Ib Biology Hl: A1.2 - Nucleic Acid
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are nucleic acid chains made of
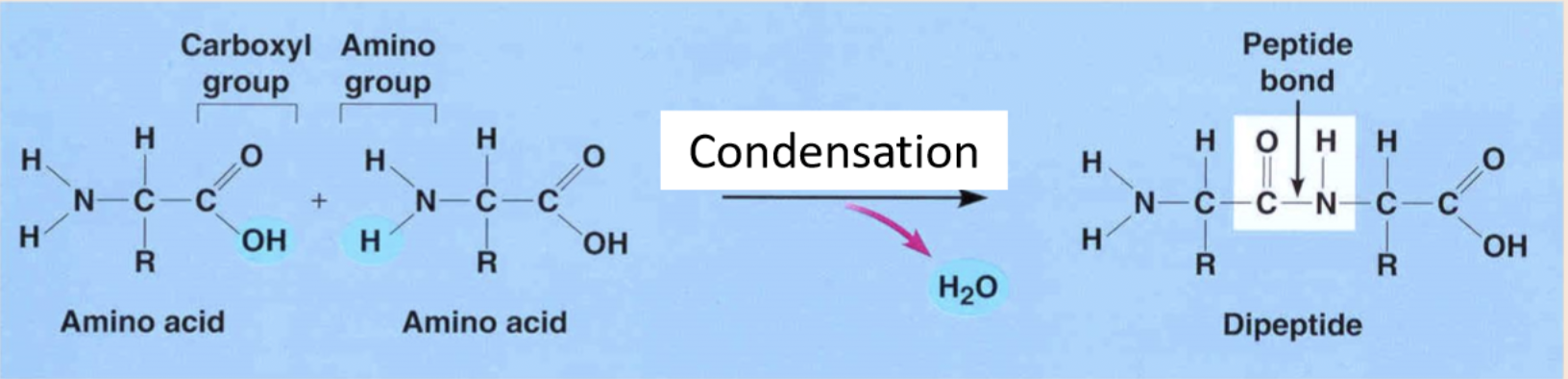
Repeating monomers ( nucleotides ) that have undergone a polymerisation ( a condensation reaction)
monomer of nucleid acid
nucleotide
Two main types of nucleic acid
Déoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA )
Ribonucleic acid ( RNA )
Components of a nucleotide
pentose sugar
Nitrogenous base
A phosphate group
Sugar phosphate bonding
The nucleotide links together through polymerisation. This requires energy and gives out a water molecule. The bond is phosphodi-ester bond.? covalent bond
Two main types of bases
purines ( two rings in their structure )( A, G)
Pyrimidines ( on ring in their structure )( T, C, U)
How are the two strands of DNA linked to each other
Complimentary base pairing between nitrogenous bases
Differences between RNA and DNA
Thymine is replaced by uracil in RNA
RNA used Deoxyribose as a sugar, while RNA uses ribose
RNA on C2 has -OH, DNA on C2 has -H
RNA is a single stranded molecule, while DNA is a double stranded molecule connected by hydrogen bonding
Thus RNA is less table, usually temporary
structure of DNA polymer
nitrogenous base attached to C1 atom, other attachment to phosphate group at C3, and own phosphate group is C5
difference between DNA and RNA
RNA:
used ribose
single stranded
has uracil
is less stable
DNA:
uses deoxyribose
double stranded
has thymine
more stable
nucleosomes
dna wrapped around 8 histone proteins/ histone octamer
different histone proteins
H2A H2B H3 H4
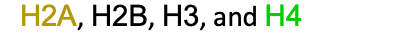
chromatin
many nucleosomes together
Chargaff’s rues
the amount of guanine is equal to the amount of cytosine, and the amount of adesine is the same as the amount of thymine
amino acid structure
amino group : NH2,
carboxyl acid : COOH
R group
central carbon .
condensation of amino acids