Community Dynamics
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Community structure
Describes how an ecological community is organized, including the number of species it contains as well as how evenly individuals are distributed among species
Includes a description of species’ feeding relationshipsSpecies richness
disturbance
any relatively discrete event in time that disrupts ecosystem, community, or population structure and changes resources, substrate availability, or the physical evironment
succession
the repeatable change in community composition through time following a disturbance
Resistance
the ability to withstand a disturbance
Allogenic engineers
alter environments through the structures they build
Trophic cascades
occur when predators indirectly limit the size of a population that they are not directly feeding upon
Species richness
Number of different species
Community dynamics
Describes how an ecological community’s structure changes over time
Changes driven by disturbances that originate outside the community or by interactions among member of the community
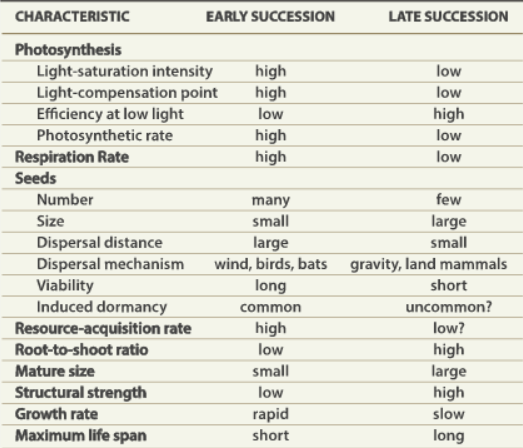
Early succession
Annuals, forbs, grass
Mid succession
Pine trees
Late succession
Steady pine tree density
Serotinous cones
Only open when heat is applied
Communities are affected by disturbance and succession
Successional sequence is driven by
Thinning and trade-offs
Life history - early successional
Having seeds/roots that can survive fires or are serotinous
These species are easily able to recolonize post-fire
Quickly dispersing seeds
Grow quickly in high-light environments
Life history - late successional
Poor dispersers
Grow slowly
Grow in low-light environments
life history traits and succession
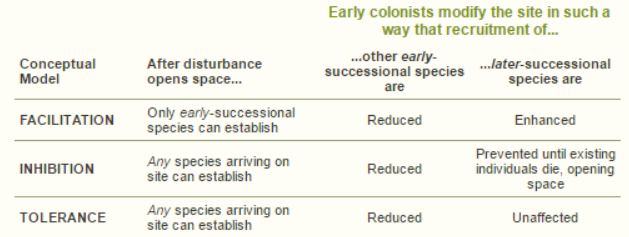
Three mechanisms responsible for succession
Assume that succession is initiated by a disturbance and proceeds without further changes in the biotic environment
Assume that species are stationary
Only focus on plant communities
Assume that initial colonists are good dispersers with life-history trait that help them reach new habitats quickly
Change the conditions where they live
Creating deeper litter, shading the ground, not well suited to grow under these changed conditions
Autogenic succession
Internally produced or generated independently of external influence
Primary succession
Disturbance removes the soil and all existing organisms
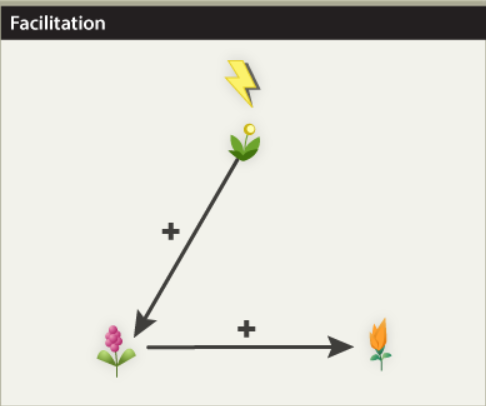
Facilitation
Primary succession
Barren ground is uninhabitable by all but the most stress tolerant of colonists
Over time, early stress tolerant colonists make the announcement more suitable for successive species by increasing nutrient availability, developing soils, reducing pH, or providing chase from the sun and shelter from the wind
Sequence continues until the more competitively dominant species no longer facilitate the invasion and growth of any other species
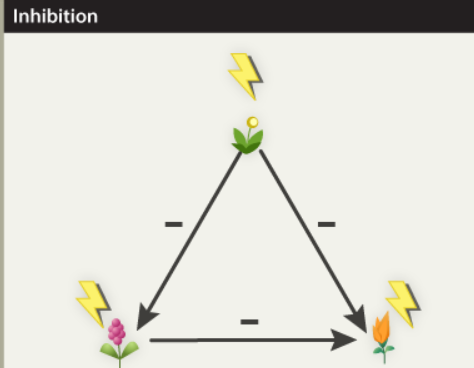
Inhibition
All species arrive on an unoccupied site and survive. Thus the initial community composition is a function of who gets there first
Once a colonist becomes established, it inhibits growth of subsequent arrivals by monopolizing space and/or other resources
Only when space and/or resources are released through the death or decay of dominant residents van new colonists invade and grow
Because short lived early species die more frequently, succession slowly progresses from short lives to long lived species
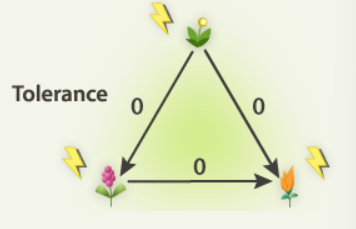
Tolerance
All species arriving on an unoccupied site can survive. Thus the initial community composition is simply a function of who gets there first
Species that appear later simply arrived later or arrives early but grew more slowly
Late arriving species tolerate the presence of early species and grow despite the presence of early successional species because they are better competitors for light and nutrients. Over time late successional species exclude other species
Early successional species have no effect on late successional species
Communities are not closed systems
External factors affect communities as much as internal dynamics
Allogeneic process ensure communities are almost never in equilibrium
Disturbance regime
Describes the characteristic pattern of disturbances experiences by a given ecosystem
Defined in terms of the timing, magnitude, frequency, and predictability of disturbance
Fire helps credit habitat diversity
Density is the greeted in patches that were burned
Only severe surface fire generate sufficient heat to open serotinous cones
Intermediate disturbance hypothesis
Predicts that species diversity will be greatest when disturbances are of intermediate frequency or of intermediate magnitude
Food chain
Description of how food/energy moves through populations in a community or ecosystem
Each trophic level contains only one population
Food web
Contains multiple populations at each trophic level and provides more detail about paths that every can take
