teeth
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what is basic teeth anatomy
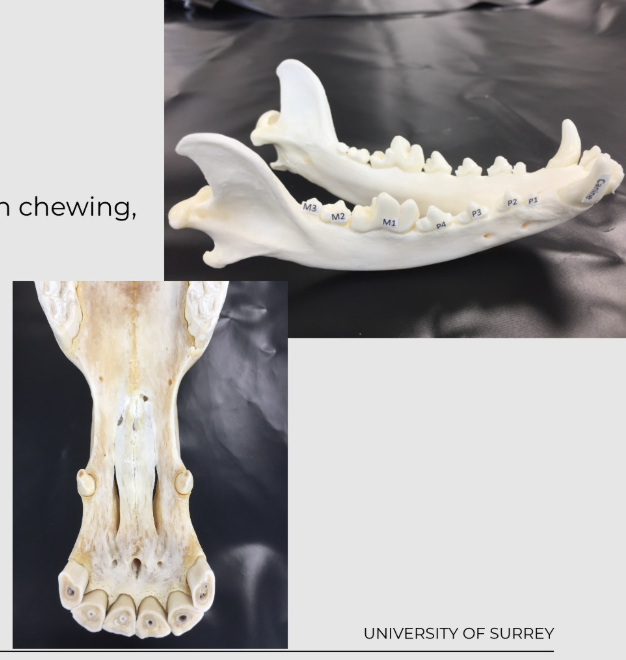
arranged in two dental arches - upper and lower arches face each other
upper teeth are inside the incisive and maxillary bones
lower teeth are in the mandibular bones
teeth specialised for chewing, tearing and prehension
some animals heterodont - I (incisors),C (canines), PM (premolars), M (molars)
other animals are diphyodont - deciduous and permanent - all teeth are the same and they are milk teeth that dont fall off and just shed over time
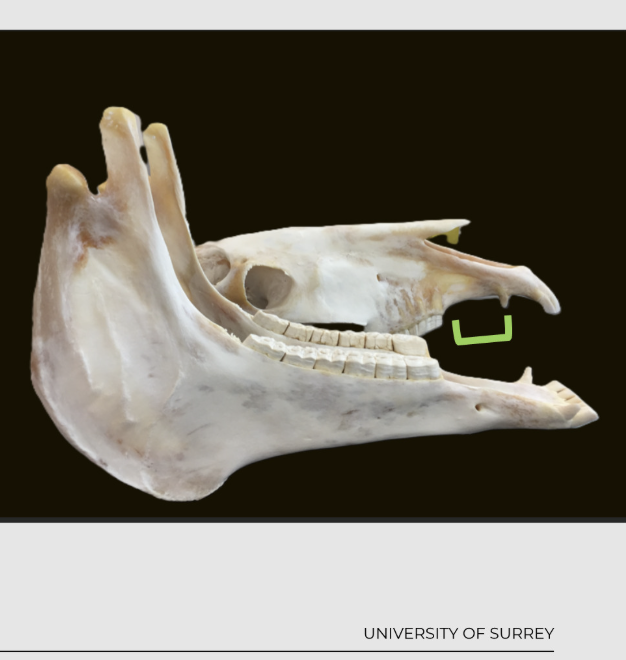
what is the diastema?
a physiological gap between the incisors and premolars
also known as interdental space
usually in farm animals and rabbits
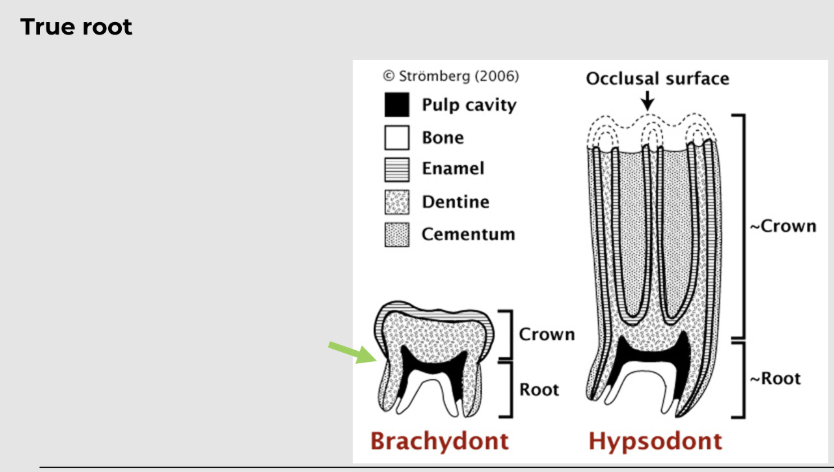
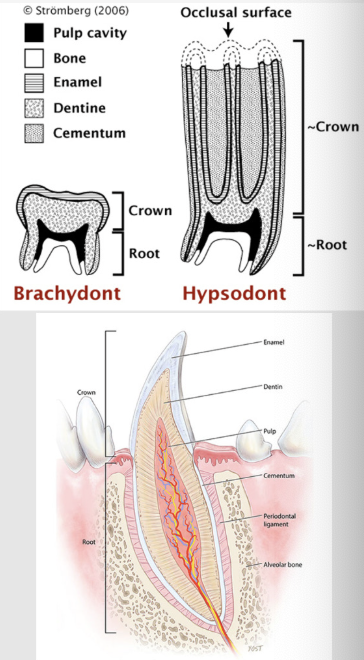
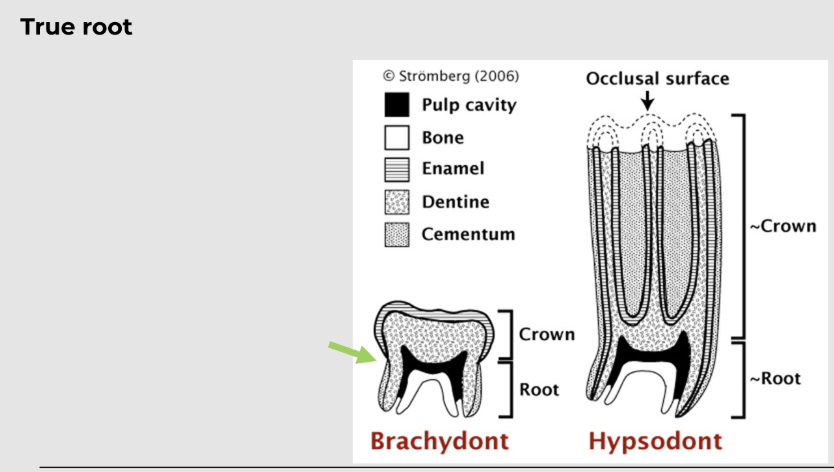
what is a brachydont?
smaller and low-crowned tooth, suitable for feeding on soft diet; dogs, cats, ferrets and pigs etc.
forms a true root
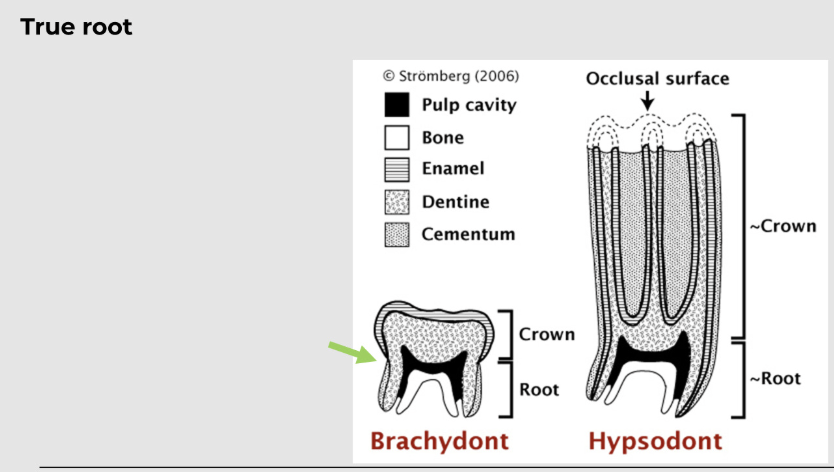
what is a hypsodont?
larger and longer crown that can resist the wear and tear of feeding on a tough and fibrous diet, as in ungulates; horses have all teeth (except canines), ruminant cheek teeth, lagomorphs, and tusks of pigs (canine teeth)
