OCHEM exam 2 unit 16
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
1) BH3 2) H2O2
solvents needed to turn c-c triple bond into aldehyde
DIBAL-H and H2O workup
solvents needed to turn ester into aldehyde
PCC
solvent need to turn primary alcohol into aldehyde
1) O3 2) DMS
solvent needed to turn double bond C into aldehyde
CuCH3 H2O workup (need weaker metal, not Li or MgX)
solvent needed to turn acid chloride into ketone
AgSO4 H2SO4 H2O
solvent needed to turn c-c triple bond into ketone
-al
ending of IUPAC for aldehyde on chain
-carbaldehyde
ending of IUPAC for aldehyde on ring
-one
ending of IUPAC for ketone
PCC
solvents needed to oxidize 1 degree alcohol to aldehyde
DIBAL-H then H2O
solvents needed to reduce an ester to an aldehyde
1) LiALH(CO(CO3)3)3 2) H2O
solvents needed to reduce acid chlorides to aldehyde
1) R2BH 2) H2O2, -OH
solvents needed to turn alkyne (triple bond) into aldehyde
1 degree alcohols, esters, acid chlorides, and alkynes
what are aldehydes prepared from
2 degree alcohols, acid chlorides, and alkynes
what are ketones prepared from
CrO3 or NaCr2O7 or PCC
solvents needed to oxidize a 2 degree alcohol into a ketone
1) R'CuLi 2) H2O
solvents needed to turn acid chloride into ketone
AlCl3
solvent needed to perform friedel crafts acylation into a ketone from an acid chloride and other organic compound
H2O H2SO4 HgSO4
solvents needed for hydration of an alkyne (triple bond) to a ketone
O3
additional solvent to make aldehydes and ketones with oxidative cleavage of alkenes
nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl carbon
general reaction that aldehydes and ketones undergo
acid catalyst
what is needed for nucleophilic addition at aldehydes or ketones if the nucleophile is more neutral?
protonation of carbonyl oxygen
first step of a reaction involving a carbonyl group and a strong acid
NaBH4, CH3OH, or 1)LiAlH4 2) H2O
solvents for carbonyl into primary alcohol and H
1) RMgX or RLi 2) H20
solvents for carbonyl into primary alcohol and R
CH3CN and HCl
solvents for carbonyl into primary alcohol with CN
Ph3P+--CR2
solvent for carbonyl into alkene with Rs sticking off double bond
RNH2 and mild acid, then H2O
solvent for carbonyl into imine (C=N)
R2NH and mild acid, then H2O
solvent for carbonyl into enamine (C=C-NR2)
ROH, H+
solvent for carbonyl into acetal (two OR groups where C=O used to be)
a 1 degree or 2 degree alcohol
result of treatment of aldehyde or ketone with either NaBH4 or LiAlH4 followed by protonation
a 1, 2, or 3 degree alcohol with a new C-C bond
