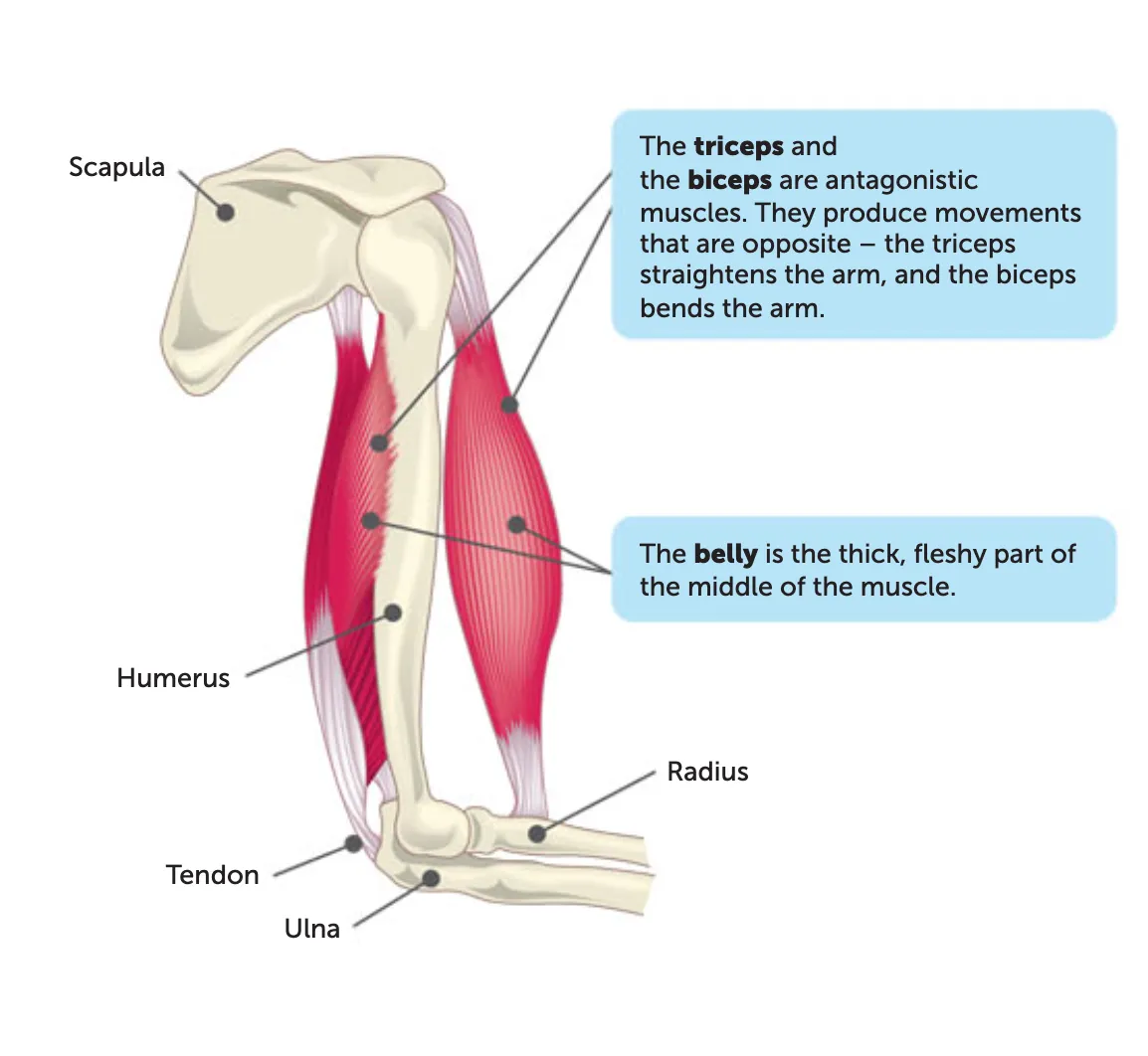
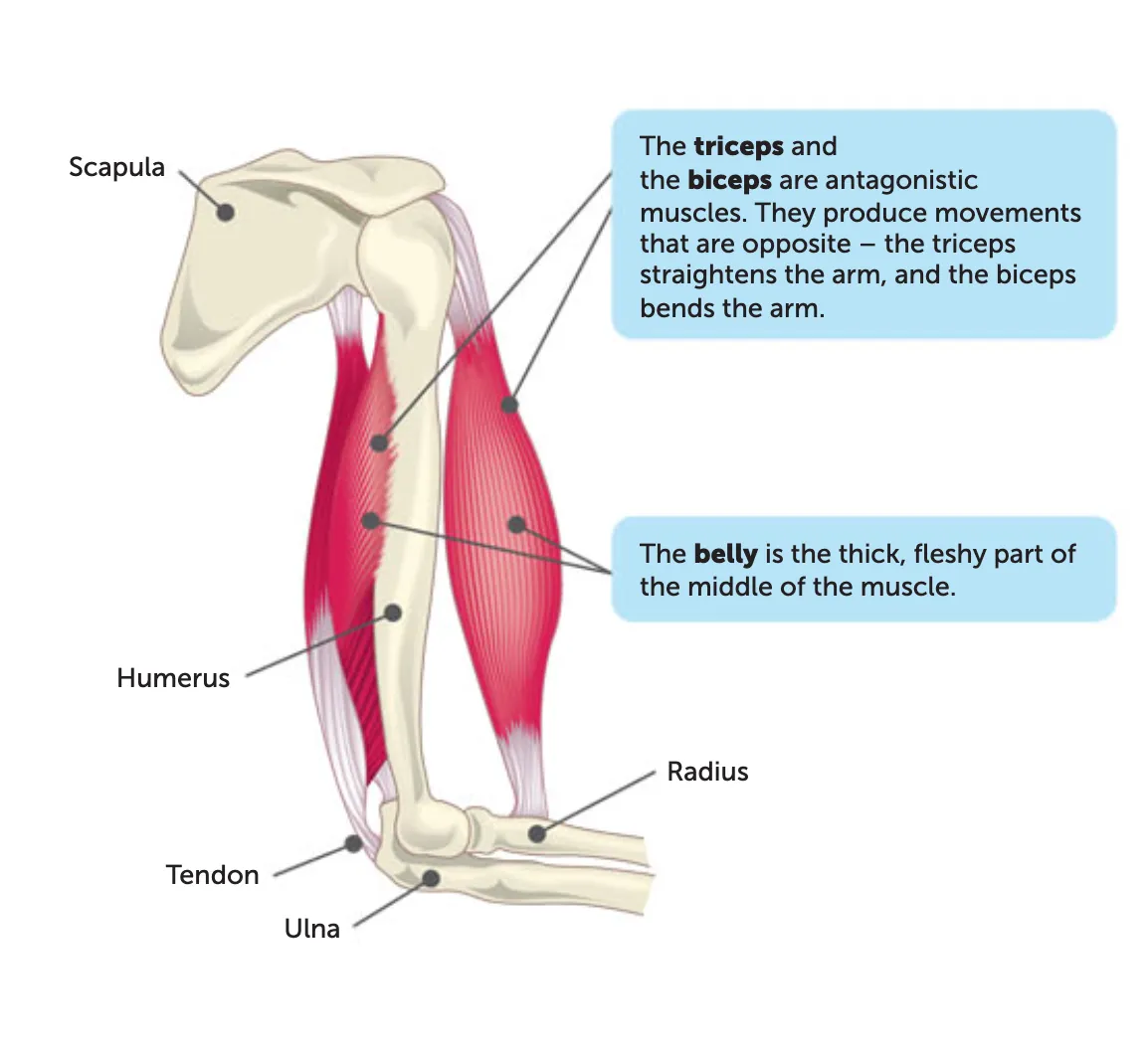
antagonistic pairs
Agonist: muscle doing the work (e.g., biceps).
Antagonist: muscle relaxing (e.g., triceps).
other roles
Synergists: assist the agonist.
Fixator: stabilise origin of prime mover.