some animals form closed root AKA radicular- like horses, cattle, deer (radicular - continuously erupting but not growing - eventually form a true root
then you got some animals like rabbits and chinchillas which always have an open root AKA aradicular - like rodents, lagomorphs, chinchillas (aradicular - continuously growing
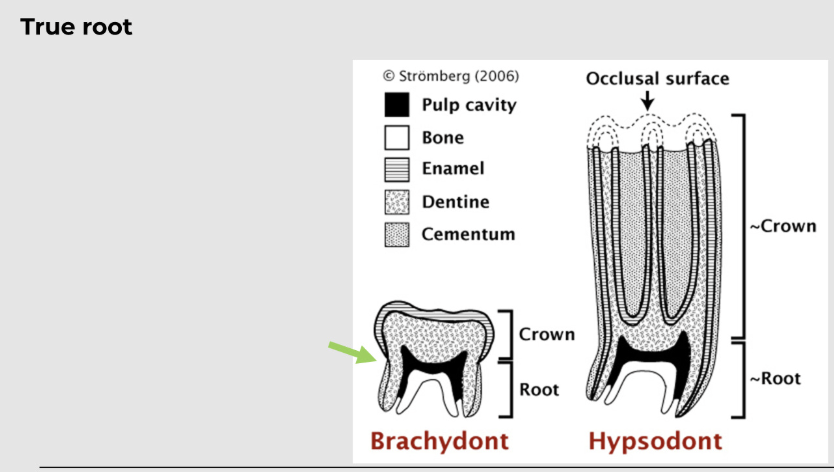
the dental crown, (neck) and root in detail
the neck is the constricted region just below the gingival line
the tooth is anchored by its root by alveolar bone or alveolus (alveoli) - socket of bone
there is the lamina dura (aka cribriform plate) which is a thin shell of dense bone lining the alveoli
the teeth consist of enamel, dentine, cementum and pulp
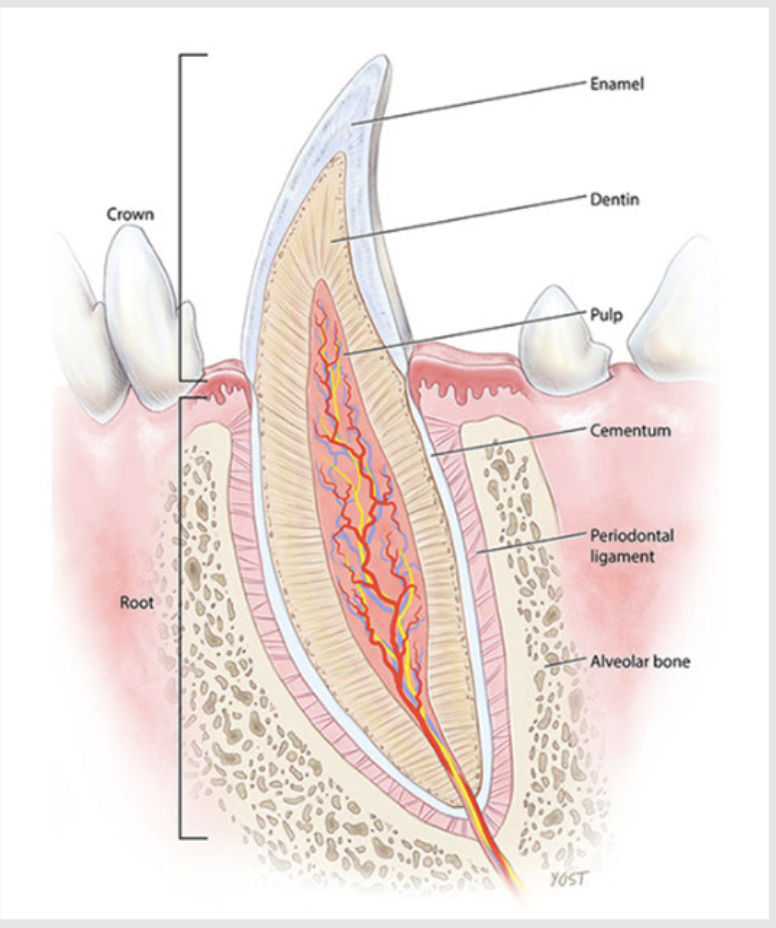
what is enamel?
hardest and most mineralized substance in the body
it is acellular - cant regenerate (except pig tusks ) as there is no nerve or blood supply
in brachydont, the enamel covers the external surface of the crown
in hyposodont, the enamel covers the entire body of the tooth, but not the root (folding of enamel: peripheral and infundibular enamel)