Trophic level
Describes an organism’s position in the food chain
PP > primary consumers > secondary consumers > tertiary consumers
Ecosystem engineers
Indirectly affect other members of the community
Physically alter their environment and as a result alter resource availability
Can impact the success of other species
Top-down control
Higher trophic level determines the structure or function of a lower trophic level
Behavioral cascade
Specific type of top-down effect
The population size of an herbivore is not directly affected by predation. Instead the predator alters the behavior of the herbivore
Ecology of fear
A conceptual framework describes how predation risk can indirectly affect population, communities, and ecosystems
Autogenic engineers
Change the environment through their own physical structures
Trees
Produce shade, dams, alter hydrology and nutrient cycling, food, nests, shelter
Must alter the availability of environmental resources
Coral
Top-down control
Primary producers
Base of the food chain
Only PP? Limited by environmental conditions and resource availability
Consumers
Limit the pop size of PP
Competition between PP becomes unimportant
Trophic levels at the top are limited by food availability
Lower trophic levels alternate between being consumer-controlled and resource limited
Odd number of links
PP limited by competition
Even number
PP limited by consumers
Green world hypothesis
Since the world is green, then herbivores are not limiting PP
Bottom-Up control
Lower trophic level influence the structure of function of higher levels via resource restriction
Organism on each trophic level are resource limited
If more energy is moving through the community, then there should be more trophic levels
Even when PP is high enough to support grazers, bottom-up control persists because many plants are low quality food
Communities support low numbers of herbivores because of the low quality food
What determines food chain length
Lake are good for studies
Food-chain length is variable
Most important PP is algae, correlated with phosphorus concentration
Relatively discrete boundaries , easy to estimate their size
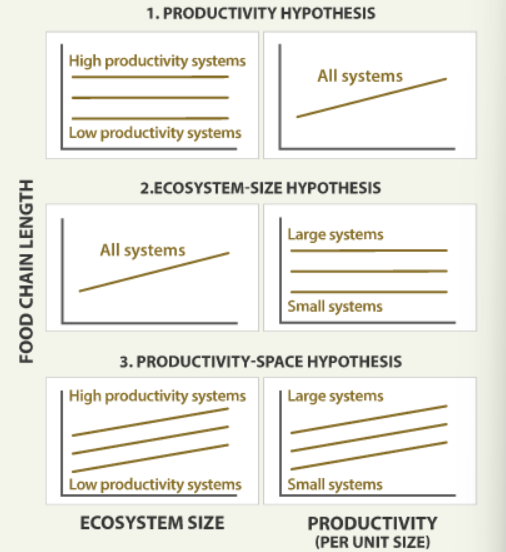
Productivity hypothesis
More productive ecosystems should have longer food chains. Lakes with higher phosphorus concentrations would have longer food chains but lake size would not matter
Ecosystem-size hypothesis
Food-chain length should increase with ecosystem size. As ecosystem size increases, species diversity, habitat diversity, and habitat availability also increase. Larger lakes would have longer food chains but that phosphorus concentration would not matter
Productive-space hypothesis
Both productivity and ecosystem size are important. Food chain length would increase with both phosphorus concentration and lake size
Resources that scale with ecosystem can affect community structure
Bottom up forces can control different aspects of community structure
In unproductive communities food chains are short
Questions asked about a disturbance
How big a change did the disturbance cause?
How quickly did the community recover from this change?
How closely did the post-recover community resemble the pre-disturbance community?
Stability
Its response to a disturbance, as characterized by resistance, return time, and resilience
Return time - how quickly a community returns to its initial condition after a disturbance
Amount of time it takes for the community to stop changing after the disturbance
Its persistence as an identifiable system through time, especially after a disturbance
Overall degree to which community stays the same over time
Its constancy, independent of disturbances
Constancy - describes how much a community varies over time, irrespective of disturbance. Communities that are less variable are more constant and thus more stable
Resilience
Should measure population sizes and species composition
how closely the post-recovery community resembles the pre-disturbance community
Alternative state
A community that can exist in a particular environment and is different from the current community
The alternative state is stable if it does not readily transition back to the original state
If it is relatively persistent following further small disturbances
Diversity promotes stability
Ecological communities with higher connectance should be more stable
decreasing biodiversity appears to lower community stability, sometimes
Some species were more important than others, removal caused bigger changes
Dominant species
Due to its large biomass or abundance, has a large impact on community structure and function
Keystone species
Large impact on community structure or function dewspure having a low biomass/abundance
Community importance
Compares a measurable ecosystem trait before and after the species is removed from the community
Indicated whether a species’ impact is greater or less than would be expected based solely on its proportional abundance
Total impact is the magnitude of the change