result of treatment of aldehyde or ketone with either an organolithium or Grignard reagent followed by water
adds the components of HCN across the C=O
treatment of aldehyde with NaCN and a strong acid such as HCl
treatment with a base (deprotonation followed by elimination of CN)
how to reconvert a cyanohydrin to a carbonyl compound
heating with aqueous acid or base (H2O)
how to hydrolyze a cyanohydrin to a carboxy group (COOH)
Ph3P=O
result of wittig reaction (additional product)
1) SN2 reaction of Ph3P with an alkyl halide to form a salt 2) deprotonation of salt with strong base to form ylide (has free elections on a carbon)
two steps for Wittig
unhindered alkyl halide
preferred wittig reagent is derived from an
organic nitrogen compounds that contain a nonbonded electron pair on the N
define amine
imine
result of treating an aldehyde or ketone with a 1 degree amine
how many R groups it is bonded to
how is degree of amine determined
N=C
critical part of an imine
RN-H2 and mild acid then H2O
solvents needed to turn aldehyde or ketone into imine
C=C-NR2
critical part of an enamine
nucleophilic addition of 2 degree amine followed by elimination of H2O
mechanism for enamine from ketone or aldehyde
R2N-H and mild acid, then H2O
solvents needed to turn aldehyde or ketone into enamine
hydrolysis with a mild acid (H3O+)
how to convert imine or enamine back into carbonyl
H2O then H+ or OH-
solvents needed to turn carbonyls or aldehyde into two OH groups (works best with carbonyls or with aldehydes with electron withdrawing groups)
converts H2O to a-OH a stronger nucleophile
how a base hydrates a aldehyde or ketone to 2 OH
protonates carbonyl group, making it more electrophilic and more susceptible to nucleophilic attack
how an acid hydrates an aldehyde or ketone to 2 OH
two equivalents of alcohol
what do aldehydes and ketones react with to form acetals (carbon bonded to 2 OR)
1) CH3OH 2) TsOH
solvents needed to turn aldehyde or ketone into acetal
acetal
image is of what functional group
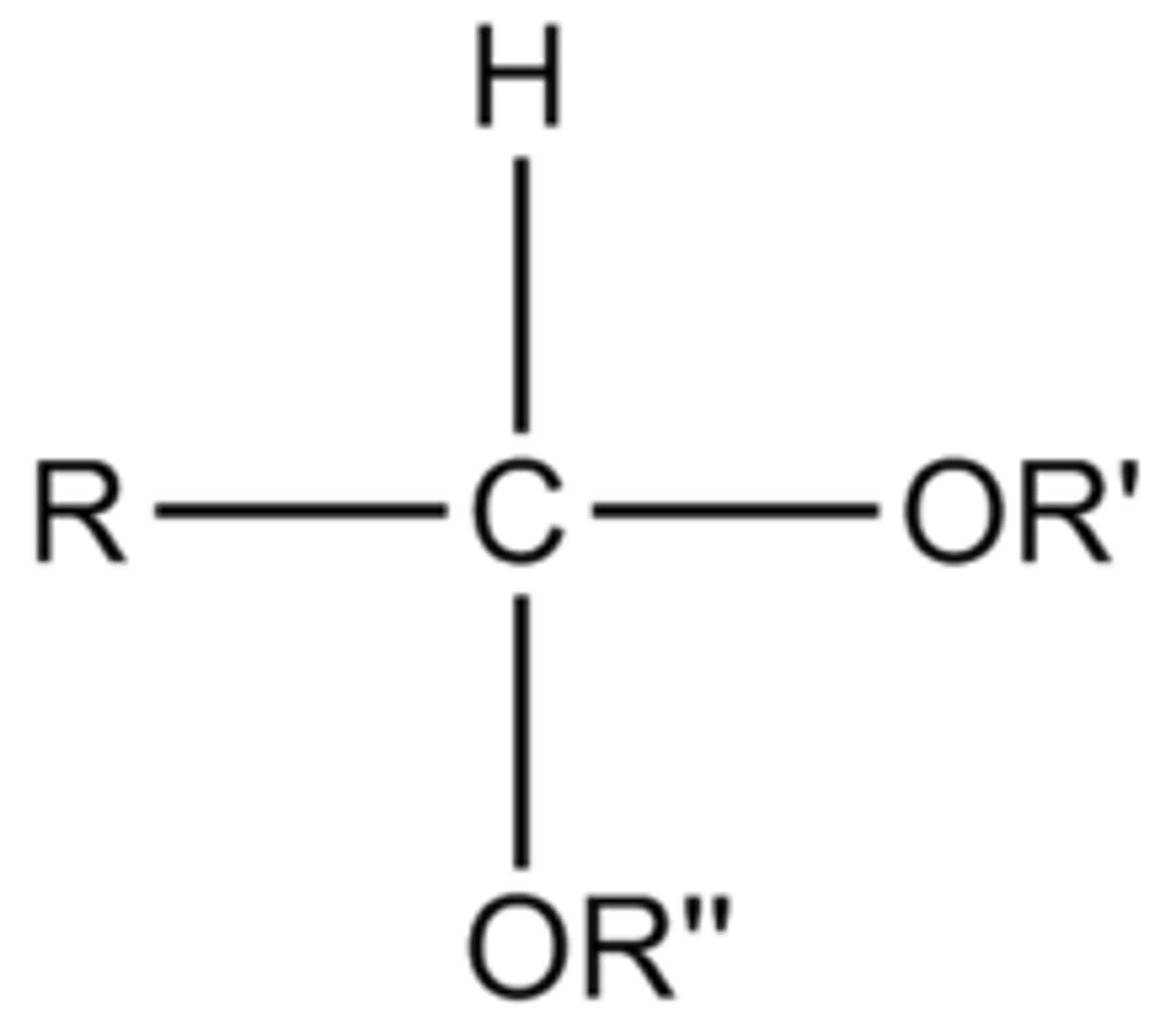
hydrolyzed by treatment with aqueous acid
how does an acetal become an aldehyde or ketone again
HO------OH and TsOH
how to turn a carbonyl into a ring to protect it
1) H2O 2) H+
how to remove the ring to turn it back into a carbonyl
only the hemiacetal group reacts to form an acetal
what happens when a compound with both an alcohol OH and hemiacetal OH is treated with an alcohol (when the OH is connected to a C connected to another O)