histologically, enamel is composed of long, slender rods and produced by ameloblasts
what is dentin?
the bulk of the tooth, a hard, substance like bone, surrounds the pulp cavity
produced by odontoblasts - tall columnar cells located at the periphery (outside) of the dental pulp
odontoblasts remain active throughout life-deposited continuously
there are 3 types of dentin
primary - formed before tooth eruption
secondary - forms at the periphery of the exposed pulp cavity-tertiary created in response
to external stimuli, darker in colour (reparative or teriatiary dentine)
what is the cementum?
least hard of all, a thin, bonelike layer
attached to the alveolar bone by periodontal ligament (interconnected, interwoven bundle of fibers, anchored to the cementum and bone)
in the brachydont - covers the root only
fills the infundibula of hypsodont teeth and covers the entire tooth
e.g. equine cementum is unique in that it is vascular and innervated-deposition continues throughout the life of the tooth
what is the dental pulp?
soft tissue with nerves, vessels, lymphatics -its contained in the pulp cavity
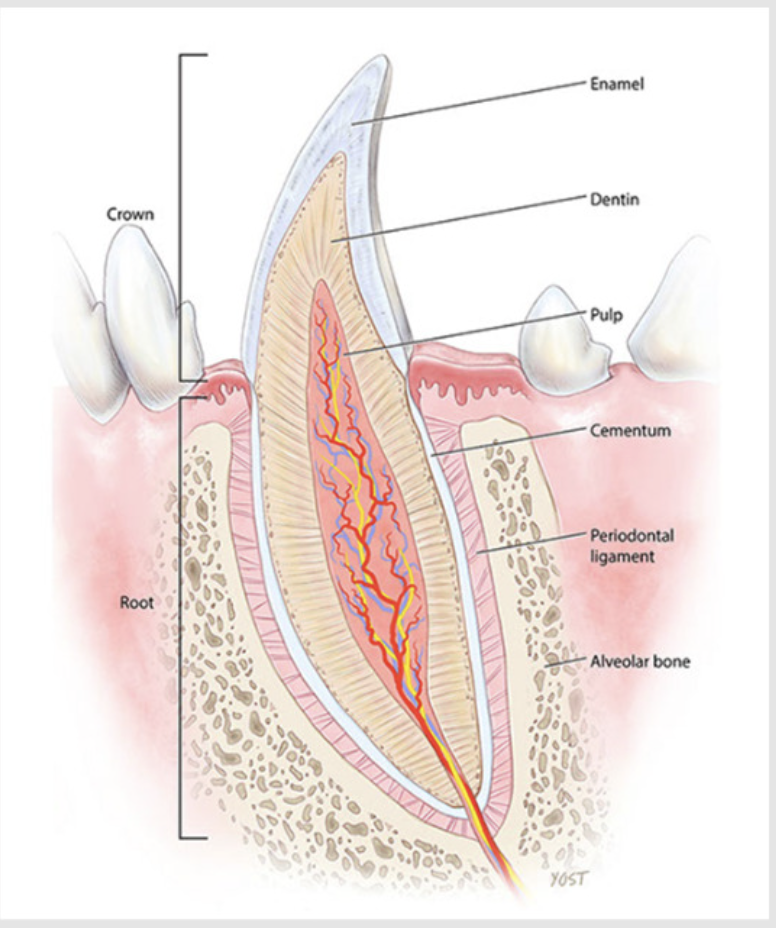
what is the periodontium?
