CS004 - MODULE 1 Fundamentals of Computer Network and Data Communication
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Components of IS (Information System) (6)
Data
Information
Hardware
Software
Telecommunication/Networks
People/Peopleware
Data communications
are the exchange of data between two devices via some forms of transmission medium such as a wire cable.
1. Message
2. Sender
3. Receiver
4. Transmission Medium
5. Protocol
Message
The _____ is the information (data) to be communicated.
Sender
sends the data message. It can be a computer, workstation, telephone handset, video camera, and so on.
Receiver
receives the message. It can be a computer, workstation, telephone handset, television, and so on.
Transmission medium
physical path by which a message travels from sender to receiver.
Protocol
set of rules that govern data communications.
1. SMTP
2. HTTP
3. HTTPS
4. TCP/IP
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
a protocol for sending and receiving emails over networks. It's the standard for email communication between clients and servers, defining their interaction.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
web protocol for fetching web pages and resources. It guides how browsers request content from servers and how servers provide responses. It's the basis of web data communication.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
a web protocol for sharing web pages and resources. It guides how browsers request and servers deliver content, forming the basis of web communication.
1. Text
2. Number
3. Images
4. Audio
1. Simplex
2. Half-Duplex
3. Full-Duplex
1. Digital Signal
2. Analog Signal
**Digital Signal**
1. GUIDED MEDIA
2. UNGUIDED MEDIA
1. Twisted Pair Cable
2. Coaxial Cable
3. Optical Fiber Cable
* Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
referred to as Wireless or Unbounded transmission media. No physical medium is required for the transmission of electromagnetic signals.
1. Radio Waves
2. Microwaves
3. Infrared
1. Repeater
2. Hub
3. Bridge
4. Switch
5. Router
A ___ operates at the physical layer. Its job is to regenerate the signal over the same network before the signal becomes too weak or corrupted to extend the length to which the signal can be transmitted over the same network. An important point to be noted about ___ is that they not only amplify the signal but also regenerate it. When the signal becomes weak, they copy it bit by bit and regenerate it at its star topology connectors connecting following the original strength. It is a 2-port device.