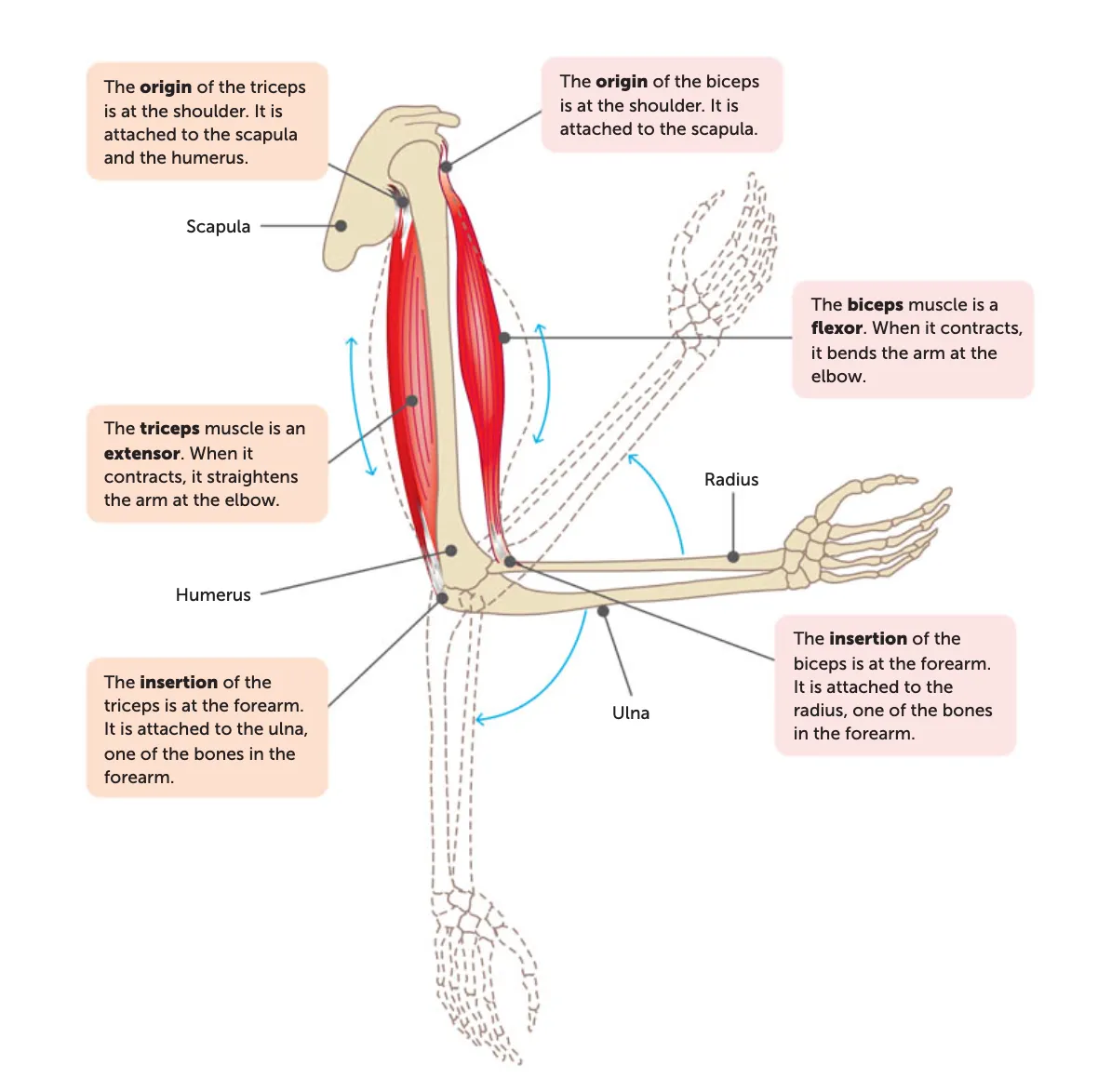
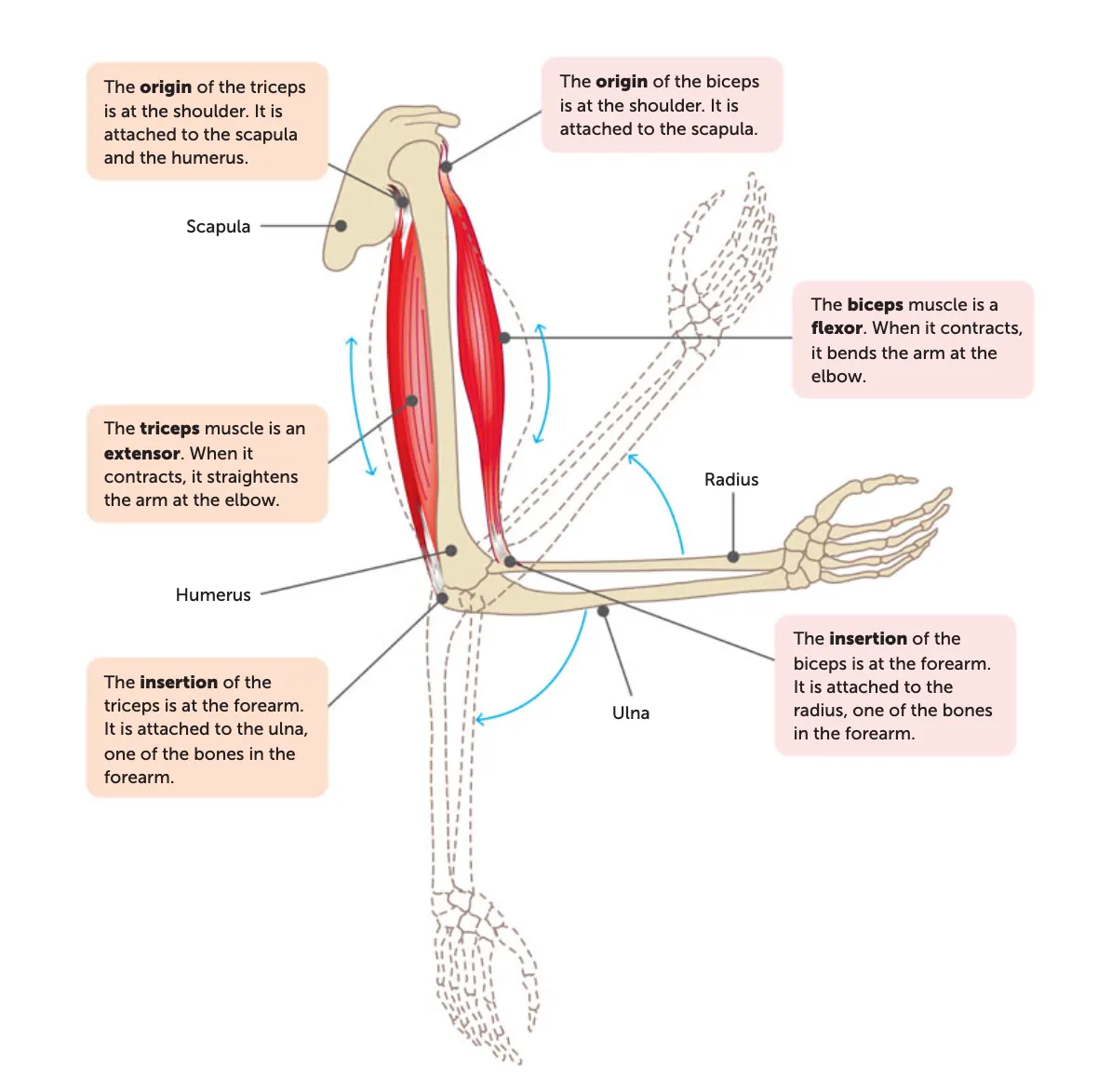
origin
the end of a muscle that is fixed to the stationary bone
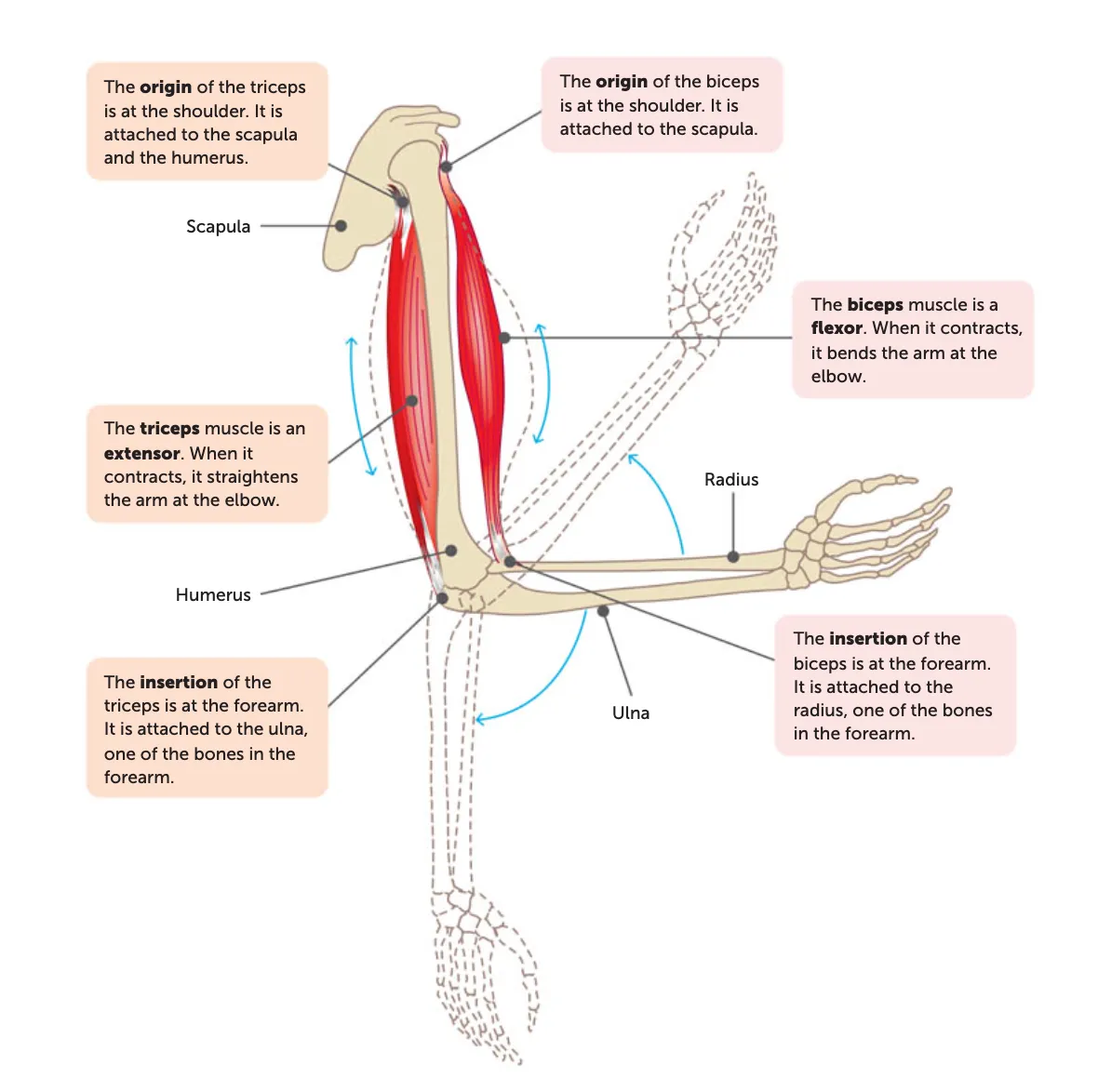
insertion
the end of a muscle fixed to the moveable bone
During contraction, the insertion is pulled toward the origin.
belly
The thick, fleshy middle part of the muscle between the origin and insertion.
this is the part that contracts and generates movement.
types of muscle contraction
concentric
eccentric
isometric
concentric
muscle shortens
for example; Lifting phase of bicep curl
eccentric
muscle lengthens
for example; lowering phase of bicep curl
isometric
no change
static
for example; Holding a weight steady, plank
muscle tone
maintaining partial contraction of skeletal muscles
some muscle fibres are contracted while others are relaxed
The fibres relieve one another so smoothly that the contraction can be kept up for long periods of time
muscle tone holds many of our body parts in position
eg; our head is help up by the partial contraction of neck muscles
posture
the way a person holds they body when standing or sitting