connective tissue
it supports the tooth, protects it against oral microflora, and makes the attachment of the tooth to the bone possible
periodontal tissues include four defined structrues: gingiva, cementum, alveolar bone, periodontal ligament
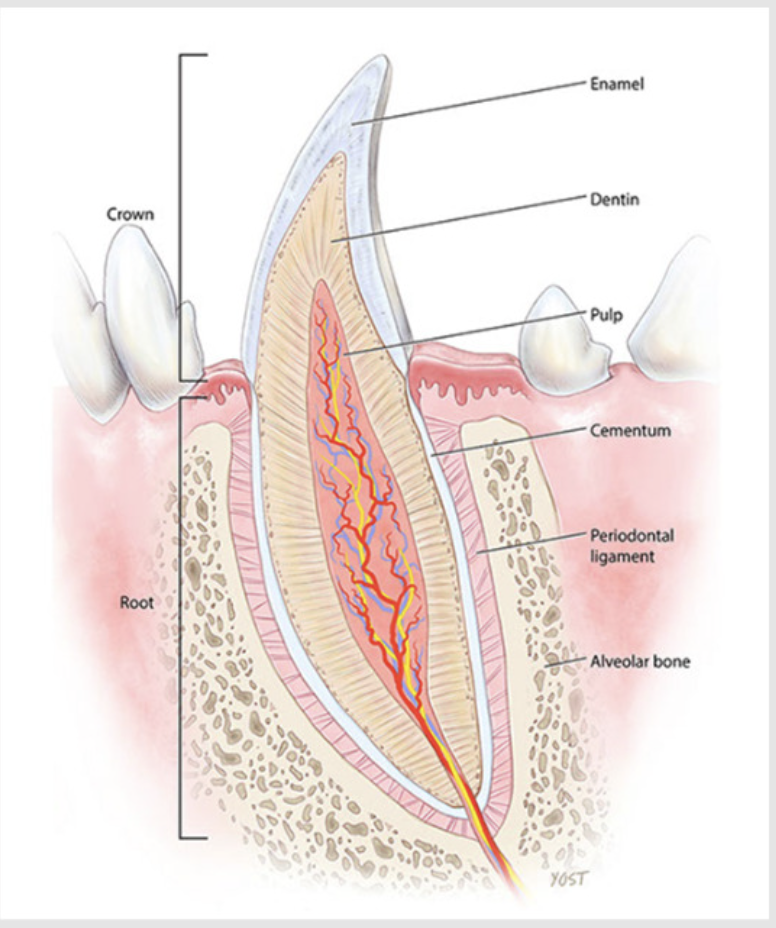
what is gingiva/gums?
keratinized oral mucosa - covering alveolar processes of the jaws, encircling necks of erupted teeth
only one of the 4 periodontal tissues seen in the mouth
forms a tight seal and prefents feed material from entering the periodontal ligament space
borderline between the crown and roots is the cementoenamel junction (CEJ)
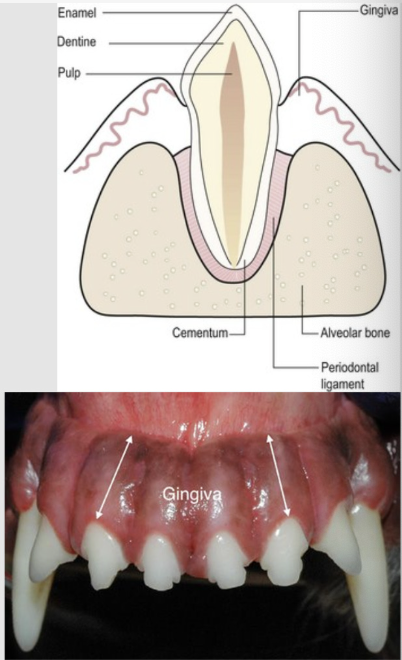
what types of gingiva are there?
attached and free
attached - firmly attached to the underlying periosteum of the alveolar bone
free - adopted to the tooth surface
at the gingival crevice (sulcus), the cells in the epithelium of the gum adhere to the tooth enamel
adherence of the gingiva to the tooth forms a tight seal
what is the function of incisors?