A ___ is a basically multi-port repeater. A --- connects multiple wires coming from different branches, for example, the connector in star topology which connects different stations. ___ cannot filter data, so data packets are sent to all connected devices. In other words, the collision domain of all hosts connected through ___ remains one. Also, they do not have the intelligence to find out the best path for data packets which leads to inefficiencies and wastage.
A ___ operates at the data link layer. A ___ is a repeater, which adds on the functionality of filtering content by reading the MAC addresses of the source and destination. It is also used for interconnecting two LANs working on the same protocol. It has a single input and single output port, thus making it a 2 port device.
A ____ is a multiport bridge with a buffer and a design that can boost its efficiency(a large number of ports imply less traffic) and performance. A ____ is a data link layer device. The ____ can perform error checking before forwarding data, which makes it very efficient as it does not forward packets that have errors and forward good packets selectively to the correct port only. In other words, the ____ divides the collision domain of hosts, but the broadcast domain remains the same.
1. Point to Point Topology
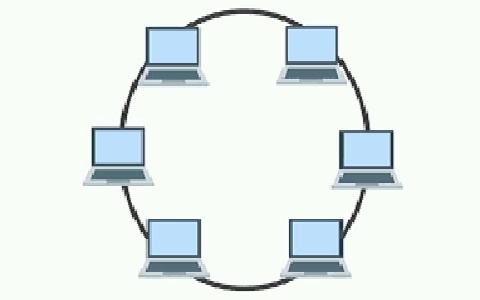
2. **Mesh Topology**
3. Star Topology
4. **Bus Topology**
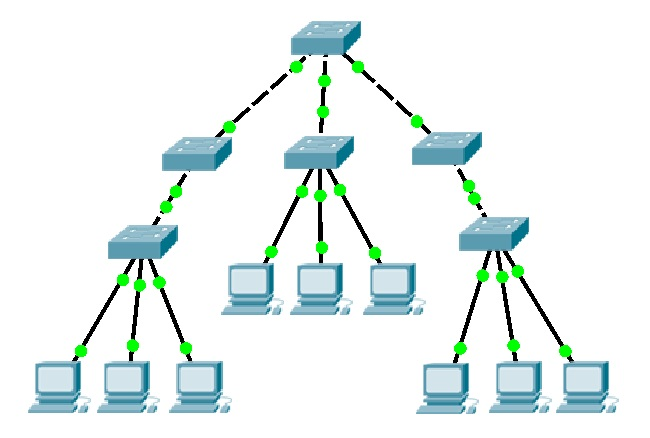
5. Tree Topology
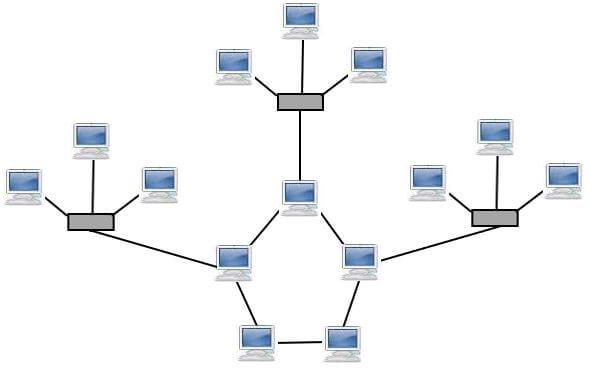
6. Hybrid Topology
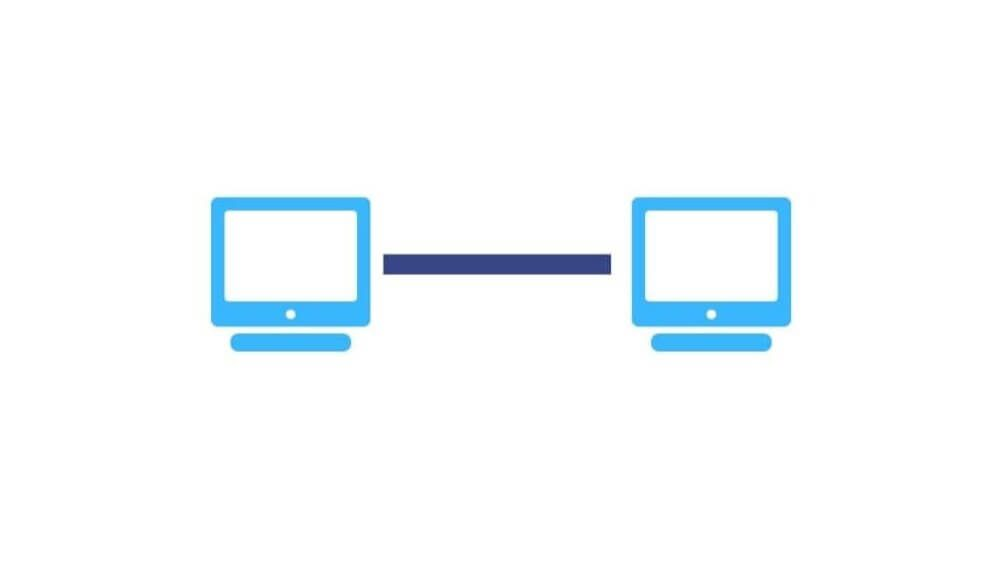
works on the functionality of the sender and receiver. It is the simplest communication between two nodes, in which one is the sender and the other one is the receiver. ____ provides high bandwidth.
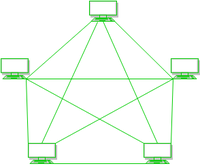
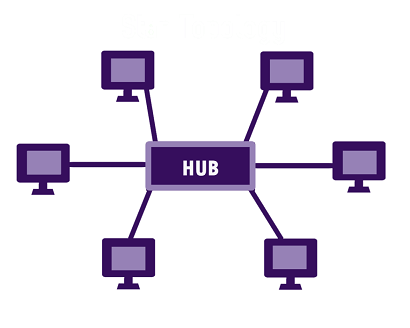
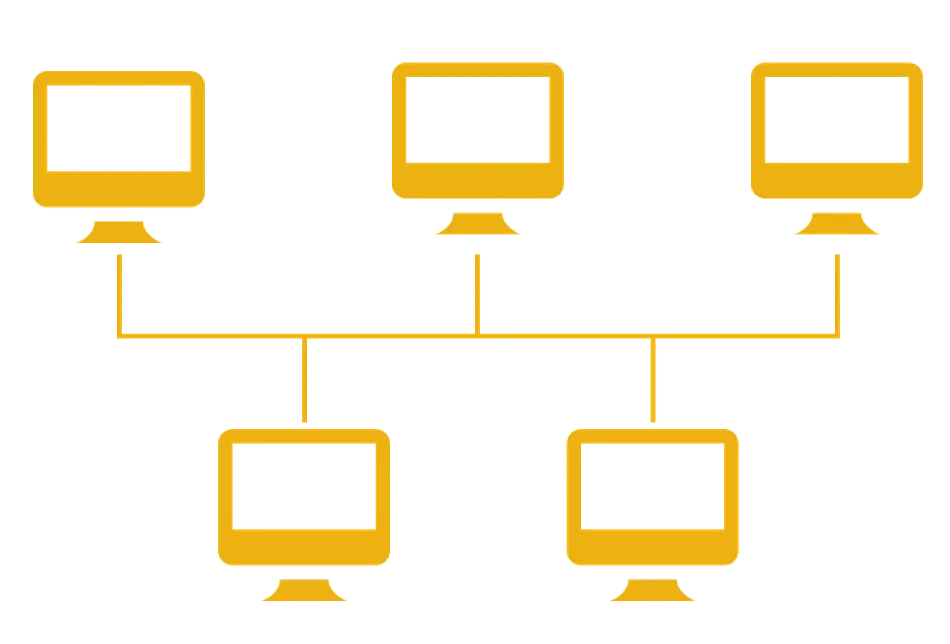
1. PAN
2. LAN
3. WAN
4. MAN
5. CAN
is a small-scale network that connects devices within a limited range, typically within a person's personal workspace or immediate vicinity.