grasping, pinching, scratching, nipping
“weapons” for tearing flesh during hunting & fighting
Premolars rostral cheek teeth which have deciduous precursors; molars do not
Molars are flattened and triangular with jagged edges; function like serrated-edged blades
Shearing [esp. upper P4 & lower M1]; grinding
![<p>grasping, pinching, scratching, nipping</p><p></p><p>“weapons” for tearing flesh during hunting & fighting</p><p></p><p>Premolars rostral cheek teeth which have deciduous precursors; molars do not</p><p></p><p>Molars are flattened and triangular with jagged edges; function like serrated-edged blades</p><p></p><p>Shearing [esp. upper P4 & lower M1]; grinding </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b8e92bf2-5834-453c-8d9b-a2fe81dd15a1.png)
what are the surfaces of the teeth
vestibular surface of the tooth - faces the vestibule or lips (labial and buccal)
for incisors and canines- labial, and molars and premolar-buccal
lingual surface of the maxillary or mandibular tooth that faces the tongue
palatal refers to the lingual surface of the maxillary teeth
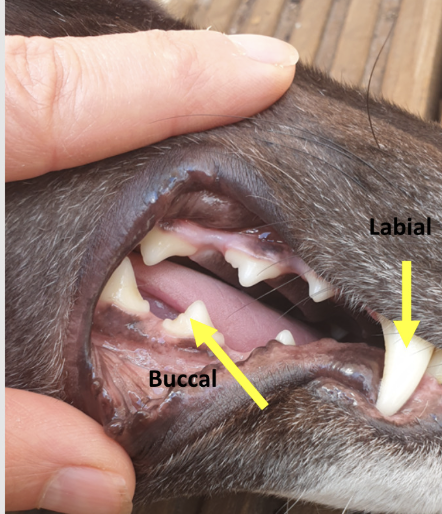
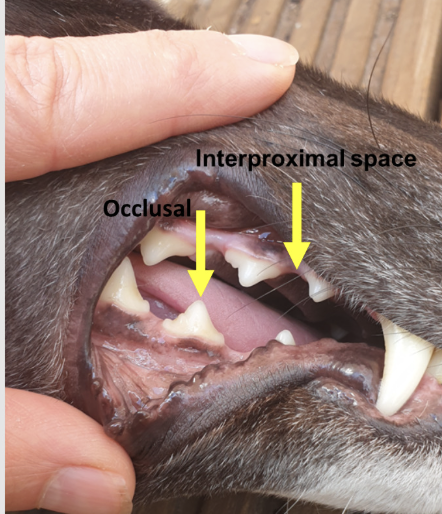
what are the occlusal and interproximal space?
occlusal surface-portion of tooth that comes in contact or faces the tooth in the opposite (PM, M)
coronal used as a term relating to the occlusal surface (crown of the tooth)
atypical - towards the apex (root) of the tooth
interproximal collective name refers to the surfaces of the tooth face next tooth in the same row
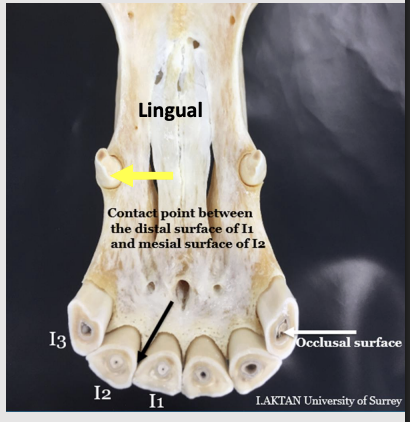
what are mesial and distal surfaces of the teeth?
mesial - surfaces of the incisor teeth that are toward the middle or median plane of the mouth
rostral surface of the C,P, M teeth
distal- surface of the incisor teeth that is away from the middle or median plane of the mouth
caudal surfaces of the C,P,M teeth
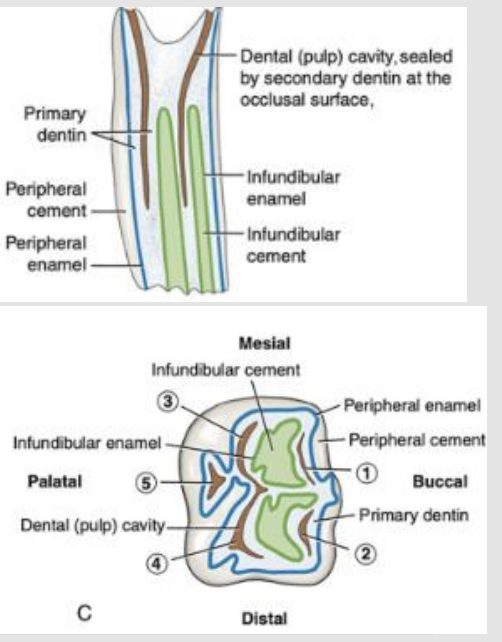
what are horse teeth like?
Complicated folding of enamel (Incisors and maxillary cheek teeth)
Cheek teeth on the maxillary arcade have 2 infundibulae, which are deep infoldings of enamel filled with cementum in the center of the teeth
Mandibular cheek teeth have the same pattern of infoldings/invaginations but no infundibulum
horse teeth pt2
As tooth continually erupts and wear down, the appearance of the occlusal surface changes
Tissues wear at varying rates
An infundibulum is a cup/funnel-shaped invagination of enamel
Wear causes the cup to get smaller and eventually disappear from all lower incisors, leaving the enamel spot in its place
Secondary dentin (forms dental stars on worn surface
of tooth)
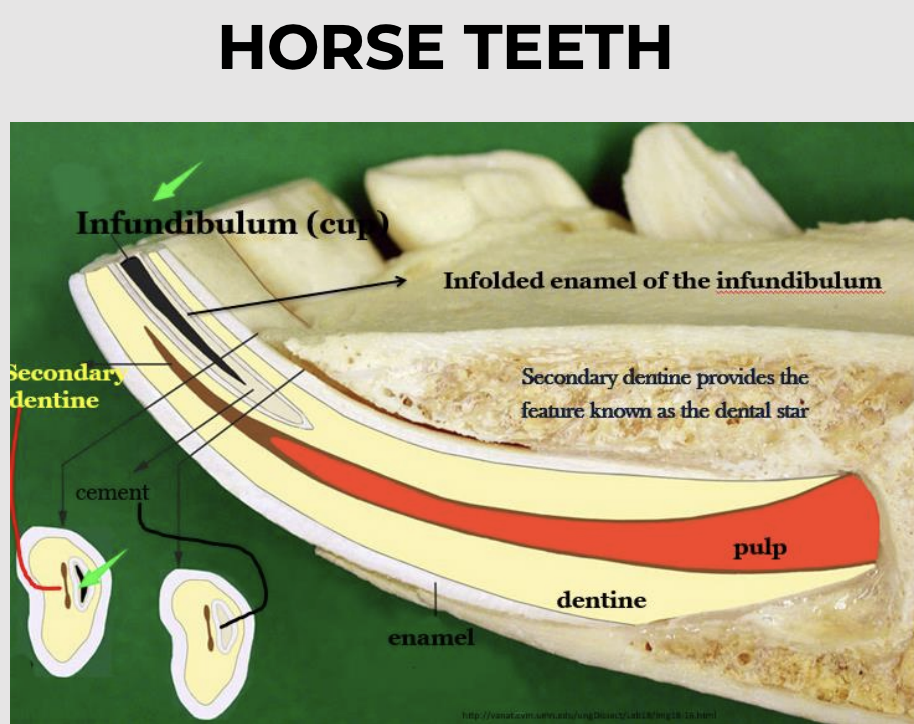
what is the infundibulum?