OSI stands for *Open Systems Interconnection*.
Voice network
a network that transmits only telephone signals (essentially xtinct)
Data network
a network that transmits voice and computer data (replacing voice networks).
Data communications
the transfer of digital or analog data using digital or analog signals
Telecommunications
the study of telephones and the systems that transmit telephone signals (becoming simply data communications)
Network management
the design, installation, and support of a network, including its hardware and software
Network cloud
a network (local or remote) that contains software, applications, and/or data.
Microcomputer-to-local area network
Highly common throughout business and academic environments, and now homes Typically a medium- to high-speed connection
Computer (device) requires a NIC (network interface card)
NIC connects to a hub-like device (switch)
Microcomputer-to-Internet
Popular with home users and small businesses
For some, a dial-up modem is used to connect user’s microcomputer to an Internet service provider
Technologies such as DSL and cable modems are quickly replacing dial-up modems
Local area network-to-local area network
Found in systems that have two or more LANs and a need for them to intercommunicate
A bridge-like device (such as a switch) is typically used to interconnect LANs
Switch can filter frames
Personal area network-to-workstation
Interconnects wireless devices such as PDAs, laptops and notebooks, and music playback devices
Used over short distances such as a few meters
Local area network-to-metropolitan area network
Used to interconnect companies (usually their local area networks) to networks that encompass a city
High-speed networks with redundant circuits
Metro Ethernet is latest form of metropolitan LAN
Local area network-to-wide area network
One of the most common ways to interconnect a user on a LAN workstation to the Internet (a wide area network)
A router is the typical device that performs LAN to WAN connections
Routers are more complex devices than switches
Wide area network-to-wide area network
High-speed routers and switches are used to connect one wide area network to another
Thousands of wide area networks across North America, many interconnected via these routers and switches
Sensor-to-local area network
Not all local area networks deal with microcomputer workstations
Often found in industrial and laboratory environments
Assembly lines and robotic controls depend heavily on sensor-based local area networks
Satellite and microwave
Typically long distance wireless connections
Many types of applications including long distance telephone, television, radio, long-haul data transfers, and wireless data services
Typically expensive services but many companies offer competitive services and rates
Newer shorter-distance services such as WiMa
Cell phones
Constantly expanding market across the U.S. and world
Third generation services available in many areas and under many types of plans with fourth generation services starting to appear
Latest generation includes higher speed data transfers (100s to 1000s of kilobits per second)
Computer terminal / microcomputer-to-mainframe
Predominant form in the 1960s and 1970s
Still used in many types of businesses for data entry and data retrieval
Few dumb terminals left today – most are microcomputers with terminal emulation card, a web browser and web interface, Telnet software, or a thin client
NETWORK ARCHITECTURES
A reference model that describes the layers of hardware and software necessary to transmit data between two points or for multiple devices / applications to interoperate
Reference models are necessary to increase likelihood that different components from different manufacturers will converse
Two models to learn: TCP/IP protocol suite and OSI model
THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE
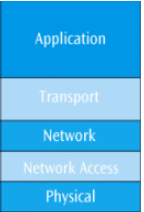
Application layer
Where the application using the network resides
Common network applications include web browsing, e-mail, file transfers, and remote logins
Transport layer
Performs a series of miscellaneous functions (at the end-points of the connection) necessary for presenting the data package properly to the sender or receiver
Network (Internet or internetwork or IP) layer
Responsible for creating, maintaining and ending network connections
Transfers data packet from node to node (e.g. router to router) within network
Network access (data link) layer
Responsible for taking the data and transforming it into a frame with header, control and address information, and error detection code, then transmitting it between the workstation and the network
Physical layer
Handles the transmission of bits over a communications channel
Includes voltage levels, connectors, media choice, modulation techniques
OSI MODEL
In 1984, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) developed the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model to describe how information is transferred from one networking component to another, from the point when a user enters information using a keyboard and mouse to when that information is converted to electrical or light signals transferred along a piece of wire (or radio waves transferred through the air).
Defines the process for connecting two layers together, promoting interoperability between vendors.
Separates complex functions into simpler components.
Allows vendors to compartmentalize their design efforts to fit a modular design, which eases implementation and simplifies troubleshooting.
Provides a teaching tool to help network administrators and students alike understand the communication process used between network components.
LAYERS OF OSI MODELS
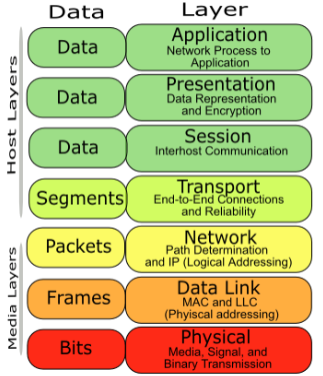
Layer 7, the application layer,
provides an interface for the end user operating a device connected to a network. This layer is what the user sees, in terms of loading an application (such as Web browser or e-mail); that is, this application layer is the data the user views while using these applications.
Examples of application layer functionality include:
Support for file transfers
Ability to print on a network
Electronic mail • Electronic messaging
Browsing the World Wide Web