Colloquially called a "cup“ in teeth
Looks like a dark mark, because food gets packed inside and turns black as it decays
Partly filled with cement, leaving a small cavity
Does not connect with the pulp cavity
Secondary dentin is formed overlying the pulp horn (dark brown D2)
Primary dentin (white/yellowish D1)
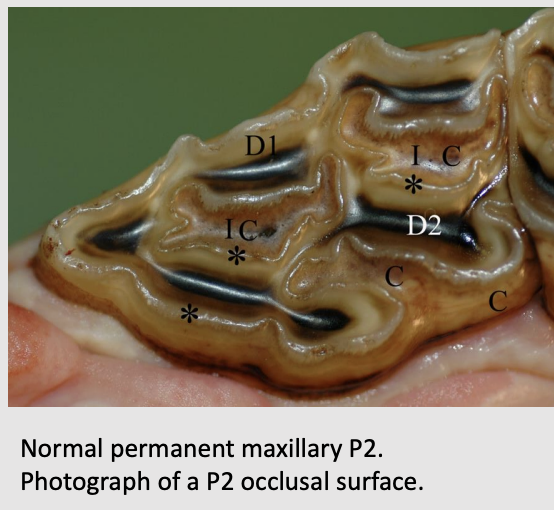
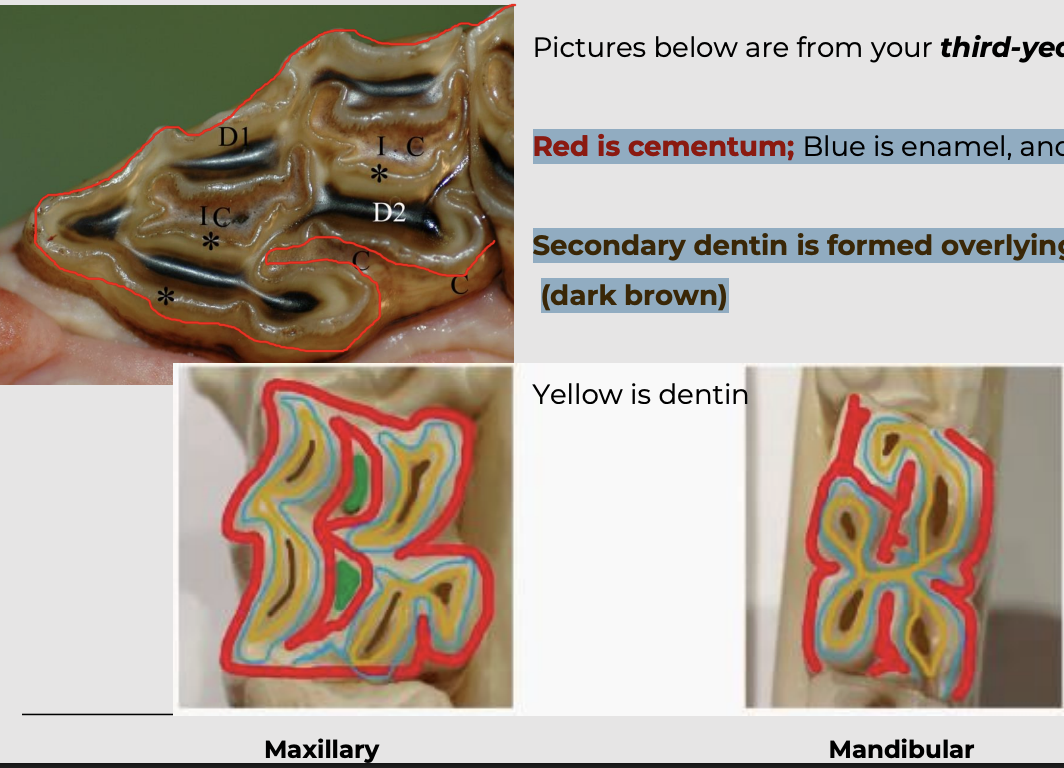
what is the maxillary cheek teeth?
3 roots; 2 buccal and 1 palatial
2 infundibulae ( a mesial and distal infundibulum)
Red is cementum; Blue is enamel, and Green is infundibulum
Secondary dentin is formed overlying the pulp horn (dark brown)
yellow is dentin
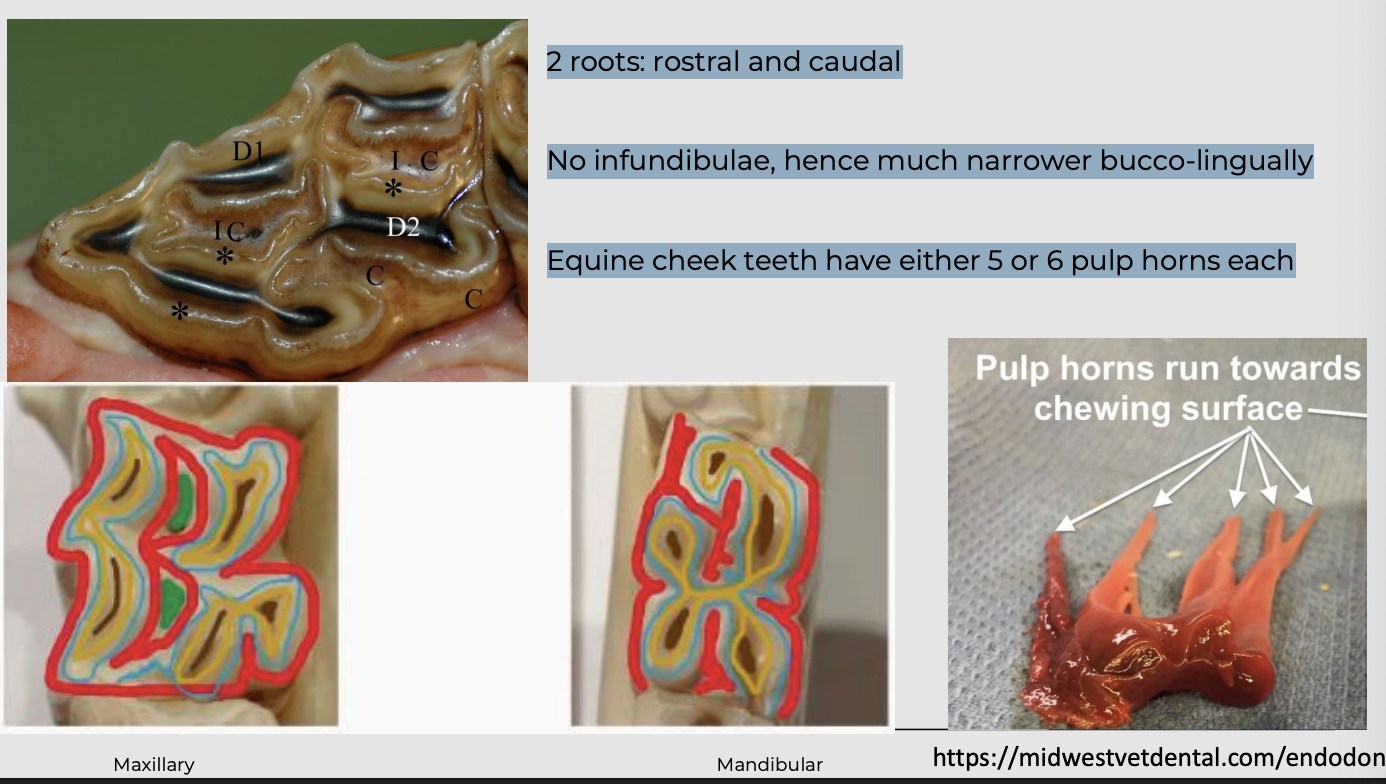
what is the mandibular cheek teeth?
2 roots: rostral and caudal
No infundibulae, hence much narrower bucco-lingually
Equine cheek teeth have either 5 or 6 pulp horns each
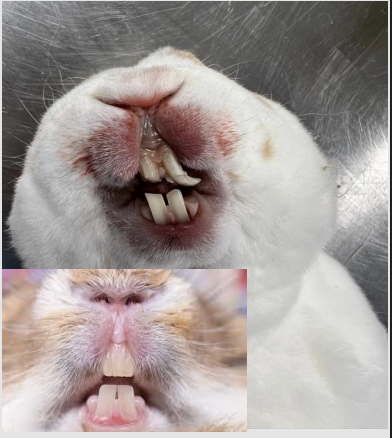
what is rabbit teeth like?
Belong to the order of Lagomorpha, because of two small second incisors (peg teeth) (Rudimentary) behind the maxillary incisors
Three pairs of incisors: two upper and one lower
Chisel-shaped incisors
Enamel of the incisors is not distributed uniformly; the enamel is thicker on the vestibular aspect and thinner on the lingual aspect
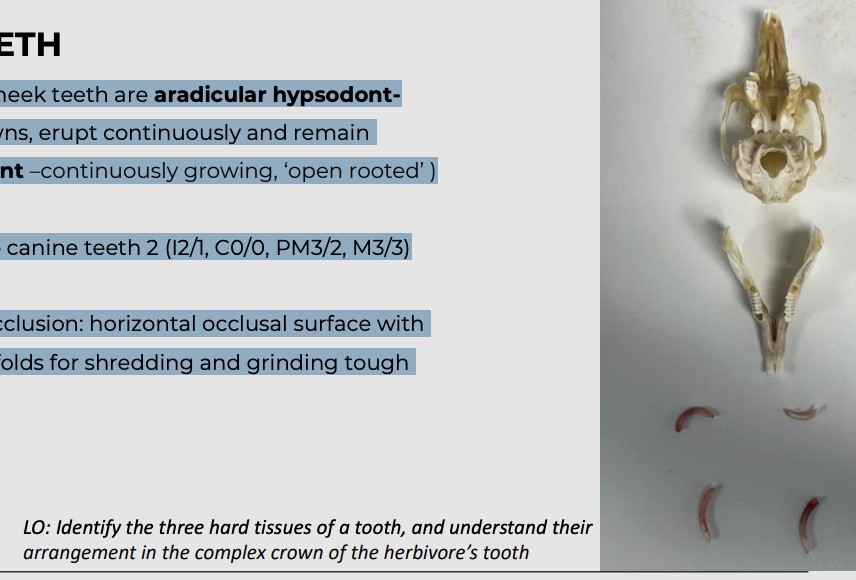
Both incisors and cheek teeth are aradicular hypsodontlong anatomic crowns, erupt continuously and remain open-rooted (elodont –continuously growing, ‘open rooted’ )
Total of 28 teeth, no canine teeth 2 (I2/1, C0/0, PM3/2, M3/3)
Typical herbivore occlusion: horizontal occlusal surface with transverse enamel folds for shredding and grinding tough fibrous food
Diastema
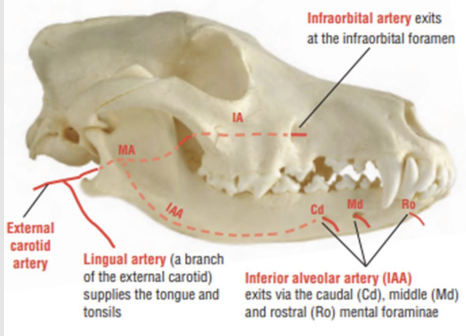
what is the blood supply like in the teeth
The maxillary artery is the terminal branch of the external carotid artery
Upper teeth supplied by infraorbital a. (branch of the maxillary artery)
Lower teeth are supplied by the inferior alveolar artery (IAA)
IAA enters the mandible through the mandibular foramen into the mandibular canal
what is the nerve supply
Trigeminal nerve [CN V] supplies the sensory innervation of the teeth through its maxillary and mandibular divisions
Upper incisor teeth are innervated by infraorbital n. (maxillary n.) which runs in the infraorbital canal
Mandibular teeth are supplied by inferior alveolar n. (mandibular n.) which runs in the mandibular canal
![<p>Trigeminal nerve [CN V] supplies the sensory innervation of the teeth through its maxillary and mandibular divisions</p><p></p><p>Upper incisor teeth are innervated by infraorbital n. (maxillary n.) which runs in the infraorbital canal</p><p></p><p>Mandibular teeth are supplied by inferior alveolar n. (mandibular n.) which runs in the mandibular canal</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1779c901-69a5-4d55-8223-9f237cf7cd18.png)